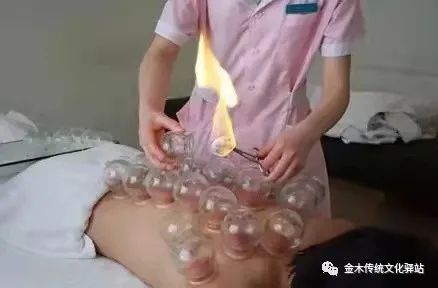
How Much Do You Know About Cupping?
What is Cupping?
Cupping therapy is an external treatment method that uses cups as tools to create negative pressure inside the cups through methods such as burning, suction, or steam. This allows the cups to adhere to specific acupuncture points (腧穴, shùxué) or areas of the body, producing beneficial stimulation to adjust bodily functions and prevent or treat diseases.
1. What Tools Are Used for Cupping?
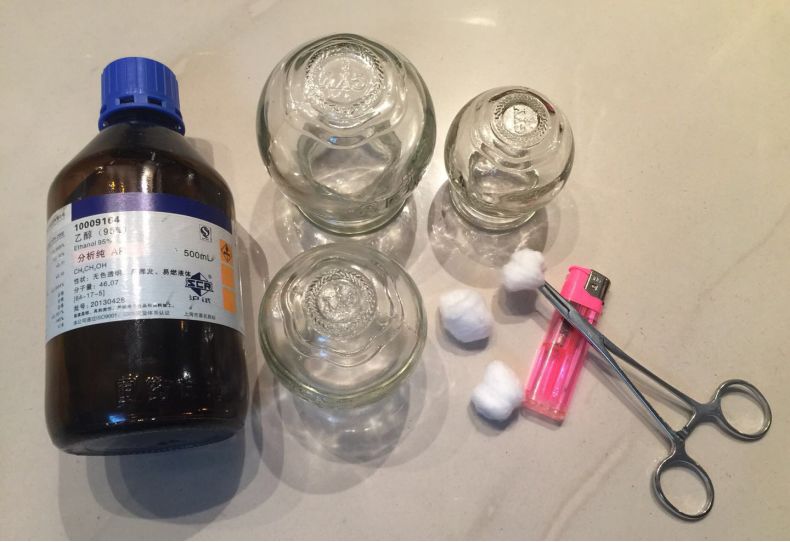
Cups, alcohol, lighter, cotton balls, hemostatic forceps (tweezers)
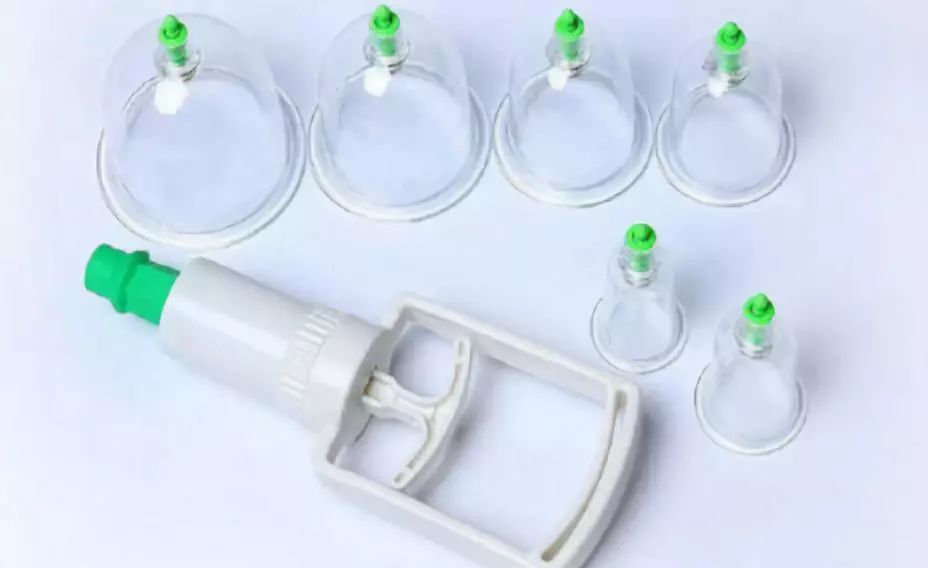

Vacuum cups
2. Commonly Used Tools
