What are the Five Elements?
What does the theory of Five Elements encompass?
Application of the Five Elements theory in Traditional Chinese Medicine?
Watch the video to learn
Learning requirements: Basic meanings and theories of the Five Elements, mutual generation and restriction, the Five Elements’ interactions, and the mother-child relationship.
Overview
The theory of Five Elements studies the intrinsic characteristics and generative-restrictive laws of the five elements: Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water. It uses the characteristics of the Five Elements to summarize various phenomena and attempts to explain the interrelations of all things in the universe through the laws of generation and restriction, which is an important philosophical theory in Chinese thought.
1. Basic Meanings of the Five Elements
Five: Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, Water (the five basic substances in nature)
Elements: Movement, change, laws
2. Basic Content of the Five Elements Theory
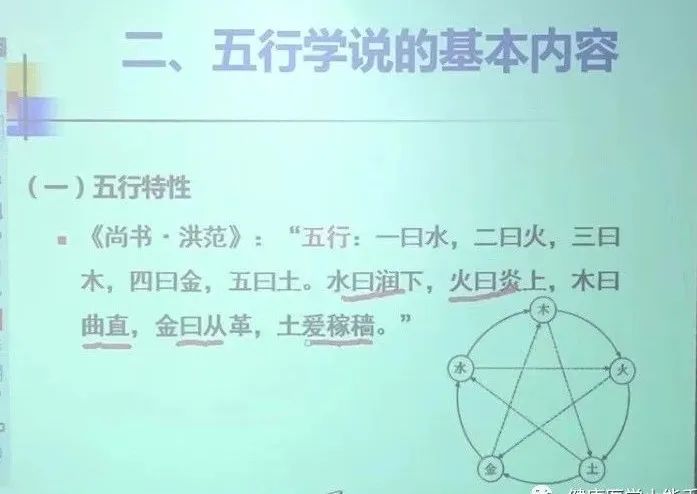
(1) Characteristics of the Five Elements
First is Water, second is Fire, third is Wood, fourth is Metal, fifth is Earth.
Water is moistening and descending, Fire is ascending and blazing, Wood is bending and straightening, Metal is transforming and cutting, Earth is nurturing and harvesting (representing the basic attributes of the five substances).
1. Wood is bending and straightening
Bending – Curving and shrinking
Straightening – Reproductive growth
Bending and straightening – Wood plants exhibit the ability to bend and stretch during growth.
Extended meaning – Things and phenomena that possess growth, development, bending, and relaxation characteristics are attributed to Wood.
2. Fire is ascending and blazing
Blazing – Heat
Ascending – Rising
Ascending and blazing – Fire has the characteristics of burning, heat, and rising.
Extended meaning – Things and phenomena that possess heat, warmth, brightness, and rising characteristics are attributed to Fire.
3. Earth is nurturing and harvesting
Nurturing – To give birth
Harvesting – To reap
Earth has the ability to nurture life and sustain all things.
Extended meaning – All phenomena that possess characteristics of nurturing, sustaining, and receiving are attributed to Earth.
4. Metal is transforming and cutting
Transforming – To comply
Cutting – To eliminate, to kill
Transforming and cutting – Metal has characteristics of transformation, elimination, and settling.
Extended meaning – All phenomena that possess characteristics of elimination, gathering, and settling are attributed to Metal.
5. Water is moistening and descending
Moistening – To hydrate
Descending – To flow downward
Moistening and descending – Water naturally flows downward, possessing the characteristics of hydrating all things and being calm and cold.
Extended meaning – All phenomena that possess characteristics of hydration, downward movement, coldness, and concealment are attributed to Water.
