Click the blue text to follow us, dear, and while you’re at it, please pin this post 

The meridians are the pathways that circulate Qi and blood throughout the body, connecting the organs and tissues, facilitating communication between the internal and external environments, and transmitting information. The twelve meridians, as the main channels for Qi and blood flow, are interconnected in a continuous loop. Familiarity with the pathways and distributions of the twelve meridians is crucial for guiding acupuncture point selection and treatment in clinical practice.
However, many people find the pathways of the twelve meridians confusing and unclear. Today, I would like to recommend an article that illustrates the pathways of the twelve meridians, complete with images!
1. **Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian**
The Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian begins in the middle jiao, connects to the large intestine, and follows the stomach (lower orifice: pylorus, upper orifice: cardia), ascending through the diaphragm and belonging to the lungs. It traverses horizontally from the lung system (including the trachea, bronchi, and throat) to the upper outer chest (Zhongfu point), exits under the armpit, descends along the inner side of the upper limb, passes through the elbow pit, enters the wrist (Cun point), reaches the thenar, and exits at the radial side of the thumb (Shaoshang point).
Branch: It branches off from the back of the wrist (Lieque point), travels to the radial side of the index finger (Shangyang point), and intersects with the Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian (Figure 1).
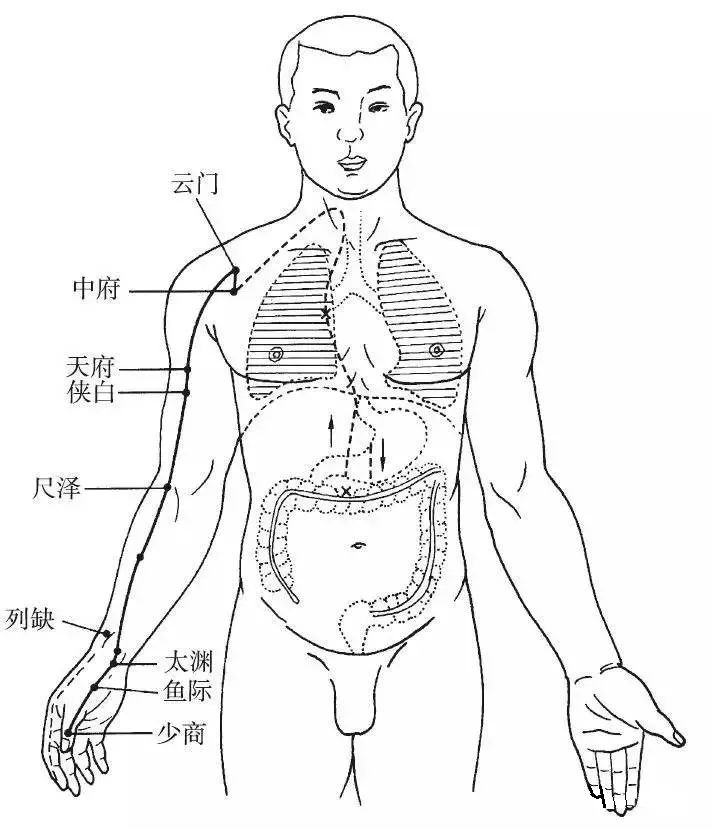
▲ Figure 1 Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian
2. **Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian**
The Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian begins at the radial side of the index finger (Shangyang point), travels along the back of the hand to the outer side of the upper limb, ascends to the shoulder, reaches the anterior edge of the shoulder joint, moves back to the seventh cervical vertebra (Dazhui point), then descends into the supraclavicular fossa, enters the thoracic cavity, connects to the lungs, and descends through the diaphragm, belonging to the large intestine.
Branch: It ascends from the supraclavicular fossa, travels through the neck to the cheek, enters the lower teeth, exits at both sides of the mouth, crosses at the philtrum, and reaches the opposite side of the nostril (Yingxiang point), intersecting with the Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian (Figure 2).
