Rehmannia glutinosa is a traditional Chinese medicinal herb known for its nourishing properties. It can replenish qi and blood, alleviate deficiencies in the body, and enrich essence while filling the marrow, significantly benefiting overall health and enhancing physical quality. However, how should Rehmannia glutinosa be consumed to maximize its health benefits? Below is a detailed introduction to its efficacy and usage methods.
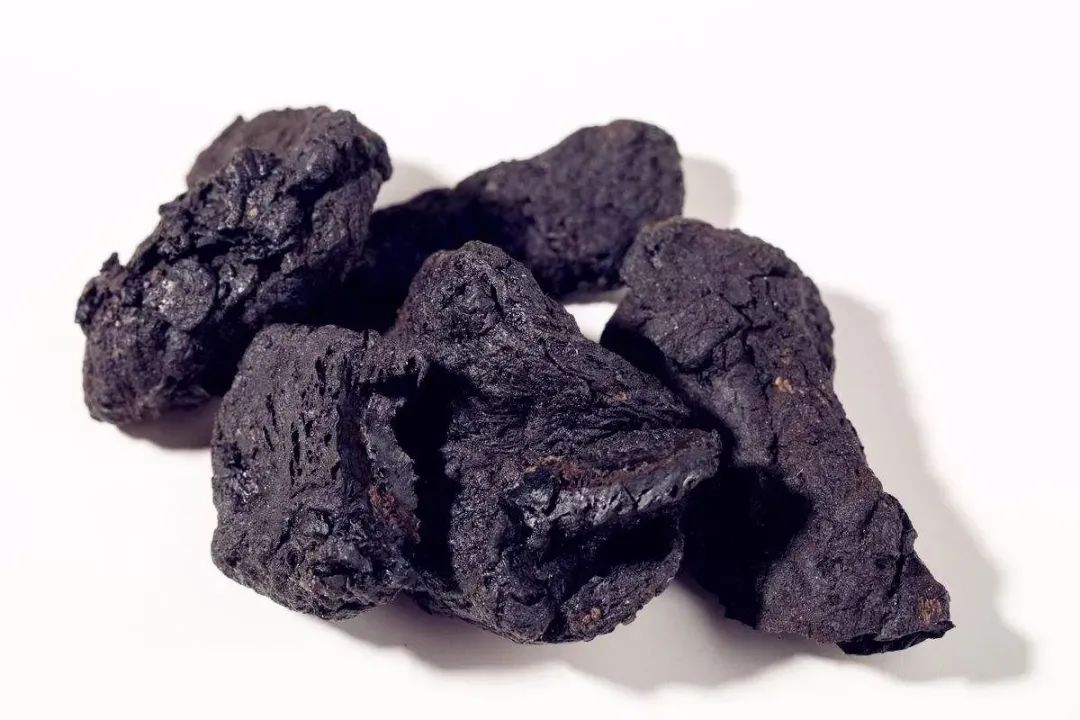

Efficacy and Functions of Rehmannia Glutinosa
1. Nourishing the Body
Rehmannia glutinosa is a highly nutritious medicinal herb, rich in alkaloids, glucose, and sucrose, and contains a significant amount of arginine and vitamins. Consuming it allows for rapid absorption and utilization of its nutrients, nourishing and alleviating physical weakness, and enhancing human physical quality. It has a beneficial effect on deficiencies in constitution and insufficient essence and blood.
2. Cardiovascular Protection
Rehmannia glutinosa has a notable protective effect on human cardiovascular health. It enhances the antioxidant capacity of the cardiovascular system, purifies the blood, and reduces blood viscosity. Regular consumption can prevent thrombosis and stroke, and improve heart function, preventing various adverse symptoms such as myocardial infarction and ischemia.

Methods of Consuming Rehmannia Glutinosa
1. Infused in Alcohol
Rehmannia glutinosa can be infused in alcohol. When preparing the infusion, it is best to pair it with appropriate amounts of Angelica sinensis (Dang Gui), Astragalus membranaceus (Huang Qi), and Lycium barbarum (Gou Qi). After washing and drying them, place them in a large clean glass jar, pour in high-purity grain alcohol, and add an appropriate amount of rock candy. Shake well and seal for infusion. After one day, the medicinal wine will be ready for direct consumption, with a dosage not exceeding 50 grams each time.
2. Stewed with Chicken
Rehmannia glutinosa can also be used to stew chicken, especially when using old hens for soup. Adding an appropriate amount of Rehmannia glutinosa enhances the nutritional value of the soup and makes the stewed chicken more flavorful. When stewing chicken with Rehmannia glutinosa, it can also be combined with appropriate amounts of Codonopsis pilosula (Dang Shen), Atractylodes macrocephala (Bai Zhu), and Glycyrrhiza uralensis (Gan Cao), as well as Angelica sinensis (Dang Gui), to further enhance the nourishing effects. Rehmannia glutinosa can be used to stew chicken wings, dog meat, or beef, among other meats.
Rehmannia glutinosa (《本草图经》)
It is the root of the plant Rehmannia, processed and prepared. Sweet and slightly warm. It has the functions of nourishing blood, enriching yin, and replenishing essence and marrow. The polysaccharides contained in this herb have significant immunosuppressive and anti-tumor activities, promoting T lymphocyte activation, directly killing tumor cells, and enhancing the production of various lymphokines by T lymphocytes to exert anti-tumor effects. This herb also has notable effects such as cardiotonic, diuretic, hepatoprotective, blood sugar-lowering, anti-proliferative, anti-exudative, anti-inflammatory, antifungal, and radioprotective properties.