(2) Classification of the Five Elements
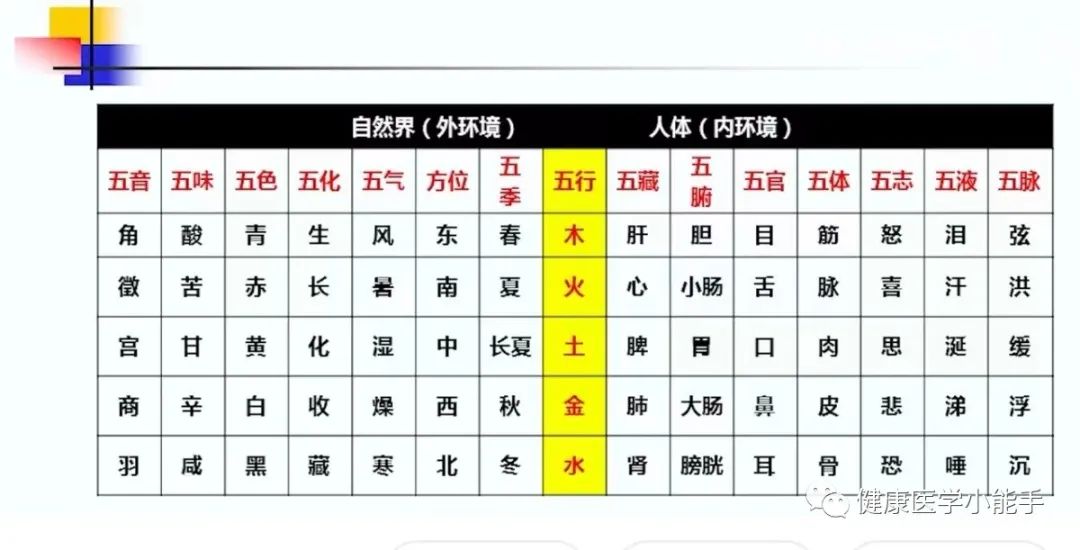
1. All things in nature belong to the Five Elements system, and the human and natural environment, as well as the social environment, are unified within this system.
Question: What is the basis for classifying things and phenomena according to the Five Elements?
Answer: Wood is bending and straightening, Fire is ascending and blazing, Earth is nurturing and harvesting, Metal is transforming and cutting, Water is moistening and descending.
Question: What is the method for classifying things and phenomena according to the Five Elements?
Answer: Using imagery and analogy, comparative reasoning, and deductive reasoning.
Using imagery and analogy – Extracting the essence of all things in nature and matching them with Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.
1-1. For example, from the perspective of seasons
In spring, all things flourish, and plants grow, so spring belongs to Wood. Because Wood is bending and straightening, it has the properties of growth and upward movement.
In summer, it is particularly hot, which resembles the properties of Fire, as Fire is ascending and blazing, possessing the attributes of heat and growth.
In late summer, the state is both hot and humid, suitable for the growth of crops, resembling the characteristics of Earth, which is nurturing and harvesting.
In autumn, leaves turn yellow and fall. This resembles the properties of Metal, which is transforming and cutting.
In winter, it is cold, resembling the properties of Water, which is moistening and descending.
1-2. From the perspective of directions, dividing into East, South, Center, West, and North
East – The sun rises in the East, related to the properties of Wood, which is bending and straightening, and growth.
South – The South is relatively hot, related to the properties of Fire, which is ascending and blazing.
Center – This is where the Chinese nation originated, suitable for the reproduction of crops, so the Center belongs to Earth.
West – The West is relatively desolate, resembling the properties of Metal, which is transforming and cutting.
North – The North is relatively cold, resembling the properties of Water, which is moistening and descending.
1-3. Classification based on the Five Organs
Liver – Governs smoothness and prefers regulation, resembling the properties of Wood.
Heart – Governs spirit and blood vessels, is a constantly moving organ, resembling the properties of Fire.
Spleen – The spleen and stomach are the source of qi and blood transformation, resembling the properties of Earth, which is nurturing.
Lungs – Govern restriction and descent; excessive lung qi can lead to cough and discomfort, resembling the properties of Metal.
Kidneys – The kidneys themselves govern Water and closure.
2. The Five Elements and the Five Organs System
It is a Five Elements system centered around the Five Organs.

👉 For example, the Liver system
The liver belongs to Wood, and the liver and gallbladder are interrelated; the liver governs tendons, opens to the eyes, and in fluids is tears, in emotions is anger.
👉 For example, the Heart system
The heart belongs to Fire, and the heart and small intestine are interrelated; the heart governs vessels, opens to the tongue, and in fluids is sweat, in emotions is joy.
👉 For example, the Spleen system
The spleen belongs to Earth, and the spleen and stomach are interrelated; the spleen opens to the mouth, governs flesh, in fluids is saliva, in emotions is thought.
👉 For example, the Lung system
The lungs belong to Metal, are related to the large intestine, open to the nose, govern skin, in fluids is mucus, in emotions is sadness.
👉 For example, the Kidney system
The kidneys belong to Water, are related to the bladder, open to the ears and the two lower orifices, in fluids is saliva, their essence is in hair, in emotions is fear.
