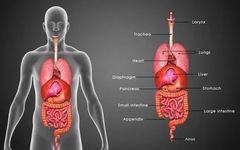
There are a total of five organs and six bowels in the human body. The five organs are: Heart (Xin), Liver (Gan), Spleen (Pi), Lung (Fei), and Kidney (Shen); the six bowels refer to the Gallbladder (Dan), Stomach (Wei), Large Intestine (Da Chang), Small Intestine (Xiao Chang), San Jiao (Triple Burner), and Bladder (Pang Guang).
The function of the five organs is to store essence and qi; the main physiological function of the six bowels is to receive and digest food, separate the clear from the turbid, transform essence, and expel waste from the body without retention.
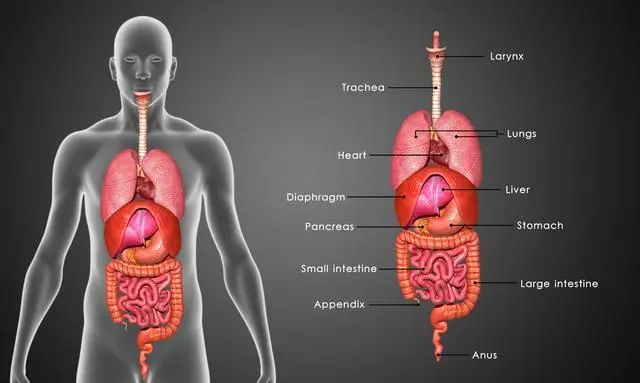
The Relationship Between the Five Organs and Health Preservation
Whenever there is an issue with the tendons, treating the Liver is appropriate.
Whenever there is an issue with the bones, treating the Kidney is appropriate.
Whenever there is an issue with the muscles, treating the Spleen and Stomach is appropriate.
Whenever there is an issue with the blood vessels, treating the Heart is appropriate.
Whenever there is an issue with the skin and hair, treating the Lung is appropriate.
 Functions of the Five Organs
Functions of the Five Organs
1. Heart (Xin): The Heart is the residence of the spirit, the master of blood, and the root of the pulse. It belongs to the Fire element;
Physiological Functions: It governs blood vessels; governs consciousness; the Heart opens to the tongue, connects with the pulse in the body, its manifestation is on the face, associated with joy, and its fluid is sweat. The Heart is interiorly related to the Small Intestine (Xiao Chang).
2. Lung (Fei): The Lung is the place of the corporeal soul, the master of qi, and belongs to the Metal element;
Physiological Functions: It governs qi and respiration; regulates the dispersing and descending of qi; controls the water passages; governs the hundred vessels and regulates the flow (stagnation); assists the Heart in regulating the circulation of qi and blood; the Lung connects to the throat, manifests on the skin, its expression is in the hair, opens to the nose, associated with worry, and its fluid is mucus. The Lung is interiorly related to the Large Intestine (Da Chang).

3. Spleen (Pi): The Spleen is the source of the generation of qi and blood, the foundation of postnatal life, and stores intention, belonging to the Earth element.
Physiological Functions: It governs transformation and transportation; governs the rising of clear qi; governs blood; opens to the mouth, connects with the flesh, governs the four limbs, its manifestation is on the lips, associated with thought, and its fluid is saliva. The Spleen is interiorly related to the Stomach (Wei).
4. Liver (Gan): The Liver is the place of the ethereal soul, the storehouse of blood, and the root of tendons, belonging to the Wood element, and governs the rising and movement.
Physiological Functions: It governs the smooth flow of qi; stores blood; opens to the eyes, connects with the tendons, its manifestation is in the nails, associated with anger, and its fluid is tears. The Liver is interiorly related to the Gallbladder (Dan).
5. Kidney (Shen): The Kidney is the foundation of pre-natal essence, stores will, and the waist is the organ of the Kidney, belonging to the Water element;
Physiological Functions: It stores essence, governs growth, development, and reproduction; governs water; governs the reception of qi; in the body, it is related to the bones, governs the production of marrow, its manifestation is in the hair, opens to the ears and the two yin (anus and perineum), associated with fear, and its fluid is saliva. The Kidney is interiorly related to the Bladder (Pang Guang).
