Complete Collection of Old Remediesto Promote Health Knowledge
Click below to follow for free↓↓↓
Feeling heavy and sluggish? Tired and sleepy? Oily skin and prone to acne? Poor appetite, abdominal bloating, or being overweight or underweight? Nausea, feeling like vomiting while brushing teeth? Dry mouth, bitter taste, or bad breath? Infrequent, yellow, and foul-smelling urination? Skin itching, sores, and oozing? Frequent dampness and inflammation in the genital area?

What is the cause of these symptoms? They are all manifestations of damp-heat in the body.
Damp-heat is a term in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that refers to the pathological change caused by the combination of dampness and heat, which obstructs the functioning of the organs and meridians, leading to systemic symptoms.
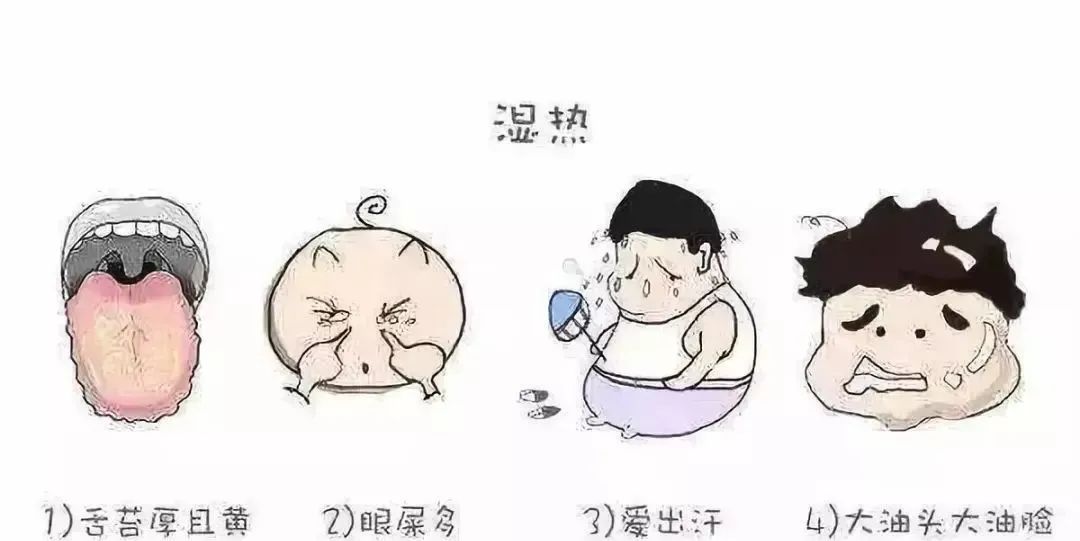

Damp-heat can accumulate in the liver and gallbladder, leading to dysfunction in their ability to disperse, resulting in fullness and discomfort in the hypochondrium, a red tongue with a yellow greasy coating, and a wiry slippery pulse. If gallbladder qi overflows, it causes a bitter mouth; if damp-heat obstructs the spleen and stomach, it leads to a sticky mouth, poor appetite, nausea, abdominal bloating, and irregular bowel movements; if damp-heat affects the liver and gallbladder, it can lead to jaundice; if damp-heat descends, it causes short, red, foul-smelling urination, scrotal eczema, and swelling and pain in the testicles, while women may experience yellow, foul-smelling vaginal discharge and vulvar itching.

