Click the blue text above to follow us
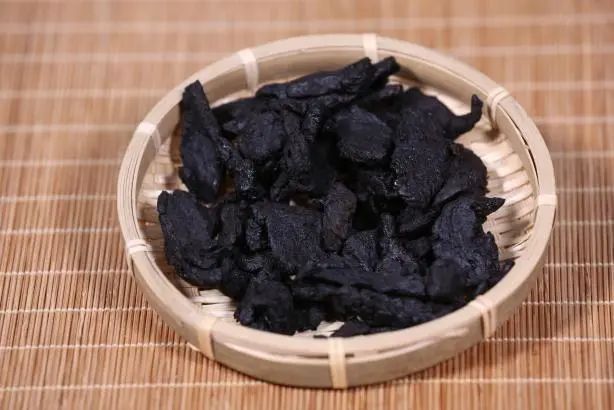
 Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root) is a common Chinese medicinal material, also known as 熟地黄 (Shu Di Huang). According to the “Compendium of Materia Medica”, Shu Di Huang has the effects of “nourishing the marrow, promoting muscle growth, generating essence and blood, replenishing the five organs for internal injuries, unblocking blood vessels, benefiting the ears and eyes, and darkening hair.” Let us learn more about this herb: 【Source】 It is the dried tuber of the Rehmannia glutinosa plant from the Scrophulariaceae family, processed through specific methods. 【Preparation Methods】 There are two methods: ① Take raw Rehmannia, stew it with yellow wine until the wine is absorbed, then take it out, dry it until the outer skin is slightly dry, and cut it into thick slices or blocks. ② Take raw Rehmannia, steam it until it becomes black and shiny. Take it out and dry it until about 80% dry, then cut it into thick slices or blocks. 【Characteristics】 It is irregularly shaped, black both inside and outside, with a wrinkled and uneven surface. It is soft, with a moist cross-section, and the center often shows shiny, oily blocks, with high stickiness. It has a sweet taste. The best quality is characterized by large blocks, a black cross-section, and a sweet taste.
Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root) is a common Chinese medicinal material, also known as 熟地黄 (Shu Di Huang). According to the “Compendium of Materia Medica”, Shu Di Huang has the effects of “nourishing the marrow, promoting muscle growth, generating essence and blood, replenishing the five organs for internal injuries, unblocking blood vessels, benefiting the ears and eyes, and darkening hair.” Let us learn more about this herb: 【Source】 It is the dried tuber of the Rehmannia glutinosa plant from the Scrophulariaceae family, processed through specific methods. 【Preparation Methods】 There are two methods: ① Take raw Rehmannia, stew it with yellow wine until the wine is absorbed, then take it out, dry it until the outer skin is slightly dry, and cut it into thick slices or blocks. ② Take raw Rehmannia, steam it until it becomes black and shiny. Take it out and dry it until about 80% dry, then cut it into thick slices or blocks. 【Characteristics】 It is irregularly shaped, black both inside and outside, with a wrinkled and uneven surface. It is soft, with a moist cross-section, and the center often shows shiny, oily blocks, with high stickiness. It has a sweet taste. The best quality is characterized by large blocks, a black cross-section, and a sweet taste.
 【Properties and Channels】 Sweet, slightly warm. It enters the Liver and Kidney meridians. 【Functions and Indications】 Nourishes blood and yin, benefits essence and fills marrow. It is used for blood deficiency with symptoms of sallow complexion, palpitations, irregular menstruation, excessive bleeding, Liver and Kidney yin deficiency, soreness of the lower back and knees, tidal fever, night sweats, seminal emission, internal heat with thirst, dizziness, tinnitus, and premature graying of hair.
【Properties and Channels】 Sweet, slightly warm. It enters the Liver and Kidney meridians. 【Functions and Indications】 Nourishes blood and yin, benefits essence and fills marrow. It is used for blood deficiency with symptoms of sallow complexion, palpitations, irregular menstruation, excessive bleeding, Liver and Kidney yin deficiency, soreness of the lower back and knees, tidal fever, night sweats, seminal emission, internal heat with thirst, dizziness, tinnitus, and premature graying of hair.
