FuziACONITI LATERALIS RADIX PRAEPARATA1. 2020 Edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia
This product is a processed product of the tuberous root of the plant Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. from the Ranunculaceae family. It is harvested from late June to early August, with the mother root, fibrous roots, and soil removed, commonly referred to as "mud Fuzi", and processed into the following specifications.



(1) Select large, uniform mud Fuzi, wash it clean, soak it in a solution of gall water overnight, then add salt and continue soaking. Remove and dry in the sun daily, gradually extending the drying time until the surface of Fuzi shows a large number of crystalline salt particles (salt frost) and the texture becomes hard, commonly referred to as "salt Fuzi".
(2) Take mud Fuzi, wash it clean according to size, soak it in gall water for several days, boil it with the soaking liquid until thoroughly cooked, remove, rinse with water, cut into slices about 0.5 cm thick, then soak in water, dye the slices with a coloring solution to a dark tea color, steam until an oily surface and gloss appear, then dry until half-dry, and finally sun-dry or continue to dry, commonly referred to as "black shun slices".
(3) Select uniform-sized mud Fuzi, wash it clean, soak it in gall water for several days, boil it with the soaking liquid until thoroughly cooked, remove, peel off the outer skin, cut into slices about 0.3 cm thick, soak in water, steam until cooked through, and sun-dry, commonly referred to as "white Fu slices".
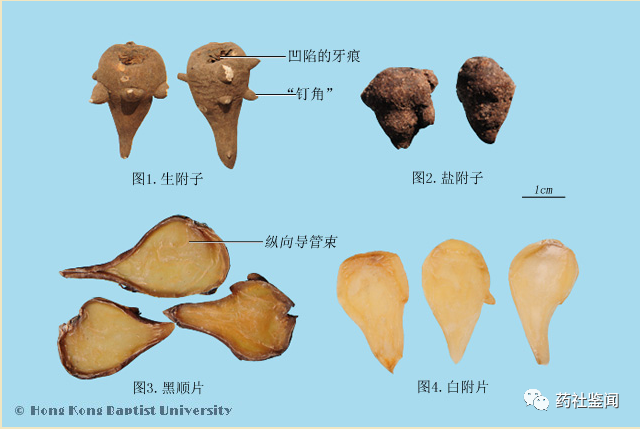
【Properties】Salt Fuzi is conical, 4-7 cm long, and 3-5 cm in diameter. The surface is gray-black, covered with salt frost, with a depressed bud scar at the top and surrounding tuberous protrusions or root scars. It is heavy, with a gray-brown cross-section showing small voids filled with salt frost and polygonal formation rings, with irregularly arranged vascular bundles on the inner side of the rings. It has a faint odor, a salty and numbing taste, and a prickly sensation on the tongue.

Black shun slices are longitudinally cut, wider at the top and narrower at the bottom, measuring 1.7-5 cm in length, 0.9-3 cm in width, and 0.2-0.5 cm in thickness. The outer skin is black-brown, the cut surface is dark yellow, oily and glossy, semi-transparent, and has longitudinal vascular bundles. It is hard and brittle, with a waxy appearance on the fracture surface. It has a faint odor and a bland taste.

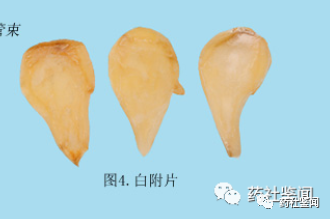
White Fu slices have no outer skin, are yellow-white, semi-transparent, and about 0.3 cm thick.
