
Dan Shen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) is a dicotyledonous plant belonging to the Lamiaceae family and is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) herb, first recorded in the Han Dynasty’s Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing, classified as a superior herb. Dan Shen has a long history of application and extensive efficacy. The Ming Dynasty physician Li Shizhen explained its name in the Ben Cao Gang Mu, stating: “Five types of ginseng correspond to five colors and five organs.” Thus, Ren Shen (Ginseng) corresponds to the spleen as Huang Shen (Yellow Ginseng), Sha Shen (Glehnia) corresponds to the lungs as Bai Shen (White Ginseng), Xuan Shen (Scrophularia) corresponds to the kidneys as Hei Shen (Black Ginseng), Mu Meng (Mori) corresponds to the liver as Zi Shen (Purple Ginseng), and Dan Shen corresponds to the heart as Chi Shen (Red Ginseng).
Introduction
Alias: Zi Dan Shen (Purple Dan Shen), Chi Shen (Red Ginseng), Shan Shen (Mountain Ginseng).
Source: The dried root of the perennial herb Dan Shen (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge) from the Lamiaceae family. It can be found in the wild or cultivated.
Characteristics: The wild roots are rough, with traces of stems at the top and several cylindrical lateral roots below. They are 10-20 cm long and 3-10 mm in diameter, with a reddish-brown or brick-red underside.
Habitat and Distribution: Mainly produced in Hebei, Anhui, Jiangsu, Sichuan, and distributed and produced throughout the country.Chemical Composition: Contains Dan Shenone A (C18H12O2), Dan Shenone B (C19H18O2), Dan Shenone C (C19H20O2), and Dihydrodanshenone (C19H20O3), as well as Vitamin E.Taste and Properties: Bitter, slightly cold. Enters the liver and heart meridians.Functions and Indications: Invigorates blood circulation, cools blood and reduces swelling, alleviates irritability and calms the heart. Indications include dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, abdominal masses, pain from blood stasis, carbuncles, and heat-related restlessness.
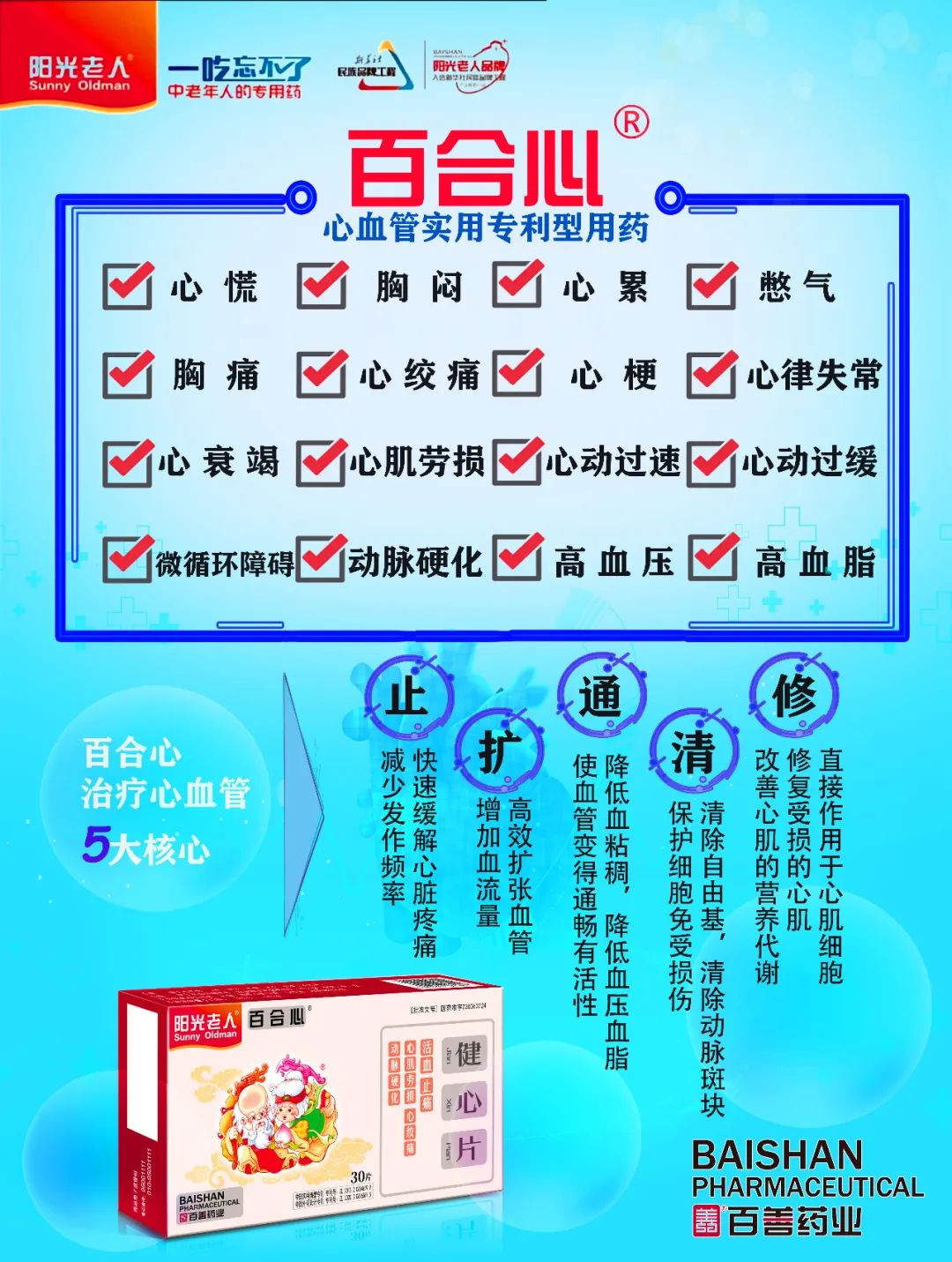
Main Effects – Cardiovascular System
Strengthens the heart, enhances myocardial contractility, and improves cardiac function without increasing myocardial oxygen consumption.
Effects on Blood Vessels: Dilates coronary arteries, increases myocardial blood flow; dilates peripheral blood vessels, increases blood flow; decreases cerebral blood flow.
Antithrombotic Effects: Increases fibrinolytic activity; prolongs bleeding and coagulation times; inhibits platelet aggregation (increases cAMP levels in platelets, inhibiting TXA2 synthesis); improves blood rheological properties (reduces blood viscosity, shortens erythrocyte electrophoresis time).
Improves microcirculation.
Repairs and Enhances Myocardial FunctionBasic Medication – Bai He Xin (Lily Heart)
The effect of enhancing coronary blood flow is more prolonged (Mao Dong Qing, Xi Xian Cao, San Qi).
Highly effective in dilating blood vessels and increasing blood flow. The effect of nitroglycerin lasts only 6-8 minutes, while a single dose of Mao Dong Qing can maintain effects for 2-3 hours or more, which is over 25 times that of nitroglycerin products.
More thorough repair effects on damaged myocardial tissue (Mao Dong Qing, Xi Xian Cao, Hong Hua).
Directly acts on myocardial cells, nourishing damaged myocardium and repairing near-death myocardial cells! Improves nutritional energy metabolism in ischemic myocardium, restoring cardiac dynamics!
More significant effects on improving arteriosclerosis (Mao Dong Qing, Xi Xian Cao).
Reduces blood viscosity, lowers blood pressure and lipids, making blood vessels smooth and elastic, thus increasing cardiac energy supply while “scrubbing” free radicals, clearing arterial plaques, and protecting cells from free radical damage, preventing arterial injury.
Patient Medication Examples