

In-depth and Broad, Just Waiting for Your Attention
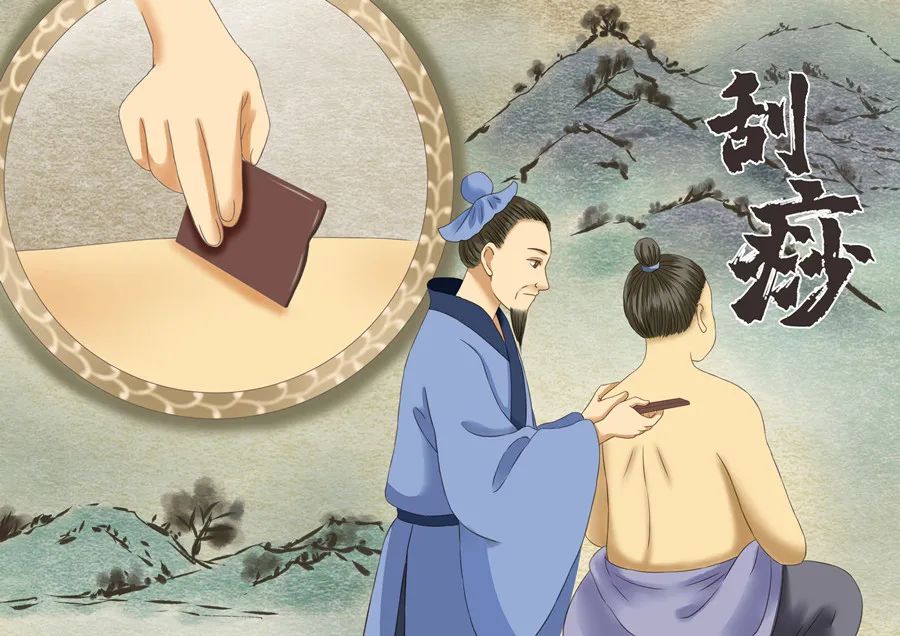

Gua Sha originated from folk practices and was first recorded in the Yuan Dynasty by the physician Wei Yilin in the book “Shi Yi De Xiao Fang”. Other medical texts also provide detailed accounts of the principles and methods of Gua Sha. For example, “Sha Zhang Yu Heng” states: “The Gua Sha method involves scraping the back and neck, as well as the chest and sides, using a coin dipped in fragrant oil.” Wu Shangxian in “Li Yue Pian Wen” noted, “For Yang Sha abdominal pain, it is best to use a porcelain spoon dipped in fragrant oil to scrape the back, as the five organs are connected to the back; scraping will expel evil qi and relieve the illness.”What is Gua Sha?
Gua Sha is a technique that uses specialized scraping tools to repeatedly scrape and rub the skin surface after applying a certain medium, causing localized “sha” to appear, thereby achieving effects such as invigorating blood circulation, relaxing muscles, detoxifying, clearing heat, relieving pain, and strengthening the spleen and stomach.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believes that qi circulates continuously in the body, and the hub that governs the rise and fall of qi is called “qi mechanism”. Therefore, diseases related to qi are primarily due to the imbalance of the “qi mechanism”. Gua Sha aims to regulate qi, stimulate the circulation of qi and blood, expel evil from the surface, and enhance self-healing capabilities to treat diseases.
The skin is closely connected to the meridians, and Gua Sha stimulates the meridians on the body surface, promoting the smooth flow of meridians, invigorating blood circulation, and regulating the qi and blood of the internal organs. According to modern medical explanations, the pores on the skin can release heat toxins and expel skin toxins, as well as evaporate moisture. These pores serve as both treatment points and pathways for expelling illness. Gua Sha can enhance local blood circulation and stimulate the body’s immune response.
What is the “sha” that appears on the skin?
Those who have experienced Gua Sha know that the scraped area often appears red, which is what we commonly refer to as “sha”.
