
What is Cupping Therapy?
Cupping therapy, also known as “Jiao Fa,” is a method that uses cups as tools to create a negative pressure by removing air through heat, allowing the cups to adhere to acupuncture points (腧穴, shùxué) or specific areas of the body. This creates stimulation that leads to local skin congestion and bruising, aiming to prevent diseases. The most commonly used method in clinical practice is fire cupping (拔火罐法, bá huǒ guàn fǎ), which has effects such as promoting qi (气, qì) and blood circulation, dispelling wind and cold, and alleviating swelling and pain. It is effective for conditions like lumbar muscle strain, lumbar disc herniation, wind-cold bi syndrome (风寒痹痛, fēng hán bì tòng), and shoulder periarthritis.
01Balanced Cupping
Balanced cupping can effectively stimulate the flow of qi, unblock the meridians (经络, jīng luò), and promote smooth circulation of qi and blood throughout the body. This reflexively causes the central nervous system to shift to a state of stress, helping to regulate and improve fatigue, stabilize kidney qi, and harmonize the liver and spleen. The back is chosen for balanced cupping because the back shu points (背俞穴, bèi shū xué) are primarily used to treat internal organ diseases. Through beneficial stimulation and the effects of cupping, balanced cupping regulates the internal organs and unblocks the meridians, achieving therapeutic effects on the liver, spleen, and kidneys.

1. Mechanism of Balanced Cupping
1. Local Effects (Acupuncture Points or Nerves)
(1) Mechanical Stimulation
Through the cup’s opening, local nerves, back shu points, etc., are pulled, warmed, scraped, compressed, and tapped, stimulating capillary dilation, tissue autolysis, histamine release, and enhancing the body’s organ and tissue responses, self-regulation, and self-repair.
(2) Thermal Stimulation
The heat inside the cupping vessel promotes blood circulation, enhances metabolism, and facilitates self-regulation of peripheral nerves.
2. Systemic Effects
Both mechanical and thermal effects act on local capillaries, peripheral nerves, primarily the spinal nerve roots, and surrounding muscle tissues. This excites the spinal cord or cerebral cortex nerves, transforming them into beneficial information that is transmitted to the organs and tissues needing treatment.
2. Techniques of Balanced Cupping
Flash Cupping
Warming the Meridians and Dispelling Cold
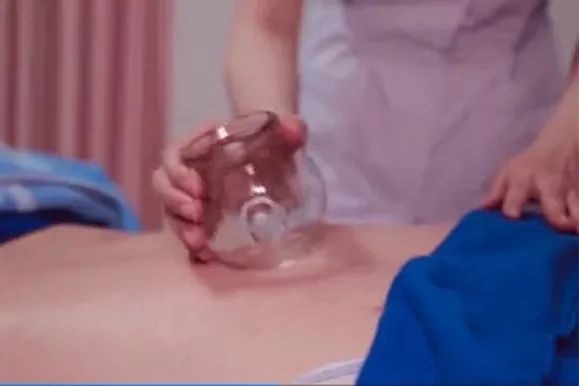
Walking Cupping: Enhances nerve and muscle excitability; accelerates blood circulation; promotes metabolism, showing good efficacy for improving central nervous system issues and peripheral nerve problems after stroke.
Rubbing Cupping: Relaxes muscles and dispels cold.
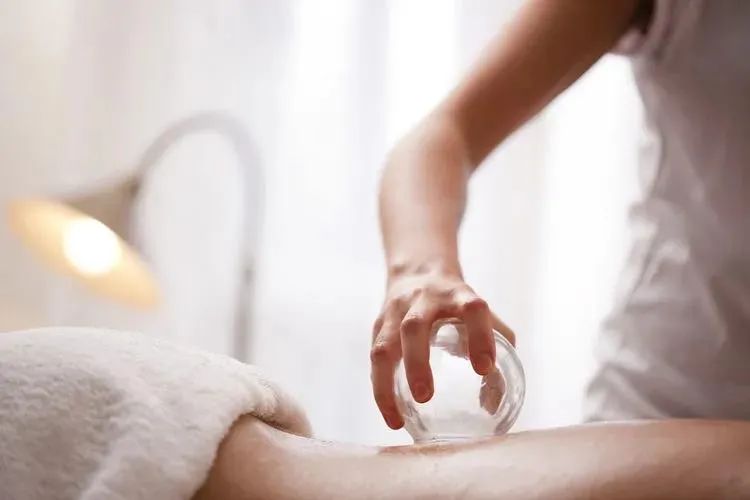