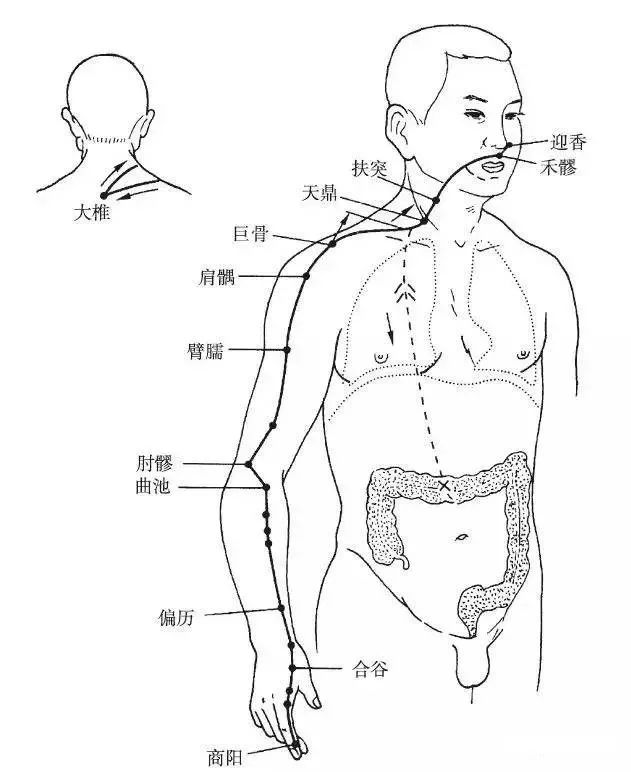
▲ Figure 2 Hand Yangming Large Intestine Meridian
3. **Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian**
The Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian begins at the side of the nostril (Yingxiang point), ascends along the nose, meets at the root of the nose, enters the inner canthus of the eye, intersects with the Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian, descends along the outer side of the nose, enters the upper teeth, exits at both sides of the mouth, encircles the lips, intersects at the Chengjiang point in the mentolabial groove, returns along the lower jaw bone to the Daying point, ascends along the angle of the jaw, passes in front of the ear, and travels to the forehead.
Branch: It branches off from the Daying point at the lower jaw, descends to the Renying point, travels down the throat to the Dazhui point, bends forward, enters the supraclavicular fossa, enters the thoracic cavity, descends through the diaphragm, belongs to the stomach, and connects to the spleen.
Direct Path: It exits from the supraclavicular fossa, descends along the midline of the breast, and travels down to the groin area (Qichong point).
Branch: It branches off from the pylorus in the abdominal cavity, descends to the Qichong point, joins the direct path, and then descends along the anterior side of the thigh to the knee, continuing down the anterior edge of the tibia to the dorsum of the foot, entering the outer side of the second toe (Lidui point).
Branch: It branches off from three inches below the knee (Zusanli point), descends to the outer side of the middle toe.
Branch: It branches off from the dorsum of the foot (Chongyang point), travels forward to the inner side of the big toe (Yinbai point), intersecting with the Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian (Figure 3).
