Hand Three Yin Meridians: Shou Taiyin Feijing (Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian), Shou Jueyin Xinbaojing (Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian), Shou Shaoyin Xinjing (Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian)
Hand Three Yang Meridians: Shou Yangming Dachangjing (Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian), Shou Shaoyang Sanjiao Jing (Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian), Shou Taiyang Xiaojing (Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian)
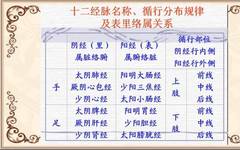
Foot Three Yang Meridians: Zu Yangming Weijing (Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian), Zu Shaoyang Danjing (Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian), Zu Taiyang Pangguangjing (Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian)Foot Three Yin Meridians: Zu Taiyin Pijing (Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian), Zu Jueyin Gan Jing (Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian), Zu Shaoyin Shenjing (Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian)Pathways: The three Yin meridians of the hand run from the chest to the hand; the three Yang meridians of the hand run from the hand to the head; the three Yang meridians of the foot run from the head to the foot; the three Yin meridians of the foot run from the foot to the abdomen. “Ling Shu – Ben Shu”: “In all needling, one must connect to the beginning and end of the twelve meridians.”The Interrelationship of the Twelve Meridians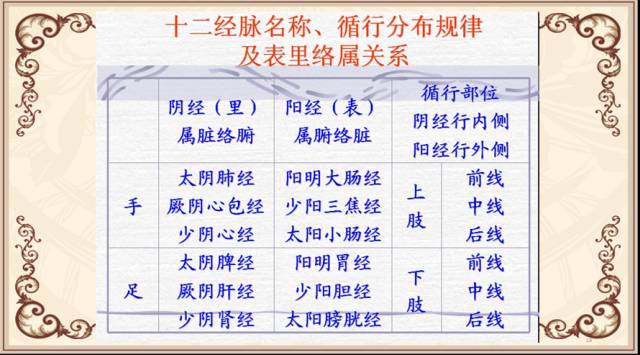 Song of the Connection Order of the Twelve MeridiansAt the Yin hour, Qi and blood flow into the lungsAt the Mao hour, the large intestine; at the Chen hour, the stomachAt the Si hour, the spleen; at the Wu hour, the heart; at the Wei hour, the small intestineAt the Shen hour, the bladder; at the You hour, the kidneyAt the Xu hour, the pericardium; at the Hai hour, the SanjiaoAt the Zi hour, the gallbladder; at the Chou hour, the liverTable of Original Points, Luo Points, and Shu Points Correspondence (Key Points)
Song of the Connection Order of the Twelve MeridiansAt the Yin hour, Qi and blood flow into the lungsAt the Mao hour, the large intestine; at the Chen hour, the stomachAt the Si hour, the spleen; at the Wu hour, the heart; at the Wei hour, the small intestineAt the Shen hour, the bladder; at the You hour, the kidneyAt the Xu hour, the pericardium; at the Hai hour, the SanjiaoAt the Zi hour, the gallbladder; at the Chou hour, the liverTable of Original Points, Luo Points, and Shu Points Correspondence (Key Points)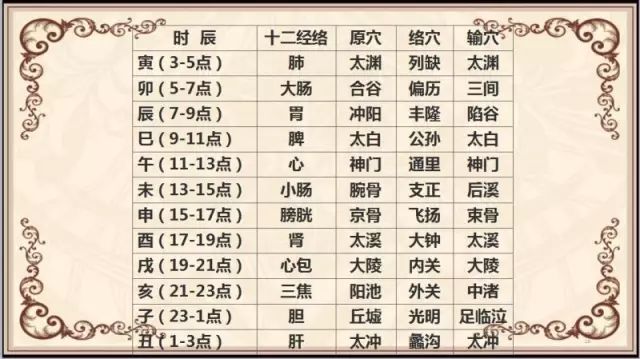 Locations of the Twelve Meridians and Their Original, Luo, and Shu Points
Locations of the Twelve Meridians and Their Original, Luo, and Shu Points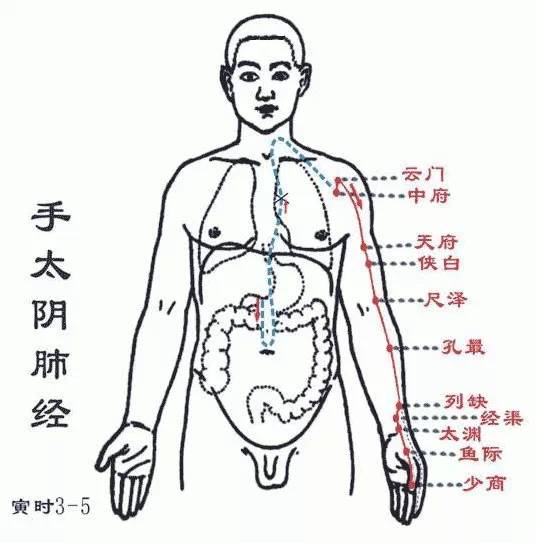 Shou Taiyin Feijing (Yin hour: 3-5 AM): Runs from the chest to the handStarts at the middle jiao (stomach), connects down to the large intestine, returns along the stomach’s upper opening, passes through the diaphragm, belonging to the lungs. From the lung system – trachea, throat, it exits under the armpit (Zhongfu, Yunmen), descends along the inner side of the upper arm, runs to the hand Shaoyin, before the hand Jueyin (Tianfu, Xiabai), descends to the elbow (Chize), along the inner side of the forearm at the radial edge (Kongzui), enters the wrist (at the radial artery pulse) (Jingqu, Taiyuan), ascends to the thenar area, along the margin (Yujie), exits at the tip of the thumb (Shaoshang).Branch: From the back of the wrist (Lieque) runs to the inner side of the index finger (radial), exits at its tip, connecting to the hand Yangming large intestine meridian.This meridian has 11 points on one side (22 points total), with 9 points distributed on the radial side of the upper limb, 2 points in the upper chest, starting point Zhongfu, ending point Shaoshang.Main indications: Respiratory system disorders and conditions in the areas traversed by this meridian.● Points of this meridian: Zhongfu, Yunmen, Tianfu, Xiabai, Chize, Kongzui, Lieque, Jingqu, Taiyuan, Yujie, Shaoshang.● Original point: Taiyuan (at the radial side of the wrist crease, in the depression at the radial side of the radial artery)● Luo point: Lieque (1.5 cun above the wrist crease, at the radial edge of the forearm)● Shu point: Taiyuan (at the radial side of the wrist crease, in the depression at the radial side of the radial artery)
Shou Taiyin Feijing (Yin hour: 3-5 AM): Runs from the chest to the handStarts at the middle jiao (stomach), connects down to the large intestine, returns along the stomach’s upper opening, passes through the diaphragm, belonging to the lungs. From the lung system – trachea, throat, it exits under the armpit (Zhongfu, Yunmen), descends along the inner side of the upper arm, runs to the hand Shaoyin, before the hand Jueyin (Tianfu, Xiabai), descends to the elbow (Chize), along the inner side of the forearm at the radial edge (Kongzui), enters the wrist (at the radial artery pulse) (Jingqu, Taiyuan), ascends to the thenar area, along the margin (Yujie), exits at the tip of the thumb (Shaoshang).Branch: From the back of the wrist (Lieque) runs to the inner side of the index finger (radial), exits at its tip, connecting to the hand Yangming large intestine meridian.This meridian has 11 points on one side (22 points total), with 9 points distributed on the radial side of the upper limb, 2 points in the upper chest, starting point Zhongfu, ending point Shaoshang.Main indications: Respiratory system disorders and conditions in the areas traversed by this meridian.● Points of this meridian: Zhongfu, Yunmen, Tianfu, Xiabai, Chize, Kongzui, Lieque, Jingqu, Taiyuan, Yujie, Shaoshang.● Original point: Taiyuan (at the radial side of the wrist crease, in the depression at the radial side of the radial artery)● Luo point: Lieque (1.5 cun above the wrist crease, at the radial edge of the forearm)● Shu point: Taiyuan (at the radial side of the wrist crease, in the depression at the radial side of the radial artery)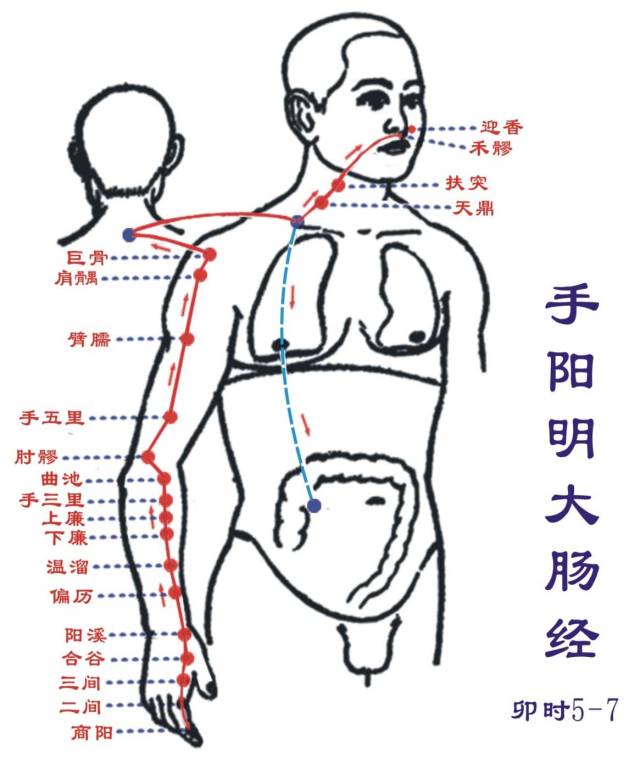 Shou Yangming Dachangjing (Mao hour: 5-7 AM): Runs from the hand to the headStarts at the tip of the index finger (Shangyang), runs along the radial edge of the index finger (Erjian, Sanjian), exits between the first and second metacarpals (Hegu), enters between the two tendons (the long and short extensor tendons of the thumb) (Yangxi), along the radial side of the forearm (Pianli, Wenliu, Xialiang, Shangliang, Shou Sanli), enters the outer side of the elbow (Quchi, Zhouliao), runs along the outer side of the upper arm (Shou Wuli, Bingna), ascends to the shoulder, exits at the front of the shoulder peak (Jianyu, Jugul, Huibingfeng), meets at the neck (Hui Dazhu), descends into the supraclavicular fossa, connects to the lungs, passes through the diaphragm, belonging to the large intestine.The hand Yangming large intestine meridian is closely related to the lung meridian. When there are diseases in the respiratory system, the Quchi point on the large intestine meridian is often used as a treatment point. When there are abnormalities in the large intestine meridian, symptoms such as toothache, nasal congestion, dry mouth, and throat swelling may occur. If pressure is applied to the shoulder to the arm area, pain may also be felt.This meridian has 20 points on one side (40 points total), with 15 points distributed on the radial side of the upper limb’s back, and 5 points in the neck and face. Starting point Shangyang, ending point Yingxiang.Main indications: Diseases of the stomach, intestines, and other abdominal conditions, neurological and psychiatric disorders, certain febrile diseases, and conditions of the eyes, ears, mouth, teeth, nose, throat, and areas traversed by this meridian.● Points of this meridian: Shangyang, Erjian, Sanjian, Hegu, Yangxi, Pianli, Wenliu, Xialiang, Shangliang, Shou Sanli, Quchi, Zhouliao, Shou Wuli, Bingna, Jianyu, Jugul, Tianding, Futuo, Kouhe, Yingxiang.● Original point: Hegu (on the back of the hand, between the first and second metacarpals, at the midpoint of the radial side of the second metacarpal)● Luo point: Pianli (on the back of the elbow, 3 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Sanjian (make a fist, in the depression at the radial side of the second metacarpal head)
