Click the blue text to follow us
Traditional Chinese Medicine Therapy – Cupping
Cupping therapy utilizes fire cups as a tool, employing combustion to expel air from within the cup, creating negative pressure that adheres to acupuncture points (zhuyue) or the surface of the body where cupping is applied. This method causes local blood congestion and bruising to prevent and treat diseases.
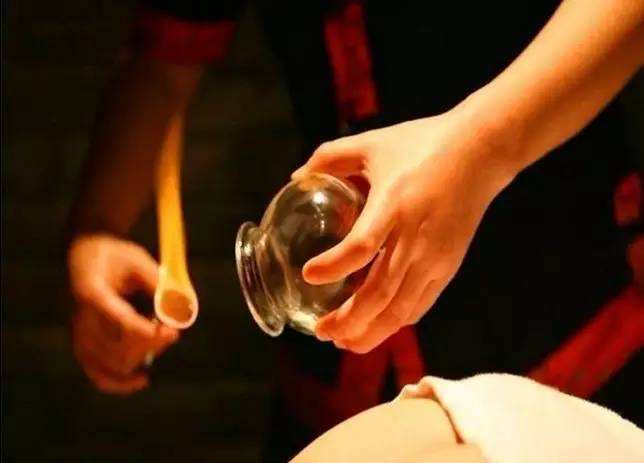

Cupping Method
The commonly used method is the flash fire technique, which involves using tweezers to grasp an alcohol cotton ball or a long strip of paper, igniting it, and then circling it inside the cup for 1-3 seconds (be careful not to heat the rim of the cup to avoid burns) before quickly removing the flame and immediately placing the cup on the targeted area. The cup will adhere to the skin, causing local blood congestion and bruising. Generally, the cup is left in place for about 10-15 minutes. When removing the cup, press the skin at the rim of the cup with a finger to allow air to enter, making it easy to take off the cup.
Precautions for Cupping
1. Choose an appropriate position and a muscular area for cupping.
2. Select a cup size suitable for the area being treated based on its size.
3. The operation must be quick and accurate to ensure the cup adheres strongly to the treatment area.
4. Be cautious to avoid burning the skin. If burns occur or blisters form due to prolonged cupping, small blisters do not require treatment; larger ones can be punctured at the edge with a sterilized needle to release the fluid, then apply a moist burn ointment or cover with sterile gauze to prevent infection.
5. Avoid cupping on areas with allergies, ulcers, or edema; do not perform cupping on individuals with high fever and convulsions; pregnant women should not have cupping on the abdomen or lower back.
Effects and Indications of Cupping
Cupping therapy has effects such as promoting circulation (tongjing), invigorating qi and blood (xingqi huoxue), reducing swelling and alleviating pain (xiaoshui zhizhong), and dispelling wind and cold (qufeng sanchan). Its indications are quite broad, commonly used for conditions such as wind-cold-damp bi syndrome (fenghan shibi), pain in the lower back, shoulders, arms, and legs, joint pain, soft tissue sprains and strains, as well as for colds, headaches, coughs, asthma, stomach pain, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dysmenorrhea, and post-stroke recovery (zhongfeng piankong).

(Ji-Bao) Medical Wide [2024] No. 07-03-118