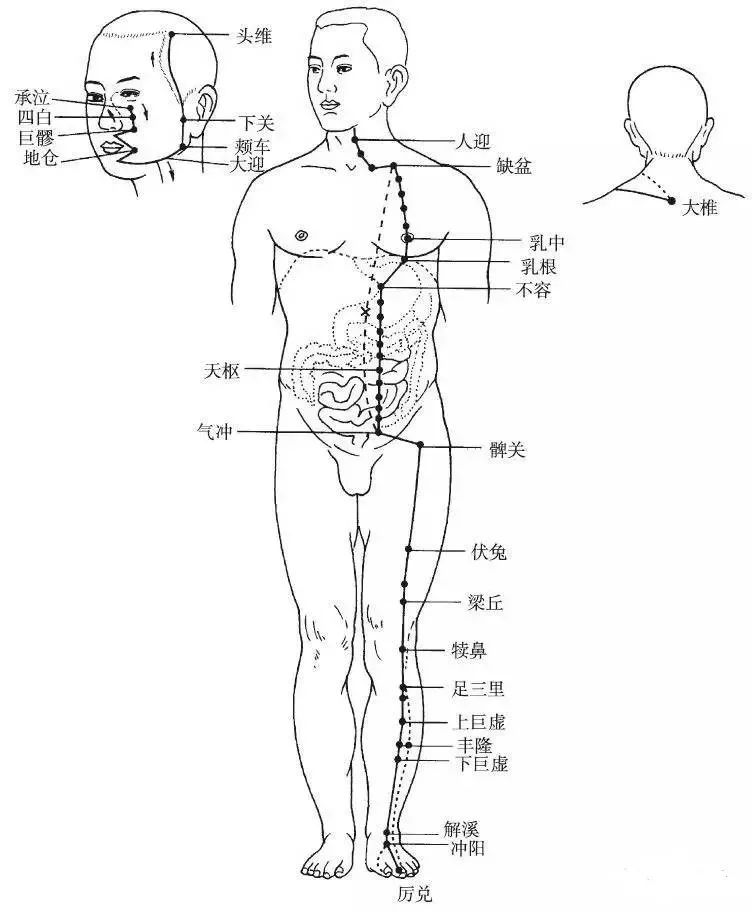
▲ Figure 3 Foot Yangming Stomach Meridian
4. **Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian**
The Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian begins at the inner side of the big toe (Yinbai point), ascends along the inner side of the foot, passes over the anterior edge of the inner ankle, ascends along the midline of the inner leg, at eight inches above the inner ankle, it intersects with the Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian, ascends along the anterior edge of the inner thigh, enters the abdomen, belongs to the spleen, and connects to the stomach. It ascends through the diaphragm, travels alongside the esophagus, connects to the root of the tongue, and disperses under the tongue.
Branch: It branches off from the stomach, ascends through the diaphragm, enters the heart, and intersects with the Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian (Figure 4).
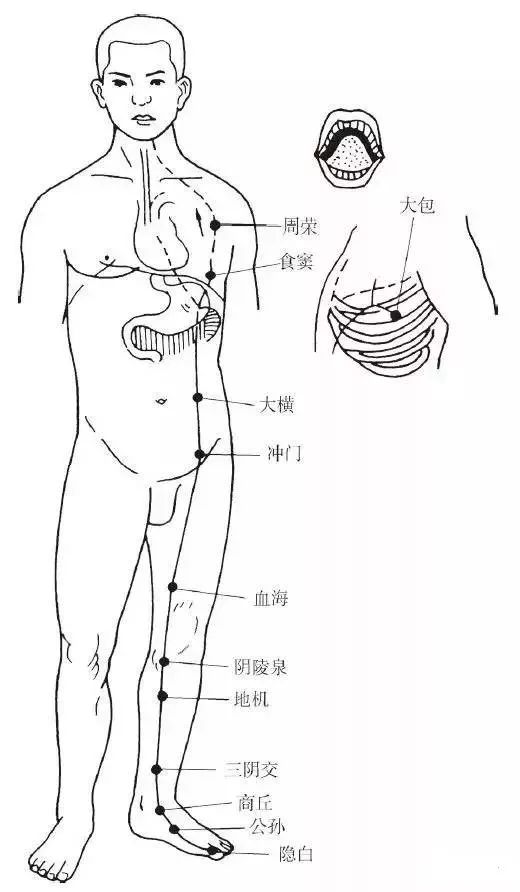
▲ Figure 4 Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian
5. **Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian**
The Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian begins in the heart, exits and belongs to the heart system, descends through the diaphragm, and connects to the small intestine.
Branch: It branches off from the heart system, ascends alongside the esophagus, and connects to the eye system.
Direct Path: It exits from the heart system, bends back and ascends, passes through the lungs, descends shallowly to the armpit (Jiquan point), travels along the inner side of the upper limb, passes through the elbow, travels through the palm, enters the palm, along the radial side of the little finger, exits at the radial side of the little finger (Shaochong point), intersecting with the Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian (Figure 5).