(3) Generation, Restriction, Transformation
Mutual generation of the Five Elements – Mutual restriction of the Five Elements – Transformation of the Five Elements – Victory and recovery of the Five Elements
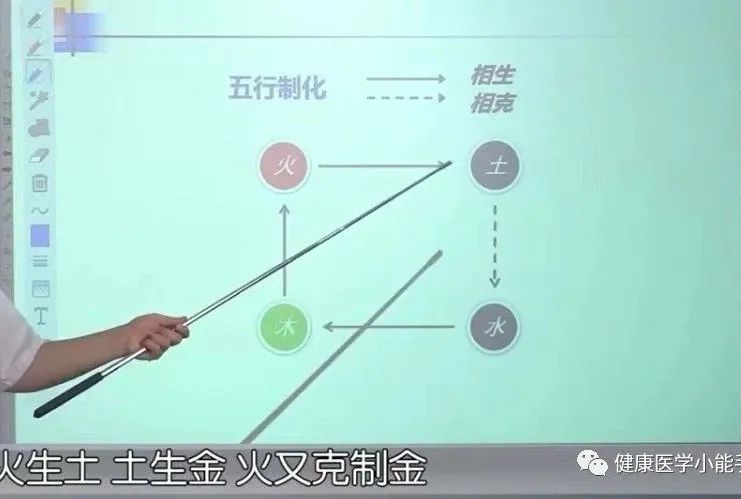
1. Mutual Generation –Refers to nourishing, assisting, and promoting
(1-1) Order of Mutual Generation of the Five Elements
Wood generates Fire, Fire generates Earth, Earth generates Metal, Metal generates Water, Water generates Wood
👉 For example – Wood generates Fire, igniting wood creates fire.
Fire generates Earth, meaning fire burns and turns into ash.
Earth generates Metal, meaning metals are mined from the earth, and gold is extracted from sand.
Metal generates Water, meaning metals can melt into liquid when heated, and metal products can be used to dig for water.
Water generates Wood, meaning water nourishes trees.
(1-2) The relationship of mutual generation – Mother-child relationship
The one that generates me is the mother, the one I generate is the child
👉 For example – Wood generates Fire, Wood is the mother of Fire, Fire is the child of Wood.
2. Mutual Restriction –Mutual restriction, suppression, and control
There is an orderly restriction and balance among the Five Elements.
(2-1) Order of Mutual Restriction
Wood restricts Earth, Earth restricts Water, Water restricts Fire, Fire restricts Metal, Metal restricts Wood
In the Five Elements, adjacent elements generate each other, while those separated by one element restrict each other.
👉 Wood restricts Earth – This means that planting trees can prevent soil erosion.
👉 Earth restricts Water – This means that earth can suppress and control the growth and function of water, as soil can cover water flow and absorb it.
👉 Water restricts Fire – This means that water can extinguish fire.
👉 Fire restricts Metal – This means that fire can melt metal; flames or heat can liquefy metals.
👉 Metal restricts Wood – This means that solid metal objects can cut down trees.
(2-2) The relationship of mutual restriction – What is overcome and what is not
The one I restrict is the “overcome”, the one that restricts me is the “not overcome”.
👉 For example, Wood restricts Earth; Earth is overcome by Wood, and Wood is not overcome by Earth. This means that in a battle between Wood and Earth, Wood ultimately prevails.
3. Transformation of the Five Elements –Within the Five Elements, there are both supportive and restrictive relationships.
Both are indispensable; without mutual generation, there is no growth and development of things; without mutual restriction, there is no orderly progression of things.
👉 For example, Wood generates Fire, Fire generates Earth, but Wood also restricts Earth.
Fire generates Earth, Earth generates Metal, but Fire can also restrict Metal. Mutual generation and restriction must be in a state of coordinated interaction to maintain the normal and orderly development of things.
