Retention Cupping Method
The retention cupping method is the most commonly used technique in cupping therapy, also known as the sitting cupping method. It involves placing the cup on the skin and leaving it in place for a period of time. The retention time ranges from 5 to 20 minutes, depending on the patient’s condition, the disease, and the season. Generally, in summer and on thinner skin areas, the retention time should not be too long.
There are two forms of retention cupping:

One is the Single Cup Method, which uses a single cup and is suitable for small areas of pathology.
The other is the Multiple Cup Method, also known as the排罐法 (排罐法, Pái Guàn Fǎ). This method uses multiple cups and is generally applied along the muscle bundles, nerves, or meridian pathways. If the patient is strong, the cups can be placed closer together; if the patient is weak, the cups should be spaced further apart. This method is suitable for broader areas of pathology.
Flash Cupping Method
The flash cupping method involves holding a cup in one hand while using tweezers to grasp an alcohol-soaked cotton ball or a cotton ball tied to a wire, igniting it, and then quickly removing it. The cup is then swiftly placed on the affected area of the patient, and immediately removed, repeating this process several times until the skin becomes red and bruised. This method is suitable for areas where the muscles are relatively relaxed.
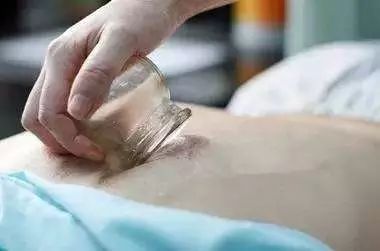
Sliding Cupping Method
The sliding cupping method, also known as the 推罐法 (Tuī Guàn Fǎ) or 拉罐法 (Lā Guàn Fǎ), involves selecting a cup with a larger opening, thicker walls, and a smooth, undamaged surface. A thin layer of lubricant, such as liquid paraffin, petroleum jelly, or other plant oils, is applied to the area where cupping will be performed. After using the flash or throwing fire method to create suction, the cup is placed on the skin, and the practitioner holds the bottom of the cup, tilting it slightly to slide it back and forth. The direction can be forward, backward, left, right, and can also include rotation. This is repeated several times until the skin becomes red and bruised. This method is suitable for larger, flatter areas of the body with well-developed muscles, such as the back and waist.
Effects of Cupping:
Cupping therapy has therapeutic effects of invigorating qi and blood, dispelling cold pathogens, and alleviating pain and swelling. It is suitable for conditions such as shoulder periarthritis, cervical spondylosis, rheumatoid arthritis, neuralgia, low back pain, trigeminal neuralgia, and sciatica.

Colors of Cupping Marks:
1. Dark purple-black cupping marks: Generally indicate insufficient blood supply and poor circulation with blood stasis.
2. Purple cupping marks with patches: Generally indicate cold congealing and blood stasis.

3. Cupping marks with scattered purple spots of varying shades: Indicate qi stagnation and blood stasis.
4. Bright red cupping marks: Generally indicate yin deficiency, deficiency of both qi and blood, or excess fire due to yin deficiency.
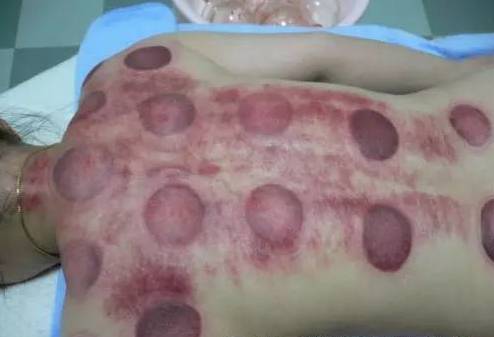
5. Dark red cupping marks: Indicate high blood lipids and the presence of heat pathogens.
6. Gray-white cupping marks that feel cool to the touch: Generally indicate deficiency cold or damp pathogens.
7. Cupping marks with skin texture or slight itching: Indicate wind pathogens or damp conditions.
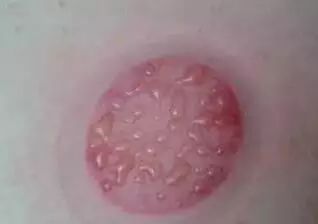
8. Water vapor on the inner wall of the cup: Indicates the presence of dampness in that area.
9. Blisters on the cupping marks: Indicate heavy internal dampness; if the blisters contain blood, it is a reaction to damp-heat toxins.
Precautions for Cupping:
1. After gua sha and cupping, do not take a cold shower or drink cold beverages for two hours. If taking a shower after two hours, use warm water.
2. During gua sha and cupping, do not use air conditioning or fans to avoid air convection.
3. Do not perform gua sha or cupping when overly full, overly hungry, or excessively thirsty; wait at least one hour after meals before performing these techniques.
MORE | 更多知识
Enter keywords on our public account homepage to search for more knowledge:皮肤学 (Dermatology), 经络 (Meridians), 面诊 (Facial Diagnosis), 艾灸 (Moxibustion), 刮痧 (Gua Sha), 拔罐 (Cupping), 泥灸 (Mud Moxibustion), 淋巴 (Lymph), 乳腺 (Breast), 宫寒 (Cold in the Uterus), 湿气 (Dampness), 臀疗 (Butt Therapy), 肝胆 (Liver and Gallbladder), …
Long press the QR code to recognize and follow