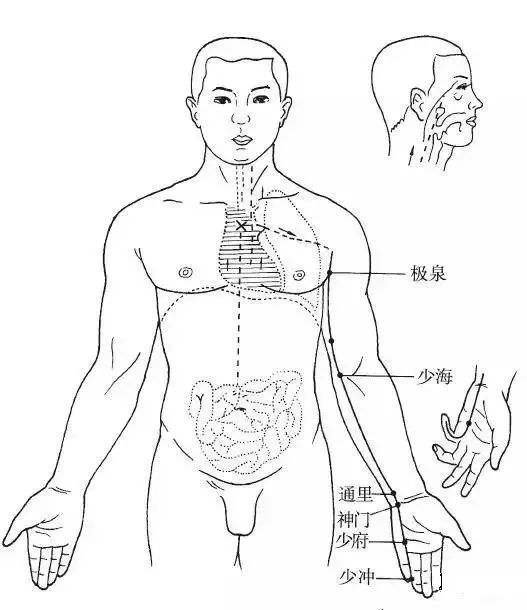
▲ Figure 5 Hand Shaoyin Heart Meridian
6. **Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian**
The Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian begins at the outer side of the little finger (Shaoze point), travels along the back of the hand, the outer side of the upper limb, passes through the elbow, reaches the back of the shoulder joint, encircles the shoulder area, intersects at the Dazhui point, bends forward into the supraclavicular fossa, enters the thoracic cavity, connects to the heart, travels alongside the esophagus, descends through the diaphragm, reaches the stomach, and descends, belonging to the small intestine.
Branch: It exits from the supraclavicular fossa, ascends along the neck to the cheek, reaches the outer canthus of the eye, retreats into the ear (Tinggong point).
Branch: It branches off from the cheek, ascends under the eye, reaches the inner canthus of the eye (Jingming point), intersecting with the Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian (Figure 6).
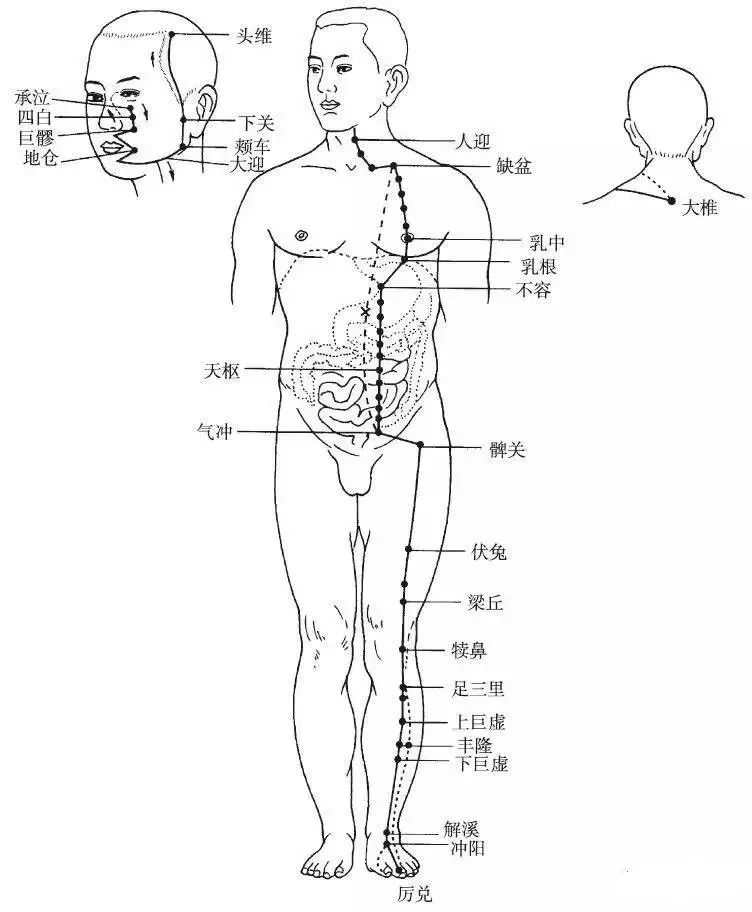
▲ Figure 6 Hand Taiyang Small Intestine Meridian
7. **Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian**
The Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian begins at the inner canthus of the eye (Jingming point), ascends to the forehead, and intersects at the top of the head (Baihui point).
Branch: It branches off from the top of the head, travels to the upper corner of the ear.
