Author: Professor Li Yan, Professor Tian Jianhui
Source: Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Oncology Clinical Medicine Center
Expert Introduction

Dr. Li Yan, Chief Physician, Professor, Doctor of Medicine, PhD Supervisor
Leader of the Oncology Clinical Medicine Center at Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Honorary Director of the Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Oncology Research Institute, National Natural Science Foundation Review Expert, Member of the Shanghai Science and Technology Progress Award Review Expert Database, Vice President of the Gaitong Branch of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chairman of the Oncology Professional Committee of the Shanghai Traditional Medicine Engineering Association, Vice Chairman of the Oncology Professional Committee of the Shanghai Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Executive Director of the Oncology Professional Committee of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Executive Member of the Oncology Professional Committee of the Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine, Executive Member of the Geriatric Oncology Professional Committee of the Chinese Geriatrics Society, Executive Committee Member of the Geriatric Oncology Professional Committee of the Chinese Geriatrics Society, Executive Member of the Oncology Professional Committee of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and Executive Member of the Oncology Branch of the Chinese Ethnic Medicine Association.
Introduction
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. For early-stage lung adenocarcinoma post-surgery, recurrence and metastasis remain the most significant factors affecting patient survival. However, the use of adjuvant therapy after surgery for early lung cancer remains controversial, and finding effective strategies to extend the disease-free survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients has become an urgent clinical need.
The Oncology Clinical Medicine Center of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, led by Professor Li Yan and Director Professor Tian Jianhui, has systematically conducted research on the prevention and control of lung cancer metastasis using traditional Chinese medicine. They have established the subclinical theory of “Zheng Xu Fu Du” (supporting the righteous and expelling the toxic) in cancer metastasis and conducted clinical and basic research to further validate it. Professor Tian Jianhui, as the founder of the “Zheng Xu Fu Du” theory, has explained the core pathogenesis of lung cancer recurrence and metastasis from a TCM perspective. This article introduces the clinical research results of the Fu Zheng Qu Xie (FZQX) formula developed by Professor Li Yan based on the TCM concept of “supporting the righteous and expelling the toxic” in anti-tumor treatment applied to lung cancer.
The research team of Professor Li Yan collaborated with Professor Jiang Lei’s team from the Thoracic Surgery Department of Tongji University Affiliated Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital and the Integrative Medicine team to conduct a dual-center, prospective cohort study that further confirmed the preventive effect of the FZQX formula on recurrence and metastasis after surgery for early lung adenocarcinoma and elucidated the molecular mechanism by which the FZQX formula inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression by regulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). The research results were published in the influential journal Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity (IF: 6.543). [Oncology News] invites you to explore together!
Research Design
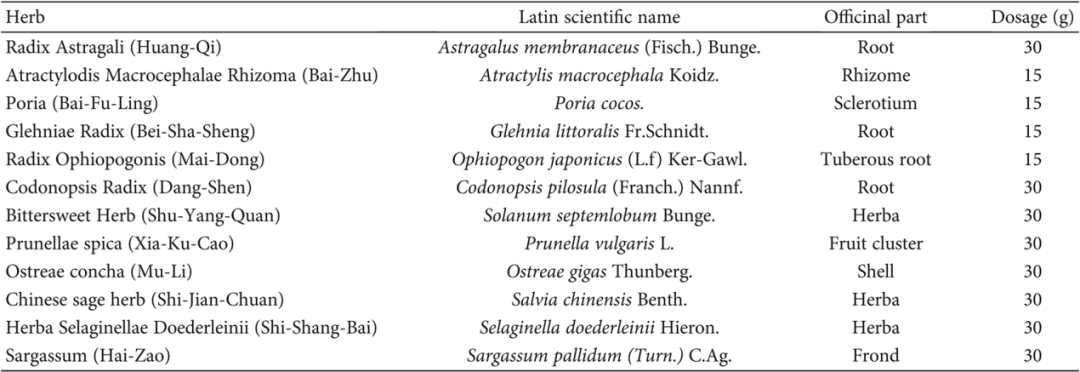
The study recruited 465 patients with early-stage lung adenocarcinoma who underwent surgical resection, among which 224 patients from Shanghai Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine received FZQX formula treatment and regular clinical follow-up (treatment group), while 241 patients from Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital only received regular follow-up (control group). The study also recruited 110 healthy volunteers as a healthy control group. The composition of the FZQX formula is shown in Table 1. The study aimed to evaluate the clinical effect of the FZQX formula in preventing recurrence and metastasis after surgery for early lung adenocarcinoma and to explore its potential mechanisms.
Table 1: Composition of the FZQX Formula
The FZQX formula can improve the quality of life, 3-year disease-free survival (DFS), and immune function after surgery for early lung adenocarcinoma.
