Overall Characteristics: The accumulation of phlegm-damp manifests primarily as obesity, fullness in the abdomen, and a greasy tongue coating.Physical Characteristics: The body is overweight, with a soft and full abdomen. Common Manifestations: Oily skin on the face, excessive sweating and stickiness, chest tightness, excessive phlegm, a greasy or sweet mouth, a preference for rich, sweet, and sticky foods, a greasy tongue coating, and a slippery pulse.
Common Manifestations: Oily skin on the face, excessive sweating and stickiness, chest tightness, excessive phlegm, a greasy or sweet mouth, a preference for rich, sweet, and sticky foods, a greasy tongue coating, and a slippery pulse.
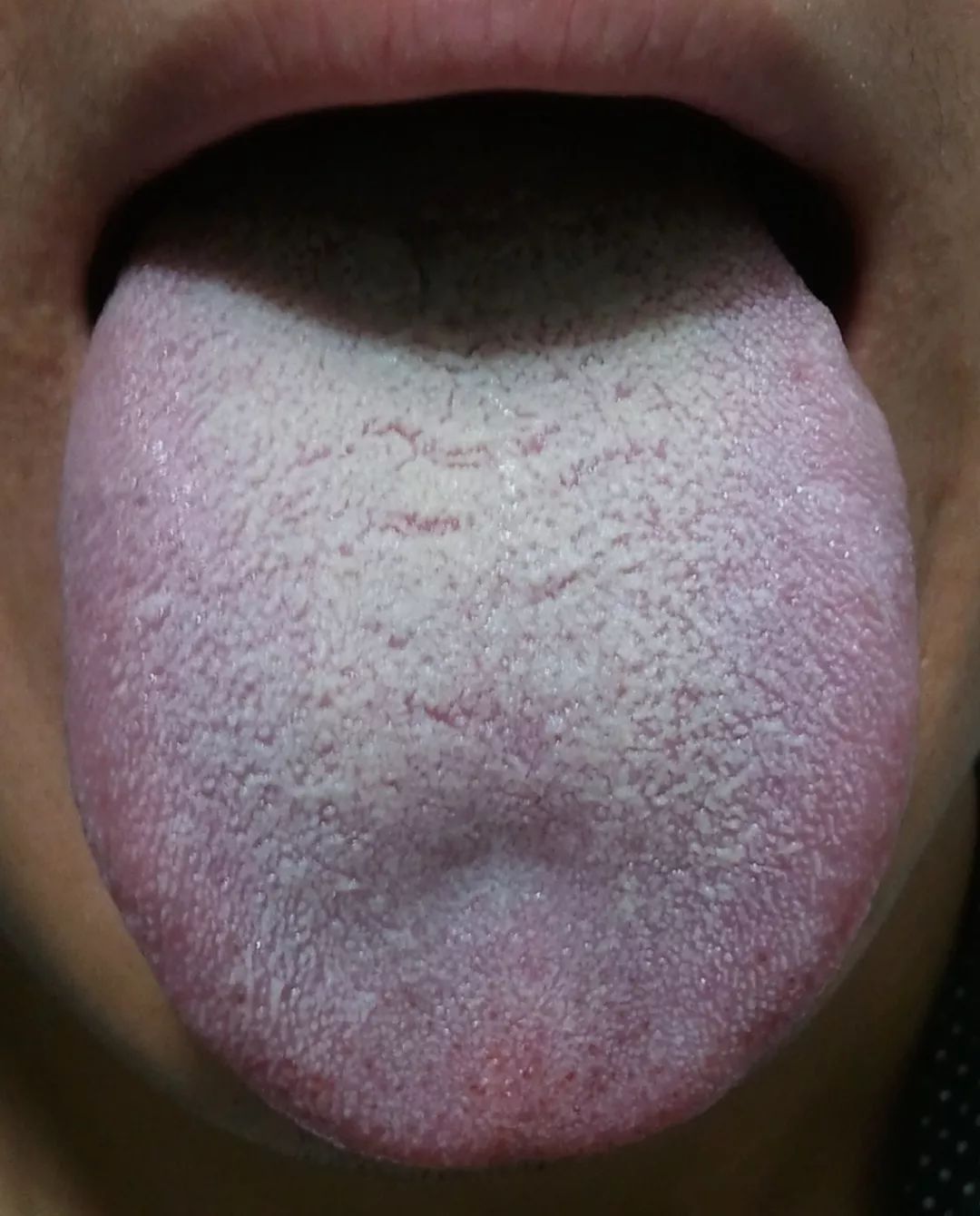
Psychological Characteristics: Generally mild and steady personality, often patient.Predisposition to Illness: Prone to conditions such as diabetes, stroke, and chest obstruction (known in Western medicine as coronary atherosclerosis).Adaptability to External Environment: Poor adaptability to the plum rain season and humid environments.TCM Perspective on “Phlegm-Damp”
- The spleen is the source of phlegm production, the lungs are the storage for phlegm, and the kidneys are the foundation for phlegm generation. —See Appendix for details.