The process of “sha” appearing involves the dilation of blood vessels leading to the rupture of capillaries, resulting in blood leakage and the formation of bruises on the skin. Blood clots soon dissolve, producing a new irritant that not only adjusts immune function and enhances immunity but also regulates brain excitation and inhibition.
Individuals with heavy dampness and deep cold may experience more pronounced “sha” after Gua Sha.

Is more “sha” better during Gua Sha?
Different individuals will have different red marks after Gua Sha. It is incorrect to judge the effectiveness of Gua Sha solely by the amount of red marks. Excessive force during Gua Sha may lead to more red marks. However, it is also incorrect to say that Gua Sha is ineffective if no “sha” appears, as it may simply be that the “sha” is not visibly apparent.
For certain special populations, Gua Sha is not recommended, such as those with fragile blood vessels, thrombocytopenia, or coagulation disorders. Blindly performing Gua Sha may lead to abnormal bleeding from blood vessels, which may appear as excessive “sha” but actually causes new harm.
Gua Sha Techniques: Supplementing and Draining
Supplementing Scraping Method
Light pressure, superficial effect, slow speed, used for elderly, weak, chronically ill, or severely ill patients with deficiency syndromes.
Draining Scraping Method
Heavy pressure, deep effect, fast speed, used to expel pathogenic factors in young, robust, newly ill, or acutely ill patients with excess syndromes.
Balanced Scraping Method
Also known as the flat scraping method, where the scraping board applies moderate pressure and speed. It focuses on balancing yin and yang, suitable for patients with mixed deficiency and excess, especially for sub-healthy individuals or healthy individuals seeking preventive Gua Sha.

Common Gua Sha Areas
Head Scraping
Can promote blood circulation in the head, relieve fatigue, alleviate headaches, and improve blood supply to the brain, providing a relaxing effect. For those with tight scalp and headaches, it can improve local blood circulation.
Neck and Shoulder Scraping
Has the effect of dispelling wind, unblocking meridians, invigorating blood circulation, and can improve stiffness and pain in the neck and shoulders, as well as treat conditions related to the head and throat.
Back Scraping
Can regulate yin and yang, adjust the internal organs, relax muscles and unblock meridians, and strengthen kidney function, enhancing the body’s defensive capabilities and expelling internal dampness. It can also increase the body’s immune function and improve lung function.
Gua Sha Tools
Commonly used Gua Sha tools include Gua Sha boards and Gua Sha oil.
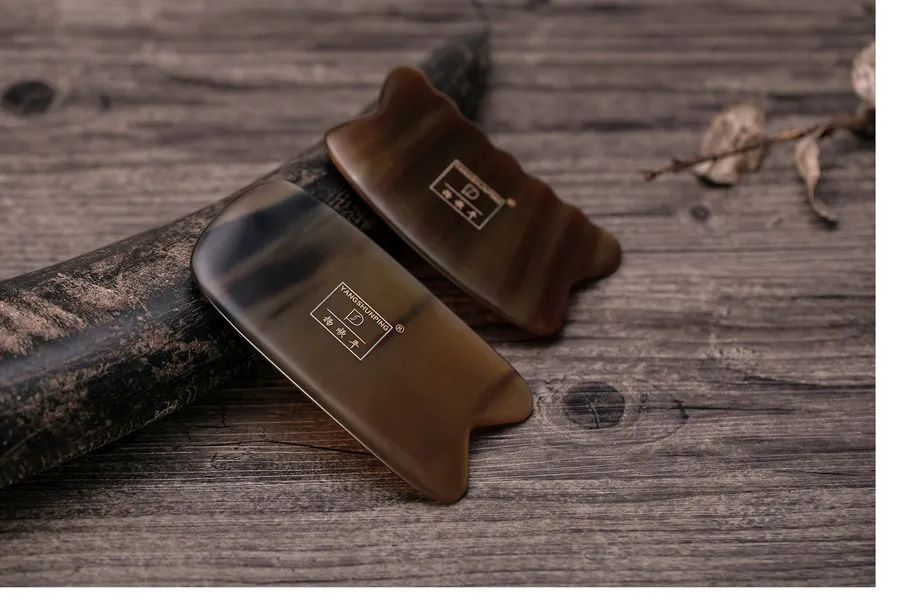

Gua Sha boards can be made of materials such as horn, jade, or Bian stone; Gua Sha oil can be liquid or cream-based, and even plain water can be used to reduce pain during the scraping process and prevent excessive friction on the skin.