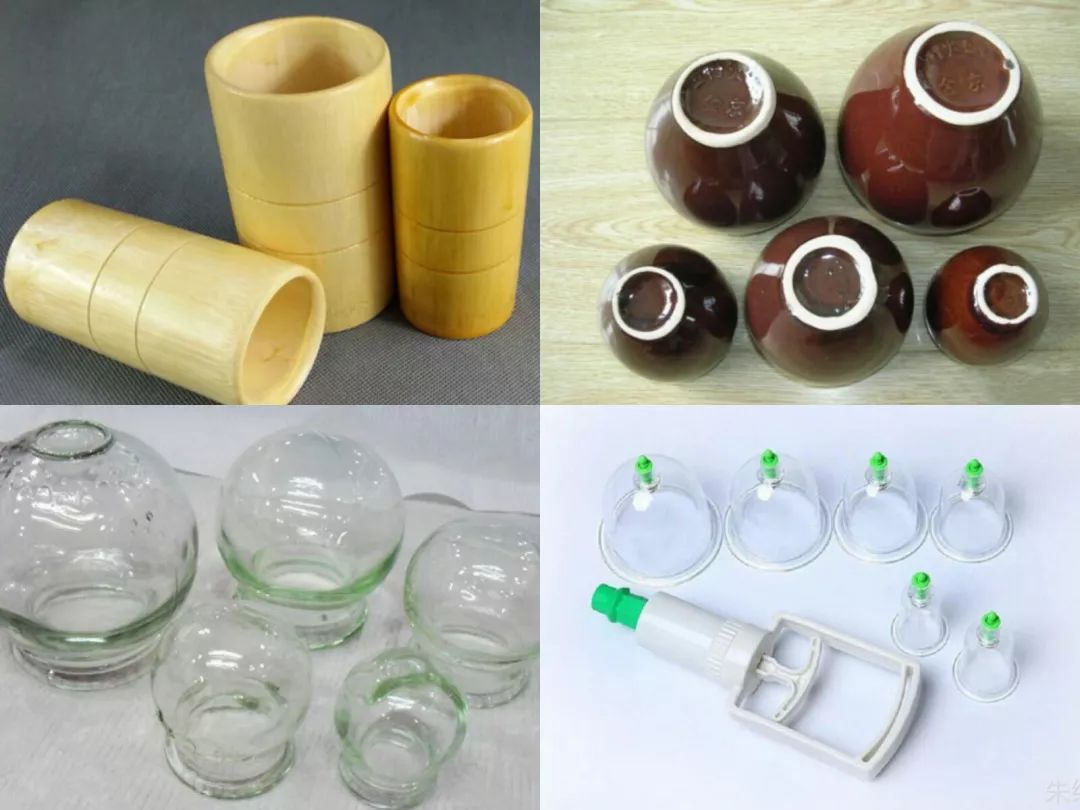

Bamboo cups, ceramic cups, glass cups, vacuum cups
3. How to Perform Cupping?
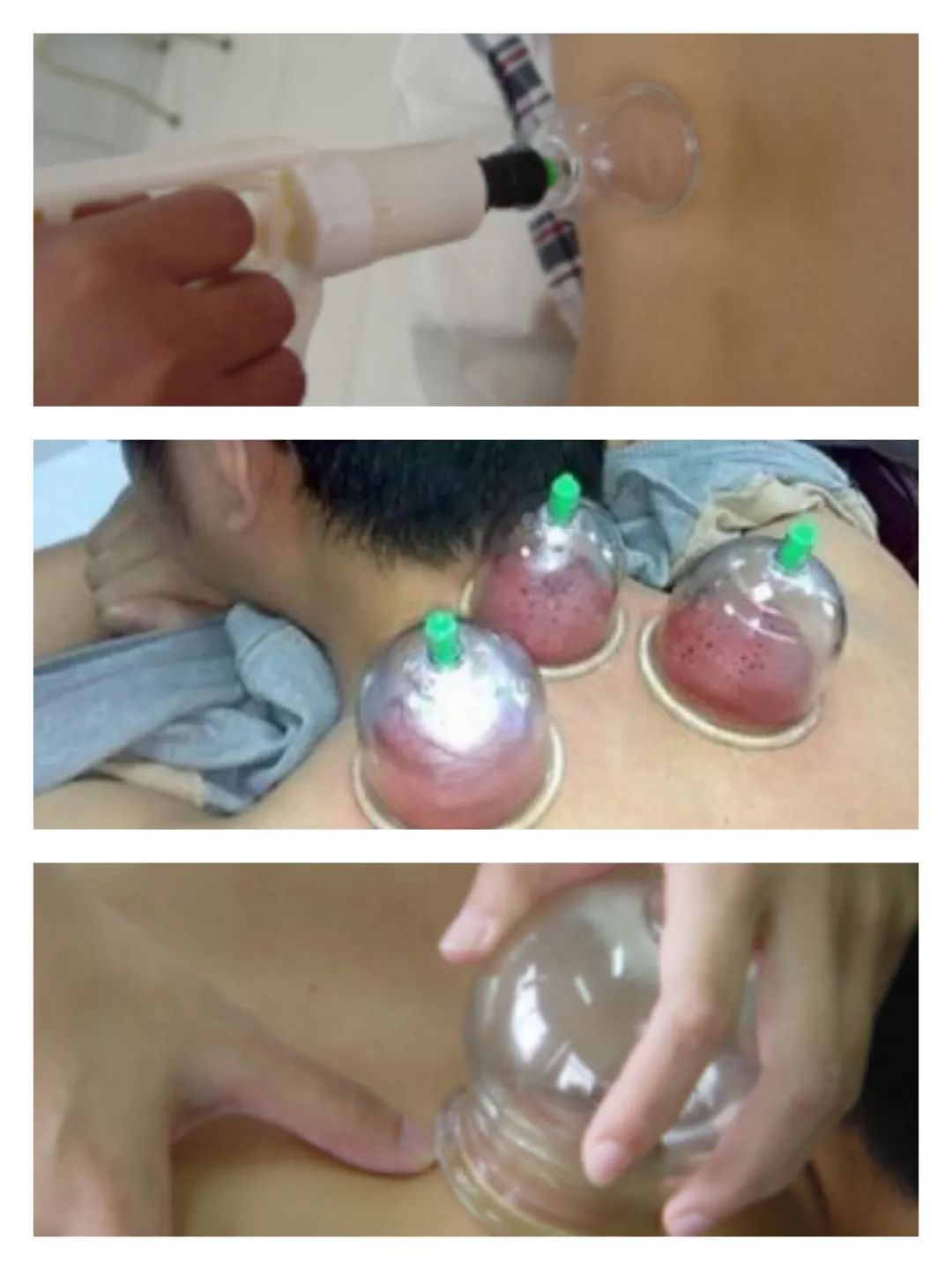
Burning, suction, or steam creates negative pressure → Adhere to the skin → Remove the cup
4. Cupping Methods
(1) Fire cupping method (flash fire method, throwing fire method, cotton sticking method, rack fire method)

(2) Flash fire method
Using hemostatic forceps or tweezers to hold a cotton ball soaked in 95% ethanol, one hand holds the cup with the opening facing down, after igniting the cotton ball, quickly insert it into the cup, shake it a few times, and then immediately place the cup on the treatment area.
This method is the most commonly used clinically and is suitable for all body parts.
Note: Use a small amount of alcohol to avoid burning the skin.

(3) Throwing fire method
Ignite a flammable soft paper (rolled) or a cotton ball soaked in 95% ethanol and quickly place it inside the cup, then swiftly place the cup on the treatment area.
This method has a risk of burning the skin due to falling burning materials.
Commonly used for lateral cupping on the sides of the body.

(4) Cotton sticking method
Place a 1-2 cm diameter cotton pad soaked in 95% ethanol on the inner wall of the cup, ignite it, and quickly place the cup on the treatment area.
Suitable for lateral cupping on the sides of the body.
