
行
五
传统
学说


The Basic Concept of the Five Elements
 The Five Elements, namely Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water, represent five categories of material properties and their dynamic changes. The term “Five” refers to the five categories of material properties that constitute all things in the universe, separated from the primordial qi of the cosmos; “Elements” refers to their movement and transformation. As stated in the “Shang Shu Zheng Yi”: “The five represent various materials and capabilities. The term ‘Elements’ indicates that in the heavens, they manifest as the flow of five qi; on earth, they are the applications of the world. From ancient philosophical concepts, the Five Elements have transcended the specific materials of Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water, evolving into a framework for categorizing all things in the universe and explaining their interrelationships.The Theory of Five Elements serves as a worldview and methodology for understanding the world, explaining phenomena, and exploring the laws of cosmic change based on the properties and movement patterns of Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.. During the Qin and Han dynasties, the Theory of Five Elements entered a phase of widespread application and development, utilized in various fields such as astronomy, geography, calendar systems, social economics, and military strategy, with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) being particularly prominent. Ancient practitioners employed the Theory of Five Elements, using metaphorical comparisons and deductions to categorize various natural and social phenomena into five categories, explaining their occurrence, development, and transformation through the relationships of generation and restriction among the Five Elements.
The Five Elements, namely Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water, represent five categories of material properties and their dynamic changes. The term “Five” refers to the five categories of material properties that constitute all things in the universe, separated from the primordial qi of the cosmos; “Elements” refers to their movement and transformation. As stated in the “Shang Shu Zheng Yi”: “The five represent various materials and capabilities. The term ‘Elements’ indicates that in the heavens, they manifest as the flow of five qi; on earth, they are the applications of the world. From ancient philosophical concepts, the Five Elements have transcended the specific materials of Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water, evolving into a framework for categorizing all things in the universe and explaining their interrelationships.The Theory of Five Elements serves as a worldview and methodology for understanding the world, explaining phenomena, and exploring the laws of cosmic change based on the properties and movement patterns of Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.. During the Qin and Han dynasties, the Theory of Five Elements entered a phase of widespread application and development, utilized in various fields such as astronomy, geography, calendar systems, social economics, and military strategy, with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) being particularly prominent. Ancient practitioners employed the Theory of Five Elements, using metaphorical comparisons and deductions to categorize various natural and social phenomena into five categories, explaining their occurrence, development, and transformation through the relationships of generation and restriction among the Five Elements.

Characteristics of the Five Elements

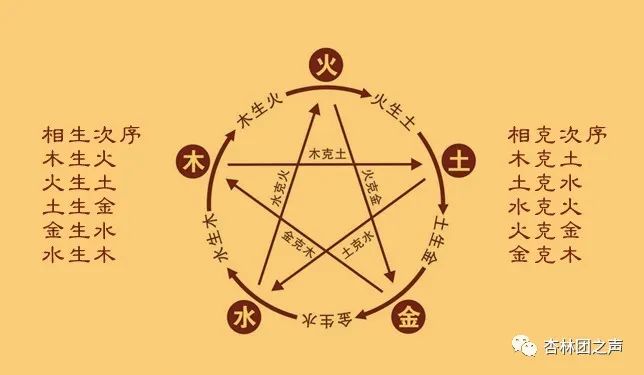 The characteristics of the Five Elements are based on the ancient people’s direct observations and basic understanding of the five fundamental materials—Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water—formed through long-term life and production practices. This rational concept was gradually abstracted to serve as the basis for categorizing various phenomena or objects according to their Five Element properties. The “Shang Shu: Hong Fan” classic states: “Water moistens downward, Fire rises upward, Wood bends and straightens, Metal transforms, Earth nurtures crops.”1. The characteristic of Wood is “bending and straightening”: This refers to the growth form of trees, which can bend or stand straight, expanding gently, symbolizing growth, elevation, and smoothness. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Wood.2. The characteristic of Fire is “rising upward”: This indicates that fire has the properties of warmth and ascension, symbolizing warmth and rising. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Fire.3. The characteristic of Earth is “nurturing crops”: The term “nurturing” refers to planting grains; “crops” refers to harvesting grains. “Nurturing crops” generally refers to human agricultural activities of sowing and harvesting, symbolizing nurturing, bearing, and receiving. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Earth, hence the saying “Earth is the mother of all things.”4. The characteristic of Metal is “transformation”: The term “transformation” refers to change. “Metal’s transformation” originally refers to the generation of metals from change, later symbolizing severity and restraint. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Metal.5. The characteristic of Water is “moistening downward”: This indicates that water has the properties of moistening and descending, symbolizing coolness, moisture, and downward movement. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Water.
The characteristics of the Five Elements are based on the ancient people’s direct observations and basic understanding of the five fundamental materials—Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water—formed through long-term life and production practices. This rational concept was gradually abstracted to serve as the basis for categorizing various phenomena or objects according to their Five Element properties. The “Shang Shu: Hong Fan” classic states: “Water moistens downward, Fire rises upward, Wood bends and straightens, Metal transforms, Earth nurtures crops.”1. The characteristic of Wood is “bending and straightening”: This refers to the growth form of trees, which can bend or stand straight, expanding gently, symbolizing growth, elevation, and smoothness. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Wood.2. The characteristic of Fire is “rising upward”: This indicates that fire has the properties of warmth and ascension, symbolizing warmth and rising. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Fire.3. The characteristic of Earth is “nurturing crops”: The term “nurturing” refers to planting grains; “crops” refers to harvesting grains. “Nurturing crops” generally refers to human agricultural activities of sowing and harvesting, symbolizing nurturing, bearing, and receiving. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Earth, hence the saying “Earth is the mother of all things.”4. The characteristic of Metal is “transformation”: The term “transformation” refers to change. “Metal’s transformation” originally refers to the generation of metals from change, later symbolizing severity and restraint. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Metal.5. The characteristic of Water is “moistening downward”: This indicates that water has the properties of moistening and descending, symbolizing coolness, moisture, and downward movement. All things or phenomena that possess these functions or properties belong to Water.