Shou Yangming Dachangjing (Mao hour: 5-7 AM): Runs from the hand to the headStarts at the tip of the index finger (Shangyang), runs along the radial edge of the index finger (Erjian, Sanjian), exits between the first and second metacarpals (Hegu), enters between the two tendons (the long and short extensor tendons of the thumb) (Yangxi), along the radial side of the forearm (Pianli, Wenliu, Xialiang, Shangliang, Shou Sanli), enters the outer side of the elbow (Quchi, Zhouliao), runs along the outer side of the upper arm (Shou Wuli, Bingna), ascends to the shoulder, exits at the front of the shoulder peak (Jianyu, Jugul, Huibingfeng), meets at the neck (Hui Dazhu), descends into the supraclavicular fossa, connects to the lungs, passes through the diaphragm, belonging to the large intestine.The hand Yangming large intestine meridian is closely related to the lung meridian. When there are diseases in the respiratory system, the Quchi point on the large intestine meridian is often used as a treatment point. When there are abnormalities in the large intestine meridian, symptoms such as toothache, nasal congestion, dry mouth, and throat swelling may occur. If pressure is applied to the shoulder to the arm area, pain may also be felt.This meridian has 20 points on one side (40 points total), with 15 points distributed on the radial side of the upper limb’s back, and 5 points in the neck and face. Starting point Shangyang, ending point Yingxiang.Main indications: Diseases of the stomach, intestines, and other abdominal conditions, neurological and psychiatric disorders, certain febrile diseases, and conditions of the eyes, ears, mouth, teeth, nose, throat, and areas traversed by this meridian.● Points of this meridian: Shangyang, Erjian, Sanjian, Hegu, Yangxi, Pianli, Wenliu, Xialiang, Shangliang, Shou Sanli, Quchi, Zhouliao, Shou Wuli, Bingna, Jianyu, Jugul, Tianding, Futuo, Kouhe, Yingxiang.● Original point: Hegu (on the back of the hand, between the first and second metacarpals, at the midpoint of the radial side of the second metacarpal)● Luo point: Pianli (on the back of the elbow, 3 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Sanjian (make a fist, in the depression at the radial side of the second metacarpal head)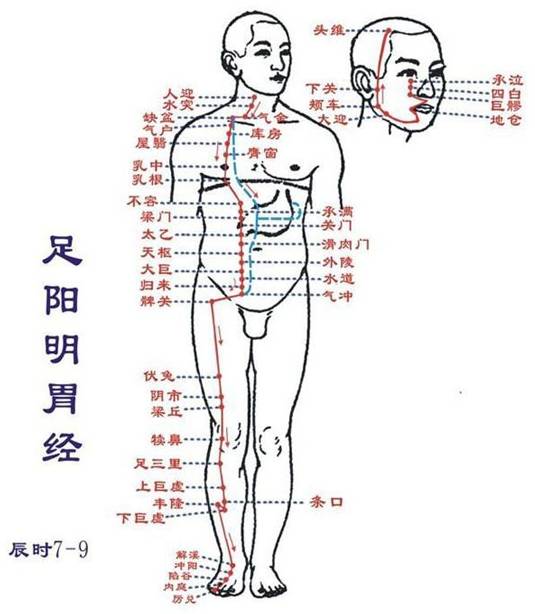 Zu Yangming Weijing (Chen hour: 7-9 AM): Runs from the head to the footStarts beside the nose (Hui Yingxiang), intersects at the root of the nose, beside the foot Taiyang meridian (Hui Jingming), descends along the outer side of the nose (Chengqi, Sibai), enters the upper dental arch (Juliao), returns to the area beside the mouth (Dizang) encircling the lips (Hui Renzhong), descends to meet at the chin-lip groove (Hui Chengjiang); returns along the lower jaw to the facial artery area (Daying), then along the jaw angle (Jiaoche), up to the front of the ear (Xiaguan), along the zygomatic arch (Hui Shangguan, Xuanli, Huan Yan), along the hairline (Touwei), to the center of the forehead (Hui Shenting).Its branch: from Daying down through the carotid area (Renying), along the throat (Shuitu, Qishe, one says Hui Dazhu), enters the supraclavicular fossa (Hui Suokong), passes through the diaphragm, belonging to the stomach (Hui Shangwan, Zhongwan), connects to the spleen.Its branch: from the stomach down, along the abdomen, to the groin area, meeting the previous one. From here, it descends through the front of the hip joint (Bigu), to the quadriceps area (Futu, Yinshi, Liangqiu), down to the knee (Dubi), along the outer side of the tibia (Zu Sanli, Shangjuxu, Tiaokou, Xiaojuxu), descending to the dorsum of the foot (Jiexi, Chongyang), entering the inner side of the second toe (Xianggu, Neiting), exiting at the tip of the second toe (Lidui).Its branch: from 3 cun below the knee (Zu Sanli) (Fenglong), descends to the outer side of the second toe, exiting at the tip of the second toe. Another branch: from the dorsum of the foot (Chongyang), enters the first toe’s web, exiting at the tip of the first toe, connecting to the foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian.This meridian has 45 points on one side (90 points total), with 15 points distributed on the front outer side of the lower limb, and 30 points in the abdomen, chest, and head/face. Starting point Chengqi, ending point Lidui.Main indications: Diseases of the digestive system, nervous system, respiratory system, circulatory system, certain conditions of the throat, head, face, mouth, teeth, nose, and areas traversed by this meridian.● Original point: Chongyang (on the dorsum of the foot, at the base of the second metatarsal and the intermediate cuneiform joint, can feel the dorsalis pedis artery)● Luo point: Fenglong (on the front outer side of the lower leg, 8 cun above the tip of the outer ankle, at the horizontal finger distance from the anterior edge of the tibia)● Shu point: Xiangu (in the depression behind the second and third metatarsophalangeal joints on the dorsum of the foot)
Zu Yangming Weijing (Chen hour: 7-9 AM): Runs from the head to the footStarts beside the nose (Hui Yingxiang), intersects at the root of the nose, beside the foot Taiyang meridian (Hui Jingming), descends along the outer side of the nose (Chengqi, Sibai), enters the upper dental arch (Juliao), returns to the area beside the mouth (Dizang) encircling the lips (Hui Renzhong), descends to meet at the chin-lip groove (Hui Chengjiang); returns along the lower jaw to the facial artery area (Daying), then along the jaw angle (Jiaoche), up to the front of the ear (Xiaguan), along the zygomatic arch (Hui Shangguan, Xuanli, Huan Yan), along the hairline (Touwei), to the center of the forehead (Hui Shenting).Its branch: from Daying down through the carotid area (Renying), along the throat (Shuitu, Qishe, one says Hui Dazhu), enters the supraclavicular fossa (Hui Suokong), passes through the diaphragm, belonging to the stomach (Hui Shangwan, Zhongwan), connects to the spleen.Its branch: from the stomach down, along the abdomen, to the groin area, meeting the previous one. From here, it descends through the front of the hip joint (Bigu), to the quadriceps area (Futu, Yinshi, Liangqiu), down to the knee (Dubi), along the outer side of the tibia (Zu Sanli, Shangjuxu, Tiaokou, Xiaojuxu), descending to the dorsum of the foot (Jiexi, Chongyang), entering the inner side of the second toe (Xianggu, Neiting), exiting at the tip of the second toe (Lidui).Its branch: from 3 cun below the knee (Zu Sanli) (Fenglong), descends to the outer side of the second toe, exiting at the tip of the second toe. Another branch: from the dorsum of the foot (Chongyang), enters the first toe’s web, exiting at the tip of the first toe, connecting to the foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian.This meridian has 45 points on one side (90 points total), with 15 points distributed on the front outer side of the lower limb, and 30 points in the abdomen, chest, and head/face. Starting point Chengqi, ending point Lidui.Main indications: Diseases of the digestive system, nervous system, respiratory system, circulatory system, certain conditions of the throat, head, face, mouth, teeth, nose, and areas traversed by this meridian.