4. Diagram of the Laws of Transformation of the Five Elements
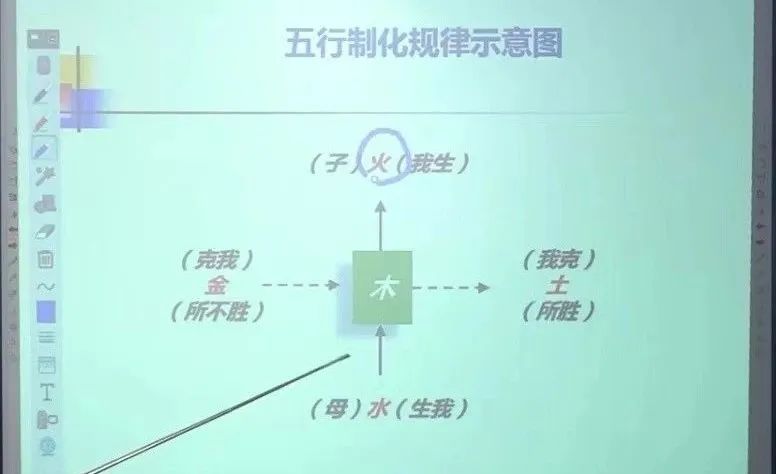
👉 Taking Wood as an example – Wood generates Fire – Wood restricts Earth – Fire generates Earth – Earth generates Metal – Fire restricts Metal
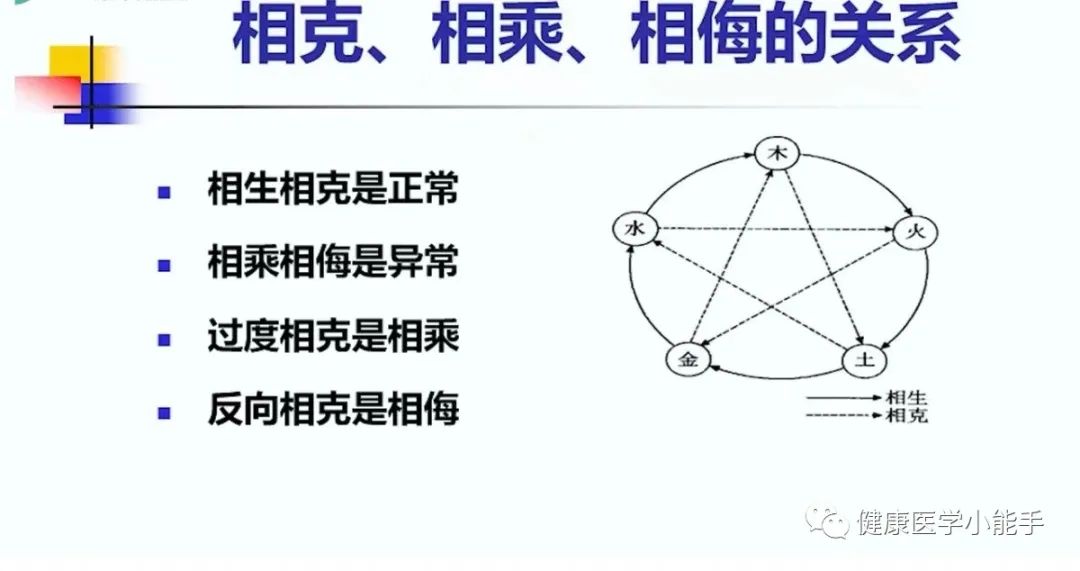
5. Mutual Generation and Mutual Restriction –These are both abnormal restrictive phenomena.
(5-1) Mutual Generation – This is excessive restriction that follows the order of mutual restriction among the Five Elements.
One element in the Five Elements excessively restricts the element it overcomes.
👉 For example, Wood restricts Earth; if Wood is too strong and excessively restricts Earth, this is mutual generation.
(5-2) Mutual Restriction – This refers to the reverse restriction phenomenon in the order of mutual restriction among the Five Elements.
👉 For example, if Wood restricts Earth, and Earth is too strong, it will reverse and restrict Wood, which is mutual restriction among the Five Elements.
(5-3) Why does mutual generation occur?

The disparity in strength between the two parties – for example, Wood restricts Earth – ratio 1:1.
One element is too strong – excessive – ratio 2:1 – Wood excessively restricts Earth.
One element is too weak – insufficient – ratio 1:1.5 – Earth is weak and Wood excessively restricts it.
This could be due to the excessive strength of the one being restricted (Earth) or the weakness of the one doing the restricting (Wood).
(5-4) Mutual Restriction among the Five Elements –One element in the Five Elements restricts another element that it does not overcome – reverse restriction.

Why does mutual restriction occur?
The disparity in strength between the two parties – for example, Metal restricts Wood – ratio 1:1.
One element is too strong – excessive – ratio 1:2 – Wood excessively restricts Metal.
One element is too weak – insufficient – ratio 0.5:1 – Metal is weak and Wood excessively restricts it.
In summary – mutual generation is excessive restriction of the one being restricted, while mutual restriction is the reverse restriction of the one being restricted.
(5) Mother-child Relationship –In the mutual generation relationship of the Five Elements, there exists a recursive nourishing relationship known as the “mother-child relationship”.