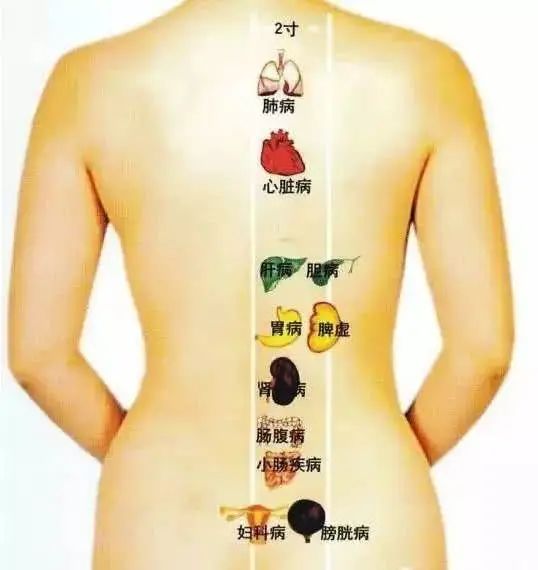
 Interactions Between the Five Organs
Interactions Between the Five Organs
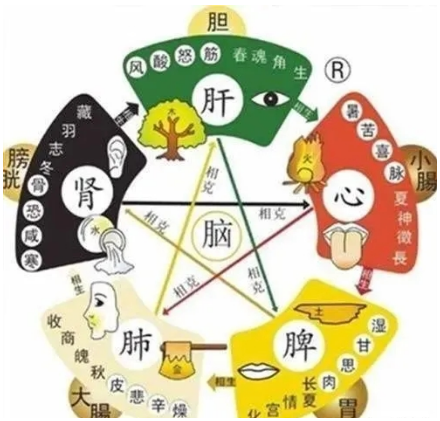
Five Organs Generating Each Other: Liver generates Heart, Heart generates Spleen, Spleen generates Lung, Lung generates Kidney, Kidney generates Liver.
Five Organs Overcoming Each Other: Liver overcomes Spleen, Spleen overcomes Kidney, Kidney overcomes Heart, Heart overcomes Lung, Lung overcomes Liver.
 The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Spirits
The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Spirits
The Five Spirits: Ethereal Soul (Hun), Spirit (Shen), Intention (Yi), Corporeal Soul (Po), Will (Zhi).
The Five Organs store: the Liver stores the Ethereal Soul, the Heart stores the Spirit, the Spleen stores Intention, the Lung stores the Corporeal Soul, and the Kidney stores Will (as stated in the Suwen, Chapter on the Five Qi).
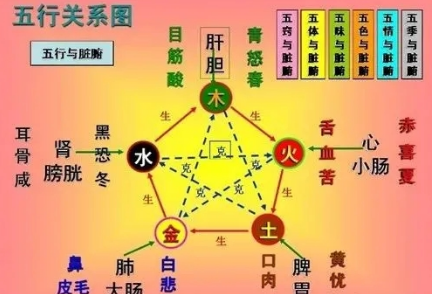
The Five Organs also generate the Five Emotions: the Heart corresponds to joy, the Liver corresponds to anger, the Spleen corresponds to thought, the Lung corresponds to worry, and the Kidney corresponds to fear. These emotions further develop into the seven emotions of joy, anger, sadness, thought, worry, fear, and shock.
 The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Fluids
The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Fluids
The Five Fluids: Tears, Sweat, Saliva, Mucus, and Spit.
The Suwen states, “The Five Organs transform into the Five Fluids: the Heart corresponds to Sweat, the Lung corresponds to Mucus, the Liver corresponds to Tears, the Spleen corresponds to Saliva, and the Kidney corresponds to Spit, which are known as the Five Fluids.
 The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Orifices
The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Orifices
The Five Orifices: Eyes, Tongue, Mouth, Nose, and Ears.
The Liver opens to the Eyes, the Heart opens to the Tongue, the Spleen opens to the Mouth, the Lung opens to the Nose, and the Kidney opens to the Ears.
