 Observation Diagnosis1. Observing SpiritThe severity of illness relies on observing the spirit; calmness indicates a yin condition,blood deficiency and fluid loss lead to confusion, dullness, and emotional distress.Restlessness and exhaustion indicate a depletion of spirit; heat in the heart leads to unclear spirit,fatigue is seen after deficiency, and no need for alarm if the chest feels clear.2. Observing ColorThe rise and fall of qi and blood is observed through color; yellow indicates dampness, red indicates heat,greenish color belongs to wind and the liver, while kidney issues often present as black.White indicates cold pathogens affecting the lungs; bright colors and dark colors should be distinguished,the latter being internal and the former external; understanding chronic and acute conditions is essential.
Observation Diagnosis1. Observing SpiritThe severity of illness relies on observing the spirit; calmness indicates a yin condition,blood deficiency and fluid loss lead to confusion, dullness, and emotional distress.Restlessness and exhaustion indicate a depletion of spirit; heat in the heart leads to unclear spirit,fatigue is seen after deficiency, and no need for alarm if the chest feels clear.2. Observing ColorThe rise and fall of qi and blood is observed through color; yellow indicates dampness, red indicates heat,greenish color belongs to wind and the liver, while kidney issues often present as black.White indicates cold pathogens affecting the lungs; bright colors and dark colors should be distinguished,the latter being internal and the former external; understanding chronic and acute conditions is essential. 3. Observing ShapeObserving shape is also important; distinguish between obesity and emaciation,the obese tend to have excess dampness leading to phlegm, while strokes and convulsions are exhausting.The thin have less fluid and blood deficiency, with excess fire leading to fatigue and cough,nails, muscles, skin, and bones are crucial for clinical differentiation.4. Other ShapesCurved and arched shapes indicate convulsive diseases; crooked mouth and eyes suggest wind,hair loss and pale color indicate lung atrophy, while skin and nails reflect blood deficiency.Stiff neck indicates wind-heat symptoms, hand and foot spasms suggest acute fright,lower limb weakness indicates foot atrophy, and tremors vary in presentation.5. Observing Head and FaceSwelling of the head and face indicates major diseases; kidney inflammation leads to swelling and sores,bulging fontanel indicates fire attacking the brain, while congenital deficiencies manifest otherwise.Fontanel closure indicates kidney qi deficiency; shaking the head helps distinguish between chronic and acute,chronic illness leads to weakness indicating deficiency, while sudden onset of wind pathogens indicates a strong constitution.6. Observing HairBlack hair is normal, while white indicates blood deficiency; heat in qi and blood leads to yellow hair,hair loss indicates essence deficiency and dry blood, while dry hair indicates severe deficiency.Fine hair in children suggests malnutrition; hair quality reflects overall health,if blood and qi are not deficient, prognosis is good; sweating and wheezing indicate lung exhaustion.7. Observing EyesBright eyes indicate good spirit, while dull eyes suggest weakness; yellow sclera indicates jaundice,red and swollen eyes suggest liver heat.Eyes open during sleep indicate spleen deficiency; sudden stroke leads to unresponsive eyes,dilated pupils are a critical sign, and fixed eyes indicate difficulty in treatment.