● Original point: Chongyang (on the dorsum of the foot, at the base of the second metatarsal and the intermediate cuneiform joint, can feel the dorsalis pedis artery)● Luo point: Fenglong (on the front outer side of the lower leg, 8 cun above the tip of the outer ankle, at the horizontal finger distance from the anterior edge of the tibia)● Shu point: Xiangu (in the depression behind the second and third metatarsophalangeal joints on the dorsum of the foot)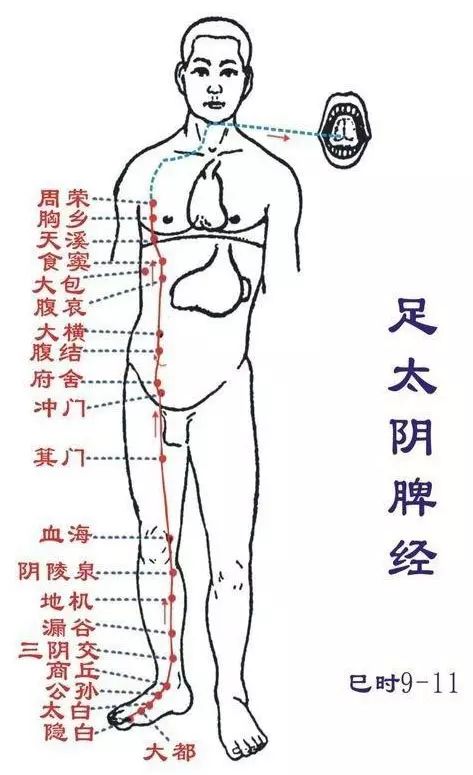 Zu Taiyin Pijing (Si hour: 9-11 AM): Runs from the foot to the abdomenStarts at the tip of the big toe (Yinbai), along the inner side of the big toe (Dadu), through the navicular bone (the first metatarsal head) (Taibai, Gongsun), ascends to the front of the inner ankle (Shangqiu), up the inner side of the lower leg, along the posterior edge of the tibia (Sanyinjiao, Lougu), intersects before the foot Jueyin liver meridian (Diji, Yinlingquan), ascends to the inner side of the thigh (Xuehai, Jimen), enters the abdomen (Chongmen, Fushi, Fuke, Dahu; Zhongji, Guanyuan, belonging to the spleen, connecting to the stomach (Fubai; Hui Xiaowan, Rihuo, Qimen), passes through the diaphragm, alongside the esophagus (Shidou, Tianxi, Xiongxiang, Zhourong; connecting to the Daba; Hui Zhongfu), connecting to the root of the tongue, dispersing under the tongue.Its branch: from the stomach, ascends through the diaphragm, flows into the heart, connecting to the hand Shaoyin heart meridian.Main indications: Spleen and stomach diseases, gynecological issues, conditions of the anterior yin, and other diseases along the meridian’s path. Such as stomach pain, vomiting after eating, belching, abdominal distension, jaundice, heaviness and weakness, pain at the root of the tongue, swelling of the inner side of the lower limbs, and coldness.This meridian has 21 points on one side (42 points total), with 11 points distributed on the front of the inner side of the lower limb, and 10 points on the lateral chest and abdomen. Starting point Yinbai, ending point Daba.● Points of this meridian: Yinbai, Dadu, Taibai, Gongsun, Shangqiu, Sanyinjiao, Lougu, Diji, Yinlingquan, Xuehai, Jimen, Chongmen, Fushi, Fuke, Dahu, Fubai, Shidou, Tianxi, Xiongxiang, Zhourong, Daba.● Original point: Taibai (behind the first metatarsal head, at the red-white inner edge)● Luo point: Gongsun (at the front lower part of the first metatarsal base)● Shu point: Taibai (behind the first metatarsal head, at the red-white inner edge)
Zu Taiyin Pijing (Si hour: 9-11 AM): Runs from the foot to the abdomenStarts at the tip of the big toe (Yinbai), along the inner side of the big toe (Dadu), through the navicular bone (the first metatarsal head) (Taibai, Gongsun), ascends to the front of the inner ankle (Shangqiu), up the inner side of the lower leg, along the posterior edge of the tibia (Sanyinjiao, Lougu), intersects before the foot Jueyin liver meridian (Diji, Yinlingquan), ascends to the inner side of the thigh (Xuehai, Jimen), enters the abdomen (Chongmen, Fushi, Fuke, Dahu; Zhongji, Guanyuan, belonging to the spleen, connecting to the stomach (Fubai; Hui Xiaowan, Rihuo, Qimen), passes through the diaphragm, alongside the esophagus (Shidou, Tianxi, Xiongxiang, Zhourong; connecting to the Daba; Hui Zhongfu), connecting to the root of the tongue, dispersing under the tongue.Its branch: from the stomach, ascends through the diaphragm, flows into the heart, connecting to the hand Shaoyin heart meridian.Main indications: Spleen and stomach diseases, gynecological issues, conditions of the anterior yin, and other diseases along the meridian’s path. Such as stomach pain, vomiting after eating, belching, abdominal distension, jaundice, heaviness and weakness, pain at the root of the tongue, swelling of the inner side of the lower limbs, and coldness.This meridian has 21 points on one side (42 points total), with 11 points distributed on the front of the inner side of the lower limb, and 10 points on the lateral chest and abdomen. Starting point Yinbai, ending point Daba.● Points of this meridian: Yinbai, Dadu, Taibai, Gongsun, Shangqiu, Sanyinjiao, Lougu, Diji, Yinlingquan, Xuehai, Jimen, Chongmen, Fushi, Fuke, Dahu, Fubai, Shidou, Tianxi, Xiongxiang, Zhourong, Daba.● Original point: Taibai (behind the first metatarsal head, at the red-white inner edge)● Luo point: Gongsun (at the front lower part of the first metatarsal base)● Shu point: Taibai (behind the first metatarsal head, at the red-white inner edge)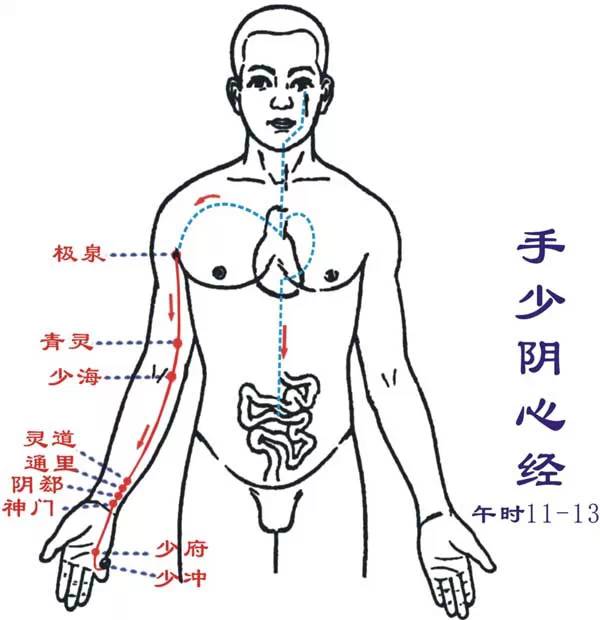 Shou Shaoyin Xinjing (Wu hour: 11 AM-1 PM): Runs from the chest to the handStarts from the heart, exits belonging to the heart and its connected organs, descends through the diaphragm, connecting to the small intestine.Its branch: from the heart’s connecting part, ascends to the throat, connecting to the brain through the eye’s connecting part.Its direct pathway runs from the heart system (the connection between the heart and its organs) up to the lungs, exits at the lower part (Jiquan), along the inner side of the upper arm, runs to the hand Taiyin, after the hand Jueyin (Qingling), descends to the inner elbow (Shaohai), along the inner side of the forearm (Lingdao, Tongli, Yinxue, Shenmen), enters the back of the palm at the pea bone (Shaofu), along the radial side of the little finger to the tip (Shaochong), connecting to the hand Taiyang small intestine meridian.This meridian has 9 points on one side (18 points total), with 8 points distributed on the ulnar side of the upper limb’s palm surface, and 1 point in the upper chest. Starting point Jiquan, ending point Shaochong.Main indications: Diseases of the chest, heart, circulatory system, neurological and psychiatric disorders, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Jiquan, Qingling, Shaohai, Lingdao, Tongli, Yinxue, Shenmen, Shaofu, Shaochong.● Original point: Shenmen (at the radial side of the wrist crease)● Luo point: Tongli (on the palm side of the forearm, at the radial edge, 1 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Shenmen (at the radial side of the wrist crease)