-
Many diseases are caused by phlegm.
-
Li Shizhen pointed out in “Binhai Pulse Studies”: Phlegm causes hundreds of diseases and food brings disasters.
-
Fish generates heat, meat generates phlegm.
-
“Phlegm travels with qi, reaching everywhere.”
In TCM, the concept of “phlegm” is very broad, including both “tangible phlegm” and “intangible phlegm.” Phlegm does not only refer to the “phlegm” that is expectorated (tangible phlegm). Some diseases such as dizziness, nausea, palpitations, shortness of breath, confusion, or mania may also be caused by phlegm. This invisible phlegm is referred to as intangible phlegm.Clinical Manifestations of Various Types of “Phlegm”● Some young and middle-aged women may have a full and overweight body, a strong appetite, and no pathological changes related to infertility found during gynecological examinations. However, they may experience long-term infertility after marriage, which is due to “phlegm obstructing the uterus.” Treatment focusing on phlegm resolution can help achieve pregnancy. ● Some individuals may develop nodules or lumps under the skin (which may only occur in certain areas such as the neck and limbs), and cytological examinations reveal no malignant tumors. This condition is known as “phlegm nodule” or “phlegm mass.” Common examples include cervical lymphadenitis and subcutaneous lipomas. TCM treatment focusing on phlegm resolution and mass dispersal can be effective.
● Some individuals may develop nodules or lumps under the skin (which may only occur in certain areas such as the neck and limbs), and cytological examinations reveal no malignant tumors. This condition is known as “phlegm nodule” or “phlegm mass.” Common examples include cervical lymphadenitis and subcutaneous lipomas. TCM treatment focusing on phlegm resolution and mass dispersal can be effective. ● Some people experience chronic headaches, a feeling of heaviness in the head, and discomfort that worsens in cold and damp weather, with a white greasy tongue coating and aversion to greasy foods. This is due to phlegm-qi rising to the brain, obstructing the normal flow of clear qi in the head, known as “phlegm-damp headache.” Among these patients, some may have high blood pressure, but long-term use of antihypertensive medications is ineffective, especially for symptoms of heaviness and headache. If treated with TCM phlegm resolution methods, symptoms can quickly disappear.