Shaking Cupping: Commonly used for heat-type diseases, has effects of clearing heat, dispelling fire, and promoting blood circulation.
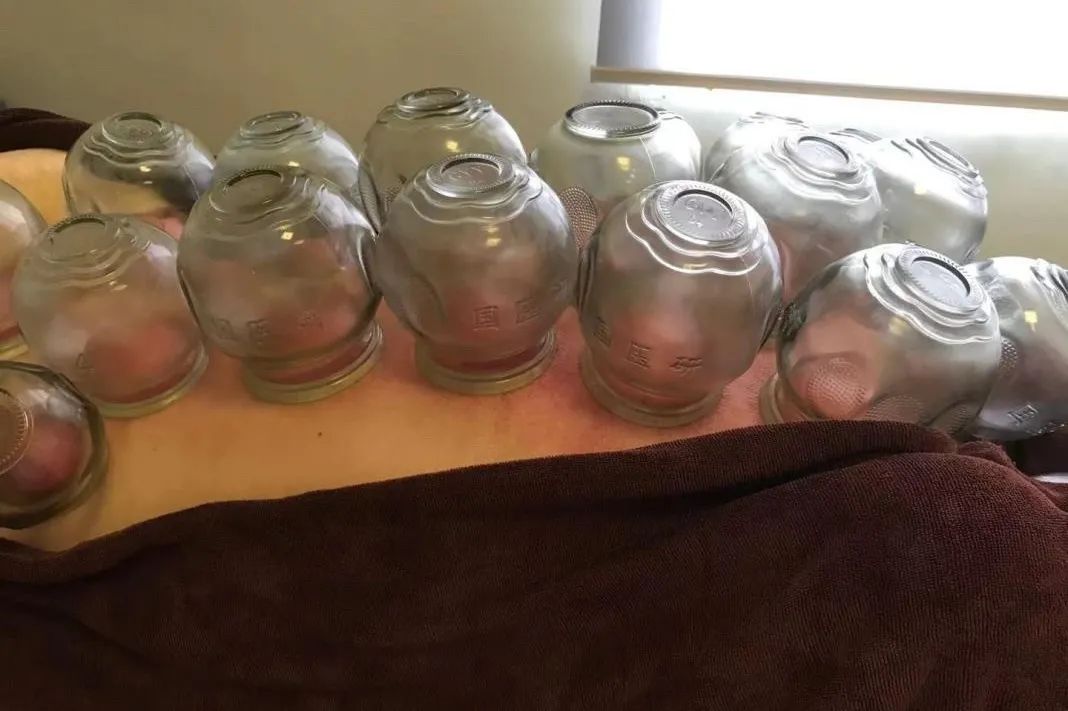

Retention Cupping: For patients with pain in the back, waist, limbs, and joints caused by wind, cold, and dampness, it warms the meridians and dispels cold.
3. Advantages of Balanced Cupping
So, what advantages does this “upgraded” cupping therapy have over traditional cupping therapy?
1. Balanced cupping is more systematic in treating diseases, primarily targeting the lumbar and back areas, focusing on the bladder meridian (足太阳膀胱经, zú tài yáng páng guāng jīng) and the governing vessel (督脉, dū mài). The technique involves heavier stimulation, gradually penetrating deeper into the painful areas during the procedure.
2. Different treatment techniques can be selected based on the disease stage, incorporating various methods such as flash cupping, flying cupping, walking cupping, rubbing cupping, shaking cupping, and retention cupping, all without side effects, treating and preventing diseases simultaneously.
4. Indications for Balanced Cupping
1. Patients with chronic fatigue syndrome
2. Patients with colds
3. Patients with neck and back pain
4. Patients with insomnia
5. Patients with obesity
6. Healthy individuals with damp-heat constitution
7. Regulating the spleen and stomach
Note: Elderly, frail individuals, and those with excessively loose skin or blood disorders should avoid this treatment.
02
What Other Amazing Cupping Techniques Are There?
01
Medicinal Clay Cupping
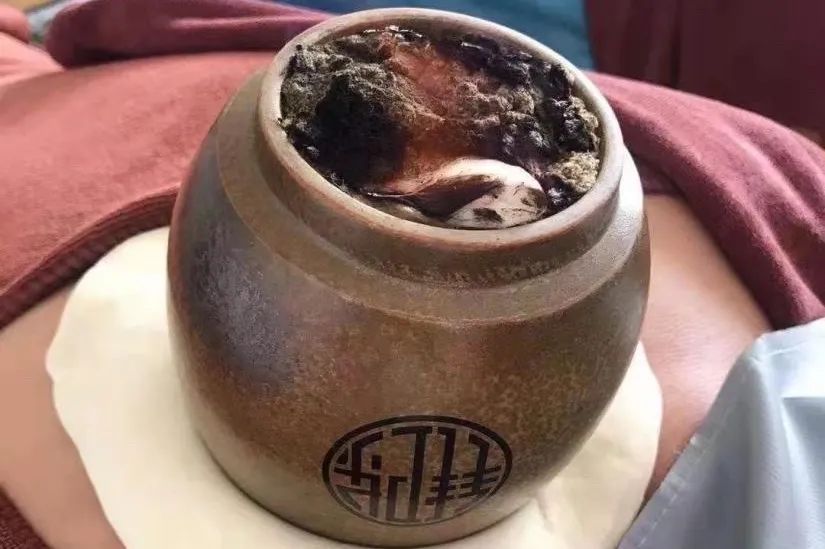
Medicinal clay cupping is a traditional technique passed down through five generations by Qian Weidong, now included in the intangible cultural heritage list. It integrates cupping, hot compresses, and moxibustion (艾灸, ài jiǔ) into one. Using a medicinal clay cup, after spraying medicinal wine inside, it creates negative pressure through combustion, adhering the cup to the skin covered with a dough-like substance, followed by burning moxa to stimulate qi, promote blood circulation, and achieve the effects of warming the meridians and dispelling cold, alleviating pain.
Medicinal clay cupping is mainly suitable for cold syndromes, pain syndromes, bi syndromes, chronic deficiency diseases, and gynecological diseases, showing significant efficacy for rheumatic musculoskeletal diseases.