Shou Shaoyin Xinjing (Wu hour: 11 AM-1 PM): Runs from the chest to the handStarts from the heart, exits belonging to the heart and its connected organs, descends through the diaphragm, connecting to the small intestine.Its branch: from the heart’s connecting part, ascends to the throat, connecting to the brain through the eye’s connecting part.Its direct pathway runs from the heart system (the connection between the heart and its organs) up to the lungs, exits at the lower part (Jiquan), along the inner side of the upper arm, runs to the hand Taiyin, after the hand Jueyin (Qingling), descends to the inner elbow (Shaohai), along the inner side of the forearm (Lingdao, Tongli, Yinxue, Shenmen), enters the back of the palm at the pea bone (Shaofu), along the radial side of the little finger to the tip (Shaochong), connecting to the hand Taiyang small intestine meridian.This meridian has 9 points on one side (18 points total), with 8 points distributed on the ulnar side of the upper limb’s palm surface, and 1 point in the upper chest. Starting point Jiquan, ending point Shaochong.Main indications: Diseases of the chest, heart, circulatory system, neurological and psychiatric disorders, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Jiquan, Qingling, Shaohai, Lingdao, Tongli, Yinxue, Shenmen, Shaofu, Shaochong.● Original point: Shenmen (at the radial side of the wrist crease)● Luo point: Tongli (on the palm side of the forearm, at the radial edge, 1 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Shenmen (at the radial side of the wrist crease)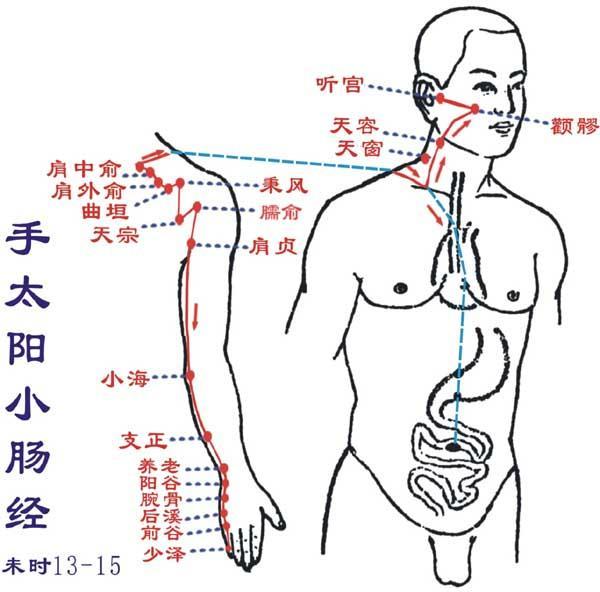 Shou Taiyang Xiaojing (Wei hour: 1-3 PM): Runs from the hand to the headStarts at the outer side of the little finger (Shaoze), runs along the ulnar side of the palm (Qian Gu, Houxi), ascends to the wrist (Wanggu, Yanggu), exits at the ulnar styloid (Yanglao), directly up along the lower edge of the ulna (Zhizheng), exits at the inner side of the elbow between the humerus and the ulnar olecranon (Xiaohai), ascends along the outer back of the upper arm, exits at the shoulder joint (Shouzheng, Nanyu), encircles the scapula (Tianzong, Bingfeng, Quyuan), meets at the shoulder (Shouwaiyu, Shouzhongyu; Hui Fufen, Dazhu, Dazhu), enters the supraclavicular fossa, connects to the heart, along the esophagus, passes through the diaphragm, to the stomach (Hui Shangwan, Zhongwan), belonging to the small intestine.Its branch: from the supraclavicular fossa, ascends along the neck (Tianchuang, Tianrong), up to the cheek (Qianliao), to the outer corner of the eye (Hui Tongzili), bends back (Hui Huanliao), enters the ear (Tinggong). Another branch: from the cheek, ascends to the zygomatic bone, near the nose to the inner corner of the eye (Hui Jingming), connecting to the foot Taiyang bladder meridian. Additionally, the small intestine connects with the foot Yangming stomach meridian at the lower juxu.This meridian has 19 points on one side (38 points total), with 8 points distributed on the ulnar side of the upper limb’s back, and 11 points in the shoulder, neck, and face. Starting point Shaoze, ending point Tinggong.Main indications: Abdominal small intestine and chest, heart, throat disorders, certain febrile diseases, neurological disorders, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Shaoze, Qian Gu, Houxi, Wanggu, Yanggu, Yanglao, Zhizheng, Xiaohai, Shouzheng, Nanyu, Tianzong, Bingfeng, Quyuan, Shouwaiyu, Shouzhong, Tianchuang, Tianrong, Qianliao, Tinggong.● Original point: Wanggu (on the palm side, at the depression between the 5th metacarpal base and the hook bone at the red-white edge)● Luo point: Zhizheng (on the back of the forearm, 5 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Houxi (make a fist, at the back of the 5th metacarpophalangeal joint, at the red-white edge)
Shou Taiyang Xiaojing (Wei hour: 1-3 PM): Runs from the hand to the headStarts at the outer side of the little finger (Shaoze), runs along the ulnar side of the palm (Qian Gu, Houxi), ascends to the wrist (Wanggu, Yanggu), exits at the ulnar styloid (Yanglao), directly up along the lower edge of the ulna (Zhizheng), exits at the inner side of the elbow between the humerus and the ulnar olecranon (Xiaohai), ascends along the outer back of the upper arm, exits at the shoulder joint (Shouzheng, Nanyu), encircles the scapula (Tianzong, Bingfeng, Quyuan), meets at the shoulder (Shouwaiyu, Shouzhongyu; Hui Fufen, Dazhu, Dazhu), enters the supraclavicular fossa, connects to the heart, along the esophagus, passes through the diaphragm, to the stomach (Hui Shangwan, Zhongwan), belonging to the small intestine.Its branch: from the supraclavicular fossa, ascends along the neck (Tianchuang, Tianrong), up to the cheek (Qianliao), to the outer corner of the eye (Hui Tongzili), bends back (Hui Huanliao), enters the ear (Tinggong). Another branch: from the cheek, ascends to the zygomatic bone, near the nose to the inner corner of the eye (Hui Jingming), connecting to the foot Taiyang bladder meridian. Additionally, the small intestine connects with the foot Yangming stomach meridian at the lower juxu.This meridian has 19 points on one side (38 points total), with 8 points distributed on the ulnar side of the upper limb’s back, and 11 points in the shoulder, neck, and face. Starting point Shaoze, ending point Tinggong.Main indications: Abdominal small intestine and chest, heart, throat disorders, certain febrile diseases, neurological disorders, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Shaoze, Qian Gu, Houxi, Wanggu, Yanggu, Yanglao, Zhizheng, Xiaohai, Shouzheng, Nanyu, Tianzong, Bingfeng, Quyuan, Shouwaiyu, Shouzhong, Tianchuang, Tianrong, Qianliao, Tinggong.● Original point: Wanggu (on the palm side, at the depression between the 5th metacarpal base and the hook bone at the red-white edge)● Luo point: Zhizheng (on the back of the forearm, 5 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Houxi (make a fist, at the back of the 5th metacarpophalangeal joint, at the red-white edge)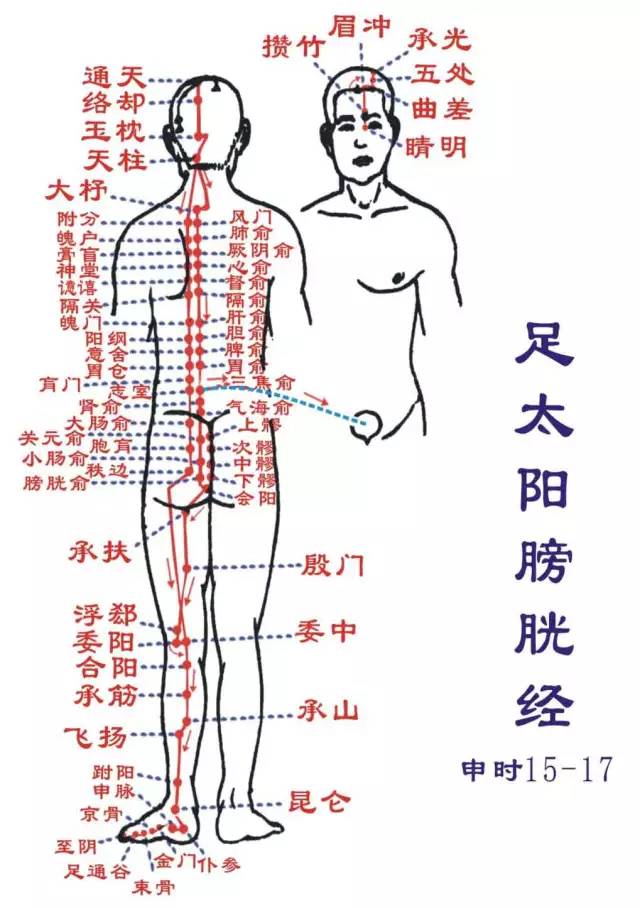 Zu Taiyang Pangguangjing (Shen hour: 3-5 PM): Runs from the head to the footStarts at the inner corner of the eye (Jingming), ascends to the forehead (Zanzhu, Meichong, Quche; Hui Shenting, Toulinqi), meets at the top of the head (Wuchu, Chengguang, Tongtian; Hui Baihui).Its branch: from the top of the head, descends to the ear (Hui Quzui, Shuaigu, Fubai, Touqiao, Wanggu). Its direct pathway: from the top of the head, enters the brain (Luoque, Yuzhen; Hui Naohu, Fengfu), exits at the neck (Tianzhuz) and descends:One branch runs along the inner side of the scapula, beside the spine (Hui Dazhu, Taodao; through Dazhu, Fengmen, Feiyu, Jueyin, Xinyu, Duyin, Geiyu), reaching the waist (Ganyu, Danfu, Piyu, Sanjiao, Shenfu, Zhongfu, Baihuan, Zhongfu).Another branch descends from the waist, through the arm (Shangliao, Ciliao, Zhongliao, Xialiao, Huiyang, Chengfu), enters the fossa (Yinmen, Weizhong).Another branch from the scapula descends, through the scapula (Fufen, Pohu, Gaohuang, Shentang, Geiguan, Hunmen, Yanggang, Yishe, Weicang, Huangmen, Zhishi, Baohang, Zhibian), passing through the hip joint (Hui Huantiao), descending along the outer side of the thigh (Fuxie, Weiyang), meeting at the fossa (Weizhong) – from here it descends through the gastrocnemius (Huyang, Chengjin, Chengshan), exiting behind the outer ankle (Feiyang, Fuyang, Kunlun), along the fifth metatarsal tuberosity (Puzhen, Shenmai, Jinduan, Jinggu), to the outer side of the little toe (Shugu, Zutonggu, Zhiyin), connecting to the foot Shaoyin kidney meridian.This meridian has 67 points on one side (134 points total), with 49 points distributed on the head, face, neck, and back, and 18 points on the midline of the lower limb’s back and the outer side of the foot. Starting point Jingming, ending point Zhiyin.Main indications: Urinary and reproductive system, neurological and psychiatric disorders, respiratory system, circulatory system, digestive system diseases, and febrile diseases, as well as conditions along the meridian’s path.● Original point: Jinggu (on the outer side of the foot, below the fifth metatarsal tuberosity, at the red-white edge)● Luo point: Feiyang (on the outer side of the lower leg, 7 cun above the midpoint of the line connecting the tip of the outer ankle and the Achilles tendon)● Shu point: Shugu (behind the fifth metatarsal head, at the red-white edge)