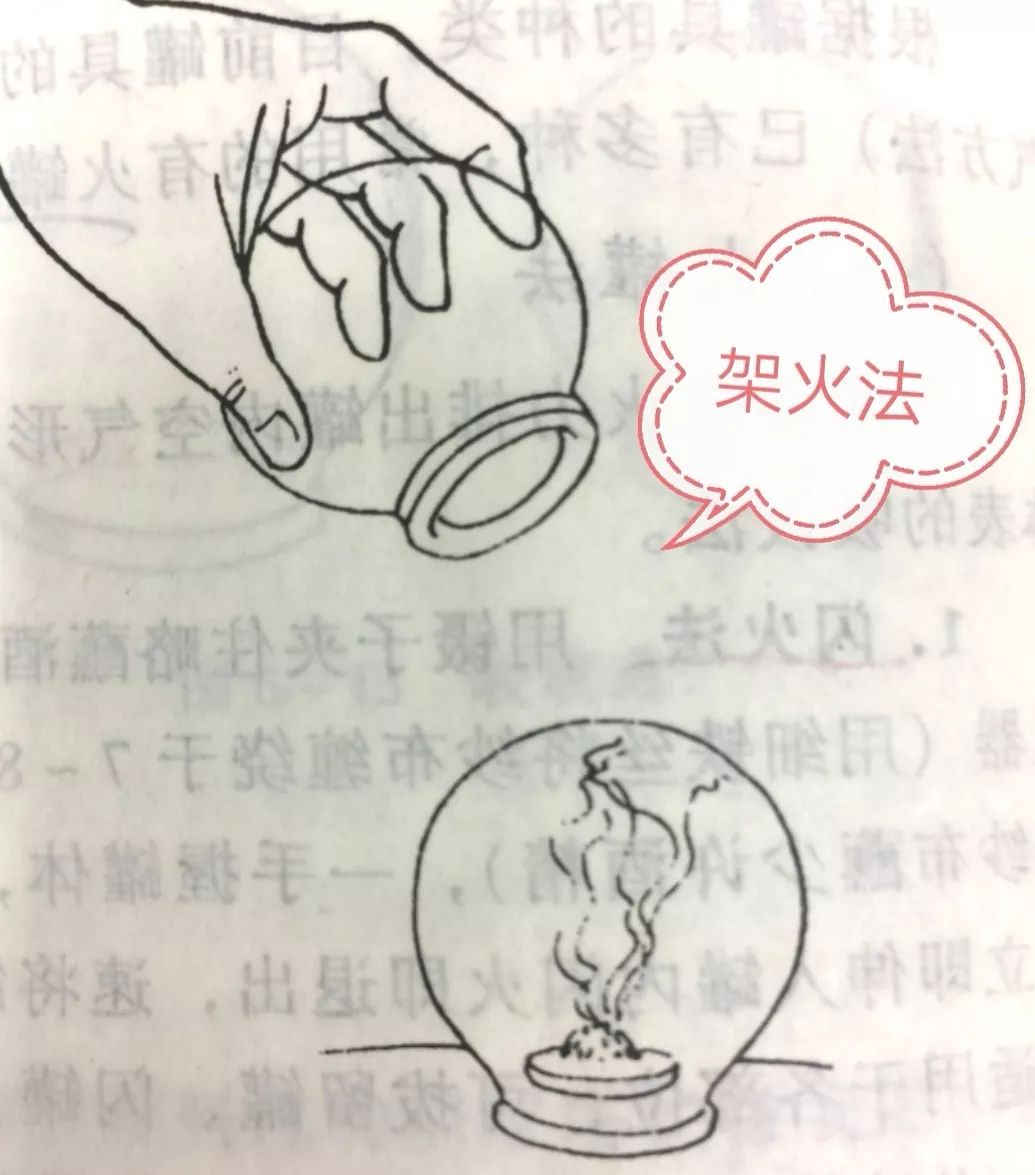
(5) Rack fire method
Place a bottle cap or a piece of dough, or Chinese herbal medicine on the treatment area, then place a cotton ball soaked in alcohol on top, ignite it, and quickly place the cup on that area.
This method is less likely to burn the skin.
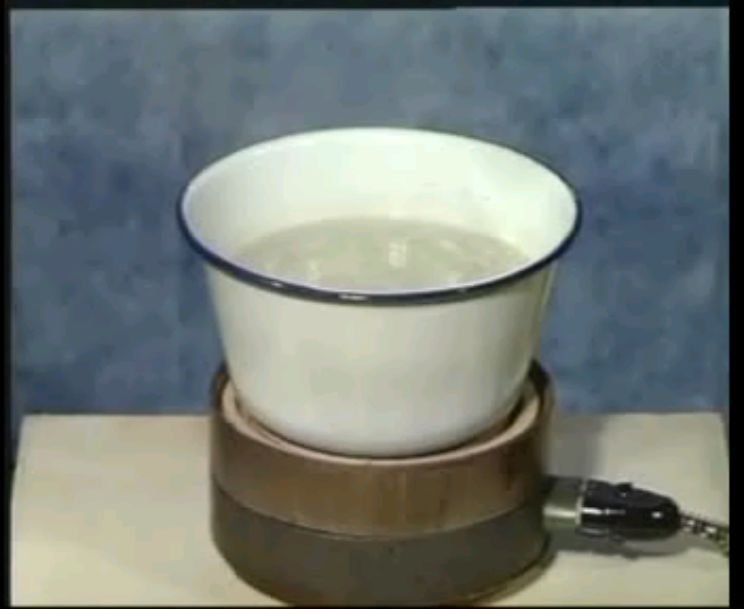

(6) Boiling method
Boil bamboo cups in water or medicinal liquid for 2-3 minutes, then use tweezers to invert the cup (opening facing down) and quickly cover the opening with multiple layers of dry towels to absorb the liquid inside the cup, lowering the temperature of the cup opening (while keeping the heat inside), and while hot, place the cup on the treatment area, then gently press the cup for about 30 seconds to secure it.
