
Eyes
1. Symptoms Around the Eyes
Swollen eyelids — Indicates reduced function of internal organs (kidneys, gastrointestinal, heart) leading to water retention in the body.
Dark circles — Occur when blood contains excessive waste, causing the area around the eyes to appear dull (kidneys).
Wrinkles below the eyes — A sign of aging.
Sunken eye sockets — Indicates excessive consumption of body energy.
White inner eyelids — A symptom of anemia.
Yellowish-white bumps on eyelids — Indicates high cholesterol levels.
2. Eye Conditions
Yellowing of the sclera — A warning sign of liver and gallbladder issues (jaundice).
Blood vessels in the sclera — Indicates liver stress causing vascular congestion.
Eye twitching — A warning sign of weakened immunity.
3. Functional Impairments of the Eyes
Inability to fully close eyes during sleep — Indicates gastrointestinal issues leading to overall muscle weakness.
Easy eye fatigue — Indicates liver dysfunction.
4. Eye Discharges
“Eye crust” — Yellow eye discharge indicates “pus” (inflammation).
Dry eyes — Can lead to eye diseases.
Excessive tearing — Occurs when liver function is weakened.
Mouth
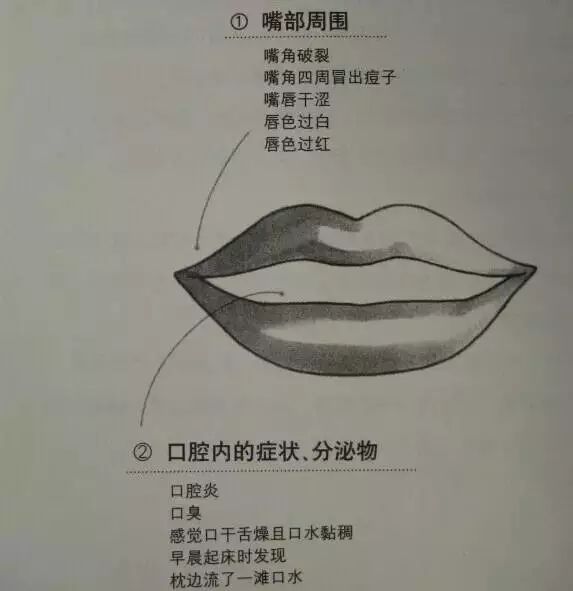
1. Symptoms Around the Mouth
Cracked corners of the mouth — Caused by gastritis leading to false appetite.
Acne around the corners of the mouth — Indicates weak gastrointestinal function.
Dry lips — Elevated body temperature can cause dry lips.
Pale lips — A warning sign of insufficient blood.
Red lips — Indicates excessive internal heat accumulation.
2. Oral Symptoms and Discharges
Stomatitis — Evidence of lowered immunity.
Bad breath — Can have five causes (active gastritis, indigestion, rhinitis, gum disease, dental plaque).
Feeling dry mouth with thick saliva — Indicates overall body dehydration.
Finding a pool of saliva on the pillow upon waking — Indicates weakened gastrointestinal function.
Tongue
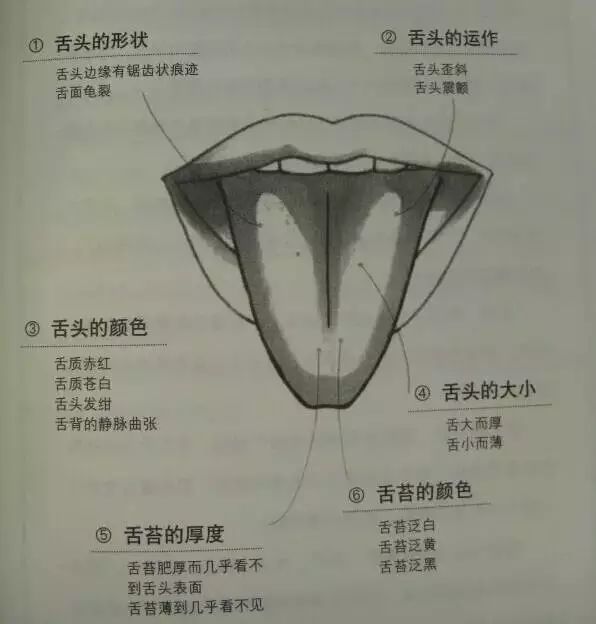
1. Shape of the Tongue
Jagged edges on the tongue — Indicates swelling due to excess water.