Zu Taiyang Pangguangjing (Shen hour: 3-5 PM): Runs from the head to the footStarts at the inner corner of the eye (Jingming), ascends to the forehead (Zanzhu, Meichong, Quche; Hui Shenting, Toulinqi), meets at the top of the head (Wuchu, Chengguang, Tongtian; Hui Baihui).Its branch: from the top of the head, descends to the ear (Hui Quzui, Shuaigu, Fubai, Touqiao, Wanggu). Its direct pathway: from the top of the head, enters the brain (Luoque, Yuzhen; Hui Naohu, Fengfu), exits at the neck (Tianzhuz) and descends:One branch runs along the inner side of the scapula, beside the spine (Hui Dazhu, Taodao; through Dazhu, Fengmen, Feiyu, Jueyin, Xinyu, Duyin, Geiyu), reaching the waist (Ganyu, Danfu, Piyu, Sanjiao, Shenfu, Zhongfu, Baihuan, Zhongfu).Another branch descends from the waist, through the arm (Shangliao, Ciliao, Zhongliao, Xialiao, Huiyang, Chengfu), enters the fossa (Yinmen, Weizhong).Another branch from the scapula descends, through the scapula (Fufen, Pohu, Gaohuang, Shentang, Geiguan, Hunmen, Yanggang, Yishe, Weicang, Huangmen, Zhishi, Baohang, Zhibian), passing through the hip joint (Hui Huantiao), descending along the outer side of the thigh (Fuxie, Weiyang), meeting at the fossa (Weizhong) – from here it descends through the gastrocnemius (Huyang, Chengjin, Chengshan), exiting behind the outer ankle (Feiyang, Fuyang, Kunlun), along the fifth metatarsal tuberosity (Puzhen, Shenmai, Jinduan, Jinggu), to the outer side of the little toe (Shugu, Zutonggu, Zhiyin), connecting to the foot Shaoyin kidney meridian.This meridian has 67 points on one side (134 points total), with 49 points distributed on the head, face, neck, and back, and 18 points on the midline of the lower limb’s back and the outer side of the foot. Starting point Jingming, ending point Zhiyin.Main indications: Urinary and reproductive system, neurological and psychiatric disorders, respiratory system, circulatory system, digestive system diseases, and febrile diseases, as well as conditions along the meridian’s path.● Original point: Jinggu (on the outer side of the foot, below the fifth metatarsal tuberosity, at the red-white edge)● Luo point: Feiyang (on the outer side of the lower leg, 7 cun above the midpoint of the line connecting the tip of the outer ankle and the Achilles tendon)● Shu point: Shugu (behind the fifth metatarsal head, at the red-white edge) Zu Shaoyin Shenjing (You hour: 5-7 PM): Runs from the foot to the abdomenStarts from the little toe, diagonally towards the center of the foot (Yongquan), exits below the navicular tuberosity (Rangu, Zhaohai, Shuiquan), along the back of the inner ankle (Taixi), branches into the heel (Dazhong); ascends to the inner side of the lower leg (Fuliu, Jiaoxin; Hui Sanyinjiao), exits at the inner side of the fossa (Zhubin, Yingu), ascends to the inner back of the thigh, through the spine (Hui Changqiang), belonging to the kidney, connecting to the bladder (Huangyu, Zhongzhu, Siman, Qixue, Dahu; Hui Guanyuan, Zhongji).Its direct pathway: from the kidney upwards (Shangqu, Shiguan, Yindu, Tonggu, Youmen), through the liver, diaphragm, entering the lungs (Bulu, Shenfeng, Lingxu, Shencang, Yuzhong, Yufu), along the throat, beside the root of the tongue (Tonglianquan).Its branch: from the lung, connects to the heart, flows into the chest, connecting to the hand Jueyin pericardium meridian.This meridian has 27 points on one side (54 points total), with 10 points distributed on the inner side of the lower limb’s back, and the remaining 17 points on the sides of the chest and abdomen. Starting point Yongquan, ending point Yufu.Main indications: Urinary and reproductive system, neurological and psychiatric disorders, respiratory system, digestive system, and circulatory system diseases, as well as conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Yongquan, Rangu, Taixi, Dazhong, Shuiquan, Zhaohai, Fuliu, Jiaoxin, Zhubin, Yingu, Huangyu, Qixue, Siman, Zhongzhu, Changqiang, Yuzhong, Yufu, Yufufu.● Original point: Taixi (in the depression between the inner ankle and the Achilles tendon, at the level of the highest point of the inner ankle)● Luo point: Dazhong (on the inner side of the foot, below the inner ankle, at the inner front of the attachment of the Achilles tendon)● Shu point: Taixi (in the depression between the inner ankle and the Achilles tendon, at the level of the highest point of the inner ankle)
Zu Shaoyin Shenjing (You hour: 5-7 PM): Runs from the foot to the abdomenStarts from the little toe, diagonally towards the center of the foot (Yongquan), exits below the navicular tuberosity (Rangu, Zhaohai, Shuiquan), along the back of the inner ankle (Taixi), branches into the heel (Dazhong); ascends to the inner side of the lower leg (Fuliu, Jiaoxin; Hui Sanyinjiao), exits at the inner side of the fossa (Zhubin, Yingu), ascends to the inner back of the thigh, through the spine (Hui Changqiang), belonging to the kidney, connecting to the bladder (Huangyu, Zhongzhu, Siman, Qixue, Dahu; Hui Guanyuan, Zhongji).Its direct pathway: from the kidney upwards (Shangqu, Shiguan, Yindu, Tonggu, Youmen), through the liver, diaphragm, entering the lungs (Bulu, Shenfeng, Lingxu, Shencang, Yuzhong, Yufu), along the throat, beside the root of the tongue (Tonglianquan).Its branch: from the lung, connects to the heart, flows into the chest, connecting to the hand Jueyin pericardium meridian.This meridian has 27 points on one side (54 points total), with 10 points distributed on the inner side of the lower limb’s back, and the remaining 17 points on the sides of the chest and abdomen. Starting point Yongquan, ending point Yufu.Main indications: Urinary and reproductive system, neurological and psychiatric disorders, respiratory system, digestive system, and circulatory system diseases, as well as conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Yongquan, Rangu, Taixi, Dazhong, Shuiquan, Zhaohai, Fuliu, Jiaoxin, Zhubin, Yingu, Huangyu, Qixue, Siman, Zhongzhu, Changqiang, Yuzhong, Yufu, Yufufu.