(7) Steam method
Boil water or medicinal liquid (not exceeding the spout) in a small kettle, when steam is emitted from the spout or a tube attached to the spout, insert the spout or tube into the cup for 2-3 minutes, then quickly place the cup on the treatment area.
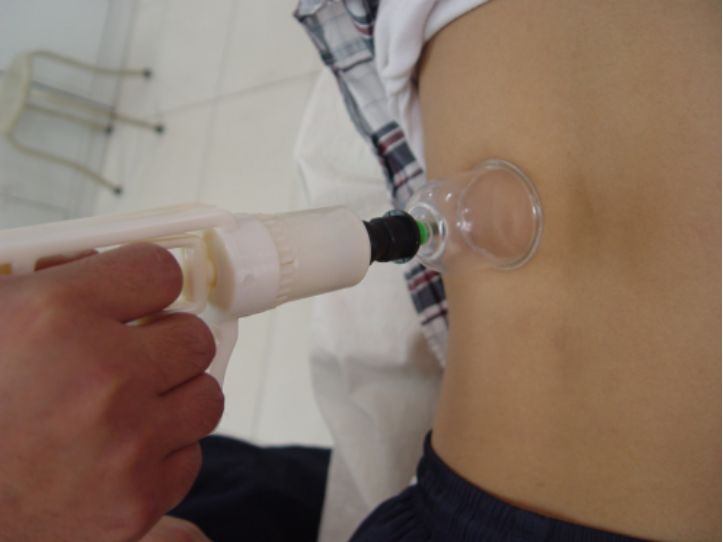
(8) Suction method
First, tightly attach the suction cup to the treatment area, then use a suction pump to remove some air from inside the cup, causing it to adhere to the skin.
5. Applications of Cupping Therapy
Applications of cupping therapy include: single cup method, multiple cup method, retention cupping method, flash cupping method, sliding cupping method, needle cupping method, retention needle cupping method, prick cupping method, medicinal cupping method.
Today, I will mainly introduce the retention cupping method and sliding cupping method~
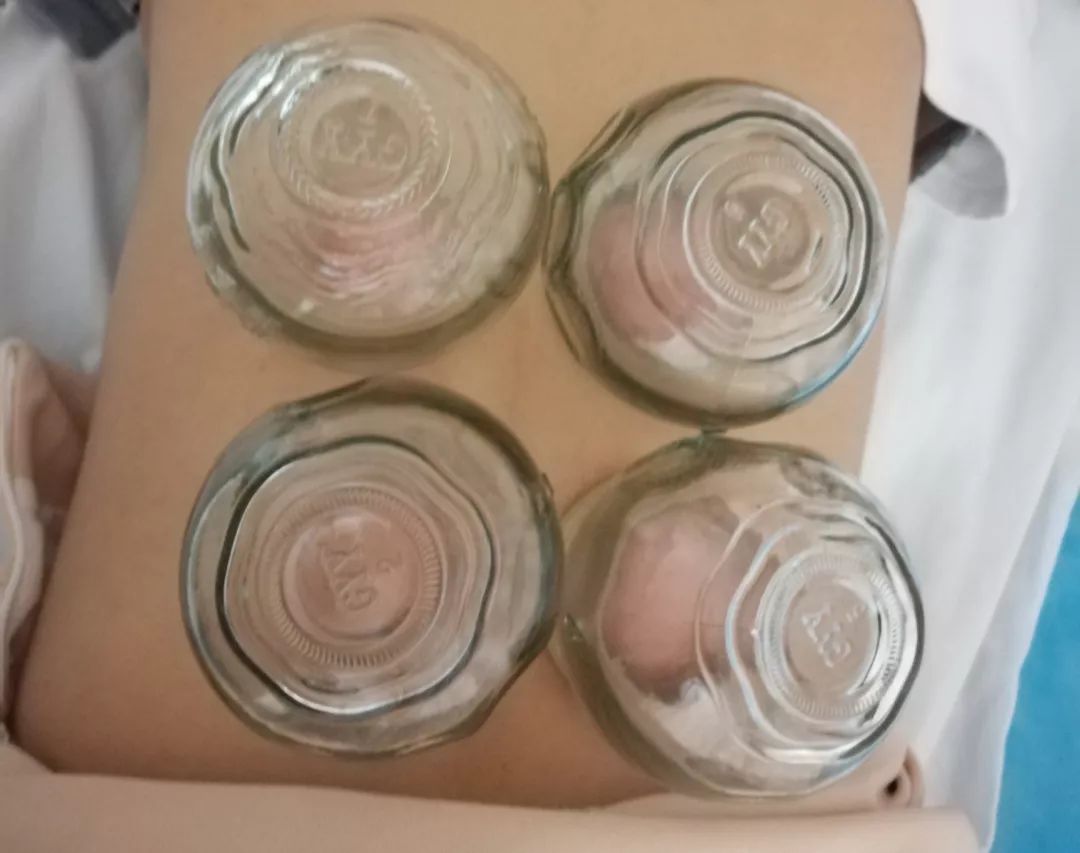

Retention Cupping Method:
After cupping, leave the cup in place for 5-15 minutes.