Cracked tongue surface — Indicates insufficient water.
2. Tongue Movement
Slanted tongue — A signal of cerebrovascular disorders.
Trembling tongue — Indicates body weakness.
3. Color of the Tongue
Red tongue body — Indicates elevated body temperature.
Pale tongue body — Indicates body weakness.
Purple tongue — A signal of overly thick blood.
Varicose veins on the tongue — A dangerous signal of poor blood flow.
4. Size of the Tongue
Large and thick tongue — Indicates excess water in the body.
Small and thin tongue — Indicates insufficient water in the body.
5. Thickness of the Tongue Coating
Thick tongue coating, almost obscuring the tongue surface — Indicates gastrointestinal disorders or serious diseases.
Thin tongue coating, almost invisible — Indicates body weakness or allergic constitution.
6. Color of the Tongue Coating
White tongue coating — Indicates low body temperature and reduced body function.
Yellow tongue coating — Indicates internal “heat”.
Black tongue coating — Indicates extreme physical exhaustion.
Nose
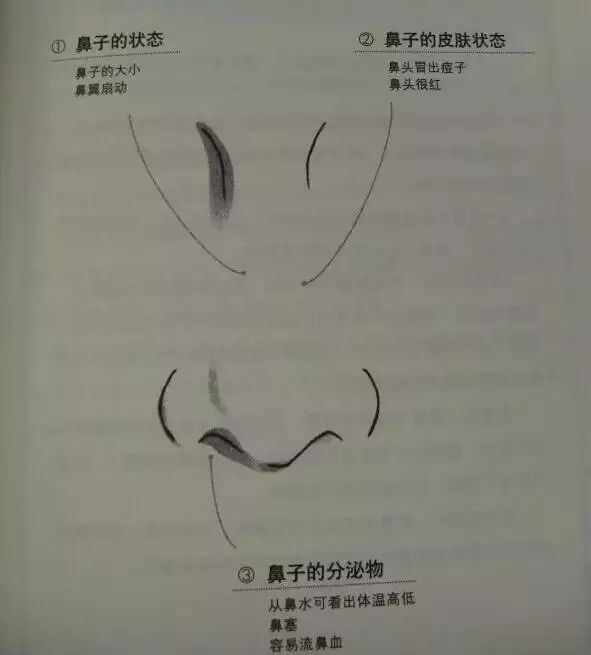
1. Condition of the Nose
Nose size — Indicates strength of respiratory function.
Nostrils flaring — Indicates respiratory distress.
2. Skin Condition of the Nose
Acne on the nose tip — May indicate respiratory issues.
Red nose tip — A signal of excessive alcohol consumption.
3. Nasal Discharges
Nasal discharge can indicate body temperature — Treatment for colds varies based on type of nasal discharge.
Nasal congestion — If ignored, can lead to systemic hypoxia.
Frequent nosebleeds — Often caused by weakened gastrointestinal function.
Cheeks
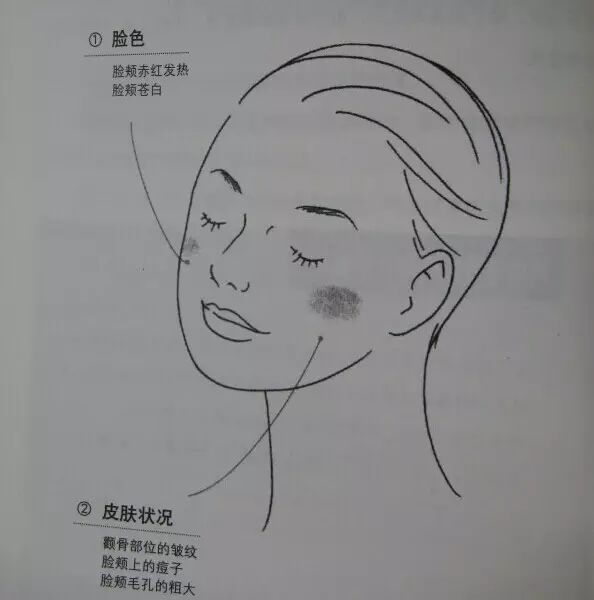
1. Complexion
Red and hot cheeks — Indicates abnormal body temperature regulation.
Pale cheeks — Indicates insufficient oxygen supply in the body.