● Some people experience chronic headaches, a feeling of heaviness in the head, and discomfort that worsens in cold and damp weather, with a white greasy tongue coating and aversion to greasy foods. This is due to phlegm-qi rising to the brain, obstructing the normal flow of clear qi in the head, known as “phlegm-damp headache.” Among these patients, some may have high blood pressure, but long-term use of antihypertensive medications is ineffective, especially for symptoms of heaviness and headache. If treated with TCM phlegm resolution methods, symptoms can quickly disappear. Phlegm-damp headache: One type of headache syndrome. The headache is caused by phlegm-damp obstructing the clear orifices. According to the “Suwen: Theory of Vital Qi” it states: “Caused by dampness, the head feels wrapped.” The characteristics of phlegm-damp headache include a heavy sensation in the head, or a feeling of being wrapped, accompanied by fullness and heaviness in the chest and abdomen, excessive phlegm, and variable onset. The tongue coating is white and greasy, and the pulse is slippery or soft. It is advisable to resolve phlegm and eliminate dampness, using formulas such as Ban Xia Bai Zhu Tian Ma Tang (Pinellia, Atractylodes, and Gastrodia Decoction).● Some individuals feel as if their throat is blocked with debris all day, unable to swallow or expectorate, or it may come and go, while in reality, there is no visible obstruction in the throat. This is due to phlegm-qi stagnating in the throat, often caused by emotional distress, commonly referred to as plum pit qi. Treatment for this condition also requires phlegm resolution and emotional release for effectiveness.● Some individuals may feel nauseous or vomit after consuming even a small amount of greasy or rich food. This is due to spleen and stomach deficiency, where greasy foods easily transform into internal phlegm. Some may feel nauseous or vomit just from the smell or sight of greasy foods, which is a reaction of spleen and stomach weakness and excessive phlegm. If these patients regularly use methods to strengthen the spleen and resolve phlegm, their aversion to greasy foods can be alleviated or eliminated.
Phlegm-damp headache: One type of headache syndrome. The headache is caused by phlegm-damp obstructing the clear orifices. According to the “Suwen: Theory of Vital Qi” it states: “Caused by dampness, the head feels wrapped.” The characteristics of phlegm-damp headache include a heavy sensation in the head, or a feeling of being wrapped, accompanied by fullness and heaviness in the chest and abdomen, excessive phlegm, and variable onset. The tongue coating is white and greasy, and the pulse is slippery or soft. It is advisable to resolve phlegm and eliminate dampness, using formulas such as Ban Xia Bai Zhu Tian Ma Tang (Pinellia, Atractylodes, and Gastrodia Decoction).● Some individuals feel as if their throat is blocked with debris all day, unable to swallow or expectorate, or it may come and go, while in reality, there is no visible obstruction in the throat. This is due to phlegm-qi stagnating in the throat, often caused by emotional distress, commonly referred to as plum pit qi. Treatment for this condition also requires phlegm resolution and emotional release for effectiveness.● Some individuals may feel nauseous or vomit after consuming even a small amount of greasy or rich food. This is due to spleen and stomach deficiency, where greasy foods easily transform into internal phlegm. Some may feel nauseous or vomit just from the smell or sight of greasy foods, which is a reaction of spleen and stomach weakness and excessive phlegm. If these patients regularly use methods to strengthen the spleen and resolve phlegm, their aversion to greasy foods can be alleviated or eliminated. Classification and Medication for Phlegm-Damp (Tangible Phlegm)In TCM, phlegm is classified into cold phlegm, wind phlegm, heat phlegm, damp phlegm, and dry phlegm.1. Cold Phlegmis caused by cold pathogens invading the lungs, leading to the condensation of lung fluids into phlegm. The phlegm is white, thin, and frothy, with patients feeling cold and preferring warm drinks, and a thin white tongue coating. Patients can use Chen Pi (Dried Tangerine Peel), Gan Jiang (Dried Ginger), and other warming herbs to make tea, or use Xiao Qing Long He Ji (Minor Blue Dragon Decoction).
Classification and Medication for Phlegm-Damp (Tangible Phlegm)In TCM, phlegm is classified into cold phlegm, wind phlegm, heat phlegm, damp phlegm, and dry phlegm.1. Cold Phlegmis caused by cold pathogens invading the lungs, leading to the condensation of lung fluids into phlegm. The phlegm is white, thin, and frothy, with patients feeling cold and preferring warm drinks, and a thin white tongue coating. Patients can use Chen Pi (Dried Tangerine Peel), Gan Jiang (Dried Ginger), and other warming herbs to make tea, or use Xiao Qing Long He Ji (Minor Blue Dragon Decoction). This formula is used for wind-cold water retention, aversion to cold, fever without sweating, and wheezing with thin phlegm.2. Dry Phlegmis thick and difficult to cough up, with patients feeling dryness in the mouth, nose, and throat, and a thin yellow tongue coating. Appropriate herbs such as Sha Shen (Adenophora) and Mai Dong (Ophiopogon) can be used as tea [Autumn and winter dryness, supplementing “water” is timely (Part 2)], while keeping the respiratory tract moist, and using a humidifier indoors. Alternatively, one can choose Yang Yin Qing Fei Tang (Nourishing Yin and Clearing Lung Syrup).