This method is often used for deep tissue injuries, neck, shoulder, waist, and leg pain, joint diseases, and various other conditions.
The retention time depends on the cupping response and the individual’s constitution.
For individuals with sensitive skin, thin skin, elderly, or children, the retention time should not be too long.
During retention, the cup can be pressed, vibrated, shaken, or rotated to enhance stimulation and improve efficacy.

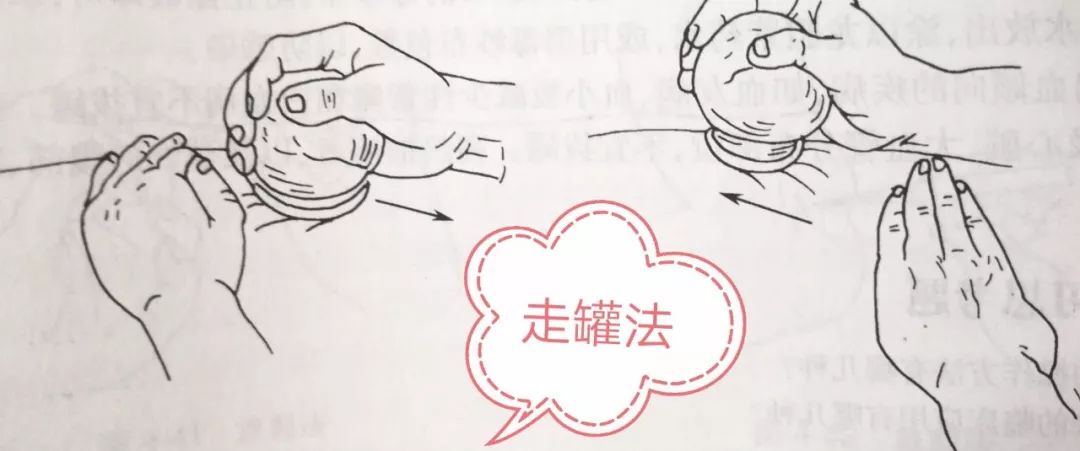
Sliding Cupping Method:
First, apply a lubricant (commonly petroleum jelly, medical glycerin, liquid paraffin, or moisturizing cream) to the area where the cup will be applied, or use warm water or medicinal liquid, and also apply oil to the rim of the cup. After suctioning, hold the cup with one hand and gently push and pull it along a designated path until the skin in the cupping area turns purplish-red. Apply even pressure while sliding the cup to prevent air leakage and falling off.
This method is suitable for areas with broad lesions, thick and flat muscles such as the sides of the spine, lower limbs, lumbar region, abdomen, and shoulder joints.
It can be used for acute febrile diseases, paralysis, numbness, rheumatic pain, and other conditions.