The Basic Content of the Theory of Five Elements

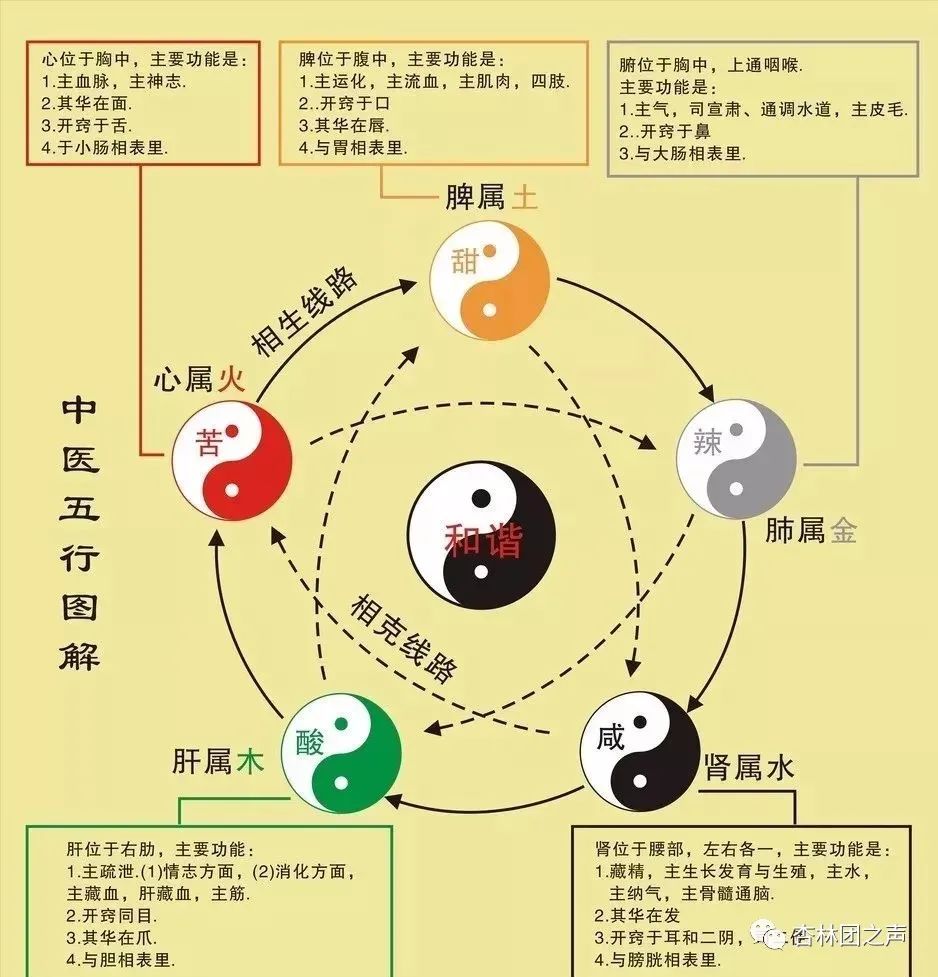 The Theory of Five Elements categorizes the properties of natural phenomena based on the characteristics of the Five Elements, comparing the nature and functions of things with the properties of Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water to derive their Five Element attributes, thus classifying various phenomena and objects in nature into five major categories: Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.The method of categorizing properties in the Theory of Five Elements primarily employs metaphorical comparisons. For example, the directions are associated with the Five Elements: since the sun rises in the east, it corresponds to the ascending nature of Wood, thus classified as Wood; the south is hot, corresponding to the rising nature of Fire, thus classified as Fire; the sun sets in the west, corresponding to the descending nature of Metal, thus classified as Metal; the north is cold, corresponding to the cool nature of Water, thus classified as Water. In terms of the internal organs, the liver, which governs ascension, belongs to Wood; the heart, which governs warmth, belongs to Fire; the spleen, which governs transformation, belongs to Earth; the lungs, which govern descent, belong to Metal; and the kidneys, which govern Water, belong to Water.Additionally, there is an indirect method of deduction, where the correlation of a certain phenomenon with the Five Elements leads to the inference that other phenomena are also related to the Five Elements. For example, since the liver belongs to Wood, the gallbladder, tendons, and eyes, which are related to the liver, also belong to Wood; the heart belongs to Fire, and the small intestine, pulse, and tongue, which are related to the heart, also belong to Fire.
The Theory of Five Elements categorizes the properties of natural phenomena based on the characteristics of the Five Elements, comparing the nature and functions of things with the properties of Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water to derive their Five Element attributes, thus classifying various phenomena and objects in nature into five major categories: Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water.The method of categorizing properties in the Theory of Five Elements primarily employs metaphorical comparisons. For example, the directions are associated with the Five Elements: since the sun rises in the east, it corresponds to the ascending nature of Wood, thus classified as Wood; the south is hot, corresponding to the rising nature of Fire, thus classified as Fire; the sun sets in the west, corresponding to the descending nature of Metal, thus classified as Metal; the north is cold, corresponding to the cool nature of Water, thus classified as Water. In terms of the internal organs, the liver, which governs ascension, belongs to Wood; the heart, which governs warmth, belongs to Fire; the spleen, which governs transformation, belongs to Earth; the lungs, which govern descent, belong to Metal; and the kidneys, which govern Water, belong to Water.Additionally, there is an indirect method of deduction, where the correlation of a certain phenomenon with the Five Elements leads to the inference that other phenomena are also related to the Five Elements. For example, since the liver belongs to Wood, the gallbladder, tendons, and eyes, which are related to the liver, also belong to Wood; the heart belongs to Fire, and the small intestine, pulse, and tongue, which are related to the heart, also belong to Fire.