3. Observing ShapeObserving shape is also important; distinguish between obesity and emaciation,the obese tend to have excess dampness leading to phlegm, while strokes and convulsions are exhausting.The thin have less fluid and blood deficiency, with excess fire leading to fatigue and cough,nails, muscles, skin, and bones are crucial for clinical differentiation.4. Other ShapesCurved and arched shapes indicate convulsive diseases; crooked mouth and eyes suggest wind,hair loss and pale color indicate lung atrophy, while skin and nails reflect blood deficiency.Stiff neck indicates wind-heat symptoms, hand and foot spasms suggest acute fright,lower limb weakness indicates foot atrophy, and tremors vary in presentation.5. Observing Head and FaceSwelling of the head and face indicates major diseases; kidney inflammation leads to swelling and sores,bulging fontanel indicates fire attacking the brain, while congenital deficiencies manifest otherwise.Fontanel closure indicates kidney qi deficiency; shaking the head helps distinguish between chronic and acute,chronic illness leads to weakness indicating deficiency, while sudden onset of wind pathogens indicates a strong constitution.6. Observing HairBlack hair is normal, while white indicates blood deficiency; heat in qi and blood leads to yellow hair,hair loss indicates essence deficiency and dry blood, while dry hair indicates severe deficiency.Fine hair in children suggests malnutrition; hair quality reflects overall health,if blood and qi are not deficient, prognosis is good; sweating and wheezing indicate lung exhaustion.7. Observing EyesBright eyes indicate good spirit, while dull eyes suggest weakness; yellow sclera indicates jaundice,red and swollen eyes suggest liver heat.Eyes open during sleep indicate spleen deficiency; sudden stroke leads to unresponsive eyes,dilated pupils are a critical sign, and fixed eyes indicate difficulty in treatment.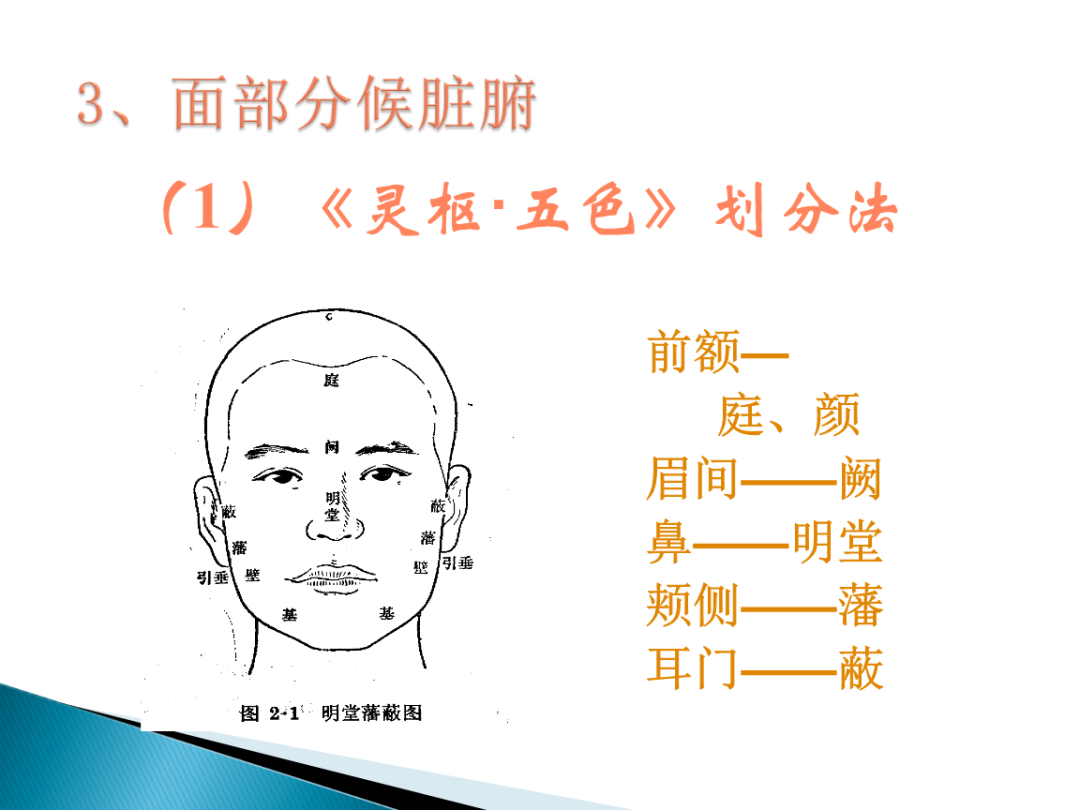 8. Observing Nose ColorA nose resembling coal indicates deep heat toxicity; red indicates wind-heat in the spleen and lung channels,white indicates qi deficiency or blood loss, while black indicates water retention.Nasal flaring indicates lung heat; nosebleeds often result from heat injuring yin,clear nasal discharge indicates wind-cold, while turbid discharge indicates wind-heat nasal congestion.9. Observing LipsLocked lips indicate spasms or stroke; open mouth indicates different diseases,oral ulcers indicate heart heat, while canker sores indicate heat attacking the heart and spleen.Asymmetrical mouth indicates stroke; oral thrush indicates excessive heat,dry lips suggest spleen deficiency, while cracked lips often indicate dryness.
