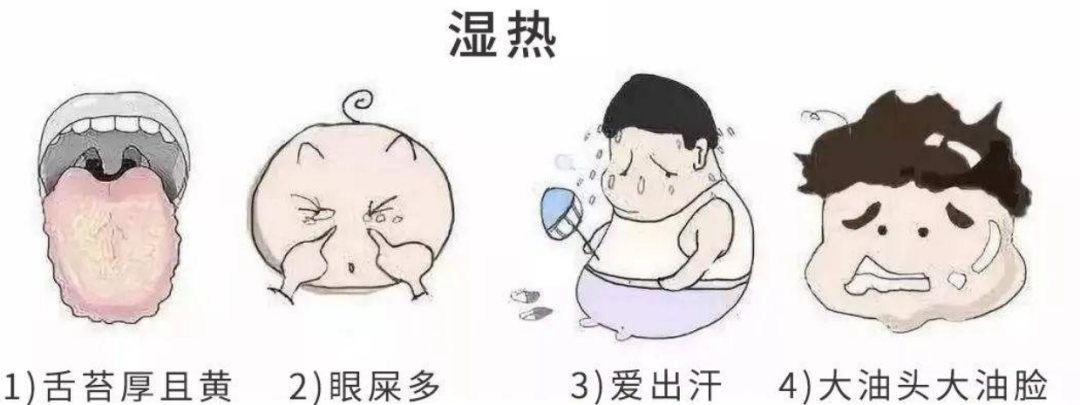
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the term “damp-heat” does not refer to a specific organ disease. Instead, it indicates a state where the body’s digestive system undergoes a series of changes. Damp-heat is not merely a physical manifestation; it reflects an imbalance within the body’s internal environment. What we commonly refer to as damp-heat does not signify a problem with a specific organ such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, or kidneys, but rather a comprehensive state of the entire body, primarily involving the digestive system and other aspects.01Mainly affects the generation of Qi and Blood
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the term “damp-heat” does not refer to a specific organ disease. Instead, it indicates a state where the body’s digestive system undergoes a series of changes. Damp-heat is not merely a physical manifestation; it reflects an imbalance within the body’s internal environment. What we commonly refer to as damp-heat does not signify a problem with a specific organ such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, or kidneys, but rather a comprehensive state of the entire body, primarily involving the digestive system and other aspects.01Mainly affects the generation of Qi and Blood
Damp-heat accumulation can obstruct the smooth flow of Qi and blood, leading to symptoms such as decreased memory, insufficient Qi and blood, poor sleep, and frequent bowel movements. This is because damp-heat hinders the generation and circulation of Qi and blood, preventing various parts of the body from receiving adequate nutrition and oxygen supply.
02Mainly affects the transformation and transportation of fluids
Damp-heat can obstruct the spleen, leading to dysfunction in the transformation and transportation of fluids. This can result in fluid accumulation in the body, causing a distended abdomen that feels soft, a state of “false obesity,” early satiety, belching, abdominal bloating, and lethargy. Damp-heat affects the normal functions of the spleen and stomach, preventing timely elimination of fluids from the body, leading to accumulation.
03Affects the lips
Under normal circumstances, healthy lips are rosy and plump. However, in a damp-heat state, the lips may appear pale, cracked, peeling, or dark purple, indicating underlying health issues.
Damp-heat can affect the circulation of Qi and blood and the metabolism of body fluids, which is reflected in the condition of the lips. Damp-heat can lead to two extreme problems:
Absorption issues (eating a lot but still thin)
Damp-heat affects the digestive and absorptive functions of the spleen and stomach, making it difficult for the body to absorb nutrients even when consuming large amounts of food, resulting in weight loss.
Metabolic issues (gaining weight even from drinking cold water)
Damp-heat obstructs normal metabolism, preventing timely elimination of fluids and waste from the body, leading to fat accumulation, which can result in weight gain even from drinking cold water.
What symptoms does damp-heat constitution bring?
1. Drooling during sleep, sticky stools, serrated edges on the tongue, pale and peeling lips, various forms of sagging, edema, insufficient Qi and blood, and decreased organ function.
2. Damp-heat can impair the transportation function of the spleen and stomach, leading to internal fluid stagnation and various discomforts. Additionally, damp-heat can affect the circulation of Qi and blood and organ function, resulting in various health issues.
How to regulate damp-heat constitution01Emotional regulation
Learn to manage emotions and maintain a positive mood. This can be achieved through exercise and yoga.