Who Should Avoid Gua Sha?
● Patients with skin diseases should avoid Gua Sha therapy; those with edema, diabetes, and heart disease should refrain from Gua Sha;
● Patients with hemophilia, hemorrhagic purpura, and other bleeding disorders should not undergo Gua Sha treatment;
● Patients with low blood pressure, low blood sugar, extreme weakness, and those particularly sensitive to pain should use gentle scraping techniques;
● Pregnant women and infants should be cautious with Gua Sha;
● Those who are overly hungry, overly full, or excessively fatigued should avoid Gua Sha.
Precautions During Gua Sha1. Do not consume alcohol within 24 hours before and after Gua Sha; intoxicated individuals should avoid it.
1. Do not consume alcohol within 24 hours before and after Gua Sha; intoxicated individuals should avoid it.
2. Avoid Gua Sha when overly full or too hungry;
3. Do not scrape over the nipples or genital areas;
4. Avoid scraping over areas with skin ulcers;
5. For those with long-term lower body stagnation, such as constipation, be cautious when scraping abdominal points to prevent qi from rising;
6. Wait three hours after Gua Sha before taking a shower. Since Gua Sha requires exposing the back, showering immediately afterward may allow cold and dampness to enter the body. It is better to wait until the skin’s pores have closed.
7. There is no need for special treatment for the sha marks that appear after Gua Sha; it is normal to feel pain and heat in the scraped areas;
8. If fainting occurs during Gua Sha, have the person lie down, ensure the room is ventilated, and apply pressure to the Neiguan (PC6) or Jiquan (PC8) points until they feel better;
9. After Gua Sha, cover the back with clothing to prevent cold pathogens from invading the skin.
Using Gua Sha to Improve Insomnia: Opening Four Points
In modern life, with fast-paced lifestyles and high stress, many people often have irregular routines due to various reasons. Those who enjoy spicy food may have disharmony in the spleen and stomach, harming the heart and spleen, leading to insufficient nourishment of the spirit, resulting in insomnia, waking easily, and having vivid dreams. TCM believes that insomnia is generally due to an imbalance of qi, blood, yin, and yang. Using a copper Gua Sha tool to scrape four points, along with the Anmian (安眠), Shenmen (神门), and Sanyinjiao (三阴交) points, can help improve insomnia.
Opening Four Points
The Dazhui (大椎) point is an important point on the Governing Vessel, which can promote yang qi throughout the body and has a lung-dispersing effect. It is located in the depression below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra.
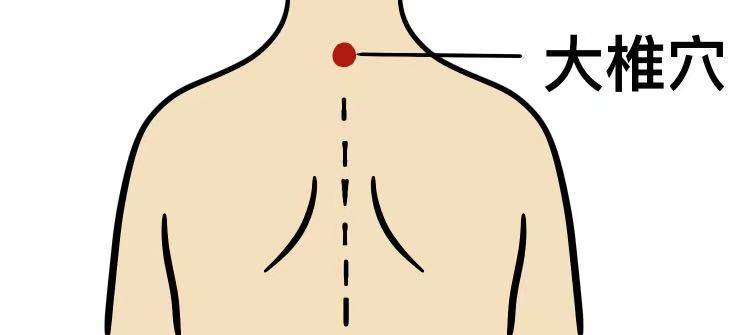
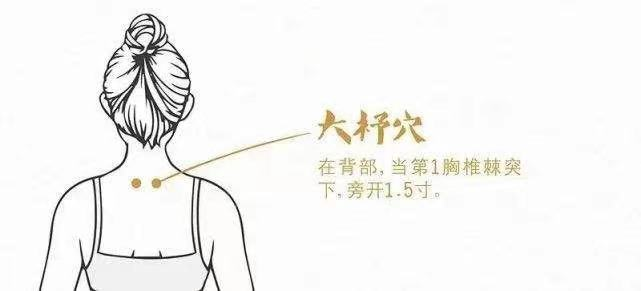
The Dazhu (大杼) point nourishes blood and mobilizes qi and blood in the body, located 1.5 cun lateral to the spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra.