2. Skin Condition
Wrinkles on the cheekbones — Mainly caused by UV exposure.
Acne on the cheeks — Indicates dietary excess or constipation.
Enlarged pores on the cheeks — Reduced sebum is the main cause of enlarged pores.
Teeth
1. Condition of the Teeth
Prone to cavities — A precursor to osteoporosis.
Gray teeth — Indicates the formation of cavities inside the teeth.
2. Condition of the Gums
Swollen gums — Indicates gastritis or fatigue.
Bleeding gums — Indicates gum inflammation or weak gastrointestinal function.
Hair
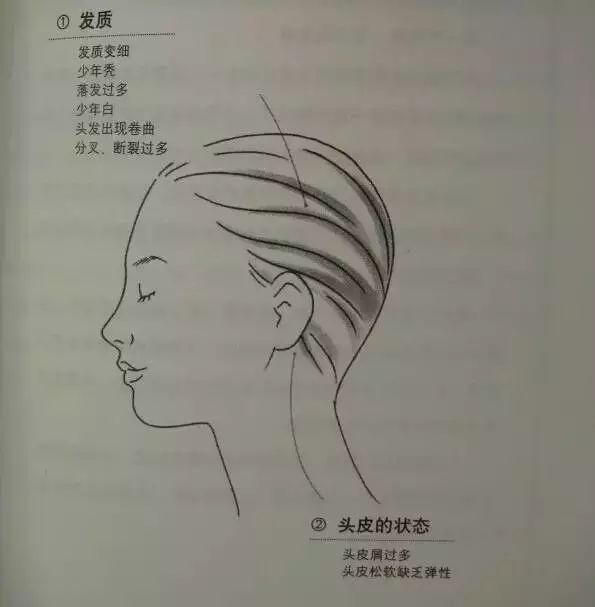
1. Hair Quality
Thinning hair — Indicates a tendency towards anemia or aging.
Adolescent baldness — Excessive fat intake can lead to hair depletion (reproductive organ decline).
Excessive hair loss — Can indicate early signs of disease.
Premature graying — Related to calcium levels and hair.
Curly hair — Indicates thinning hair quality.
Excessive split ends and breakage — Menstruation can cause hair anemia.
2. Scalp Condition
Excessive dandruff — Can be classified into “dry” (iron and protein supplementation) and “oily” (improving lipid metabolism, supplementing Vitamin B).
Soft and lack of elasticity scalp — Indicates symptoms of swelling.
Nails
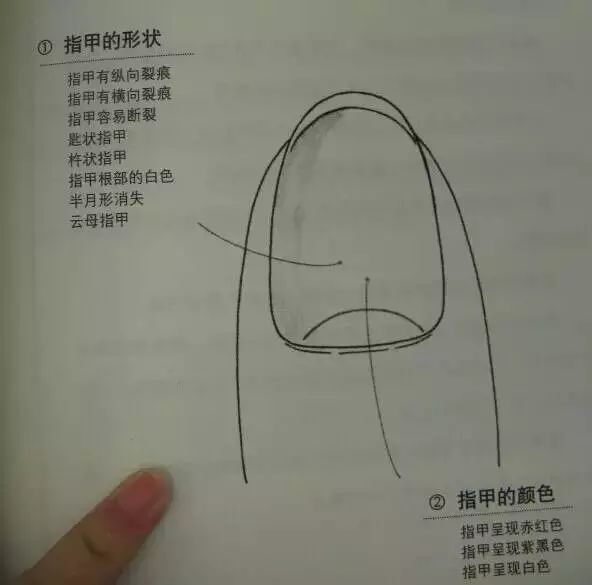
1. Shape of the Nails
Vertical ridges on the nails — Indicate “wrinkles” formed by aging.
Horizontal ridges on the nails — Indicate records of “past” (body discomfort).
Prone to breaking nails — Indicates anemia or poor liver function.
Spoon nails — A distress signal from the body (severe anemia, uterine fibroids, endometriosis; detailed examination recommended).
Clubbing nails (feeling of pressure deformation) — Common in individuals with heart disease.
Disappearance of the white crescent at the nail base — Indicates physical decline.
Dry nails — Indicate a state of dryness.
2. Color of the Nails
Red nails — Indicates overly thick blood (pay attention to cardiovascular health).
Purple-black nails — Indicate unclear blood or poor heart function.
White nails — Indicate a tendency towards anemia.