6. Effects of Cupping
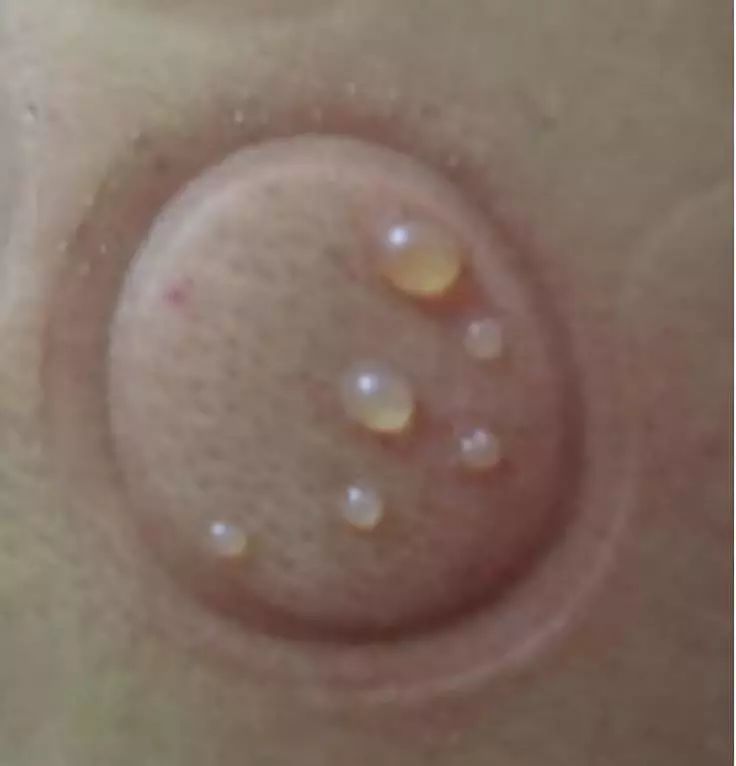
Treatment effects include localized purplish-red spots or bruises at the suction site, or mild heat and pain, referred to as cupping marks or cupping impressions, which are normal reactions and will disappear after a few days.
Pathological Reactions: Cupping marks with blisters, edema, or watery appearance indicate excess dampness or cold dampness.
Cupping marks that are dark purple indicate blood stasis.
Cupping marks that are dark purple-black and painful to touch, accompanied by fever indicate heat toxin and blood stasis.
Cupping marks with no skin color change and not warm to the touch indicate deficiency cold.
Cupping marks that are slightly itchy or have skin lines indicate wind pathogen.
Cupping marks or blood blisters that are pale indicate deficiency syndrome.
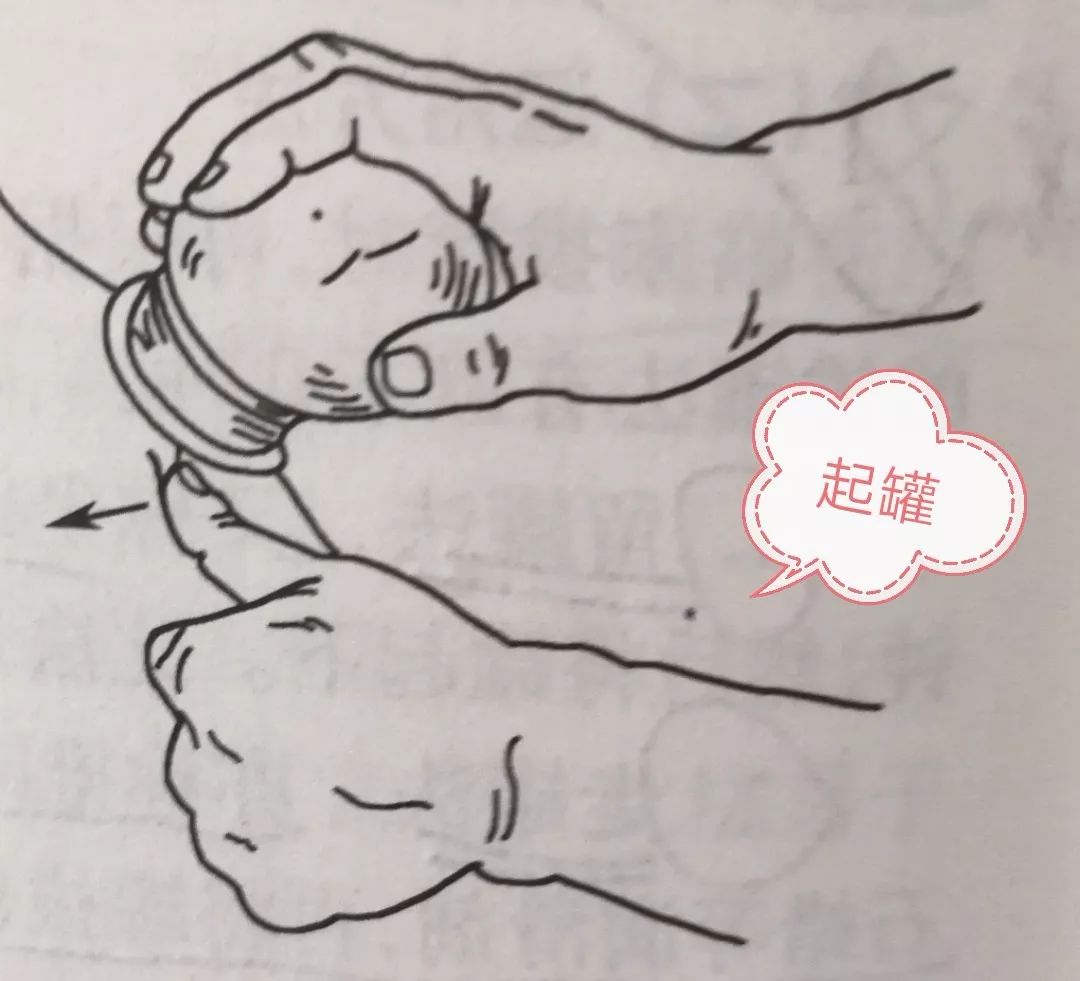
7. How to Remove the Cups
To remove a standard cup: Hold the cup with one hand at a slight angle, and with the other hand, press the skin at the edge of the cup to create a gap for air to enter, allowing the cup to fall off.
To remove a suction cup: Inject air into the cup, and it will detach.
To remove a water (medicinal) cup: Prevent water (medicinal) liquid from spilling out; if the suction area is horizontal, adjust the cupping area to the side before removing the cup.
8. Post-Cupping Care