● Original point: Taixi (in the depression between the inner ankle and the Achilles tendon, at the level of the highest point of the inner ankle)● Luo point: Dazhong (on the inner side of the foot, below the inner ankle, at the inner front of the attachment of the Achilles tendon)● Shu point: Taixi (in the depression between the inner ankle and the Achilles tendon, at the level of the highest point of the inner ankle)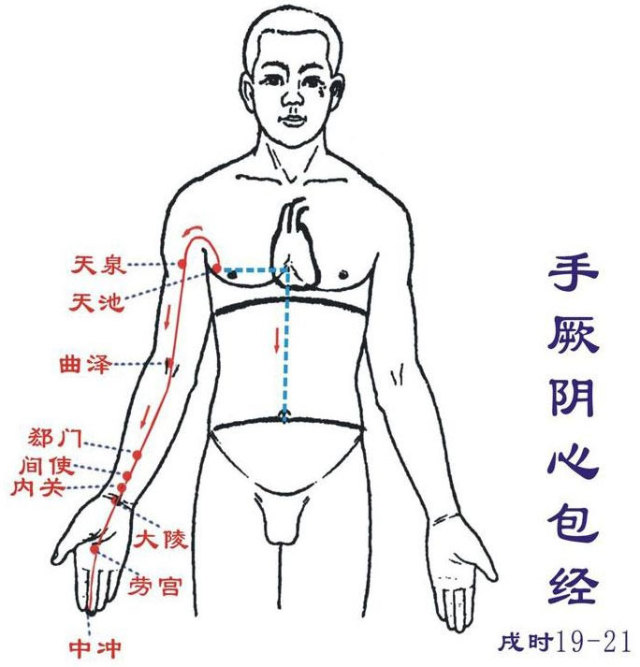 Shou Jueyin Xinbaojing (Xu hour: 7-9 PM): Runs from the chest to the handThe pericardium meridian passes through three important points that separate the chest and abdomen: Tianzhong, Zhongwan, and Yinjiao. It runs through the chest, the lateral abdomen, the inner side of the hand, the palm, and the middle finger continuously. Starting from the chest, it exits belonging to the pericardium, passes through the diaphragm, traverses the chest, upper abdomen, and lower abdomen, connecting to the Sanjiao.Its branch runs along the chest, exits at the side, at the three cun under the armpit (Tianchi), ascends to the armpit, along the inner side of the upper arm (Tianquan), between the hand Taiyin and hand Shaoyin, enters the elbow (Quxi), descends to the forearm, runs between the two tendons (the radial flexor tendon and the palmaris longus tendon) (Qimen, Jianshi, Neiguan, Daling), enters the palm (Laogong), along the radial side of the middle finger to the tip (Zhongchong).Its branch: from the palm, runs along the ring finger to the tip, connecting to the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian.This meridian has 9 points on one side (18 points total), with 8 points distributed on the palm surface’s midline, and 1 point in the upper chest. Starting point Tianchi, ending point Zhongchong.Main indications: Heart, chest, stomach, mental disorders, and other diseases along the meridian’s path. Such as heart pain, chest tightness, palpitations, irritability, mania, swelling of the armpit, and elbow spasms.● Points of this meridian: Tianchi, Tianquan, Quxi, Qimen, Jianshi, Neiguan, Daling, Laogong, Zhongchong.● Original point: Daling (with the palm up, above the wrist crease, between the radial flexor tendon and the palmaris longus tendon)● Luo point: Neiguan (on the palm side of the forearm, 2 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Daling (with the palm up, above the wrist crease, between the radial flexor tendon and the palmaris longus tendon)
Shou Jueyin Xinbaojing (Xu hour: 7-9 PM): Runs from the chest to the handThe pericardium meridian passes through three important points that separate the chest and abdomen: Tianzhong, Zhongwan, and Yinjiao. It runs through the chest, the lateral abdomen, the inner side of the hand, the palm, and the middle finger continuously. Starting from the chest, it exits belonging to the pericardium, passes through the diaphragm, traverses the chest, upper abdomen, and lower abdomen, connecting to the Sanjiao.Its branch runs along the chest, exits at the side, at the three cun under the armpit (Tianchi), ascends to the armpit, along the inner side of the upper arm (Tianquan), between the hand Taiyin and hand Shaoyin, enters the elbow (Quxi), descends to the forearm, runs between the two tendons (the radial flexor tendon and the palmaris longus tendon) (Qimen, Jianshi, Neiguan, Daling), enters the palm (Laogong), along the radial side of the middle finger to the tip (Zhongchong).Its branch: from the palm, runs along the ring finger to the tip, connecting to the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian.This meridian has 9 points on one side (18 points total), with 8 points distributed on the palm surface’s midline, and 1 point in the upper chest. Starting point Tianchi, ending point Zhongchong.Main indications: Heart, chest, stomach, mental disorders, and other diseases along the meridian’s path. Such as heart pain, chest tightness, palpitations, irritability, mania, swelling of the armpit, and elbow spasms.● Points of this meridian: Tianchi, Tianquan, Quxi, Qimen, Jianshi, Neiguan, Daling, Laogong, Zhongchong.● Original point: Daling (with the palm up, above the wrist crease, between the radial flexor tendon and the palmaris longus tendon)● Luo point: Neiguan (on the palm side of the forearm, 2 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Daling (with the palm up, above the wrist crease, between the radial flexor tendon and the palmaris longus tendon)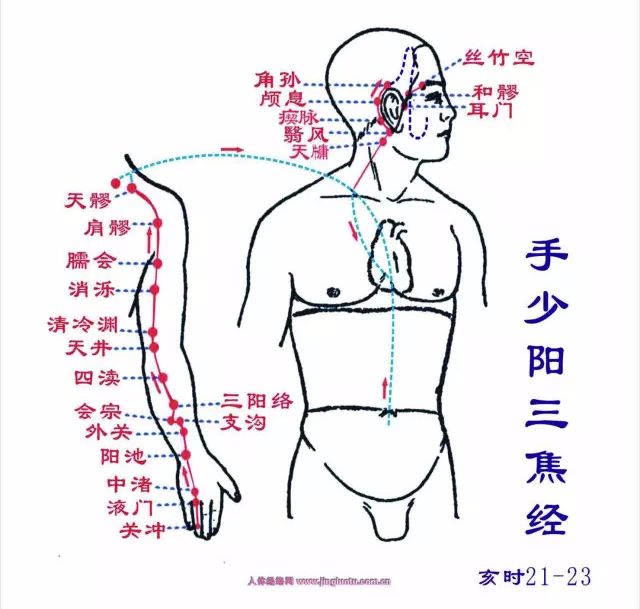 Shou Shaoyang Sanjiao Jing (Hai hour: 9-11 PM): Runs from the hand to the headStarts at the tip of the ring finger (Guanchong), ascends between the little finger and the ring finger (Yemeng), along the back of the hand (Zhongzhu, Yangchi), exits between the two bones of the forearm (the ulna and radius) (Waiwan, Zhigou, Huizong, Sanyangluo, Sidu), ascends through the elbow (Tianjing), along the outer side of the upper arm (Qinglengyuan, Xiaoluo), ascends through the shoulder (Nuanhui, Jianliao), meets the back of the foot Shaoyang meridian (Tianliao; Hui Bingfeng, Shouzhong, Dazhu), enters the supraclavicular fossa, distributes in the middle of the chest (Zongge), disperses into the pericardium, passes through the diaphragm, widely belonging to the upper, middle, and lower Sanjiao.Its branch: from the middle of the chest, ascends to the supraclavicular fossa, upwards to the back of the neck, connecting to the ear (Tianyou, Yifeng, Luyin), directly upwards to the top of the ear (Jiaosun; Hui Huanliao, Xuanli, Shangguan), bends down to the cheek, to below the eye (Qianliao).Its branch: from behind the ear, enters the ear, exits in front of the ear (Huiliao, Ermen; Hui Tinghui), passing through Shangguan, connecting to the cheek, to the outer corner of the eye (Sizhu Kong; Hui Tongzili) connecting to the foot Shaoyang gallbladder meridian. Additionally, the Sanjiao connects with the foot Taiyang bladder meridian at the Weiyang pulse.This meridian has 23 points on one side (46 points total), with 13 points distributed on the midline of the upper limb’s back, and 10 points in the neck and side of the head. Starting point Guanchong, ending point Sizhukong.Main indications: Chest, heart, lung, throat disorders, certain febrile diseases, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Guanchong, Yemeng, Zhongzhu, Yangchi, Waiwan, Zhigou, Huizong, Sanyang, Luo, Sidu, Tianjing, Qinglengyuan, Xiaoluo, Nuanhui, Jianliao, Tianliao, Tianyou, Yifeng, Chuanmai, Jiao, Ermen, Tinghui, Sizhukong.● Original point: Yangchi (in the middle of the wrist crease)● Luo point: Waiwan (2 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Zhongzhu (make a fist, in the depression between the 4th and 5th metacarpal heads)