This formula is used for wind-cold water retention, aversion to cold, fever without sweating, and wheezing with thin phlegm.2. Dry Phlegmis thick and difficult to cough up, with patients feeling dryness in the mouth, nose, and throat, and a thin yellow tongue coating. Appropriate herbs such as Sha Shen (Adenophora) and Mai Dong (Ophiopogon) can be used as tea [Autumn and winter dryness, supplementing “water” is timely (Part 2)], while keeping the respiratory tract moist, and using a humidifier indoors. Alternatively, one can choose Yang Yin Qing Fei Tang (Nourishing Yin and Clearing Lung Syrup). This formula is used for dry throat pain, dry cough, little or no phlegm.3. Heat Phlegmis yellow and thick, caused by heat pathogens invading the lungs or by a prior wind-cold condition leading to high fever for several days. Patients feel hot and prefer cold drinks, with a red tongue and yellow coating. The diet should be light, avoiding foods that easily cause heat, and one can choose Fu Fang Xian Zhu Li Ye (Compound Fresh Bamboo Juice).
This formula is used for dry throat pain, dry cough, little or no phlegm.3. Heat Phlegmis yellow and thick, caused by heat pathogens invading the lungs or by a prior wind-cold condition leading to high fever for several days. Patients feel hot and prefer cold drinks, with a red tongue and yellow coating. The diet should be light, avoiding foods that easily cause heat, and one can choose Fu Fang Xian Zhu Li Ye (Compound Fresh Bamboo Juice). This formula is used for phlegm-heat cough with yellow and thick phlegm.4. Damp Phlegmis white and watery, with patients experiencing heaviness, fatigue, or loose stools, and a thin white or greasy tongue coating. This is due to damp pathogens invading the body (such as living in a humid environment), leading to dysfunction of the lungs and spleen. The formula Er Chen Wan (Two Aged Pills) can be used for treatment.
This formula is used for phlegm-heat cough with yellow and thick phlegm.4. Damp Phlegmis white and watery, with patients experiencing heaviness, fatigue, or loose stools, and a thin white or greasy tongue coating. This is due to damp pathogens invading the body (such as living in a humid environment), leading to dysfunction of the lungs and spleen. The formula Er Chen Wan (Two Aged Pills) can be used for treatment. It dries dampness, resolves phlegm, and regulates qi and stomach. It is used for cough with excessive phlegm, chest fullness, and nausea or vomiting.5. Spleen Qi Deficiency with Phlegm-Dampis characterized by weak spleen qi, internal phlegm accumulation, with common symptoms including reduced appetite, abdominal distension, loose stools, overweight body, heavy limbs, fatigue, and excessive phlegm. The tongue is pale and swollen, with a white greasy coating, and the pulse is soft and slow. Various factors can lead to dysfunction of the spleen’s transport function. Foods that strengthen the spleen, such as Fu Ling (Poria) and Huai Shan (Chinese Yam), can be consumed [No worries about spleen deficiency, delicious spleen-strengthening soup relieves worries]. The formula Liu Jun Zi Wan (Six Gentlemen Pills) can be used.