After removing the cup, wipe away any small droplets of water with a disinfected cotton ball.
Small blisters: Allow them to absorb naturally without treatment.
Large blisters: Use a disinfected needle to puncture and release the fluid, then cover with a disinfected dressing.
Bleeding: Wipe clean with a cotton ball.
Skin damage: Regular disinfection and cover with a sterile dressing.
Cupping for abscesses: After removing the cup, clean the pus and blood, and treat the wound conventionally.
9. What Conditions Are Suitable for Cupping?
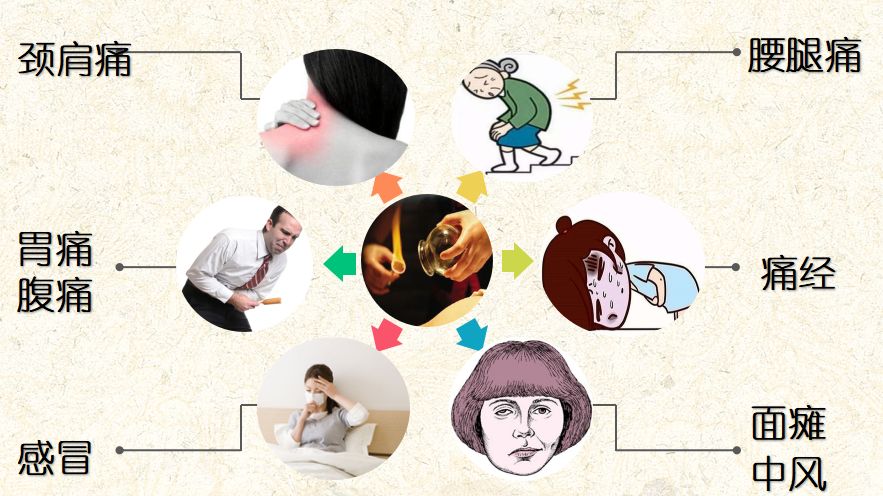
And so on…
10. Contraindications for Cupping
(1) Acute severe diseases, chronic systemic weakness diseases, contact infectious diseases
(2) Acute traumatic fractures
(3) Schizophrenia, convulsions, uncooperative individuals
(4) Apex of the heart, areas with large superficial artery pulsations, varicose veins
(5) Lymphadenitis, hernias, active pulmonary tuberculosis
(6) Abdomen, lumbar region, and breast area of pregnant women
(7) Infants and young children, etc.
Spreading knowledge of TCM health preservation, promoting traditional Chinese culture, sharing health concepts, and conveying care, passing health knowledge and traditional culture to more friends…
People are great because of their dreams, we are different because of our love.
Liu Ling Ning: 186 9643 6785 or (WeChat ID)
Yang Shun Song: 138 7171 7447 or (WeChat ID)