 The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Tastes
The Relationship Between the Five Organs and the Five Tastes
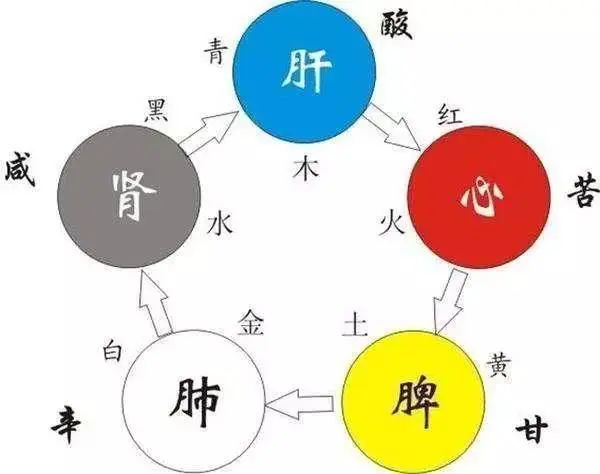
The Liver corresponds to Sour (affecting the tendons), the Heart corresponds to Bitter (affecting the blood), the Spleen corresponds to Sweet (affecting the flesh), the Lung corresponds to Pungent (affecting qi), and the Kidney corresponds to Salty (affecting the bones).
Emotional Conflicts
Excessive anger harms the Liver, excessive joy harms the Heart, excessive thinking harms the Spleen, excessive worry harms the Lung, excessive fear harms the Kidney; anger causes qi to rise, joy causes qi to relax, sadness causes qi to dissipate, fear causes qi to descend, cold causes qi to contract, heat causes qi to leak, shock causes qi to become chaotic, overwork causes qi to deplete, thinking causes qi to stagnate; joy overcomes sadness, sadness overcomes anger, anger overcomes thinking, thinking overcomes fear, fear overcomes joy.
Prolonged staring harms blood (Heart), prolonged lying harms qi (Kidney), prolonged sitting harms flesh (Spleen), prolonged standing harms bones (Lung), prolonged walking harms tendons (Liver).
 The Relationship Between the Six Bowels and Health Preservation
The Relationship Between the Six Bowels and Health Preservation
1. Gallbladder (Dan): Known as the official of decision-making.
Physiological Functions: It stores and excretes bile, and the Gallbladder governs decision-making.
2. Stomach (Wei): Known as the official of storage, when Stomach fire is excessive, hunger is quick, and pain in the upper teeth is related to the Stomach meridian, the Neiting point;
Physiological Functions: It receives and digests food, and the Stomach descends to harmonize.
3. Small Intestine (Xiao Chang): The official of receiving and transforming, it collects essence;
Physiological Functions: It governs receiving and transforming substances, separating the clear from the turbid, “the Small Intestine governs fluids.”
4. Large Intestine (Da Chang): The official of transmission, it expels waste, pain in the lower teeth is related to the Large Intestine meridian, the Hegu point and the Jaw point.
Physiological Functions: It transforms waste, and the Large Intestine governs fluids.
5. Bladder (Pang Guang): The official of the capital, it governs qi transformation.
Physiological Functions: It stores and excretes urine, relying on the qi transformation function of the Kidney.
6. San Jiao (Triple Burner): The official of regulation, it governs the water passages, overseeing the five organs and six bowels and the internal and external pathways;
Physiological Functions: It facilitates the flow of original qi, governs the qi mechanism and transformation, and is the pathway for the movement of water and fluids.
Click the text below to learn more exciting content:
The World's Most Unique Education - Traditional Chinese Medicine
Promoting TCM Culture for the Health of the People - Intangible Cultural Heritage - Baicao Tongjing Huoluo
Intangible Heritage Baicao Tongluo Shaolin Zhequanta: Spreading TCM Culture, Leading a Healthy Life
Intangible Heritage Baicao Tongluo Shaolin Zhequanta's Nine Home Remedies
Inheriting TCM Adjustment Therapy - Nine Methods for Cervical Spine Adjustment