Direct Path: It branches off from the top of the head, travels back to the occipital bone, enters the cranial cavity, connects to the brain, exits and descends to the nape (Tianzhu point), descends and intersects at the Dazhui point, then branches left and right along the inner side of the scapula, descending alongside the spine (1.5 inches lateral to the spine), reaching the lumbar region (Shenxiu point), entering the muscles beside the spine (Liu), deeply entering the abdominal cavity, connecting to the kidneys, belonging to the bladder.
Branch: It branches off from the lumbar region, descends alongside the spine, passes through the buttocks, descends along the outer edge of the thigh to the popliteal fossa (Weizhong point).
Branch: It branches off from the nape (Tianzhu point), descends through the inner side of the scapula, descends alongside the spine (3 inches lateral to the spine) to the hip joint (Dazhu point), descends along the back of the thigh to the popliteal fossa, where it joins the previous branch, then descends through the gastrocnemius muscle, exits behind the outer ankle, and travels along the outer edge of the foot to the outer side of the little toe (Zhiyin point), intersecting with the Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian (Figure 7).
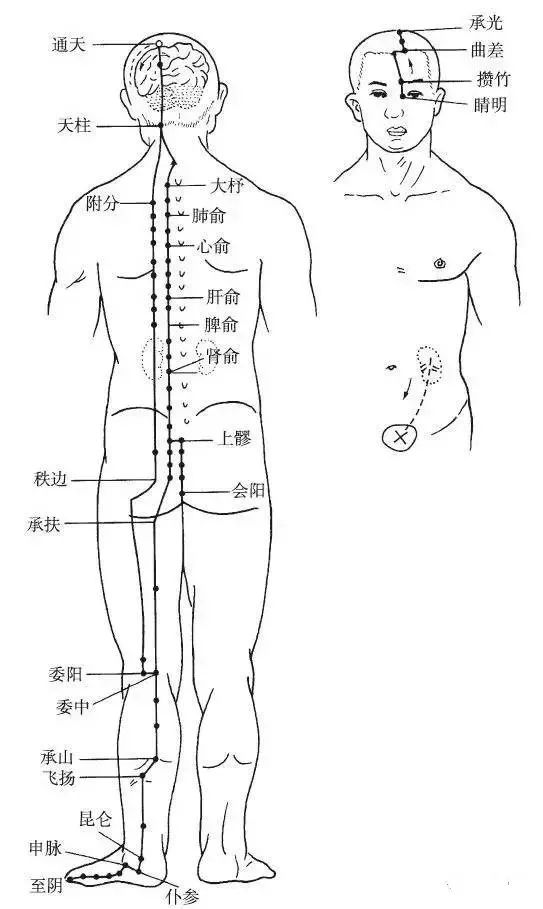
▲ Figure 7 Foot Taiyang Bladder Meridian
Foot Taiyang has sixty-seven points, Jingming, Cuanzhu, Quchao,
Directly above the brow, five points connect to heaven,
Connecting to Yuzhen, Tianzhu, and Dazhui,
Jueyin, Heart, and Liver, Spleen, and Stomach follow,
Qi, Daguang, and Xiaobai,
Huiyang must be taken beside the buttocks.
8. **Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian**
The Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian begins at the outer side of the little toe, diagonally traverses the sole of the foot (Yongquan point), exits beneath the tuberosity of the navicular bone, travels along the posterior edge of the inner ankle, ascends along the inner side of the leg, reaches the inner side of the popliteal fossa, enters the inner side of the thigh, enters the spine (Changqiang point), passes through the spine, belongs to the kidneys, and connects to the bladder.
Direct Path: It ascends from the kidneys, passes through the liver and diaphragm, enters the lungs, travels along the throat, and reaches both sides of the root of the tongue.
Branch: It branches off from the lungs, connects to the heart, enters the chest, and intersects with the Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian (Figure 8).