【Identification】Take 2 g of the powdered product, add 3 ml of ammonia test solution to moisten, add 25 ml of ether, and treat with ultrasound for 30 minutes, filter, evaporate the filtrate, and dissolve the residue in 0.5 ml of dichloromethane to prepare the test solution. Take reference substances of benzoylaconitine, benzoylaconitine, and benzoylmesaconitine, and prepare a mixed solution containing 1 mg of each in 1 ml using isopropanol-dichloromethane (1:1) as the reference solution (monoester alkaloids). Then take reference substances of aconitine, mesaconitine, and hypaconitine, and prepare a mixed solution containing 1 mg of each in 1 ml using isopropanol-dichloromethane (1:1) as the reference solution (diester alkaloids). Perform thin-layer chromatography (General Rule 0502) test, applying 5-10 μl of the test solution and reference solution on the same silica gel G thin-layer plate, using n-hexane-ethyl acetate-methanol (6.4:3.6:1) as the developing agent, place in a chamber saturated with ammonia vapor for 20 minutes, develop, remove, dry, and spray with dilute potassium iodide solution. In the test chromatogram, salt Fuzi shows spots of the same color at the corresponding positions of aconitine, mesaconitine, and hypaconitine reference substances; black shun slices or white Fu slices show spots of the same color at the corresponding positions of benzoylaconitine, benzoylaconitine, and benzoylmesaconitine reference substances.
【Examination】Moisture content must not exceed 15.0% (General Rule 0832, Method 2).
Diester alkaloids content determination under chromatographic conditions, preparation method of the test solution.
Preparation of reference solution: Take appropriate amounts of aconitine, mesaconitine, and hypaconitine reference substances, accurately weigh, and prepare a mixed solution containing 5 μg in each 1 ml using isopropanol-dichloromethane (1:1).
Determination method: Accurately take 10 μl of the above reference solution and test solution, inject into the liquid chromatography instrument for measurement.
This product contains diester alkaloids calculated as aconitine (C33H45NO11), mesaconitine (C33H45NO10), and hypaconitine (C34H47NO11) with a total amount not exceeding 0.020%.
【Content Determination】Determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (General Rule 0512).
Chromatographic conditions and system suitability test: Use octadecylsilyl-bonded silica gel as the stationary phase; use acetonitrile-tetrahydrofuran (25:15) as mobile phase A, and 0.1 mol/L ammonium acetate solution (add 0.5 ml of glacial acetic acid to every 1000 ml) as mobile phase B, perform gradient elution according to the specified table, and detect at a wavelength of 235 nm. Theoretical plate number calculated based on the peak of benzoylaconitine should not be less than 3000.
Preparation of reference solution: Take appropriate amounts of benzoylaconitine, benzoylaconitine, and benzoylmesaconitine reference substances, accurately weigh, and prepare a mixed solution containing 10 μg in each 1 ml using isopropanol-dichloromethane (1:1).
Preparation of test solution: Take about 2 g of the powdered product (sieved through a No. 3 sieve), accurately weigh, place in a stoppered conical flask, add 3 ml of ammonia test solution, accurately add 50 ml of isopropanol-ethyl acetate (1:1) mixed solution, weigh, treat with ultrasound (power 300W, frequency 40kHz, water temperature below 25°C) for 30 minutes, cool, reweigh, and use isopropanol-ethyl acetate (1:1) mixed solution to make up for the weight loss, shake well, and filter. Accurately take 25 ml of the filtrate, recover the solvent under reduced pressure at below 40°C until dry, dissolve the residue in 3 ml of isopropanol-dichloromethane (1:1) mixed solution, filter, and take the filtrate for measurement.
Determination method: Accurately take 10 μl of the reference solution and test solution, inject into the liquid chromatography instrument for measurement.
This product contains benzoylaconitine (C31H43NO10), benzoylaconitine (C32H45NO10), and benzoylmesaconitine (C31H43NO9) with a total amount not less than 0.010%.
2. Chinese Herbal Pieces
【Processing】Fu slices (black shun slices, white Fu slices) are used directly in medicine.
【Examination】Total ash content must not exceed 6.0% (General Rule 2302).
Acid-insoluble ash content must not exceed 1.0% (General Rule 2302).
【Properties】【Identification】【Examination】 (Moisture diester alkaloids)【Content Determination】 same as medicinal materials.
Light Fu slices: Take salt Fuzi, soak in clean water, changing water 2-3 times daily, until the salt is completely leached out, then boil with licorice and black beans until thoroughly cooked, until there is no numbing sensation when tasted after cutting open, then remove, discard licorice and black beans, cut into thin slices, and sun-dry.
For every 100 kg of salt Fuzi, use 5 kg of licorice and 10 kg of black beans.