1. Mutual Generation
In abnormal states, the “mother-child relationship” becomes a disease, and the transmission path is called “mutual generation”. An abnormality in one element can affect its child element, leading to abnormalities in both.
2. Child Affects Mother
An abnormality in one element can affect its mother element, leading to abnormalities in both.
3. Child Affects Mother
If the child element is excessive, it can cause the mother element to become overly active, leading to both elements being overly active.
4. Child Steals Mother’s Qi
If the child element is insufficient, it can lead to the mother element also being insufficient, resulting in both elements being deficient.
👉 For example: The Heart belongs to Fire – the Liver belongs to Wood.
The Heart is the child – the Liver is the mother.
Wood generates Fire.
First, there is a deficiency of Heart blood, followed by a deficiency of Liver blood, leading to deficiencies in both Heart and Liver blood.
5. Mother Affects Child
An abnormality in one element can affect its child element, leading to abnormalities in both.
👉 For example – Water generates Wood.
The Kidneys belong to Water, the Liver belongs to Wood.
Water is the mother, Wood is the child.
A deficiency in Kidney Yin can affect Liver Yin, leading to deficiencies in both Liver and Kidney Yin.
3. Application of the Five Elements Theory in Traditional Chinese Medicine
(1) Explaining the physiological functions and characteristics of the human body
1. It is a Five Organs system centered around the Five Organs.
2. It explains the physiological functions and interrelations of the Five Organs.
It categorizes the Five Organs of the human body according to the Five Elements, explaining the intrinsic connections of the physiological functions of the body’s organs (in the meridian theory, the corresponding organs are linked with the external limbs and the nine orifices).
(2) Explaining pathological changes in the human body
1. It elucidates the patterns of disease in the organs.
The basic rule is that the organ that governs the time is the first to be affected by pathogens.
2. It explains the transmission patterns of diseases in the organs.
Note:Not all organ diseases follow the Five Elements transmission patterns.
(3) Guiding the diagnosis of diseases
It mainly uses the classification method of the Five Elements to connect the affected organs, body, and orifices with the symptoms expressed in pulse, color, taste, shape, tongue, etc., to diagnose diseases.
👉 For example, a blue complexion, preference for sour foods, and a stringy pulse indicate a disease in the Liver.
For example, a red complexion, bitter taste, and a surging pulse indicate excessive Heart Fire.
(4) Guiding the prevention and treatment of diseases
Preventing the transmission of diseases – determining treatment principles and methods – guiding acupuncture point selection.
<Nanjing> records: If you see a disease of the Liver, you should know that the Liver will transmit to the Spleen, so first strengthen the Spleen Qi to prevent it from receiving the Liver’s pathogen.
👉 This means knowing that the Liver’s disease will transmit to the Spleen, so first regulate the Spleen to prevent it from being affected by the Liver.
(5) Determining treatment methods and principles
1. According to the mutual generation principle: If deficient, nourish the mother; if excessive, drain the child.
Nourishing Water to support Wood (Liver and Kidney Yin deficiency)
👉 For example – Kidney Water generates Liver Wood; the Kidney is the mother, and the Liver is the child. If there is a deficiency in Liver Wood, do not directly nourish the Liver, but nourish the Kidney that generates the Liver.
Metal and Water mutual generation method (Lung and Kidney Yin deficiency)
Nourishing Earth to generate Metal method (Spleen and Lung Qi deficiency)
Nourishing Fire to support Earth method (Heart and Kidney Yang deficiency)
2. According to the mutual restriction principle: Suppress the strong, support the weak.
Suppressing Wood and supporting Earth method (Soothe the Liver and strengthen the Spleen)
👉 For example – Wood refers to the Liver, Earth refers to the Spleen. In the Five Elements, they mutually restrict each other; thus, Wood restricts Earth. If the Liver fails to regulate, and Liver Yang is excessive, the strong must be suppressed, while the weak must be supported. This is a condition of soothing the Liver and strengthening the Spleen in Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Nourishing Earth to treat Water (Strengthening the Spleen and warming the Kidneys)
Assisting Metal to pacify Wood (Nourishing the Lungs and clearing the Liver)
Draining the South and nourishing the North (Heart and Kidney not communicating)
3. Guiding acupuncture point selection
“Five Transport Points” correspond to the Five Elements
The Jing, Ying, Shu, and Jing points correspond to Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.
For example, taking the Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian as an example, the Jing, Ying, Shu, and Jing points are — Shaoshang, Yujie, Jingqu, Chize, corresponding to the Five Elements of — Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, Water.