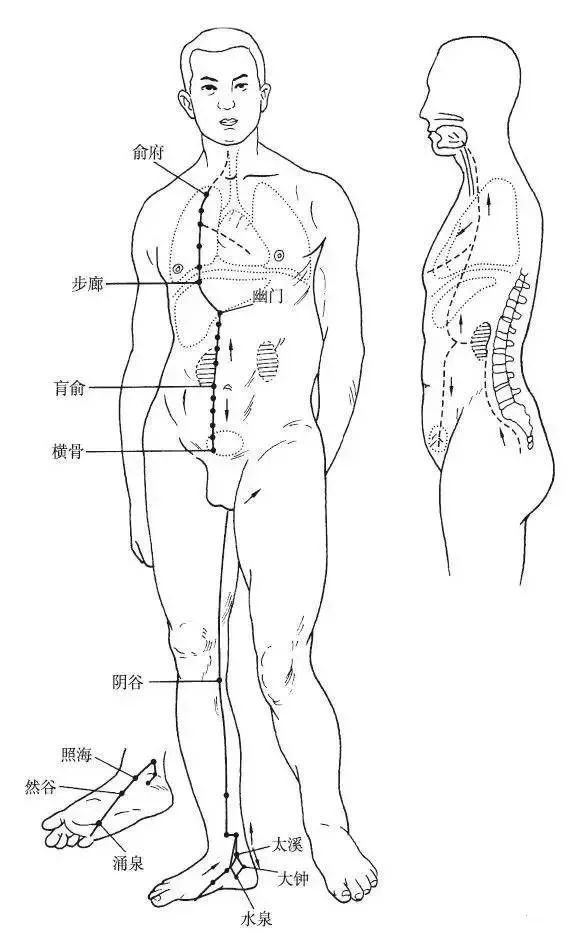
▲ Figure 8 Foot Shaoyin Kidney Meridian
Foot Shaoyin has twenty-seven points, Yongquan, then Guai,
Taixi, Dazhong, and Shuiling,
Fuliu, Jiaxin, and Zhiyin,
Huangyu, Shanggu, and Yinjiao,
Shenmen, Yuzhong, and Yufeng.
9. **Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian**
The Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian begins in the chest, exits and belongs to the pericardium, descends through the diaphragm, and connects to the upper, middle, and lower jiao.
Branch: It branches off from the chest, shallowly exits at the side of the ribs (Tianchi point), ascends to the armpit, travels along the inner side of the upper limb to the elbow, passes through the wrist, enters the palm (Laogong point), travels along the radial side of the middle finger, and exits at the radial side of the middle finger (Zhongchong point).
Branch: It branches off from the palm, travels along the ring finger to its ulnar side (Guanchong point), intersecting with the Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian (Figure 9).
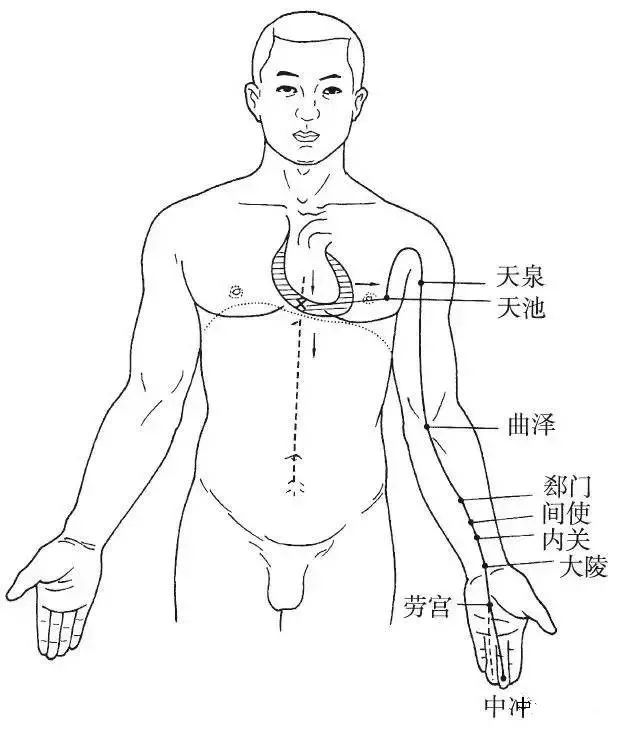
▲ Figure 9 Hand Jueyin Pericardium Meridian
10. **Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian**
The Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian begins at the ulnar side of the ring finger (Guanchong point), ascends along the ulnar side of the ring finger to the back of the wrist, travels up the outer side of the forearm between the ulna and radius, passes through the elbow, ascends along the outer side of the upper arm to the shoulder, moves forward into the supraclavicular fossa, spreads in the chest, connects to the heart, descends through the diaphragm, and belongs to the upper, middle, and lower jiao.