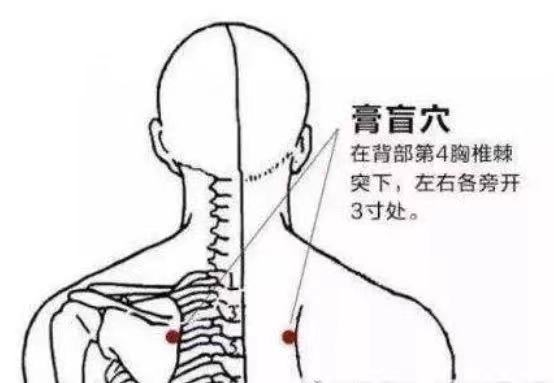
The Gaohuang (膏肓) point nourishes yin and is located 3 cun lateral to the spinous process of the fourth thoracic vertebra, at the medial border of the scapula.
The Shentang (神堂) point calms the spirit and is located 3 cun lateral to the spinous process of the fifth thoracic vertebra, at the medial border of the scapula.
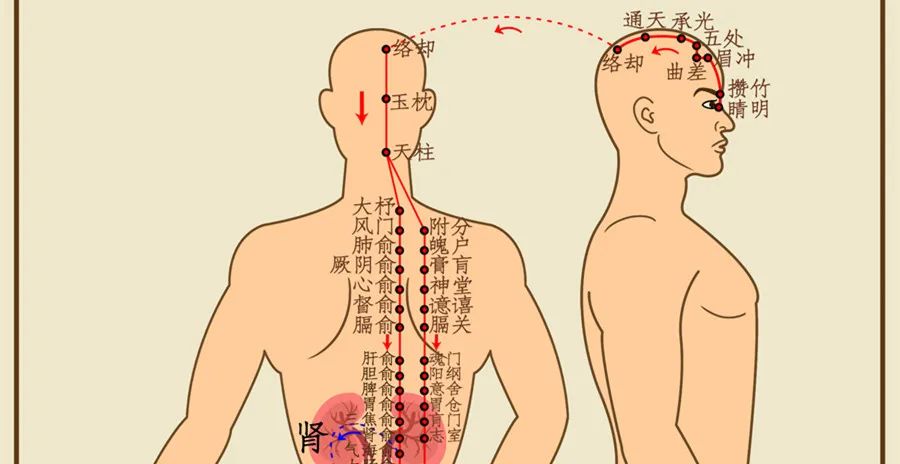
To improve insomnia, you can also add the Anmian (安眠), Shenmen (神门), and Sanyinjiao (三阴交) points. You can also use your fingers to press and rub these points, applying pressure until you feel a sense of soreness and distension. Press each point for 2 minutes, which can also help improve insomnia.
Gua Sha Prescription
Apply Gua Sha oil, scrape the Dazhui, bilateral Dazhu, bilateral Gaohuang, and Shentang points, 30-40 times each, scraping from top to bottom until the skin shows “sha” or the pores are fully opened; press the Anmian and Shenmen points for 2 minutes each, applying pressure until you feel a sense of soreness and distension; scrape the Sanyinjiao point for 30-40 times, also scraping from top to bottom. Wait for the “sha” to subside before performing the next scraping, generally 5-7 days for the “sha” to fade.
Finally, I remind everyone that if you need Gua Sha, it is best to go to a reputable hospital or therapy center for professional treatment. If you feel any discomfort during Gua Sha, be sure to inform the medical staff promptly.■
Source: Guangzhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Sichuan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Guangdong Traditional Chinese Medicine WeChat Official Account
-END-

