Gua Sha, one of the external treatment methods in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), involves scraping the skin with a hard object to stimulate the meridians and acupoints, thereby promoting the flow of qi, adjusting the qi and blood of the organs, expelling pathogenic factors, and maintaining the body’s vital energy.
Many common minor ailments in daily life can be easily resolved by learning the technique of Gua Sha.
Conditions That Can Be Alleviated by Gua Sha
Neck and Shoulder Pain
-
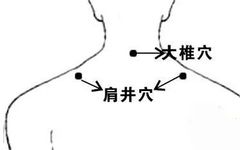
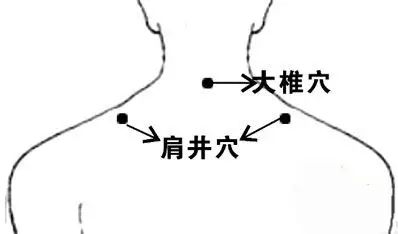
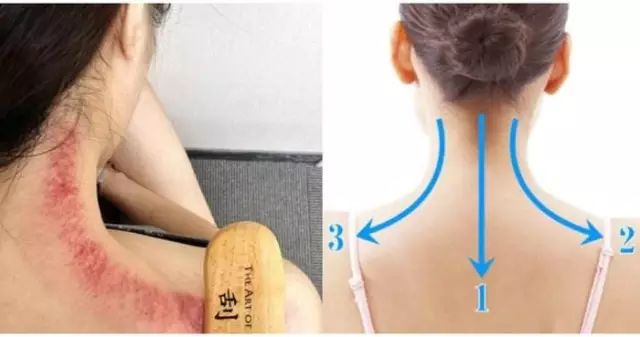
For neck and shoulder pain, Gua Sha can be performed along the direction from Da Zhui (Dazhui) to Jian Jing (Jianjing).
-
Da Zhui (Dazhui): Located at the junction of the neck and back, it is the most prominent bony protrusion, with the depression just below it being this acupoint.
-
Jian Jing (Jianjing): The midpoint of the line connecting Da Zhui (Dazhui) and the acromion.
Lower Back Pain
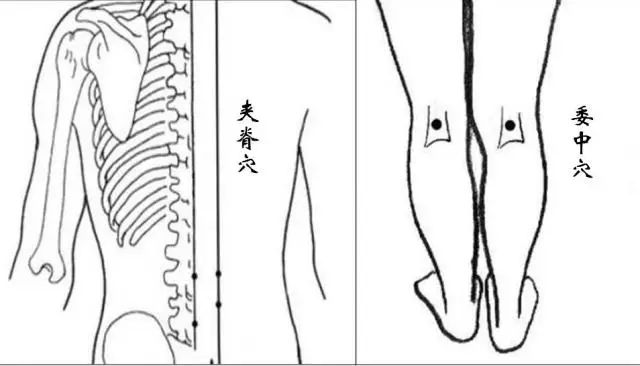
Gua Sha can be performed along the direction from Da Zhui (Dazhui) to Jia Ji (Jiaji), or by scraping the Wei Zhong (Weizhong) acupoint.
-
Jia Ji (Jiaji): A collective term for multiple acupoints located about 0.5 cun lateral to the spinous processes from the first thoracic vertebra to the fifth lumbar vertebra, totaling 34 acupoints.
-
Wei Zhong (Weizhong): Located at the center of the popliteal fossa behind the knee.
When using Gua Sha to relieve neck, shoulder, and lower back pain, Wan Hua Oil can be used instead of Gua Sha oil. Wan Hua Oil promotes blood circulation, resolves stasis, and opens the meridians, also helping to alleviate pain.
Common Cold
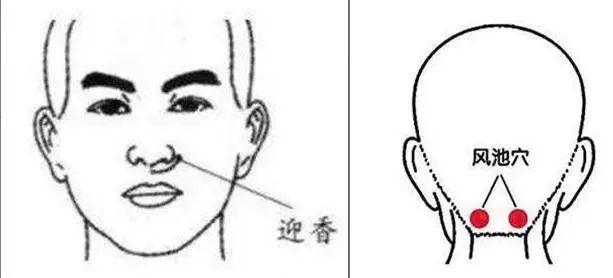
Gua Sha can be performed along the direction from Feng Chi (Fengchi) to Da Zhui (Dazhui) to Jia Ji (Jiaji) to assist in reducing fever.
-
Ying Xiang (Yingxiang): Located on both sides of the nostrils. (You can use the edge of the Gua Sha board to press and rub at this point, or scrape from Ying Xiang towards the nasolabial groove.)
-
Feng Chi (Fengchi): Located at the junction of the neck and hairline, with a depression on each side.