Shou Shaoyang Sanjiao Jing (Hai hour: 9-11 PM): Runs from the hand to the headStarts at the tip of the ring finger (Guanchong), ascends between the little finger and the ring finger (Yemeng), along the back of the hand (Zhongzhu, Yangchi), exits between the two bones of the forearm (the ulna and radius) (Waiwan, Zhigou, Huizong, Sanyangluo, Sidu), ascends through the elbow (Tianjing), along the outer side of the upper arm (Qinglengyuan, Xiaoluo), ascends through the shoulder (Nuanhui, Jianliao), meets the back of the foot Shaoyang meridian (Tianliao; Hui Bingfeng, Shouzhong, Dazhu), enters the supraclavicular fossa, distributes in the middle of the chest (Zongge), disperses into the pericardium, passes through the diaphragm, widely belonging to the upper, middle, and lower Sanjiao.Its branch: from the middle of the chest, ascends to the supraclavicular fossa, upwards to the back of the neck, connecting to the ear (Tianyou, Yifeng, Luyin), directly upwards to the top of the ear (Jiaosun; Hui Huanliao, Xuanli, Shangguan), bends down to the cheek, to below the eye (Qianliao).Its branch: from behind the ear, enters the ear, exits in front of the ear (Huiliao, Ermen; Hui Tinghui), passing through Shangguan, connecting to the cheek, to the outer corner of the eye (Sizhu Kong; Hui Tongzili) connecting to the foot Shaoyang gallbladder meridian. Additionally, the Sanjiao connects with the foot Taiyang bladder meridian at the Weiyang pulse.This meridian has 23 points on one side (46 points total), with 13 points distributed on the midline of the upper limb’s back, and 10 points in the neck and side of the head. Starting point Guanchong, ending point Sizhukong.Main indications: Chest, heart, lung, throat disorders, certain febrile diseases, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Guanchong, Yemeng, Zhongzhu, Yangchi, Waiwan, Zhigou, Huizong, Sanyang, Luo, Sidu, Tianjing, Qinglengyuan, Xiaoluo, Nuanhui, Jianliao, Tianliao, Tianyou, Yifeng, Chuanmai, Jiao, Ermen, Tinghui, Sizhukong.● Original point: Yangchi (in the middle of the wrist crease)● Luo point: Waiwan (2 cun above the wrist crease)● Shu point: Zhongzhu (make a fist, in the depression between the 4th and 5th metacarpal heads)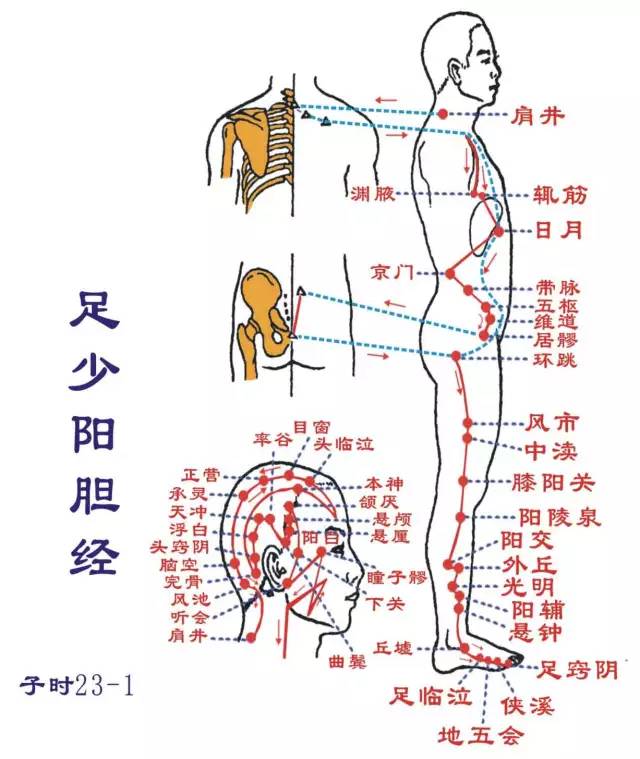 Zu Shaoyang Danjing (Zi hour: 11 PM-1 AM): Runs from the head to the footStarts at the outer corner of the eye (Tongzili), ascends to the corner of the forehead (Huanlian, Xuanlu, Xuanli, Quzui; Hui Touwei, Huiliao, Jiao, Yifeng), descends behind the ear (Shuaigu, Tianchong, Fubai, Touqiao, Wanggu, Benshen, Yangbai, Toulinqi, Muxiang, Zhengying, Chengling, Naokong, Fengchi), along the neck, running along the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian (Jing Tianrong), to the shoulder, retreating, meeting the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian (Hui Dazhu, connecting to the shoulder, entering the supraclavicular fossa).Its branch: from behind the ear, enters the ear (Hui Yifeng), runs in front of the ear (Tinghui, Shangguan; Hui Tinggong, Xiaguan), to the outer corner of the eye.Another branch: from the outer corner of the eye, descends to Daying, meeting the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian to below the eye; descends over the jaw (Jiaojiao), down the neck, meeting at the supraclavicular fossa (Hui Suokong). From here, it descends into the chest, passing through the diaphragm, connecting to the liver, belonging to the gallbladder; along the ribs, exiting at the Qijie (inguinal artery), encircling the pubic hair, horizontally entering the hip joint.Its main branch (direct pathway): from the supraclavicular fossa down to the armpit (Yuanye, Zhejin; Hui Tianchi), along the side of the chest, passing through the ribs (Rihuo, Jingmen; Hui Zhangmen), descending to meet at the hip joint (Dai Mai, Wushu, Weidao, Juyiao… Huantiao). From here, it descends along the outer side of the thigh (Fengshi, Zhongdu), exiting at the outer side of the knee (Xiyangguan), descending to the front of the fibula (Yanglingquan), directly down to the lower part of the fibula (Yangjiao, Waiqiu, Guangming, Yangfu, Xuanzhong), exiting before the outer ankle (Qiuxu), along the dorsum of the foot entering the fourth toe’s outer side (Zutong, Dihui, Xiakong, Zhi Yin).This meridian has 44 points on one side (88 points total), with 15 points distributed on the outer side of the lower limb, and 29 points in the buttocks, lateral chest, and side of the head. Starting point Tongzili, ending point Zhi Yin.Main indications: Disorders of the chest and ribs, liver and gallbladder diseases, febrile diseases, neurological disorders, and conditions of the head, side, eyes, ears, and throat, as well as conditions along the meridian’s path.● Original point: Qiuxu (in front of the outer ankle)● Luo point: Guangming (on the outer side of the lower leg, 5 cun above the tip of the outer ankle, at the anterior edge of the fibula)● Shu point: Zhitong (on the outer side of the foot, behind the fourth toe joint)
Zu Shaoyang Danjing (Zi hour: 11 PM-1 AM): Runs from the head to the footStarts at the outer corner of the eye (Tongzili), ascends to the corner of the forehead (Huanlian, Xuanlu, Xuanli, Quzui; Hui Touwei, Huiliao, Jiao, Yifeng), descends behind the ear (Shuaigu, Tianchong, Fubai, Touqiao, Wanggu, Benshen, Yangbai, Toulinqi, Muxiang, Zhengying, Chengling, Naokong, Fengchi), along the neck, running along the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian (Jing Tianrong), to the shoulder, retreating, meeting the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian (Hui Dazhu, connecting to the shoulder, entering the supraclavicular fossa).Its branch: from behind the ear, enters the ear (Hui Yifeng), runs in front of the ear (Tinghui, Shangguan; Hui Tinggong, Xiaguan), to the outer corner of the eye.Another branch: from the outer corner of the eye, descends to Daying, meeting the hand Shaoyang Sanjiao meridian to below the eye; descends over the jaw (Jiaojiao), down the neck, meeting at the supraclavicular fossa (Hui Suokong). From here, it descends into the chest, passing through the diaphragm, connecting to the liver, belonging to the gallbladder; along the ribs, exiting at the Qijie (inguinal artery), encircling the pubic hair, horizontally entering the hip joint.Its main branch (direct pathway): from the supraclavicular fossa down to the armpit (Yuanye, Zhejin; Hui Tianchi), along the side of the chest, passing through the ribs (Rihuo, Jingmen; Hui Zhangmen), descending to meet at the hip joint (Dai Mai, Wushu, Weidao, Juyiao… Huantiao). From here, it descends along the outer side of the thigh (Fengshi, Zhongdu), exiting at the outer side of the knee (Xiyangguan), descending to the front of the fibula (Yanglingquan), directly down to the lower part of the fibula (Yangjiao, Waiqiu, Guangming, Yangfu, Xuanzhong), exiting before the outer ankle (Qiuxu), along the dorsum of the foot entering the fourth toe’s outer side (Zutong, Dihui, Xiakong, Zhi Yin).This meridian has 44 points on one side (88 points total), with 15 points distributed on the outer side of the lower limb, and 29 points in the buttocks, lateral chest, and side of the head. Starting point Tongzili, ending point Zhi Yin.Main indications: Disorders of the chest and ribs, liver and gallbladder diseases, febrile diseases, neurological disorders, and conditions of the head, side, eyes, ears, and throat, as well as conditions along the meridian’s path.