Branch: It branches off from the chest, ascends from the supraclavicular fossa to the shoulder, intersects at the Dazhui point, and branches off to the nape, passing behind the ear (Yifeng point) and then upward, exiting at the upper corner of the ear, then bending downward through the cheek to the lower eye socket.
Branch: It branches off from behind the ear, enters the ear, exits in front of the ear, travels in front of the Shangguan point, intersects with the previous branch at the outer canthus of the eye (Tongziliao point), intersecting with the Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian (Figure 10).
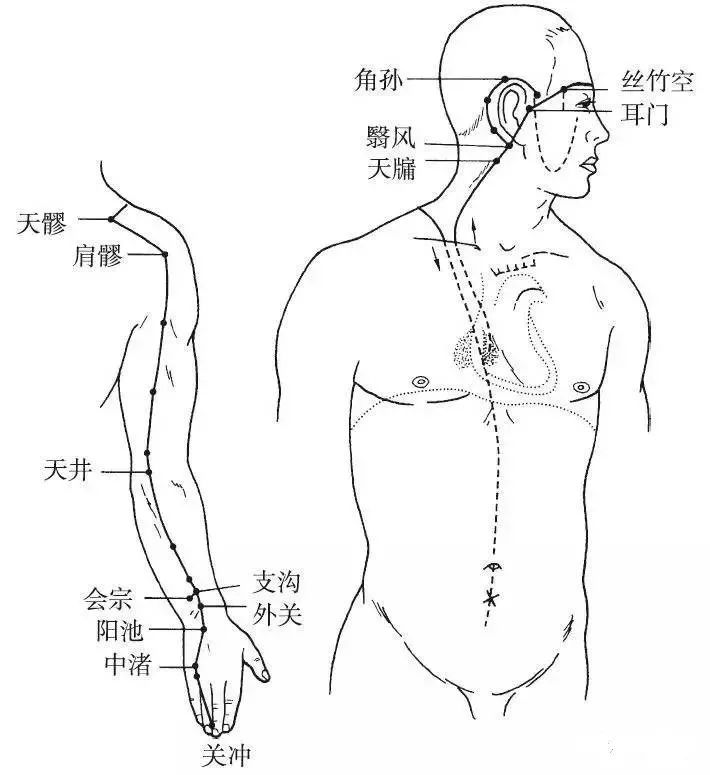
▲ Figure 10 Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian
The Shaoyang Sanjiao has twenty-three points, starting from Guanchong,
Yuemeng, Zhongzhu, and Yangchi,
Sanli, Qichong, and Tianjing,
Shenmen, Yuzhong, and Yufeng.
11. **Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian**
The Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian begins at the outer canthus of the eye (Tongziliao point), ascends to the head corner (Hanyan point), descends to the back of the ear (Wangu point), then bends upward, travels through the forehead to above the eyebrow (Yangbai point), bends backward to Fengchi point, descends along the neck to the shoulder, intersects at the Dazhui point, and branches forward into the supraclavicular fossa.
Branch: It branches off from the back of the ear (Wangu point), travels through Yifeng point into the ear, exits in front of the ear, passes through Tinggong point, and reaches the outer canthus of the eye.
Branch: It branches off from the outer canthus of the eye, descends to the Daying point at the lower jaw, intersects with the Hand Shaoyang Sanjiao Meridian in the cheek area, then travels to the lower eye socket, descends through the lower jaw, and reaches the neck, where it intersects with the previous meridian at the supraclavicular fossa, then enters the thoracic cavity, descends through the diaphragm, connects to the liver, belongs to the gallbladder, and descends from the ribs, shallowly exiting at the Qichong point, encircling the hairline, and horizontally reaching the Huantiao point.