02
Fire Dragon Cupping
“Fire Dragon Cupping” is a special therapeutic tool that combines massage, guasha (刮痧, guā shā), and moxibustion, integrating techniques such as kneading, rolling, pushing, pressing, tapping, shaking, flashing, vibrating, and heating. It introduces moxibustion essential oil into the subcutaneous tissue for systemic treatment. The goal is to regulate the internal organs, unblock the meridians, promote qi and blood circulation, lubricate joints, and warm and tonify yang qi.
Indications:
1. Soft tissue injuries of the spine, such as cervical spondylosis, lumbar disc herniation, and ankylosing spondylitis.
2. Muscle injuries in the back, such as upper back pain, acute lumbar sprains, and local muscle strains.
3. Gastrointestinal diseases, such as constipation, diarrhea, abdominal distension, and indigestion.
4. Gynecological diseases, such as irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and uterine fibroids.
5. Bi syndromes caused by wind, cold, and dampness.
6. Edema after fractures.
7. Stroke sequelae.
8. Symptoms of acid, numbness, swelling, and pain caused by diabetic microcirculation disorders.

03Caring for Yourself After Cupping
1. What Do Different Colors of Cupping Marks Indicate?
1. Dark purple-black marks: Generally indicate insufficient blood supply and poor circulation with blood stasis.
2. Purple marks with spots: Generally indicate cold congealing and blood stasis.
3. Scattered purple spots with uniform depth: Indicate qi stagnation and blood stasis.
4. Bright red marks: Generally indicate yin deficiency, qi and blood deficiency, or excess fire due to yin deficiency.
5. Dark red marks: Indicate high blood lipids and heat evil.
6. Gray-white marks that are cool to the touch: Generally indicate deficiency-cold or damp evil.
7. Marks with skin texture or slight itching: Indicate wind evil or dampness.
8. Water vapor on the inner wall of the cup: Indicates dampness in that area.
9. Blisters appearing on the cupping marks indicate heavy internal dampness; if the blisters contain blood, it reflects damp-heat toxicity.
2. What Should You Pay Attention to After Cupping?
1. It is not advisable to take a bath after cupping; it is better to bathe before cupping. Care should be taken to avoid skin injury or burns during cupping. Cupping should not be performed on areas with allergies, ulcers, edema, or large blood vessel distribution. Patients with high fever and convulsions, as well as pregnant women, should avoid cupping on the abdomen and lower back.
2. Patients with chronic lung diseases should use cupping cautiously. Those with underlying lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pulmonary tuberculosis, lung abscess, or bronchiectasis, should avoid cupping. Inflammation in the lungs often accompanies damage to the alveoli or fluid retention in the lungs. Using cupping for treatment can cause rapid changes in thoracic pressure, leading to the rupture of pulmonary blebs and resulting in spontaneous pneumothorax.
In summary, cupping therapy can dispel dampness and cold, unblock meridians, eliminate stagnation, invigorate blood and qi, relieve pain and swelling, clear heat and detoxify, and help regulate the body’s yin-yang balance, eliminate fatigue, and enhance physical fitness. Thus, many ailments can be treated with cupping therapy. For example, in traditional Chinese medicine, lumbar and leg pain in middle-aged and elderly individuals is understood as invasion by damp-cold. Placing the cup on the affected area can gradually draw out the dampness while promoting blood circulation, alleviating discomfort, and restoring function. Additionally, cupping can also treat muscle strain, lumbar disc herniation, and other symptoms. It can be applied to acupuncture points to treat chest tightness, shortness of breath, dizziness, and abdominal discomfort.
Source: Daye City Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital
Copyright belongs to the original author. If there is any infringement, please contact us for modification or deletion. Contact number: 0731-85054048
Recommended Reading
Join Groups: Various specialized nursing WeChat groups, join now!
Submissions:Original articles related to nursing are welcome for submission.
Video Channel:Nursing tips and live broadcasts from experts.
Follow: WeChat public account categorized by nursing departments.
Buy Books:Nursing books, click “Read More” below to purchase.

