

Promotion of Appropriate Techniques
Dissemination of Traditional Chinese Medicine Culture

Cupping therapy utilizes cups as tools, employing methods such as combustion, suction, and steam to create negative pressure within the cups. This allows the cups to adhere to acupuncture points (腧穴, shùxué) or corresponding areas on the body, causing local skin congestion or bruising, thereby serving as an external treatment method for disease prevention and treatment. Historically known as the horn method (角法, jiǎofǎ), it is also referred to as the suction tube method. It is commonly used for conditions such as colds, insomnia, shoulder stiffness, low back pain, and neck pain.


1. Commonly Used Tools and Basic Operating Methods
(1) Commonly Used Tools
Glass cups, bamboo cups, ceramic cups, and suction cups.

(2) Methods of Cupping
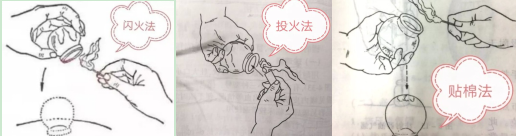
1. Fire cupping method
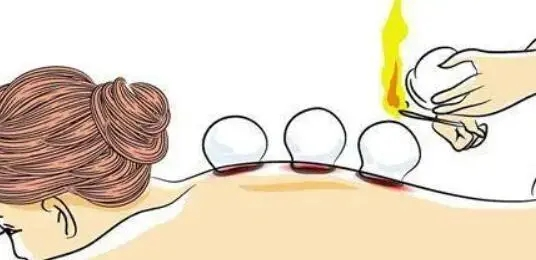
(1) Flash fire method: Use a needle holder or hemostat to grasp a cotton ball soaked in 95% ethanol, holding a lighting tool in one hand and the cup in the other, with the cup opening facing down. Ignite the cotton ball, quickly insert it into the cup, rotate it once, and then swiftly place the cup on the selected area.
Special note: Instruct the patient to maintain a relatively fixed position; ensure the cup opening is smooth and undamaged; prevent ethanol from dripping and burning the skin during cupping; do not leave the ignited cotton ball in the cup for too long to avoid burning the skin.
(2) Fire throwing method: Ignite a cotton ball or paper, drop it into the cup, and quickly place the cup on the selected area.
Special note: Due to the presence of burning material inside the cup, the falling fireball can easily burn the skin, so this method is only suitable for lateral cupping.
(3) Cotton sticking method: Use a cotton piece of 1-2 cm size, stick it to the inner wall of the cup or the bottom of the cup, ignite it, and quickly place the cup on the selected area.
Special note: Do not soak the cotton in too much ethanol to avoid burning the skin.
2. Boiling cup method
This method generally uses bamboo cups, which are inverted in boiling water or medicinal liquid for 1-2 minutes. Use tweezers to grasp the bottom of the cup, remove it, and use a towel to absorb surface moisture, then apply it to the skin while hot. The medicinal liquid used can be determined based on the condition.
3. Suction cup method
Place the suction cup on the selected area, remove the air to create negative pressure, and adhere it to the body surface.
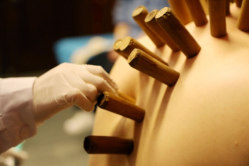
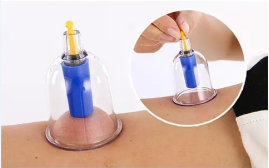
(3) Cupping Operation
1. Retaining the cup: Also known as sitting cupping, this method involves leaving the cup on the treatment area for 10-15 minutes after suctioning, then removing the cup.
Indications: This method is suitable for most clinical conditions and is the most commonly used cupping method.
Special note: For children, the suction force should not be too strong, and the duration should not be too long; when cupping on areas with thin muscles or strong suction, the retention time should not be too long.
2. Moving the cup: Also known as pushing cupping, first apply a layer of lubricant on the cup opening or suction area, place the cup on the skin, then hold the bottom of the cup with one hand, slightly tilt the cup body, and push and pull it back and forth or make circular movements repeatedly until the skin becomes flushed, deep red, or develops petechiae.
Indications: Acute febrile diseases or pain due to stagnation of qi and blood in deep tissues, external invasion of wind and cold, neuralgia, rheumatic pain, and widespread pain.
Special note: Choose larger diameter, thicker-walled, and smooth glass cups; the treatment area should be broad and muscular, such as the chest, back, waist, abdomen, and thighs.
3. Flash cupping: Using the flash fire method or suction method to attach the cup to the skin, then immediately remove it, repeating this process until the skin becomes flushed and warm, indicating the desired level of cupping.
Indications: Colds, skin numbness, facial conditions, post-stroke sequelae, or weakness.
Special note: The technique should be performed skillfully, with movements that are light, quick, and precise; at least three cups of the same diameter should be used interchangeably to avoid burns from hot cups.

(4) Removing the cup
To remove the cup, gently press beside the cup opening with the thumb or index finger to allow air to enter the cup, then remove it smoothly. Do not forcibly pull or twist the cup.