● Original point: Qiuxu (in front of the outer ankle)● Luo point: Guangming (on the outer side of the lower leg, 5 cun above the tip of the outer ankle, at the anterior edge of the fibula)● Shu point: Zhitong (on the outer side of the foot, behind the fourth toe joint)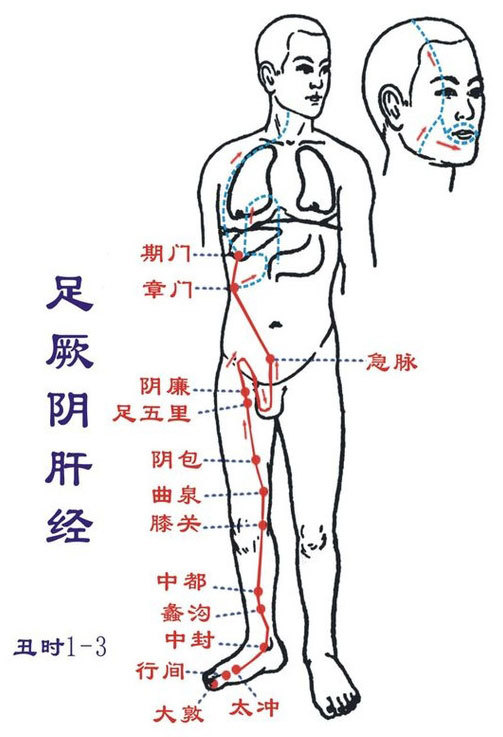 Zu Jueyin Gan Jing (Chou hour: 1-3 AM): Runs from the foot to the abdomenStarts at the back of the big toe (Dadu), ascends along the inner side of the foot (Xingjian, Taichong), 1 cun from the inner ankle (Zhongfeng), ascends along the inner side of the lower leg (Hui Sanyinjiao; through Ligou, Zhongdu, Xiguan), 8 cun from the inner ankle, intersects after the foot Taiyin spleen meridian, ascends to the inner side of the knee (Ququan), along the inner side of the thigh (Yinbao, Zu Wuli, Yinlian), enters the pubic area, encircling the area, to the lower abdomen (Jima; Hui Chongmen, Fushi, Qugu, Zhongji, Guanyuan), beside the stomach, belonging to the liver, connecting to the gallbladder (Zhangmen, Qimen); ascends through the diaphragm, distributing to the ribs, along the trachea, ascending to the forehead, connecting to the eye system (the vascular connection behind the eyeball), ascending to the forehead, meeting the governor meridian at the top of the head.Its branch: from the eye system, descends to the cheek, encircling the lips.Its branch: from the liver, ascends through the diaphragm, flows into the lungs (connecting to the hand Taiyin lung meridian).This meridian has 14 points on one side (28 points total), with 12 points distributed on the inner side of the lower limb, and the remaining 2 points in the abdomen and chest. Starting point Dadu, ending point Qimen.Main indications: Disorders of the urinary and reproductive systems, neurological disorders, liver and gallbladder diseases, eye diseases, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Dadu, Xingjian, Taichong, Zhongfeng, Ligou, Zhongdu, Xiguan, Ququan, Yinbao, Zu Wuli, Yinlian, Jima, Zhangmen, Qimen.● Original point: Taichong (on the dorsum of the foot, at the depression behind the first metatarsal space)● Luo point: Ligou (on the inner side of the lower leg, 5 cun above the tip of the inner ankle, at the center of the inner side of the tibia)● Shu point: Taichong (on the dorsum of the foot, at the depression behind the first metatarsal space)
Zu Jueyin Gan Jing (Chou hour: 1-3 AM): Runs from the foot to the abdomenStarts at the back of the big toe (Dadu), ascends along the inner side of the foot (Xingjian, Taichong), 1 cun from the inner ankle (Zhongfeng), ascends along the inner side of the lower leg (Hui Sanyinjiao; through Ligou, Zhongdu, Xiguan), 8 cun from the inner ankle, intersects after the foot Taiyin spleen meridian, ascends to the inner side of the knee (Ququan), along the inner side of the thigh (Yinbao, Zu Wuli, Yinlian), enters the pubic area, encircling the area, to the lower abdomen (Jima; Hui Chongmen, Fushi, Qugu, Zhongji, Guanyuan), beside the stomach, belonging to the liver, connecting to the gallbladder (Zhangmen, Qimen); ascends through the diaphragm, distributing to the ribs, along the trachea, ascending to the forehead, connecting to the eye system (the vascular connection behind the eyeball), ascending to the forehead, meeting the governor meridian at the top of the head.Its branch: from the eye system, descends to the cheek, encircling the lips.Its branch: from the liver, ascends through the diaphragm, flows into the lungs (connecting to the hand Taiyin lung meridian).This meridian has 14 points on one side (28 points total), with 12 points distributed on the inner side of the lower limb, and the remaining 2 points in the abdomen and chest. Starting point Dadu, ending point Qimen.Main indications: Disorders of the urinary and reproductive systems, neurological disorders, liver and gallbladder diseases, eye diseases, and conditions along the meridian’s path.● Points of this meridian: Dadu, Xingjian, Taichong, Zhongfeng, Ligou, Zhongdu, Xiguan, Ququan, Yinbao, Zu Wuli, Yinlian, Jima, Zhangmen, Qimen.● Original point: Taichong (on the dorsum of the foot, at the depression behind the first metatarsal space)● Luo point: Ligou (on the inner side of the lower leg, 5 cun above the tip of the inner ankle, at the center of the inner side of the tibia)● Shu point: Taichong (on the dorsum of the foot, at the depression behind the first metatarsal space)

Summary of Original, Luo, and Shu Point Locations1. Lung MeridianOriginal and Shu point: Taiyuan: at the radial side of the wrist crease, in the depression at the radial side of the radial arteryLuo point: Lieque: 1.5 cun above the wrist crease, at the radial edge (forearm)2. Large Intestine MeridianOriginal point: Hegu: on the back of the hand, between the first and second metacarpals, at the midpoint of the radial side of the second metacarpalLuo point: Pianli: on the back of the elbow, 3 cun above the wrist creaseShu point: Sanjian: make a fist, in the depression at the radial side of the second metacarpal head3. Stomach MeridianOriginal point: Chongyang: on the dorsum of the foot, at the base of the second metatarsal and the intermediate cuneiform joint, can feel the dorsalis pedis arteryLuo point: Fenglong: on the front outer side of the lower leg, 8 cun above the tip of the outer ankle, at the horizontal finger distance from the anterior edge of the tibiaShu point: Xiangu: in the depression behind the second and third metatarsophalangeal joints on the dorsum of the foot4. Spleen MeridianOriginal and Shu point: Taibai: behind the first metatarsal head, at the red-white inner edgeLuo point: Gongsun: at the front lower part of the first metatarsal base5. Heart MeridianOriginal and Shu point: Shenmen: at the radial side of the wrist creaseLuo point: Tongli: on the palm side of the forearm, at the radial edge, 1 cun above the wrist crease6. Small Intestine MeridianOriginal point: Wanggu: on the palm side, at the depression between the 5th metacarpal base and the hook bone at the red-white edgeLuo point: Zhizheng: on the back of the forearm, 5 cun above the wrist creaseShu point: Houxi: make a fist, at the back of the 5th metacarpophalangeal joint, at the red-white edge7. Bladder MeridianOriginal point: Jinggu: on the outer side of the foot, below the fifth metatarsal tuberosity, at the red-white edgeLuo point: Feiyang: on the outer side of the lower leg, 7 cun above the midpoint of the line connecting the tip of the outer ankle and the Achilles tendonShu point: Shugu: behind the fifth metatarsal head, at the red-white edge8. Kidney MeridianOriginal and Shu point: Taixi: in the depression between the inner ankle and the Achilles tendon, at the level of the highest point of the inner ankleLuo point: Dazhong: on the inner side of the foot, below the inner ankle, at the inner front of the attachment of the Achilles tendon9. Pericardium MeridianOriginal and Shu point: Daling: with the palm up, above the wrist crease, between the radial flexor tendon and the palmaris longus tendonLuo point: Neiguan: on the palm side of the forearm, 2 cun above the wrist crease10. Sanjiao MeridianOriginal point: Yangchi: in the middle of the wrist creaseLuo point: Waiwan: 2 cun above the wrist creaseShu point: Zhongzhu: make a fist, in the depression between the 4th and 5th metacarpal heads11. Gallbladder MeridianOriginal point: Qiuxu: in front of the outer ankleLuo point: Guangming: on the outer side of the lower leg, 5 cun above the tip of the outer ankle, at the anterior edge of the fibulaShu point: Zhitong: on the outer side of the foot, behind the fourth toe joint12. Liver MeridianOriginal and Shu point: Taichong: on the dorsum of the foot, at the depression behind the first metatarsal spaceLuo point: Ligou: on the inner side of the lower leg, 5 cun above the tip of the inner ankle, at the center of the inner side of the tibia.
DisseminatingTraditional Chinese Medicine health knowledge, promoting Chinese traditional culture,sharing health concepts, conveying care, passing health knowledge and traditional culture to more friends…
People are great because of their dreams; we are different because of our love.
Liu Qingning: 186 9643 6785 or (WeChat ID)
Yang Shunsong: 138 7171 7447 or (WeChat ID)