Dosage and Administration: For internal use: decoction, 10-30g. It is advisable to use it with spleen and stomach tonics such as dried tangerine peel (Chen Pi) and Amomum villosum (Sha Ren). Charred Rehmannia glutinosa is used for stopping bleeding.
Anti-Cancer Efficacy: Commonly used clinically for lung cancer, esophageal cancer, gastric cancer, breast cancer, bone tumors, multiple myeloma, leukemia, malignant lymphoma, brain tumors, etc., particularly for those with liver and kidney yin deficiency.
1. Lung Cancer
Sheng Di Huang (Raw Rehmannia) and Shu Di Huang (Prepared Rehmannia) each 15g, Asparagus cochinchinensis (Tian Dong), Ophiopogon japonicus (Mai Dong), and Scrophularia ningpoensis (Xuan Shen) each 12g, Astragalus (Huang Qi) and Codonopsis (Dang Shen) each 20g, and others. Decoction for oral administration. (Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine)
2. Esophageal Cancer
Shu Di Huang 50g, Cinnamon powder 5g, Ephedra 2.5g, Deer antler glue 15g, White mustard seed 10g, Charred ginger 2.5g, Raw licorice 5g. Decoction for oral administration, one dose per day. (《抗癌良方》)
3. Gastric Cancer
Shu Di Huang, Salvia miltiorrhiza (Dan Shen), Lycium barbarum (Gou Qi), and prepared Polygonum multiflorum (He Shou Wu) each 15g, Codonopsis (Dang Shen), Astragalus (Huang Qi), and Poria cocos (Fu Ling) each 12g, Atractylodes (Bai Zhu), Chinese yam (Huang Shan Yao), deer antler, Angelica sinensis (Dang Gui), and white peony (Bai Shao) each 9g, and roasted licorice 3g. Decoction for oral administration. (《抗癌植物药及其验方》)
4. Multiple Myeloma
Sheng Di Huang and Shu Di Huang each 15g, Chinese yam 12g, Poria 12g, Ligustrum lucidum (Nu Zhen Zi) 30g, Cuscuta chinensis (Tu Si Zi) 30g, Peony root 12g, red peony (Chi Shao) and white peony (Bai Shao) each 9g, Corydalis yanhusuo (Yan Hu Suo) 9g, white vine (Bai Lian) 30g, dandelion (Pu Gong Ying) 30g, and chicken blood vine (Ji Xue Teng) 15g. Decoction for oral administration. [Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 1986, 6(9): 552]
5. Acute Non-Lymphocytic Leukemia
Shu Di Huang, Poria, Astragalus, Hedyotis diffusa (Bai Hua She She Cao), Solanum nigrum (Long Kui), Mountain bean root (Shan Dou Gen), and Lithospermum erythrorhizon (Zi Cao) each 30g, Chinese yam 15g, Cornus officinalis (Shan Zhu Yu), Cistanche deserticola (Rou Cong Rong), Morinda officinalis (Ba Jitian), and Psoralea corylifolia (Bu Guo Zhi), ginseng (or Codonopsis), Ophiopogon, and Schisandra chinensis (Wu Wei Zi) each 10g, Angelica 6g decoction for oral administration. [Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 1985, 5(9): 542]
↓《民方推荐》6. Malignant Lymphoma
Shu Di Huang 30g, Cinnamon and licorice each 3g, Ephedra and roasted ginger each 1.5g, Deer antler glue (melted in aged wine) and Pinellia ternata (Ban Xia) each 9g, white mustard seed (stir-fried and ground) 5g, and dried tangerine peel 6g. Decoction for oral administration. [Shanghai Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 1984, (9): 7]
7. Brain Tumor
① Sheng Di Huang and Shu Di Huang each 10g, Cornus officinalis 15g, Chinese yam 10g, Alisma orientale (Ze Xie) 10g, Poria 10g, Chrysanthemum 10g, and Achyranthes bidentata (Hua Niu Xi) 10g, Uncaria rhynchophylla (Gou Teng) 10g, white peony 15g, Xuan Shen 15g, raw oyster shell 30g, Lycium barbarum 12g, raw tortoise shell 20g, Ligustrum lucidum 15g, and raw red ochre 20g. Decoction for oral administration. (《中医肿瘤学》)② Shu Di Huang, Dragon’s blood (Xue Jie), and mother-of-pearl (Zhen Zhu Mu) each 20g, red peony, white peony, and Angelica each 15g, Sparganium (San Leng) and Curcuma zedoaria (E Zhu) each 12g, peach kernel 10g, Acorus calamus (Shi Chang Pu) 5g, Chuanxiong (Chuan Xiong) 3g, and musk 0.3g (swallowed). Decoction for oral administration. (《抗癌植物药及其验方》)
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from the internet and published materials. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal. The various prescriptions and formulas mentioned are for informational sharing only and do not constitute medical advice, recommendations, or guidance. Please use them under the guidance of a physician.
Don’t forget to follow us So you won’t miss us next time
So you won’t miss us next time
Recommended Reading
-
Summary of the Efficacy of Chinese Herbs (Most Comprehensive)
-
The Best Dietary Therapy for Spleen and Stomach, Passed Down for Three Hundred Years!
-
The Amazing Medicinal Herb: The Efficacy and Functions of Motherwort