2. Common Diseases Treated with Cupping Therapy
(1) Common Cold (Common Cold and Influenza)
The common cold is a prevalent external pathogenic disease, characterized by nasal congestion, runny nose, sneezing, headache, chills, fever, and general malaise. It is often caused by pathogenic factors invading the body’s surface. The evil qi enters through the skin and nose, in cases of cold predominance, it leads to cold evil binding the surface, obstructing lung qi, and blocking the pores; in cases of heat predominance, it results in heat evil scorching the lungs, causing the pores to open, and the lungs to lose their ability to clear and regulate. This condition is diagnosed according to the “Standards for Diagnosis and Efficacy of TCM Diseases” issued by the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 1994. This therapy is most effective for early-stage symptoms, especially suitable for treating wind-cold type colds.
[Treatment Principle] Disperse wind, resolve the exterior, and open the meridians.
[Operating Steps] Focus on the back’s governor vessel and bladder meridian points, using the moving cupping and retaining cupping methods.
[Acupuncture Points] Dazhui (大椎, Dàzhuī), Fengmen (风门, Fēngmén), Feishu (肺俞, Fèishū), Shenzhu (身柱, Shēnzhù).
[Precautions] The selected cups should not be too large, and the stimulation should not be too strong, aiming for skin flushing; instruct the patient to keep the back warm.
(2) Cough (Acute and Chronic Bronchitis)
Coughing is the main symptom of lung-related diseases. External pathogens invade the lungs, either entering through the mouth and nose or affecting the skin. When the lung’s defensive qi is compromised, it loses its ability to disperse and regulate, leading to coughing. The lungs are delicate organs that prefer moisture and dislike dryness; if dryness injures the lungs, it can deplete lung yin, causing a dry cough with phlegm that is difficult to expel. Phlegm and fluids can accumulate, and if the spleen fails to transport fluids properly, it can lead to phlegm obstruction, preventing lung qi from descending, resulting in a cough with abundant phlegm. This condition is diagnosed according to the “Standards for Diagnosis and Efficacy of TCM Diseases” issued by the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 1994.
[Treatment Principle] Disseminate lung qi, regulate qi, stop cough, and transform phlegm.
[Operating Steps] Focus on the back’s acupuncture points, using the moving cupping and retaining cupping methods.
[Acupuncture Points] Dingchuan (定喘, Dìngchuǎn), Feishu (肺俞, Fèishū), Feidi (肺底, Fèidǐ) (an empirical point located at the midpoint of the line connecting the posterior axillary line and the midline of the back at the level of the seventh thoracic vertebra).
(3) Low Back Pain (Lumbar Disc Herniation)
Low back pain is a type of condition characterized by self-reported pain in the lower back, presenting as heavy pain, soreness, numbness, and stiffness, making it difficult to bend or stretch. Coughing or sneezing can exacerbate the pain; there may be limitations in movement in all directions, particularly in extension and flexion. The occurrence of this condition is mainly related to the invasion of external pathogens, falls, injuries, or excessive labor. This condition is diagnosed according to the “Standards for Diagnosis and Efficacy of TCM Diseases” issued by the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine in 1994.
[Treatment Principle] Relax muscles, invigorate blood circulation, open the meridians, and relieve pain.
[Operating Steps] Focus on the back’s governor vessel and bladder meridian points, using the moving cupping and retaining cupping methods.
[Acupuncture Points] Dachangshu (大肠俞, Dàchángshū), Yaoyan (腰眼, Yāoyǎn), Shenshu (肾俞, Shènshū), Ashi points (阿是穴, Āshìxué).

3. Contraindications
1. Individuals who are overly tense, intoxicated, excessively hungry, overly full, fatigued, or experiencing convulsions are not suitable candidates.
2. Patients with severe heart disease, respiratory failure, localized skin ulcers or severe allergies, active pulmonary tuberculosis, significant weight loss leading to loss of skin elasticity, generalized edema, or malignant tumors.
3. Individuals with bleeding disorders.
4. Pregnant women should avoid cupping on the abdomen, lower back, facial areas, and the perineum; heavy techniques should not be used on the face or children.
5. Localized hernias (such as umbilical hernia, abdominal wall hernia, inguinal hernia), varicose veins, tumors, etc.

4. Precautions
1. When cupping, choose appropriate positions and areas with sufficient muscle; areas with uneven bones or excessive hair are not suitable.
2. Select appropriately sized cups based on different areas, and the suction strength should be adjusted according to the condition; stronger suction can be used for robust individuals, while weaker suction should be applied for the elderly, weak, and children.
3. During cupping and retention, observe the patient’s reactions; if the patient feels discomfort, the cup should be removed immediately; in severe cases, allow the patient to lie down, keep warm, and drink hot water or sugar water, and massage points such as Neiguan (内关, Nèiguān), Hegu (合谷, Hégǔ), Taiyang (太阳, Tàiyáng), and Zusanli (足三里, Zúsānlǐ).
4. Take care to avoid burns or scalds; if burns occur or if the cup is left on too long causing blisters, do not treat the blisters; simply cover them with sterile gauze to prevent rupture. If the blisters are large, use a sterile needle to drain the fluid, apply gentian violet, or cover with sterile gauze to prevent infection.
5. Individuals with skin allergies, ulcers, edema, high fever, convulsions, and pregnant women should avoid cupping on the abdomen and lower back.
6. Take precautions against fire during cupping.
-END-

Scan
Code
Follow
To Get More Exciting Content