There are two main causes of damp-heat: one is the invasion of damp-heat from the external environment, and the other is the internal transformation of dampness into heat due to spleen and stomach deficiency.
The external damp-heat invasion is relatively easier to treat, while internal damp-heat is more complicated to manage.
In TCM treatment, damp-heat is often categorized based on the location of accumulation, leading to targeted treatment. TCM classifies damp-heat into five major types: Spleen-Stomach Damp-Heat Syndrome, Liver-Gallbladder Damp-Heat Syndrome, Large Intestine Damp-Heat Syndrome, Bladder Damp-Heat Syndrome, and Damp-Heat Bi Syndrome.
1. Spleen-Stomach Damp-Heat
Symptoms: Abdominal fullness, nausea, poor appetite, fatigue, loose stools, body heat with a bitter mouth, little thirst, and yellow urine.
Tongue and pulse: Yellow greasy tongue coating, slippery and rapid pulse.
Common diseases: Chronic gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastric or duodenal ulcers, cholelithiasis, pharyngitis, etc.
Treatment method: Clear heat and transform dampness.
Common formulas: Huo Po Xia Ling Tang (Huo Xiang, Hou Po, Ban Xia, Fu Ling, Xing Ren, Yi Yi Ren, Bai Dou Kou, Zhu Ling, Ze Xie, Dan Dou Chi) or Qing Zhong Tang (Huang Lian, Shan Zhi Zi, Chen Pi, Fu Ling, Ban Xia, Dou Kou, Zhi Gan Cao) with modifications.
Applicable patent medicines: Si Wei Pi Wei Shu Granules, Si Xiao Wan, Mu Xiang Shun Qi Wan, etc.
2. Liver-Gallbladder Damp-Heat
Symptoms: Pain or fullness in the hypochondrium, burning sensation, abdominal bloating, bitter mouth, nausea, short red urine, irregular bowel movements, or jaundice.
Tongue and pulse: Enlarged tongue, red tongue with thick yellow greasy coating, wiry and rapid pulse.
Common diseases: Liver and gallbladder stones, jaundice, cholecystitis, fatty liver, conjunctivitis, dry eye syndrome, otitis media, yellow and thick vaginal discharge, scrotal eczema, vulvar itching, testicular swelling, etc.
Treatment method: Clear heat, drain fire, and promote urination.
Common formulas: Long Dan Xie Gan Tang (Long Dan Cao, Huang Qin, Shan Zhi Zi, Ze Xie, Mu Tong, Che Qian Zi, Dang Gui, Sheng Di, Chai Hu, Sheng Gan Cao) with modifications.
Applicable patent medicines: Long Dan Xie Gan Wan (for excess heat in the upper jiao), Yin Chen Wu Ling Wan (for excess dampness in the lower jiao), etc.
3. Large Intestine Damp-Heat
Symptoms: Abdominal pain and diarrhea, foul-smelling stools, urgency, pus and blood in stools, burning sensation in the anus, thirst, and short yellow urine.
Tongue and pulse: Red tongue with yellow greasy coating, slippery and rapid pulse.
Common diseases: Acute and chronic enteritis, acute and chronic bacterial dysentery, bacterial food poisoning, acute and chronic amoebic dysentery, chronic nonspecific ulcerative colitis, acute appendicitis, hemorrhoids, etc.
Treatment method: Clear heat, detoxify, and cool the blood to stop diarrhea.
Common formulas: Bai Tou Weng Tang (Bai Tou Weng, Huang Bai, Huang Lian, Qin Pi) with modifications.
Applicable patent medicines: Compound Huang Lian Su Tablets, Intestinal Health Tablets, Xiang Lian Wan, Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang, etc.
4. Bladder Damp-Heat
Symptoms: Frequent and urgent urination, burning pain in the urethra, yellow and scanty urine, possibly accompanied by fever, low back pain, discomfort and fullness in the lower abdomen, or blood in urine, or sand and stones in urine, with dry stools.
Tongue and pulse: Red tongue with yellow greasy coating, rapid pulse.
Common diseases: Acute and chronic cystitis, prostatitis, urinary stones, acute and chronic pyelonephritis, etc.
Treatment method: Clear heat, drain fire, and promote urination.
Common formulas: Ba Zheng San (Che Qian Zi, Qu Mai, Bian Xu, Hua Shi, Shan Zhi Zi, Gan Cao, Mu Tong, Da Huang) with modifications.
Applicable patent medicines: Qing Lin Granules, Bi Lin Qing Capsules, Ba Zheng Granules, San Jin Tablets, etc.
5. Damp-Heat Bi Syndrome
Symptoms: Localized burning, redness, swelling, and pain in joints, difficulty in movement, relief with warmth, soreness and weakness in the lower back and knees, accompanied by fever, irritability, thirst, yellow urine, and dry stools, possibly with subcutaneous nodules or erythema.
Tongue and pulse: Red tongue, yellow greasy coating, slippery or rapid pulse.
Common diseases: Upper respiratory infections, rheumatic heart disease, rheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
Treatment method: Promote urination, clear heat, and dispel wind to relieve pain.
Common formulas: Bai Hu Jia Gui Zhi Tang (Zhi Mu, Gan Cao, Shi Gao, Jing Mi, Gui Zhi) or Dang Gui Nian Tong Tang (Qiang Huo, Fang Feng, Sheng Ma, Ge Gen, Bai Zhu, Cang Zhu, Dang Gui, Ren Shen, Gan Cao, Ku Shen, Huang Qin, Zhi Mu, Yin Chen, Zhu Ling, Ze Xie) with modifications.
Applicable patent medicines: Damp-Heat Bi Powder, Si Miao Wan, Feng Tong An Capsules, Dang Gui Nian Tong Wan, etc.
In treating damp-heat, TCM not only addresses the symptoms but also strengthens the root cause. Therefore, conditions caused by damp-heat generally have a low recurrence rate after TCM treatment, provided that patients pay attention to their lifestyle. However, TCM treatment must be conducted under the guidance of a qualified practitioner; patients should not self-medicate blindly.
In addition to symptomatic treatment with herbs, daily maintenance is also crucial. Patients should develop good lifestyle habits, avoid overeating, refrain from greasy and rich foods, maintain a balanced diet, avoid prolonged exposure to damp and cool environments, avoid staying up late, and learn to manage their emotions.
Health Experience Sharing to Promote Health Knowledge
Click below to follow for free↓↓↓
Editor’s Circle Shares Good Articles
1. A Simple Herb Infusion Can Nourish Lung Qi, Spleen Qi, and Kidney Qi, Boosting Immunity
2. Waking Up Naturally Between 3-5 AM? It’s Due to Lung Qi Deficiency; Consider These Three Herbs to Nourish Lung Qi and Improve Insomnia
3. So Precious! Over 800 Old Remedies, There’s No Illness That Can’t Be Treated, Save for Future Use!
4. The Most Comprehensive Collection of Tuina Techniques Videos—If You Want to Learn Tuina Massage, Hurry and Save!
Like is a form of encouragement Share to spread joy