8. Observing Nose ColorA nose resembling coal indicates deep heat toxicity; red indicates wind-heat in the spleen and lung channels,white indicates qi deficiency or blood loss, while black indicates water retention.Nasal flaring indicates lung heat; nosebleeds often result from heat injuring yin,clear nasal discharge indicates wind-cold, while turbid discharge indicates wind-heat nasal congestion.9. Observing LipsLocked lips indicate spasms or stroke; open mouth indicates different diseases,oral ulcers indicate heart heat, while canker sores indicate heat attacking the heart and spleen.Asymmetrical mouth indicates stroke; oral thrush indicates excessive heat,dry lips suggest spleen deficiency, while cracked lips often indicate dryness.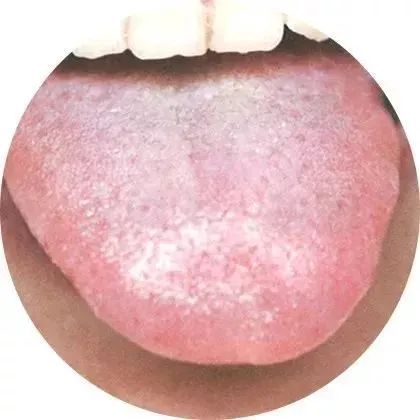 10. Observing Tongue ShapeA tongue with prickles indicates deep heat accumulation; swelling often indicates water retention,heavy tongue indicates heart and spleen heat accumulation, while a wood tongue indicates heart fire.Protruding tongue indicates qi deficiency; a curled tongue indicates yin collapse,stiff tongue indicates wind and loss of nourishment, while a slippery tongue indicates damp phlegm and dryness.11. Observing Tongue CoatingThick coating indicates phlegm-dampness, while thin coating indicates exterior conditions; greasy coating indicates external pathogens,slippery coating indicates normal cold dampness, while dry tongue indicates yin injury and fluid deficiency.White coating indicates lung abscess, yellow coating indicates stomach heat,cracked tongue indicates yin deficiency, and mottled tongue indicates severe conditions.
10. Observing Tongue ShapeA tongue with prickles indicates deep heat accumulation; swelling often indicates water retention,heavy tongue indicates heart and spleen heat accumulation, while a wood tongue indicates heart fire.Protruding tongue indicates qi deficiency; a curled tongue indicates yin collapse,stiff tongue indicates wind and loss of nourishment, while a slippery tongue indicates damp phlegm and dryness.11. Observing Tongue CoatingThick coating indicates phlegm-dampness, while thin coating indicates exterior conditions; greasy coating indicates external pathogens,slippery coating indicates normal cold dampness, while dry tongue indicates yin injury and fluid deficiency.White coating indicates lung abscess, yellow coating indicates stomach heat,cracked tongue indicates yin deficiency, and mottled tongue indicates severe conditions.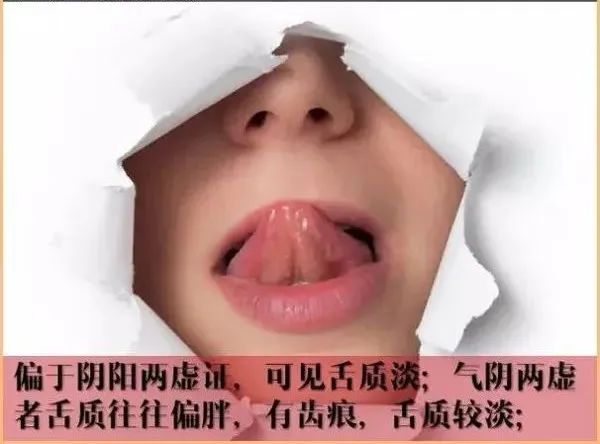 12. Observing Red TongueA bright red tongue indicates heat disease; yin deficiency and excess fire may also be present,red sides indicate liver heat, while a red tip indicates heart fire.A mirror tongue indicates internal fluid depletion; stomach yin deficiency leads to a dry red tongue,bleeding from the tongue indicates heart heat, while red spots indicate heat toxins in the blood.13. Observing Crimson TongueA crimson tongue indicates heat affecting the nutrient level; both qi and blood are scorched,heart pericardium affected leads to a moist crimson tongue, while a dry crimson tongue indicates stomach fire.A crimson tip indicates heart fire; a crimson tongue with greasy coating indicates dampness,dry and withered tongue indicates kidney yin depletion, while crimson with red spots indicates toxic heat attacking the heart.