Application of the Theory of Five Elements in Traditional Chinese Medicine

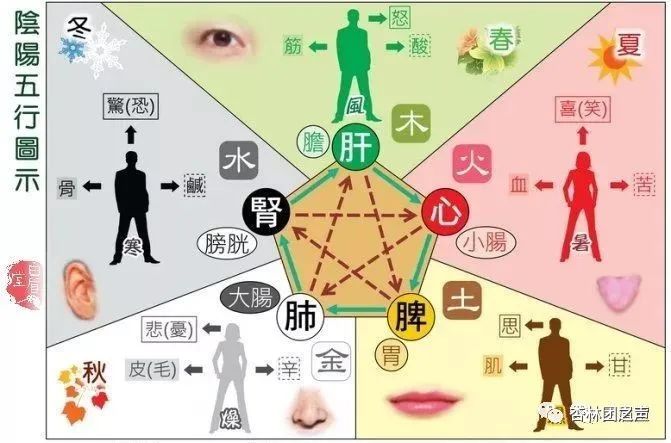 1. Explaining the organizational structure of the human body in relation to the cosmos. 2. Explaining the physiological functions and interrelationships of the five organs. 3. Explaining the pathological influences of the organs. 4. Used for disease diagnosis. 5. Used for disease treatment.
1. Explaining the organizational structure of the human body in relation to the cosmos. 2. Explaining the physiological functions and interrelationships of the five organs. 3. Explaining the pathological influences of the organs. 4. Used for disease diagnosis. 5. Used for disease treatment.


-END-
Planning/Review | Cheng Haiyan
Editor | Xie Min
Chief Editor | Cai Bozhen
Content Source | “Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine”
Audio Source | “Reading Material on Chinese Medicine Culture”
Audio | Li Duo
Editors | Lei Jing, Che Rui
Some images sourced from the internet
Gansu University of Chinese Medicine Youth Media Center
Scan to follow us
Get more exciting content