02Develop good habits
Avoid staying up late, limit alcohol consumption, eat a balanced diet, and reduce spicy and cold foods to nourish the spleen and stomach.
03Meridian care for the spleen and stomach
The presence of dampness indicates insufficient spleen and stomach function. Strengthening the spleen is crucial; regular massage of the Yinlingquan (Yin Mound Spring) point, Quchi (Pool at the Bend) point, and Zhongwan (Middle Cavity) point is recommended.
04Improve diet
Those with damp-heat should avoid overly warming and nourishing foods such as white fungus, garlic, lamb, and certain tonics.
Foods that are suitable for clearing heat and transforming dampness include Job’s tears, lotus seeds, Poria (Fu Ling), red adzuki beans, mung beans, fish, winter melon, loofah, bitter melon, cucumber, cabbage, celery, and lotus root.
Dietary recipes to strengthen Qi and blood while eliminating dampness:
1. Five-finger peach and Poria soup with pork ribs
Poria, Huai yam, lotus seeds, water chestnuts, dried tangerine peel, five-finger peach.
2. Danggui Shaoyao San from the Han Dynasty’s “Jinkui Yaolue”.
Danggui 9g, Shaoyao 18g, Poria 12g, Baizhu 12g, Zexie 12g, Chuanxiong 9g.
After grinding, take 3-5g each time, 1-2 times a day, mixed with warm wine.
3. External application of Ai Tui (Moxa) from Nan Huai Jin
One longan meat, six or seven Sichuan peppercorns, mixed with moxa wool, applied at the navel and Yongquan (Bubbling Spring) point on the sole of the foot before sleep.
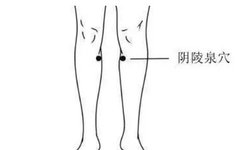
Acupoint massage can also improve damp-heatYinlingquan (Yin Mound Spring)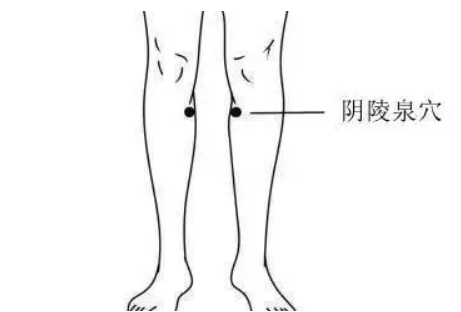
This is the primary acupoint for dispelling dampness. Use your thumb to perform lateral kneading on the local muscles. Each session should last 5-10 minutes, with 15-20 presses per minute. Repeat 2-3 times daily.
Zhongwan (Middle Cavity)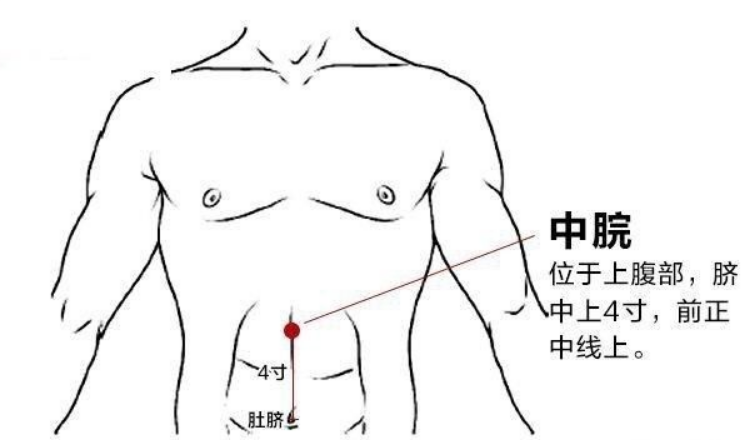
Located on the midline of the upper abdomen, 4 cun above the navel.
Functions: Harmonizes the stomach, strengthens the spleen, reduces counterflow, and promotes fluid metabolism.
In summary, in a damp-heat state, the body can exhibit various discomforts. It is essential to regulate through a balanced diet, exercise, and lifestyle to maintain health.
Note:This account aims to promote TCM culture. The TCM knowledge mentioned is for learning and exchange purposes only.
WeChat has been updated! If youneither★starred me nor liked or “viewed” my articles,the system will assume you do not wish to receive information about herbal knowledge, and ultimatelyyou will not receive updates on our articles
End of article. Thank you for your patience in reading. If you find it helpful, please click “ Like” and “
Like” and “ View”!~
View”!~