12. Observing Red TongueA bright red tongue indicates heat disease; yin deficiency and excess fire may also be present,red sides indicate liver heat, while a red tip indicates heart fire.A mirror tongue indicates internal fluid depletion; stomach yin deficiency leads to a dry red tongue,bleeding from the tongue indicates heart heat, while red spots indicate heat toxins in the blood.13. Observing Crimson TongueA crimson tongue indicates heat affecting the nutrient level; both qi and blood are scorched,heart pericardium affected leads to a moist crimson tongue, while a dry crimson tongue indicates stomach fire.A crimson tip indicates heart fire; a crimson tongue with greasy coating indicates dampness,dry and withered tongue indicates kidney yin depletion, while crimson with red spots indicates toxic heat attacking the heart.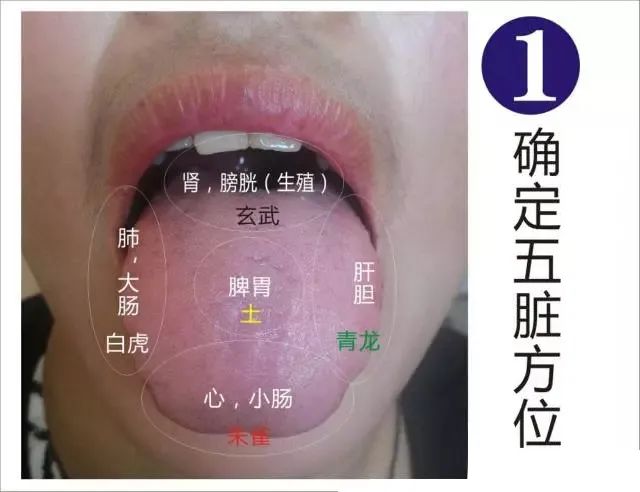 14. Observing Purple TongueA purple tongue indicates swelling and heart disturbance; dark purple indicates blood stasis,blue-purple indicates yin conditions, while disease directly affecting the liver and kidney channels.A purple tongue with a white slippery coating indicates alcohol-induced damage; a purple tongue with dry yellow coating indicates internal heat,while a purple tongue with dry yellow coating indicates excess heat in the organs.15. Observing White CoatingPathogens attacking the spleen lead to white coating; external wind-cold presents with white slippery coating,internal phlegm-dampness presents with sticky coating, while red edges indicate wind-heat affecting the lungs.Yellowish white indicates internal heat; thick white indicates severe heat,accumulated powder indicates epidemic toxins, while a white, slippery, and tender tongue indicates deficiency-cold.
14. Observing Purple TongueA purple tongue indicates swelling and heart disturbance; dark purple indicates blood stasis,blue-purple indicates yin conditions, while disease directly affecting the liver and kidney channels.A purple tongue with a white slippery coating indicates alcohol-induced damage; a purple tongue with dry yellow coating indicates internal heat,while a purple tongue with dry yellow coating indicates excess heat in the organs.15. Observing White CoatingPathogens attacking the spleen lead to white coating; external wind-cold presents with white slippery coating,internal phlegm-dampness presents with sticky coating, while red edges indicate wind-heat affecting the lungs.Yellowish white indicates internal heat; thick white indicates severe heat,accumulated powder indicates epidemic toxins, while a white, slippery, and tender tongue indicates deficiency-cold.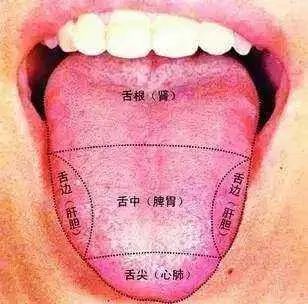 16. Observing Yellow CoatingYellow coating often follows white coating; yellow indicates internal heat,damp-heat leads to yellow, while thick yellow indicates excess heat.Dry yellow indicates internal fire; dryness leads to cracks,deep heat leads to depletion of yin, and improper treatment leads to difficult recovery.17. Observing Gray CoatingGray indicates internal yin conditions; gray and dry indicate heat and fluid depletion,dark spots indicate retained food and heat.Black coating indicates blood stasis; closed eyes and delirium indicate severe conditions,gray and black coating indicates spleen suffering from water damage.