【Differentiation and Application】 Raw Rehmannia vs. Cooked Rehmannia
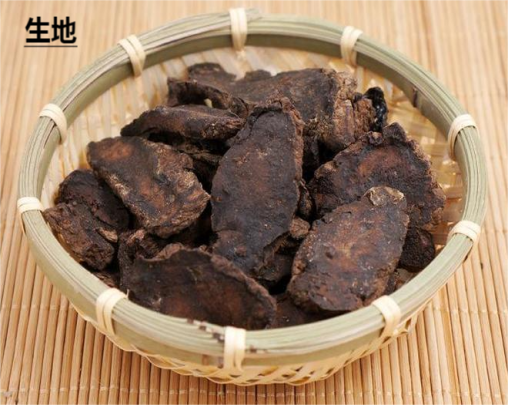
 Both raw Rehmannia and cooked Rehmannia belong to the same plant, but one is raw and the other is cooked. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” states, “Raw Rehmannia is very cold and cools the blood; it is needed for blood heat, while cooked Rehmannia is slightly warm and nourishes the kidneys; it is needed for blood deficiency.” Raw Rehmannia has a sweet, bitter, and cold nature, with the effects of clearing heat and cooling the blood, nourishing yin, and generating fluids. It is used for heat entering the blood, warm toxin causing rashes, vomiting blood, bleeding, heat illness damaging yin, red tongue with thirst, fluid damage causing constipation, yin deficiency with fever, bone steaming, and internal heat with thirst.
Both raw Rehmannia and cooked Rehmannia belong to the same plant, but one is raw and the other is cooked. The “Compendium of Materia Medica” states, “Raw Rehmannia is very cold and cools the blood; it is needed for blood heat, while cooked Rehmannia is slightly warm and nourishes the kidneys; it is needed for blood deficiency.” Raw Rehmannia has a sweet, bitter, and cold nature, with the effects of clearing heat and cooling the blood, nourishing yin, and generating fluids. It is used for heat entering the blood, warm toxin causing rashes, vomiting blood, bleeding, heat illness damaging yin, red tongue with thirst, fluid damage causing constipation, yin deficiency with fever, bone steaming, and internal heat with thirst.
 【Dosage】 9-15g 【Caution】 This product is greasy in nature and may hinder digestion, so it should be used cautiously in cases of spleen and stomach deficiency, fullness, and phlegm. Use with caution in cases of qi stagnation and excessive phlegm. 【Chemical Composition】 It mainly contains phenylethanoid glycosides, such as Rehmannia glycoside, as well as monosaccharides and various amino acids. 【Pharmacological Effects】 This product promotes hematopoiesis, lowers blood sugar, enhances memory, and boosts immunity.
【Dosage】 9-15g 【Caution】 This product is greasy in nature and may hinder digestion, so it should be used cautiously in cases of spleen and stomach deficiency, fullness, and phlegm. Use with caution in cases of qi stagnation and excessive phlegm. 【Chemical Composition】 It mainly contains phenylethanoid glycosides, such as Rehmannia glycoside, as well as monosaccharides and various amino acids. 【Pharmacological Effects】 This product promotes hematopoiesis, lowers blood sugar, enhances memory, and boosts immunity.
【Example Formulation】
|
Six-Flavor Rehmannia Pill |
|
|
Source |
“Pediatric Drug Evidence” |
|
Composition |
Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root), Shan Zhu Yu (Cornelian Cherry), Shan Yao (Chinese Yam), Ze Xie (Alisma), Mu Dan Pi (Moutan Root), Fu Ling (Poria) |
|
Functions and Indications |
Nourishes the Liver and Kidneys. It is suitable for Liver and Kidney yin deficiency syndrome, with symptoms of soreness in the lower back and knees, dizziness, tinnitus, night sweats, seminal emission, thirst, bone steaming, heat in the palms and soles, dry mouth and throat, loose teeth, heel pain, and dribbling urination, as well as for children with unclosed fontanelles, red tongue with little coating, and a deep, thin, rapid pulse. |
【Dietary Applications】
01
Shu Di Congee
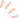

 Ingredients: Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root), japonica rice, rock sugar. Method: Wash Shu Di Huang, decoct to extract the medicinal juice; wash japonica rice, boil with water, then add the Shu Di Huang juice, and cook until thickened, adding sugar to taste. Effects: Nourishes blood and moistens, fills essence and marrow. Suitable for blood deficiency with sallow complexion, dizziness, and irregular menstruation.