It dries dampness, resolves phlegm, and regulates qi and stomach. It is used for cough with excessive phlegm, chest fullness, and nausea or vomiting.5. Spleen Qi Deficiency with Phlegm-Dampis characterized by weak spleen qi, internal phlegm accumulation, with common symptoms including reduced appetite, abdominal distension, loose stools, overweight body, heavy limbs, fatigue, and excessive phlegm. The tongue is pale and swollen, with a white greasy coating, and the pulse is soft and slow. Various factors can lead to dysfunction of the spleen’s transport function. Foods that strengthen the spleen, such as Fu Ling (Poria) and Huai Shan (Chinese Yam), can be consumed [No worries about spleen deficiency, delicious spleen-strengthening soup relieves worries]. The formula Liu Jun Zi Wan (Six Gentlemen Pills) can be used. This formula is used for spleen and stomach deficiency, low appetite, qi deficiency with excessive phlegm, abdominal distension, and loose stools.Dietary Restrictions1. An old saying goes: Fish generates heat, meat generates phlegm. Eating too much meat, especially pork, can easily lead to phlegm production, so those with excessive phlegm should reduce their meat intake and eat lighter foods.
This formula is used for spleen and stomach deficiency, low appetite, qi deficiency with excessive phlegm, abdominal distension, and loose stools.Dietary Restrictions1. An old saying goes: Fish generates heat, meat generates phlegm. Eating too much meat, especially pork, can easily lead to phlegm production, so those with excessive phlegm should reduce their meat intake and eat lighter foods.
2. Peanut milk and yogurt are also phlegm-producing foods, and those with excessive phlegm should avoid them.

3. Industrial eggs, produced by caged hens (depressed hens), are likely to generate phlegm and stagnation, so they should be eaten sparingly.
 Appendix:In clinical practice, the spleen is most afraid of being obstructed, either by qi obstruction (anger not being expressed) or damp obstruction.The spleen acts as the central hub for the body’s qi mechanism, responsible for the transport of food and fluids. If one is overly worried, the vital energy is harmed, leading to qi stagnation in the spleen, or if one lives in damp areas, gets rained on, or is exposed to external dampness, it can further obstruct the spleen’s yang, resulting in poor fluid transport, which must transform into phlegm-damp and rise to the lungs. At the same time, the spleen is also troubled by phlegm-damp, exacerbating qi stagnation. The more deficient the spleen becomes, the more phlegm accumulates. Hence, it is said that the spleen is the source of phlegm production, and the lungs are the storage for phlegm.How do we understand the saying that the kidneys are the foundation for phlegm production? Because the spleen’s yang is rooted in the kidneys’ yang, sufficient kidney yang is the fundamental basis for strong spleen yang. A strong spleen yang is the foundation for the preservation of righteous qi, and the preservation of righteous qi ensures that pathogens cannot invade. Therefore, in clinical practice, while strengthening spleen yang, one must also consider whether there is a deficiency of kidney yang, and appropriately include warming and tonifying kidney yang herbs such as Fu Zi (Aconite), Rou Gui (Cinnamon), Xi Xin (Asarum), Yin Yang Huo (Epimedium), and Wu Zhu Yu (Evodia).
Appendix:In clinical practice, the spleen is most afraid of being obstructed, either by qi obstruction (anger not being expressed) or damp obstruction.The spleen acts as the central hub for the body’s qi mechanism, responsible for the transport of food and fluids. If one is overly worried, the vital energy is harmed, leading to qi stagnation in the spleen, or if one lives in damp areas, gets rained on, or is exposed to external dampness, it can further obstruct the spleen’s yang, resulting in poor fluid transport, which must transform into phlegm-damp and rise to the lungs. At the same time, the spleen is also troubled by phlegm-damp, exacerbating qi stagnation. The more deficient the spleen becomes, the more phlegm accumulates. Hence, it is said that the spleen is the source of phlegm production, and the lungs are the storage for phlegm.How do we understand the saying that the kidneys are the foundation for phlegm production? Because the spleen’s yang is rooted in the kidneys’ yang, sufficient kidney yang is the fundamental basis for strong spleen yang. A strong spleen yang is the foundation for the preservation of righteous qi, and the preservation of righteous qi ensures that pathogens cannot invade. Therefore, in clinical practice, while strengthening spleen yang, one must also consider whether there is a deficiency of kidney yang, and appropriately include warming and tonifying kidney yang herbs such as Fu Zi (Aconite), Rou Gui (Cinnamon), Xi Xin (Asarum), Yin Yang Huo (Epimedium), and Wu Zhu Yu (Evodia).