16. Observing Yellow CoatingYellow coating often follows white coating; yellow indicates internal heat,damp-heat leads to yellow, while thick yellow indicates excess heat.Dry yellow indicates internal fire; dryness leads to cracks,deep heat leads to depletion of yin, and improper treatment leads to difficult recovery.17. Observing Gray CoatingGray indicates internal yin conditions; gray and dry indicate heat and fluid depletion,dark spots indicate retained food and heat.Black coating indicates blood stasis; closed eyes and delirium indicate severe conditions,gray and black coating indicates spleen suffering from water damage. 18. Observing Black CoatingWhite coating turning black indicates internal heat; black indicates severe conditions,black and dry indicates fluid depletion, while black and slippery indicates cold conditions.Excess heat in the lower jiao leads to dry roots, while no coating indicates dry heart fire.19. Observing PhlegmThick phlegm indicates heat, while thin phlegm indicates cold; purulent phlegm indicates lung abscess,blood-streaked phlegm indicates lung vessel injury, while chronic illness leads to internal heat.20. Observing BloodRed indicates excess heat, while pale indicates deficiency; dark red indicates heat,clots indicate liver blood stasis, while purple indicates excess qi and black indicates stasis.21. Observing StoolLoose stools indicate cold in the intestines, while heat leads to dry stools;blood in stools indicates spleen deficiency or hemorrhoids, while shape resembling sheep droppings indicates poor prognosis.Dysentery often presents with blood and pus; undigested food indicates deficiency in middle yang,black stools often indicate bleeding, while deep yellow indicates internal heat.
18. Observing Black CoatingWhite coating turning black indicates internal heat; black indicates severe conditions,black and dry indicates fluid depletion, while black and slippery indicates cold conditions.Excess heat in the lower jiao leads to dry roots, while no coating indicates dry heart fire.19. Observing PhlegmThick phlegm indicates heat, while thin phlegm indicates cold; purulent phlegm indicates lung abscess,blood-streaked phlegm indicates lung vessel injury, while chronic illness leads to internal heat.20. Observing BloodRed indicates excess heat, while pale indicates deficiency; dark red indicates heat,clots indicate liver blood stasis, while purple indicates excess qi and black indicates stasis.21. Observing StoolLoose stools indicate cold in the intestines, while heat leads to dry stools;blood in stools indicates spleen deficiency or hemorrhoids, while shape resembling sheep droppings indicates poor prognosis.Dysentery often presents with blood and pus; undigested food indicates deficiency in middle yang,black stools often indicate bleeding, while deep yellow indicates internal heat. 22. Observing UrineDamp-heat leads to turbid urine; blood in urine indicates bladder or kidney issues,deep yellow indicates liver and gallbladder heat, while clear urine indicates cold deficiency.Increased volume indicates diabetes; damp-heat in the lower jiao leads to frequent urination,decreased urine indicates edema or heat, while obstruction leads to stagnation.23. Observing Hands and FeetSpasms in hands and feet indicate wind; joint pain indicates bi syndrome,hemiplegia often results from stroke, while damp-heat leads to redness and pain.Tremors indicate qi and blood deficiency; flaccid hands indicate yang collapse,clubbing fingers indicate lung-heart disease, while foot inversion or eversion indicates different conditions.
22. Observing UrineDamp-heat leads to turbid urine; blood in urine indicates bladder or kidney issues,deep yellow indicates liver and gallbladder heat, while clear urine indicates cold deficiency.Increased volume indicates diabetes; damp-heat in the lower jiao leads to frequent urination,decreased urine indicates edema or heat, while obstruction leads to stagnation.23. Observing Hands and FeetSpasms in hands and feet indicate wind; joint pain indicates bi syndrome,hemiplegia often results from stroke, while damp-heat leads to redness and pain.Tremors indicate qi and blood deficiency; flaccid hands indicate yang collapse,clubbing fingers indicate lung-heart disease, while foot inversion or eversion indicates different conditions. 24. Observing SkinNail abnormalities indicate lung atrophy and blood deficiency; hair loss indicates severe conditions,yellow indicates damp-heat, while black indicates cold retention.Red indicates heat disease or damp-heat; jaundice indicates severe conditions,measles and chickenpox each have distinct symptoms to remember.25. Observing Chest and AbdomenSoft cartilage indicates chicken breast disease; barrel chest indicates emphysema,abdominal swelling indicates yang heat, while pale skin indicates deficiency.Abdominal distension feels like a drum; water retention sounds dull,depressed navel indicates chronic illness, while protruding indicates edema.
24. Observing SkinNail abnormalities indicate lung atrophy and blood deficiency; hair loss indicates severe conditions,yellow indicates damp-heat, while black indicates cold retention.Red indicates heat disease or damp-heat; jaundice indicates severe conditions,measles and chickenpox each have distinct symptoms to remember.25. Observing Chest and AbdomenSoft cartilage indicates chicken breast disease; barrel chest indicates emphysema,abdominal swelling indicates yang heat, while pale skin indicates deficiency.Abdominal distension feels like a drum; water retention sounds dull,depressed navel indicates chronic illness, while protruding indicates edema.
Source from the internet, for reference~~

