
Today, let us get to know one of the medicinal herbs:Angelica Sinensis.
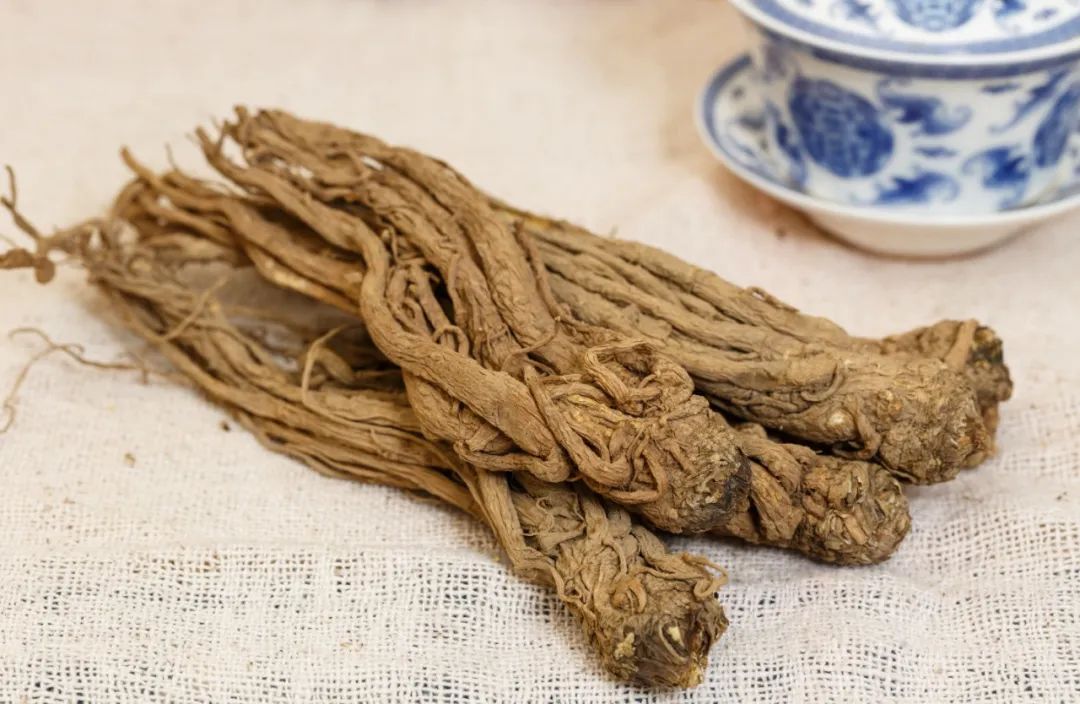 Image source: Baotu Network Material No. pki105653
Image source: Baotu Network Material No. pki105653
Angelica Sinensis
 Angelica Sinensis is one of the commonly used medicinal materials in China, known as the “Holy Herb of Blood“, and is one of the frequently used Chinese herbs, often referred to as “Ten Parts Nine Returns“. Its medicinal history is long, first recorded in the “Shennong Bencao Jing”.Angelica Sinensis is the dried root of the plant of the Apiaceae family, historically called “Shanqi” because it resembles and is larger than celery, growing in the mountains, hence the name. The recognized production area of Angelica Sinensis is Min County, Gansu and surrounding areas.
Angelica Sinensis is one of the commonly used medicinal materials in China, known as the “Holy Herb of Blood“, and is one of the frequently used Chinese herbs, often referred to as “Ten Parts Nine Returns“. Its medicinal history is long, first recorded in the “Shennong Bencao Jing”.Angelica Sinensis is the dried root of the plant of the Apiaceae family, historically called “Shanqi” because it resembles and is larger than celery, growing in the mountains, hence the name. The recognized production area of Angelica Sinensis is Min County, Gansu and surrounding areas.
Effects
 Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believes that Angelica Sinensis has a sweet and pungent flavor, is warm in nature, and enters the liver, heart, and spleen meridians. It has the effects of nourishing blood and invigorating blood circulation, regulating menstruation and alleviating pain, and moistening the intestines and promoting bowel movements. It can be used to treat blood deficiency, dizziness, palpitations, irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and abdominal pain due to deficiency and cold.Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Angelica Sinensis enhances blood and cardiovascular function, regulates immunity, has antibacterial and antioxidant properties, and protects the liver and strengthens the kidneys. It is now widely used in the treatment of vascular diseases, heart diseases, and more.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believes that Angelica Sinensis has a sweet and pungent flavor, is warm in nature, and enters the liver, heart, and spleen meridians. It has the effects of nourishing blood and invigorating blood circulation, regulating menstruation and alleviating pain, and moistening the intestines and promoting bowel movements. It can be used to treat blood deficiency, dizziness, palpitations, irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and abdominal pain due to deficiency and cold.Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Angelica Sinensis enhances blood and cardiovascular function, regulates immunity, has antibacterial and antioxidant properties, and protects the liver and strengthens the kidneys. It is now widely used in the treatment of vascular diseases, heart diseases, and more.