【Properties】This product is longitudinally cut, wider at the top and narrower at the bottom, measuring 1.7-5 cm in length, 0.9-3 cm in width, and 0.2-0.5 cm in thickness. The outer skin is brown. The cut surface is brown, semi-transparent, with longitudinal vascular bundles. It is hard, with a waxy appearance on the fracture surface. It has a faint odor, a bland taste, and no numbing sensation when tasted.
【Examination】Diester alkaloids same as medicinal materials, containing diester alkaloids calculated as aconitine (C33H45NO11), mesaconitine (C33H45NO10), and hypaconitine (C34H47NO11) with a total amount not exceeding 0.010%.
Total ash content must not exceed 7.0% (General Rule 2302).
Acid-insoluble ash content must not exceed 1.0% (General Rule 2302).
【Identification】【Examination】 (Moisture)【Content Determination】 same as medicinal materials.
Processed Fu slices: Take Fu slices, and fry according to the frying method (General Rule 0213) until puffed and slightly discolored.
【Properties】This product resembles black shun slices or white Fu slices, with a surface that is puffed and yellow-brown, and a loose and brittle texture. It has a faint odor and a bland taste.
【Identification】【Examination】 same as Fu slices.
【Flavor and Meridian Entry】 Spicy, sweet, very hot; toxic. Enters the Heart, Kidney, and Spleen meridians.
【Functions and Indications】 Revives Yang, rescues from collapse, supplements fire and assists Yang, disperses cold and alleviates pain. Used for Yang collapse, cold limbs, weak pulse, insufficient heart Yang, chest obstruction and heart pain, cold and deficient vomiting and diarrhea, cold abdominal pain, kidney Yang deficiency, impotence, cold in the palace, cold water swelling, Yang deficiency with external pathogens, cold damp obstruction and pain.
【Dosage and Administration】 3-15 g, decocted first, long decoction.
【Precautions】 Use with caution in pregnant women; not suitable for use with Banxia (Pinellia ternata), Guo Lou (Trichosanthes fruit), Guo Louzi (Trichosanthes seeds), Guo Loupizi (Trichosanthes peel), Tianhuafen (Trichosanthes root), Chuanbei (Fritillaria cirrhosa), Zhebei (Fritillaria thunbergii), Pingbei (Fritillaria pallidiflora), Yibei (Fritillaria unibracteata), Hubeibei (Fritillaria hupehensis), Bailian (Bletilla striata), and Bai Ji (Bletilla striata tuber).
【Storage】 Salt Fuzi: Sealed, stored in a cool, dry place; black shun slices and white Fu slices: stored in a dry place, protected from moisture.
Note: Salt Fuzi is only for [Properties] testing.
3. Authenticity Identification:
(1)【Source】 A processed product of the tuberous root of the plant Aconitum carmichaelii Debx. from the Ranunculaceae family. It is harvested from late June to early August, with the mother root, fibrous roots, and soil removed, commonly referred to as "mud Fuzi", and processed into the following specifications. 1. Select large, uniform mud Fuzi, wash it clean, soak it in a solution of gall water overnight, then add salt and continue soaking. Remove and dry in the sun daily, gradually extending the drying time until the surface of Fuzi shows a large number of crystalline salt particles (salt frost) and the texture becomes hard, commonly referred to as "salt Fuzi".
2. Take mud Fuzi, wash it clean according to size, soak it in gall water for several days, boil it with the soaking liquid until thoroughly cooked, remove, rinse with water, cut into slices about 0.5 cm thick, then soak in water, dye the slices with a coloring solution to a dark tea color, steam until an oily surface and gloss appear, then dry until half-dry, and finally sun-dry or continue to dry, commonly referred to as "black shun slices".
3. Select uniform-sized mud Fuzi, wash it clean, soak it in gall water for several days, boil it with the soaking liquid until thoroughly cooked, remove, peel off the outer skin, cut into slices about 0.3 cm thick, soak in water, steam until cooked through, and sun-dry, commonly referred to as "white Fu slices".
