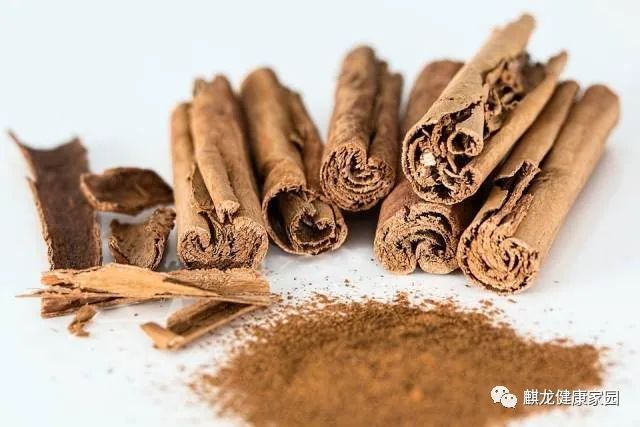


肉桂 (Ròuguì), known as cinnamon, is the bark of the 樟科 (zhāng kē) plant, specifically the cinnamon tree (not the osmanthus tree). The cinnamon tree is native to China and is a plant with a distinctive aromatic scent, used to produce a unique spice. In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), cinnamon can help to 温中 (wēn zhōng) (warm the middle), 健胃 (jiàn wèi) (strengthen the stomach), warm the lower back and knees, and alleviate bloating.
【化学成分 (Huàxué chéngfèn)】
The main active component of cinnamon is 桂油 (guì yóu), which is present at about 5.1%. The primary constituents of cinnamon oil include 肉桂醛 (ròuguì quán) (cinnamaldehyde), 苯甲醛 (běn jiǎ quán) (benzaldehyde), 肉桂醇 (ròuguì chún) (cinnamyl alcohol), 丁香烯 (dīng xiāng xī) (eugenol), 香豆素 (xiāng dòu sù) (coumarin), among more than ten other components.

【性味归经 (Xìngwèi guī jīng)】
Cinnamon is characterized as being very warm in nature, with a spicy and sweet flavor, and it enters the 肾 (shèn) (Kidney), 脾 (pí) (Spleen), 心 (xīn) (Heart), and 肝 (gān) (Liver) meridians.
【功能主治 (Gōngnéng zhǔzhì)】
Cinnamon has the functions of 补火助阳 (bǔ huǒ zhù yáng) (tonifying fire and assisting yang), 引火归源 (yǐn huǒ guī yuán) (guiding fire back to its source), 散寒止痛 (sàn hán zhǐ tòng) (dispelling cold and alleviating pain), and 活血通经 (huó xuè tōng jīng) (invigorating blood and regulating menstruation). It is indicated for conditions such as 阳痿遗精 (yáng wěi yí jīng) (impotence and nocturnal emissions), 宫冷不孕 (gōng lěng bù yùn) (cold uterus and infertility), 心腹冷痛 (xīn fù lěng tòng) (cold pain in the heart and abdomen), 虚寒吐泻 (xū hán tǔ xiè) (deficiency cold with vomiting and diarrhea), 痛经闭经 (tòng jīng bì jīng) (dysmenorrhea and amenorrhea), 肢冷畏寒 (zhī lěng wèi hán) (cold limbs and fear of cold), 腰膝酸软 (yāo xī suān ruǎn) (soreness and weakness of the lower back and knees), 小便不利 (xiǎo biàn bù lì) (difficult urination), 短气喘促 (duǎn qì chuǎn cù) (shortness of breath), 浮肿 (fú zhǒng) (edema), 阴疽 (yīn jué) (yin sores), 上热下寒 (shàng rè xià hán) (heat above and cold below), 寒湿痹痛 (hán shī bì tòng) (cold damp bi pain), and 寒疝疼痛 (hán shàn téng tòng) (cold hernia pain).
【使用禁忌 (Shǐyòng jìn jì)】
Although cinnamon has beneficial effects, it should not be misused. An overdose can lead to acute poisoning, and even normal doses taken over a long period can cause cumulative toxicity. If symptoms such as dizziness, blurred vision, eye swelling, dryness of the mouth, body pain, irritability, flushed face, or numbness of the lips and tongue occur after taking cinnamon, one should stop using it immediately. Additionally, cinnamon is a very warming substance and should be avoided by those with 阴虚火旺 (yīn xū huǒ wàng) (yin deficiency with excess heat), during heat illness that damages yin, or in cases of false cold with true heat, as well as during pregnancy and menstruation. Caution is also advised for individuals with severely weakened heart and lung function. (The medicinal effects of herbs are for informational reference only and should be used under the guidance of a qualified physician or pharmacist; self-medication is not recommended.) (All images and content are sourced from the internet.)Recommended reading: What is fasting? Why fast? Confucius’ thoughts and ten types of cured meats.
Additionally, cinnamon is a very warming substance and should be avoided by those with 阴虚火旺 (yīn xū huǒ wàng) (yin deficiency with excess heat), during heat illness that damages yin, or in cases of false cold with true heat, as well as during pregnancy and menstruation. Caution is also advised for individuals with severely weakened heart and lung function. (The medicinal effects of herbs are for informational reference only and should be used under the guidance of a qualified physician or pharmacist; self-medication is not recommended.) (All images and content are sourced from the internet.)Recommended reading: What is fasting? Why fast? Confucius’ thoughts and ten types of cured meats.

