A Brief Overview of the Five Zang and Six Fu Organs in Traditional Chinese Medicine
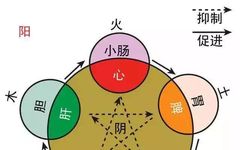
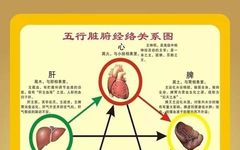
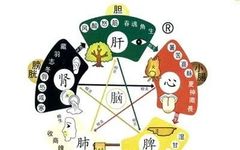
Five Zang Organs 1. Heart: The heart is the residence of the spirit, the master of blood, and the root of the pulse. It belongs to the fire element in the Five Elements theory. Physiological functions: ① Governs blood vessels; ② Governs consciousness; The heart opens to the tongue, connects with the pulse in the … Read more