Figure 1: Salt Fuzi Medicinal Material Image
(Taken at the Beijing Museum of Traditional Chinese Medicine Processing Technology)
Figure 2: Black Shun Slices Medicinal Material Image
Figure 3: White Fu Slices Medicinal Material Image
(2)【Main Identification Points】1. Appearance Characteristics
Salt Fuzi is conical, 4-7 cm long, and 3-5 cm in diameter. The surface is gray-black, covered with salt frost, with a depressed bud scar at the top and surrounding tuberous protrusions or root scars. It is heavy, with a gray-brown cross-section showing small voids filled with salt frost and polygonal formation rings, with irregularly arranged vascular bundles on the inner side of the rings. It has a faint odor, a salty and numbing taste, and a prickly sensation on the tongue.
Black shun slices are longitudinally cut, wider at the top and narrower at the bottom, measuring 1.7-5 cm in length, 0.9-3 cm in width, and 0.2-0.5 cm in thickness. The outer skin is black-brown, the cut surface is dark yellow, oily and glossy, semi-transparent, and has longitudinal vascular bundles. It is hard and brittle, with a waxy appearance on the fracture surface. It has a faint odor and a bland taste.
White Fu slices have no outer skin, are yellow-white, semi-transparent, and about 0.3 cm thick.
Figure 4: Salt Fuzi Identification Points
① Surface gray-black, covered with salt frost;
② Top has a depressed bud scar, surrounded by tuberous protrusions (commonly referred to as "nail angle") or root scars.
Figure 5: Black Shun Slices Identification Points
① Outer skin black-brown;
② Cut surface dark yellow, oily and glossy, semi-transparent;
③ Contains longitudinal vascular bundles.
Figure 6: White Fu Slices Identification Points
① No outer skin, yellow-white, semi-transparent.
2. Herbal Pieces
(1) Fu slices (black shun slices, white Fu slices) are used directly in medicine.
(2) Light Fu slices
Processing: Take salt Fuzi, soak in clean water, changing water 2-3 times daily, until the salt is completely leached out, then boil with licorice and black beans until thoroughly cooked, until there is no numbing sensation when tasted after cutting open, then remove, discard licorice and black beans, cut into thin slices, and sun-dry.
Properties: This product is longitudinally cut, wider at the top and narrower at the bottom, measuring 1.7-5 cm in length, 0.9-3 cm in width, and 0.2-0.5 cm in thickness. The outer skin is brown. The cut surface is brown, semi-transparent, with longitudinal vascular bundles. It is hard, with a waxy appearance on the fracture surface. It has a faint odor, a bland taste, and no numbing sensation when tasted.
Examination: Diester alkaloids same as medicinal materials, containing diester alkaloids calculated as aconitine (C33H45NO11), mesaconitine (C33H45NO10), and hypaconitine (C34H47NO11) with a total amount not exceeding 0.010%.
Total ash content must not exceed 7.0% (General Rule 2302).
Acid-insoluble ash content must not exceed 1.0% (General Rule 2302).
Identification, examination (moisture), and content determination same as medicinal materials.
Processed Fu slices: Take Fu slices, and fry according to the frying method (General Rule 0213) until puffed and slightly discolored.
Properties: This product resembles black shun slices or white Fu slices, with a surface that is puffed and yellow-brown, and a loose and brittle texture. It has a faint odor and a bland taste.
Figure 8: Processed Fu Slices
(From "Quick Image Identification of Authenticity and Quality of Chinese Medicine (Volume 2)")
Note:
1. This product is toxic. Use with caution in pregnant women; not suitable for use with Banxia (Pinellia ternata), Guo Lou (Trichosanthes fruit), Guo Louzi (Trichosanthes seeds), Guo Loupizi (Trichosanthes peel), Tianhuafen (Trichosanthes root), Chuanbei (Fritillaria cirrhosa), Zhebei (Fritillaria thunbergii), Pingbei (Fritillaria pallidiflora), Yibei (Fritillaria unibracteata), Hubeibei (Fritillaria hupehensis), Bailian (Bletilla striata), and Bai Ji (Bletilla striata tuber).
2. Summary of processing methods and properties of salt Fuzi, black shun slices, white Fu slices, light Fu slices, and processed Fu slices.