Direct Path: It descends from the supraclavicular fossa to the armpit, travels along the side of the chest, passes through the ribs, descends to the Huantiao point, intersects with the previous meridian, then descends along the outer side of the thigh, along the outer edge of the knee joint, travels along the front of the fibula, directly down to the lower end of the fibula (Juegu point), exits in front of the outer ankle, and travels along the dorsum of the foot to the outer side of the fourth toe (Qiaoyin point).
Branch: It branches off from the dorsum of the foot (Zutiming point), travels forward to the outer side of the big toe, bends back, passes through the nail, and reaches the hair at the back of the big toe, intersecting with the Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian (Figure 11).
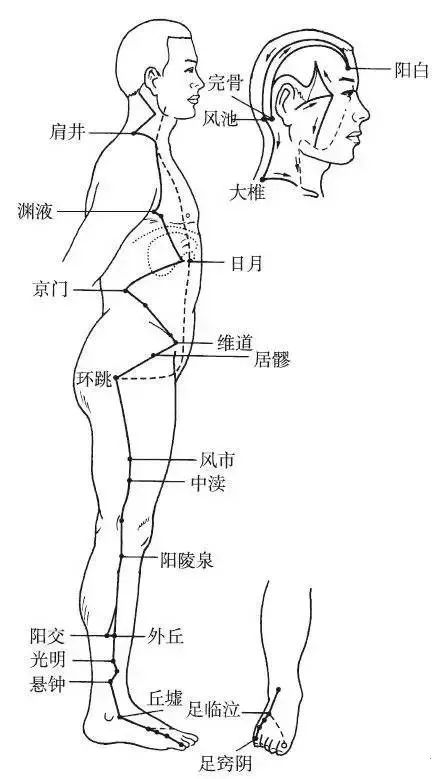
▲ Figure 11 Foot Shaoyang Gallbladder Meridian
12. **Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian**
The Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian begins at the hair at the back of the big toe, ascends along the dorsum of the foot to one inch in front of the inner ankle (Zhongfeng point), ascends along the inner edge of the tibia, intersects with the Foot Taiyin Spleen Meridian eight inches above the inner ankle, ascends along the inner side of the knee, along the midline of the inner thigh, enters the pubic area, encircles the genitals, reaches the lower abdomen, flanks the stomach, belongs to the liver, connects to the gallbladder, ascends through the diaphragm, spreads in the hypochondriac region, travels behind the throat, ascends into the nasopharynx, ascends to connect with the eye system, exits at the forehead, and ascends to meet the Governing Vessel at the top of the head.
Branch: It branches off from the eye system, descends through the cheek, encircles the inside of the lips.
Branch: It branches off from the liver, passes through the diaphragm, ascends to the lungs, and intersects with the Hand Taiyin Lung Meridian (Figure 12).
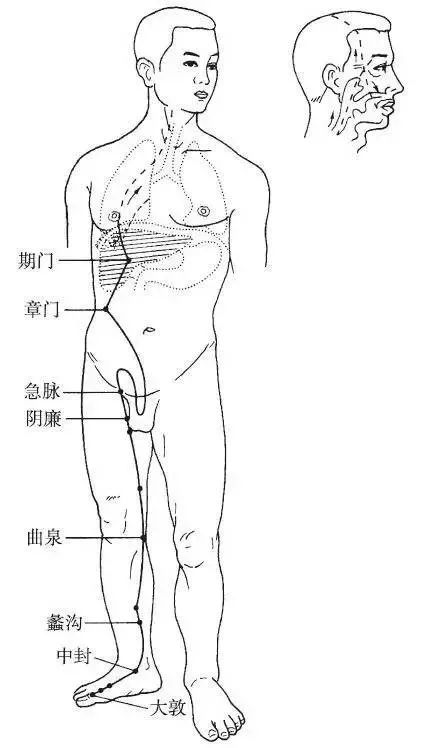
▲ Figure 12 Foot Jueyin Liver Meridian

Long press the fingerprint > Scan the QR code > Add to follow
Follow the Xinghai public account,
Learn and improve, and pass every exam!
If you are reading this, please click “Looking” before you leave! Thank you~ 