Health Usage
 Angelica Sinensis can be used in combination with various medicinal materials such as Astragalus (Huang Qi), Rehmannia (Di Huang), White Peony (Bai Shao), and Salvia (Dan Shen) to create various health-preserving formulas.Angelica Sinensis Blood Nourishing Decoction: Take 10g of Angelica Sinensis and 60g of Astragalus, decoct in water to make Angelica Sinensis Blood Nourishing Decoction. The “Nei Wai Shang Bian Huo Lun” mentions that this decoction can tonify qi and nourish blood, improving pale complexion and fatigue.Angelica Sinensis and Peony Powder: Take 9g of Angelica Sinensis, 48g of Peony, 12g of Poria, 12g of Atractylodes (Bai Zhu), 24g of Alisma (Ze Xie), and 10g of Chuanxiong, to prepare Angelica Sinensis and Peony Powder. First mentioned in the “Jin Kui Yao Lue”, it has the effects of nourishing blood, regulating the liver, and strengthening the spleen while promoting dampness.
Angelica Sinensis can be used in combination with various medicinal materials such as Astragalus (Huang Qi), Rehmannia (Di Huang), White Peony (Bai Shao), and Salvia (Dan Shen) to create various health-preserving formulas.Angelica Sinensis Blood Nourishing Decoction: Take 10g of Angelica Sinensis and 60g of Astragalus, decoct in water to make Angelica Sinensis Blood Nourishing Decoction. The “Nei Wai Shang Bian Huo Lun” mentions that this decoction can tonify qi and nourish blood, improving pale complexion and fatigue.Angelica Sinensis and Peony Powder: Take 9g of Angelica Sinensis, 48g of Peony, 12g of Poria, 12g of Atractylodes (Bai Zhu), 24g of Alisma (Ze Xie), and 10g of Chuanxiong, to prepare Angelica Sinensis and Peony Powder. First mentioned in the “Jin Kui Yao Lue”, it has the effects of nourishing blood, regulating the liver, and strengthening the spleen while promoting dampness.
Usage Contraindications
 Although Angelica Sinensis is beneficial, it is not suitable for everyone.Angelica Sinensis can invigorate blood circulation, but those with heavy menstrual flow or gum bleeding should avoid it, as it may increase bleeding. Pregnant women should also avoid it during the first three months of pregnancy to prevent miscarriage.Using Angelica Sinensis in large doses can easily lead to nutritional excess and diarrhea, so it is not suitable for those with diarrhea. Angelica Sinensis is warm in nature, and should not be consumed with cold foods, avoiding cold and raw foods to prevent affecting its efficacy.
Although Angelica Sinensis is beneficial, it is not suitable for everyone.Angelica Sinensis can invigorate blood circulation, but those with heavy menstrual flow or gum bleeding should avoid it, as it may increase bleeding. Pregnant women should also avoid it during the first three months of pregnancy to prevent miscarriage.Using Angelica Sinensis in large doses can easily lead to nutritional excess and diarrhea, so it is not suitable for those with diarrhea. Angelica Sinensis is warm in nature, and should not be consumed with cold foods, avoiding cold and raw foods to prevent affecting its efficacy.
References:
[1] National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (Part One) [M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2015: 133.
[2] Ma Qinglin, Wu Guotai, Sun Min, Ren Yuan. Research Progress on the Blood Nourishing Effect of Angelica Sinensis [J]. Journal of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, 2019, 36(03): 93-97.
[3] Ma Yanchun, Wu Wenxuan, Hu Jianhui, et al. Research Progress on the Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Effects of Angelica Sinensis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 50(1): 111-114, ISTIC CA, 2022: National Natural Science Foundation.
[4] Weng Qianqian, Zhao Jiachun, Jin Yan, et al. Botanical Research on Angelica Sinensis in Classic Formulas [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2021, 23(2): 218-227, ISTIC CA, 2021: Basic Research Fund of the Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
[5] Niu Li, Yu Hongling. Analysis of Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Research of Angelica Sinensis [J]. Electronic Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine for Cardiovascular Diseases, 2018: 98+100.
The content is sourced from the Jingxin public account.
If there are any copyright issues, please contact us for removal.
 END
END

 DisclaimerThis article’s content is sourced from publicly available online materials and is for reference only. The specific use of medicines and medical devices should follow medical advice or instructions. For any issues regarding the content, copyright, or other matters, please contact us for resolution.Contact phone: 400-000-9182828Email: [email protected].Copywriter | JingxinReview | Kuang Xiuhong
DisclaimerThis article’s content is sourced from publicly available online materials and is for reference only. The specific use of medicines and medical devices should follow medical advice or instructions. For any issues regarding the content, copyright, or other matters, please contact us for resolution.Contact phone: 400-000-9182828Email: [email protected].Copywriter | JingxinReview | Kuang Xiuhong
Since you are here, please give alike and a look before you go~~~


