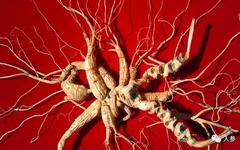
Throughout history, ginseng has been revered as a miraculous herb, known for its unique therapeutic effects and wide-ranging applications. Ancient practitioners observed nature and through their experiences discovered that ginseng possesses the ability to nourish and strengthen the body, prolong life, and regarded it as a precious gift and a potent medicine.
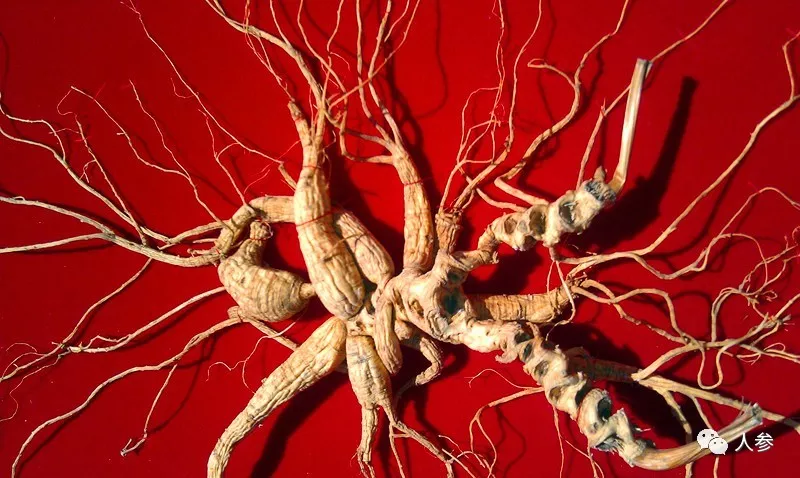
With the advancement of modern science and technology, researchers have begun to study ginseng from a molecular biology perspective, revealing the secrets hidden beneath its mysterious facade. Scientists have utilized gene sequencing technology to analyze the genomic structure of ginseng, laying the groundwork for further exploration of its functions. Additionally, during the study of ginseng’s active components, various compounds beneficial to human health have been discovered.
Main Active Components of Ginseng:
Ginsenosides: Ginsenosides Rg1, Rb2, Rc, Rg1, Rb1, etc. Ginsenosides are the basis of ginseng’s physiological activity. During the isolation of aglycones, due to the action of dilute acid, the hydroxyl groups and alkene bonds in the molecular side chains cyclize to form ginsenoside diol and ginsenoside triol, both of which are triterpenoid compounds.
Monosaccharides: Glucose, fructose, sucrose, and three types of trisaccharides: glucose-fructose-fructose, maltotriose, glucose-glucose-fructose.
Organic acids and esters: Citric acid, isocitric acid, ferulic acid, ketopentanedioic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, succinic acid, malic acid, pyruvic acid, succinic acid, tartaric acid, ginseng acid, salicylic acid, vanillic acid, p-hydroxycinnamic acid, triglycerides, palmitic acid, tripalmitin, α, γ-dipalmitin, triolein, and glyceryl diglucoside.
Vitamins: Vitamins B1, B2, B12, C; niacin, folic acid, pantothenic acid, biotin, and niacinamide.
Sterols and their glycosides: β-sitosterol, stigmasterol, carotenes, brassicasterol, ginsenoside P, and ester sterols.
Additionally, ginseng contains adenosine deaminase, L-aspartate aminotransferase, β-amylase, sucrose isomerase; maltitol, tricosane; kaempferol, ginseng flavonoids, and over twenty trace elements such as copper, zinc, iron, and manganese.

Modern scientific research has also confirmed that ginseng not only possesses traditional health benefits but can also be applied in many new fields.
1. Emergency Use
Large doses of ginseng (15-50 grams) can be decocted or stewed, or ginseng injection (0.57 grams of raw herb per milliliter) can be administered intramuscularly or intravenously at 2-4 milliliters for emergency treatment of cardiogenic shock or other critically ill patients; ginseng combined with other treatments can rescue patients with yang deficiency collapse.
2. Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases
Ginseng has certain therapeutic effects on hypertension, myocardial dystrophy, coronary artery sclerosis, and angina pectoris, which can alleviate various symptoms. Ginseng has a regulatory effect on abnormal blood pressure, with different doses producing different effects: low doses can raise blood pressure, while high doses can lower it. The common daily dosage for adults is 0.2-3 qian; ginseng extract (1 gram of raw herb per milliliter) is taken at 20-40 drops per dose, 2-3 times a day; ginseng tincture (10% concentration) is taken at 5 milliliters per dose, 2-3 times a day; ginseng powder is taken at 3-6 fen per dose, 2-3 times a day.
3. For Stomach and Liver Diseases
For chronic gastritis with low gastric acid secretion, taking ginseng can increase appetite and alleviate or eliminate symptoms, but it does not significantly affect gastric juice secretion or acidity. Reports also indicate that ginseng can relieve stomach pain in chronic gastritis patients, enhance appetite, normalize bowel movements, and increase total acidity of gastric juice. For acute infectious hepatitis, under certain treatment conditions, taking ginseng may have a positive significance in preventing the transition to chronic hepatitis.
4. Treatment of Diabetes
Ginseng can improve the general condition of diabetic patients without altering the degree of hyperglycemia. It is said that ginseng can reduce urinary sugar in mild diabetes and lower blood sugar by 40-50 mg%, maintaining this effect for over two weeks after discontinuation; in moderate diabetes, although the blood sugar-lowering effect is not significant, most patients experience overall improvement in conditions such as thirst, with symptoms alleviating or disappearing; some patients may reduce their insulin dosage after taking ginseng.
5. For Mental Disorders
Ginseng has therapeutic effects on asthenic and asthenic-depressive types of mental disorders, regardless of their etiology (schizophrenia, toxic or infectious mental disorders, degenerative mental disorders, etc.). It is also believed that oral ginseng can only improve the subjective symptoms of patients with organic neurological diseases without significant objective therapeutic effects.
6. Treatment of Neurasthenia
Ginseng has a significant stimulating effect on the nervous system, enhancing physical activity and reducing fatigue; it has a certain therapeutic effect on different types of neurasthenia patients, leading to weight gain and alleviating or eliminating symptoms such as general weakness, headaches, and insomnia.
7. Treatment of Impotence
In traditional Chinese medicine, ginseng is generally used as a tonic to replenish vital energy; recent studies have confirmed its role in enhancing gonadal function. Ginseng tincture has significant efficacy for impotence of the paralysis type and premature ejaculation type, but is ineffective for the psychological type; it also has certain therapeutic effects on cortical and spinal impotence caused by neurasthenia.
8. Effects on the Endocrine System
Ginseng stimulates the pituitary-adrenal cortex system, with its effective components being ginsenosides. Various ginsenosides have different stimulating effects due to their chemical structures. Many ginsenosides in ginseng can increase the secretion activity of adrenal cortex hormones, with ginsenoside Rb being the most potent. Ginsenosides stimulate the adrenal cortex, leading to elevated plasma cortisol levels.
9. Ginseng also improves vision and enhances visual dark adaptation.
Selected Content
《How to Clean Fresh Ginseng? Why Are There Black Spots After Washing?》
《Is Ginseng Toxic Since “All Medicine Has Some Poison”? 》
《Ginseng + Old Hen is Simply a Perfect Match》
《Identifying the Age of Ginseng》
《Can Hypertensive Patients Consume Ginseng?》
《The Ginseng Industry is Near Its End If Prices Keep Dropping!》
《A Real Look at the Entire Process of Harvesting Ginseng, It’s About Life!》
《Ginseng Auction: Three-Hundred-Year-Old Ginseng Worth Over Ten Million》
《Wild Ginseng Appreciation》
《CCTV: Wild Ginseng Prices Are Rising Against the Trend》
《How Much Wild Ginseng Can China Produce in a Year?》
《Ginseng is Not the Last Straw for Cancer Treatment》
 Inheriting Ginseng Culture, Inheriting TCM Philosophy
Inheriting Ginseng Culture, Inheriting TCM Philosophy Follow UsFOLLOW US
Follow UsFOLLOW US
 Long press to follow @Ginseng Official Account
Long press to follow @Ginseng Official Account Long press to follow @American Ginseng Encyclopedia
Long press to follow @American Ginseng Encyclopedia Long press to follow @Ginseng Sanqi Official Account
Long press to follow @Ginseng Sanqi Official Account