
Five Zang Organs: The “Huangdi Neijing” states, “The five zang are those that store the spirit, blood, qi, and soul.” Here, the five zang refer to the five organs, which are responsible for storing the spirit, blood, qi, and soul. They possess the characteristic of “storing without excreting”; excretion refers to the discharge of essence. This means that the five zang only store essence and do not discharge qi, similar to a warehouse that contains formless essence. People utilize the six fu organs to transport and transform the essence of digested food into this warehouse.

Six Fu Organs: The “Huangdi Neijing” states that the six fu organs “are responsible for transforming food and transporting fluids.” “Transforming food” refers to the digestion and absorption of tangible food, allowing the fluids to circulate for secretion and absorption. In contrast to the five zang, a significant characteristic of the six fu organs is “excreting without storing”; they function like a conveyor belt for tangible food, responsible only for excretion and not for storage. However, not storing does not mean absolutely not storing, but rather not storing for long periods.

It is precisely due to the cooperation and division of labor between the five zang and six fu organs that the body can function normally. The importance of this can be seen, with the gallbladder being the chief of the six fu organs, so let us first examine the gallbladder.
The Gallbladder – The Official of Central Justice, Responsible for Decision-Making!
The gallbladder has two main functions: one is to store and excrete bile; the other is to govern decision-making.
The gallbladder stores and excretes bile, as it is related to the digestive and absorptive functions of the small intestine, participating in the “transformation of substances” by the six fu organs. Thus, the gallbladder is one of the six fu organs. However, the gallbladder differs from the other fu organs in that it does not accommodate food and does not transform turbid substances.
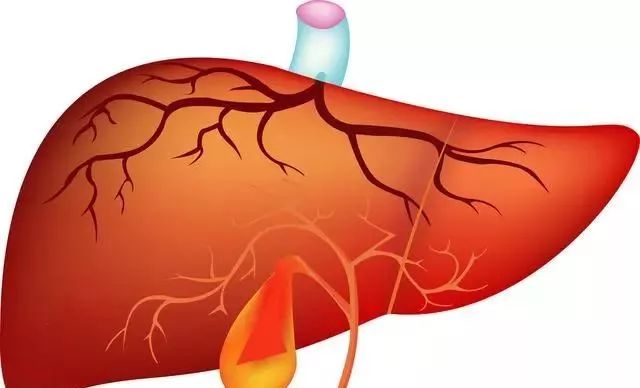
The Gallbladder Stores and Excretes Bile The gallbladder is connected to the liver above, where the liver’s residual qi transforms into bile, flowing through this duct into the gallbladder; below, it connects to the small intestine, where bile is excreted into the small intestine as needed for digestion. The gallbladder continuously produces bile, but the excretion of bile into the small intestine is intermittent. To regulate the balance between bile production and excretion, the gallbladder also takes on the function of storing bile.

The Gallbladder Governs Decision-Making The “Suwen: Linglan Mijian Lun” states: “The gallbladder is the official of central justice, responsible for decision-making.” The gallbladder’s role in decision-making is primarily manifested in its ability to resist adverse influences when faced with certain stimuli, regulate and control the normal flow of qi and blood, and maintain the normal functioning of the zang and fu organs. Individuals with strong gallbladder qi can recover more easily after being stimulated, while those with weak gallbladder qi may develop chronic issues as a result.
As the saying goes, “the liver and gallbladder reflect each other”; the gallbladder’s decision-making is inseparable from the liver’s governance of planning. This is akin to the relationship between a strategist and a ruler; without planning, one cannot implement actions, and only through decision-making can one translate plans into actions.
Eleven Organs Depend on the Gallbladder The “Suwen: Liu Jie Zang Xiang Lun” states: “How do the organ images manifest? … All eleven organs depend on the gallbladder.” This means that the other organs in the body all depend on the gallbladder’s development.
There are various interpretations of its original meaning, and opinions are diverse, but it remains difficult to reach a consensus, requiring further research and exploration by scholars, and thus will not be explained here.
Why are more and more people suffering from gallbladder diseases or gallstones in daily life? What are the reasons?

1. Mood
The gallbladder is the abode of clarity, preferring tranquility and disliking disturbance. If there is evil in the gallbladder, whether heat, dampness, phlegm, or depression, the gallbladder loses its clarity and tranquility, losing its gentle and harmonious nature, leading to symptoms such as bitter vomiting, restlessness, palpitations, insomnia, and even severe anxiety as if one is about to be captured.
When a person’s vitality is suppressed, the lesser yang qi cannot rise, which significantly impacts the gallbladder’s development; this is a very important point.

2. Irregular Work and Rest
The gallbladder governs development, and the time from 11 PM to 1 AM is the time for the gallbladder meridian to develop. Nowadays, many people face high work pressure and often do not rest until after 1 AM. Such individuals excessively deplete their lesser yang fire, gradually causing issues with their gallbladder meridian, leading to gallbladder problems.

3. Irregular Diet
Since diet is closely related to bile secretion, long-term irregular eating habits can increase the burden on the gallbladder, leading to gallbladder issues.
Regulation: Maintain a cheerful mood, appropriately reduce stress, keep good work and dietary habits, and drink more warm water.
Other common gallbladder meridian diseases:
1. Bitter mouth: bile cannot be properly discharged
2. Frequent sighing: lesser yang gallbladder meridian is suppressed
3. Face appears dusty: face is not moisturized, dull and lackluster
4. Causes discomfort in the heart: pain in the heart and ribs cannot turn sideways
5. Headache: pain on both sides of the head
6. Pain at the outer canthus of the eye: pain at the outer corner of the eye
7. Malaria: alternating chills and fever

Everyone should not seek medical advice in a panic; any symptoms should be diagnosed properly, and when feeling unwell, please consult a qualified physician.
Summary: The gallbladder is the chief of the six fu organs, and one should maintain good lifestyle habits. May everyone have a healthy body.


 Collection of Quality Resources for Learning TCMComprehensive Guide to TCM Treatment MethodsUnderstanding Each Chinese HerbCollection of TCM Health Preservation MethodsCollection of TCM Health Preservation TheoriesCollection of Chinese Herbal FormulasCollection of Dietary Therapy RecipesMethods for TCM Diagnostic Differentiation
Collection of Quality Resources for Learning TCMComprehensive Guide to TCM Treatment MethodsUnderstanding Each Chinese HerbCollection of TCM Health Preservation MethodsCollection of TCM Health Preservation TheoriesCollection of Chinese Herbal FormulasCollection of Dietary Therapy RecipesMethods for TCM Diagnostic Differentiation