Ingredients: Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root), japonica rice, rock sugar. Method: Wash Shu Di Huang, decoct to extract the medicinal juice; wash japonica rice, boil with water, then add the Shu Di Huang juice, and cook until thickened, adding sugar to taste. Effects: Nourishes blood and moistens, fills essence and marrow. Suitable for blood deficiency with sallow complexion, dizziness, and irregular menstruation.
02
Shu Di Wine
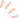 Ingredients: Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root), Gou Qi Zi (Goji Berries), white wine. Method: Wash Shu Di Huang and Gou Qi Zi, soak in white wine, seal, and steep for more than 7 days. Effects: Unblocks meridians and nourishes blood vessels.
Ingredients: Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root), Gou Qi Zi (Goji Berries), white wine. Method: Wash Shu Di Huang and Gou Qi Zi, soak in white wine, seal, and steep for more than 7 days. Effects: Unblocks meridians and nourishes blood vessels.
03
Shu Di Winter Melon Soup
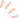

 Ingredients: 20g Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root), 500-750g winter melon, appropriate amount of pork bones. Method: Wash Shu Di Huang and soak slightly; wash winter melon and cut into pieces with skin; wash pork bones and cut into pieces; then put them all into a clay pot, add water, bring to a boil over high heat, then simmer on low heat for 2 hours. Effects: Winter melon helps to clear heat and promote urination, while pork bones nourish the marrow and benefit yin. Together, they create a soup that dispels dampness, strengthens the spleen, nourishes yin, and replenishes blood, especially effective for those fatigued from prolonged heat exposure.
Ingredients: 20g Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia Root), 500-750g winter melon, appropriate amount of pork bones. Method: Wash Shu Di Huang and soak slightly; wash winter melon and cut into pieces with skin; wash pork bones and cut into pieces; then put them all into a clay pot, add water, bring to a boil over high heat, then simmer on low heat for 2 hours. Effects: Winter melon helps to clear heat and promote urination, while pork bones nourish the marrow and benefit yin. Together, they create a soup that dispels dampness, strengthens the spleen, nourishes yin, and replenishes blood, especially effective for those fatigued from prolonged heat exposure.
References:
 【1】National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Clinical Use Guidelines of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: 2015 Edition. Chinese Herbal Medicine Volume [M] Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2017【2】Jiangsu New Medical College. Chinese Herbal Medicine Dictionary (Volume 2) [M] Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1986
【1】National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Clinical Use Guidelines of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: 2015 Edition. Chinese Herbal Medicine Volume [M] Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2017【2】Jiangsu New Medical College. Chinese Herbal Medicine Dictionary (Volume 2) [M] Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, 1986 Note: Some images in the article are sourced from the internet, and we thank the authors of these images! Author: Cai Liuping, Pharmacy Department, Dongguan Tea Mountain Hospital Reviewed by: Shi Yuping, Pharmacy Department, Dongguan Tea Mountain Hospital Edited by: Zhong Chongjie, Pharmacy Department, Dongguan Tea Mountain Hospital
Note: Some images in the article are sourced from the internet, and we thank the authors of these images! Author: Cai Liuping, Pharmacy Department, Dongguan Tea Mountain Hospital Reviewed by: Shi Yuping, Pharmacy Department, Dongguan Tea Mountain Hospital Edited by: Zhong Chongjie, Pharmacy Department, Dongguan Tea Mountain Hospital
 Scan to follow us
Scan to follow us