Heat Stroke
If a heat stroke patient has symptoms of fever and headache, Gua Sha can be performed using the same method as for the common cold.
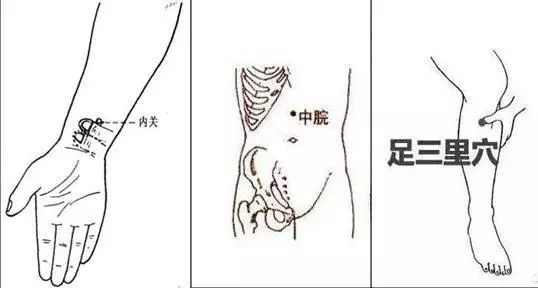
If nausea occurs, scrape the Zhong Wan (Zhongwan), Nei Guan (Neiguan), and Zu San Li (Zusanli) acupoints.
If there is chest tightness and fullness, scrape the Tan Zhong (Tanzhong) acupoint, which is the midpoint between the two nipples.
-
Zhong Wan (Zhongwan): Located about six fingerbreadths above the navel.
-
Nei Guan (Neiguan): Located in the center of the forearm, about two fingerbreadths from the palm.
-
Zu San Li (Zusanli): Located about four fingerbreadths below the outer knee.
Gastrointestinal Issues
For gastrointestinal issues, Gua Sha can be performed on two areas:
-
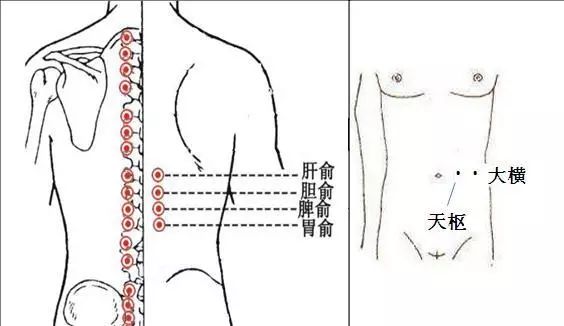
First, the lumbar and sacral region, where the Da Chang Shu (Dachangshu), Xiao Chang Shu (Xiaochangshu), Wei Shu (Weishu), and Pi Shu (Pishu) acupoints are located, which help strengthen the spleen and stomach and aid digestion;
-
Second, the abdomen, where the spleen and stomach meridians run, including the Tian Shu (Tianshu) and Da Heng (Daheng) acupoints, which can regulate and harmonize the stomach and strengthen the spleen.
These acupoints have a bidirectional regulation effect, capable of stopping diarrhea as well as relieving constipation.
Generally, for diarrhea, scrape in a counterclockwise direction; for constipation, scrape in a clockwise direction.
-
Tian Shu (Tianshu): Located about three fingerbreadths to the left and right of the navel.
-
Da Heng (Daheng): Located about six fingerbreadths to the left and right of the navel.
Precautions
Before Gua Sha
-
Prepare the Gua Sha board and Gua Sha oil.
-
The Gua Sha board must be disinfected, and Gua Sha oil should be applied to the area to be scraped.
-
If Gua Sha oil is not available, moisturizing oil, hand cream, or even cooking oil can be used as a substitute.
During Gua Sha
-
The area being scraped should not be exposed to cold or wind.
-
The scraping force should be moderate, and the speed should not be too fast; scraping until the skin becomes slightly red and shows petechiae is sufficient.
-
The duration of Gua Sha should not exceed 20 minutes in total.
After Gua Sha
-
After Gua Sha, drink a cup of warm water (preferably with a little salt).
-
Avoid bathing for at least one hour.
-
Do not perform Gua Sha again until the petechiae have faded.
Conditions Not Suitable for Gua Sha:
○ Skin lesions such as cuts, moles, abscesses, or blisters, as Gua Sha may lead to infection.
○ Body edema, as Gua Sha may exacerbate swelling.
○ Pregnancy, as Gua Sha may cause miscarriage.
○ Acute sprains or fractures, as Gua Sha may worsen bleeding and pain at the injury site.
○ Individuals with bleeding tendencies, such as those with thrombocytopenia, late-stage diabetes, or cardiovascular patients on anticoagulants like aspirin, as Gua Sha may lead to excessive bleeding.
○ Heart failure patients, as Gua Sha may lead to acute heart failure.
○ Patients with tumors, tuberculosis, or renal failure should avoid Gua Sha.
Customer Service WeChat ID: lishishi-1
MORE | More Knowledge
Enter keywords on our public account homepage to find more knowledge: Dermatology, Meridians, Facial Diagnosis, Moxibustion, Gua Sha, Cupping, Mud Moxibustion, Lymphatic, Breast, Cold in the Uterus, Dampness, Hip Therapy, Liver and Gallbladder, …
Long press the QR code to recognize and follow