Improving Quality of Life
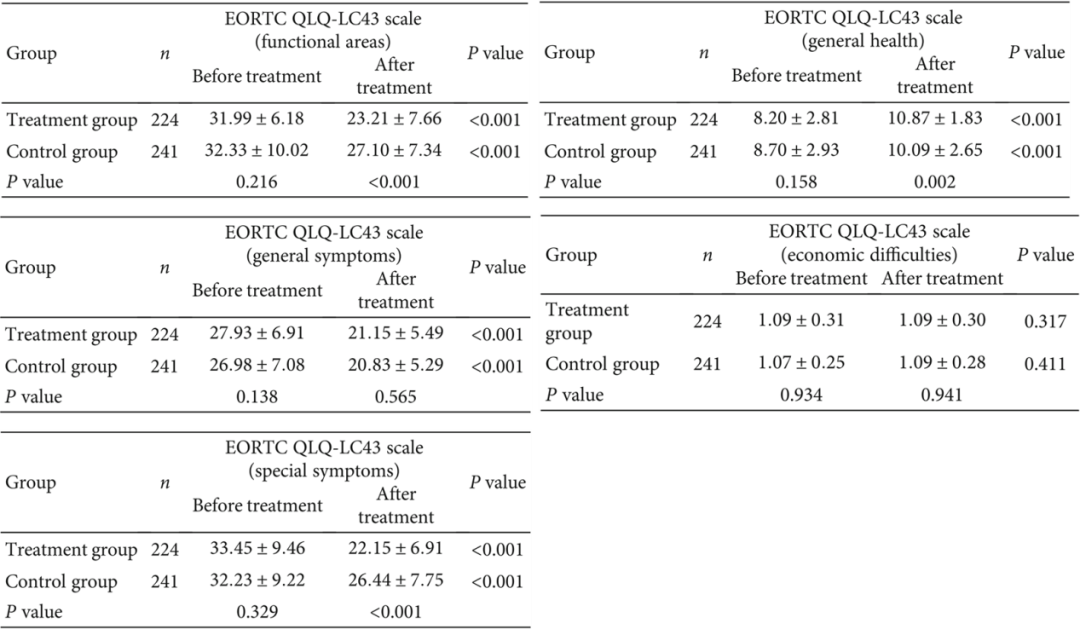
According to the quality of life questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-LC43) (Table 2), all patients showed varying degrees of improvement in quality of life after 6 months of treatment or follow-up alone, with patients who received FZQX formula intervention showing better improvements in functional areas, specific symptoms, and general health.
Table 2: EORTC QLQ-LC43 Scale
From the Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) scores (Tables 3, 4), the treatment group patients’ KPS scores (87.14 vs. 83.11) and improvement rates (58.5% vs. 41.5%) were significantly higher than those of the control group after FZQX formula intervention.
The improvement rate is defined as the proportion of patients with a KPS score increase of >10, while deterioration is defined as a KPS score decrease of >10.
Table 3: KPS Scores
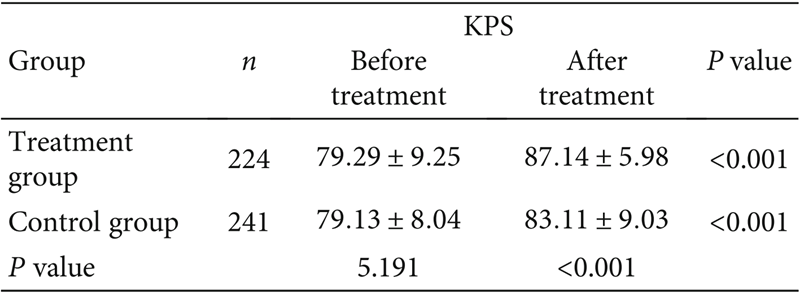
Table 4: Quality of Life Improvement

Delaying Recurrence and Metastasis
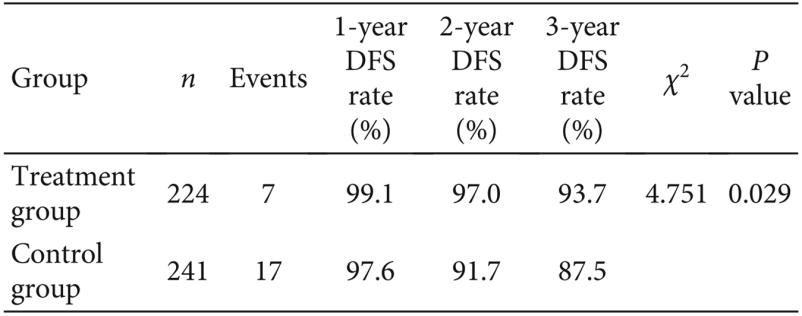
A total of 7 patients (3.1%) in the treatment group experienced recurrence, while 17 patients (7.1%) in the control group did. The incidence of disease-free survival (DFS) at 1, 2, and 3 years in the treatment group receiving FZQX formula intervention was higher than that of the control group (Table 5), indicating that the FZQX formula can significantly reduce the postoperative 3-year recurrence rate and prolong DFS.
Table 5: Disease-Free Survival (DFS)
Positive Regulation of Immune Function
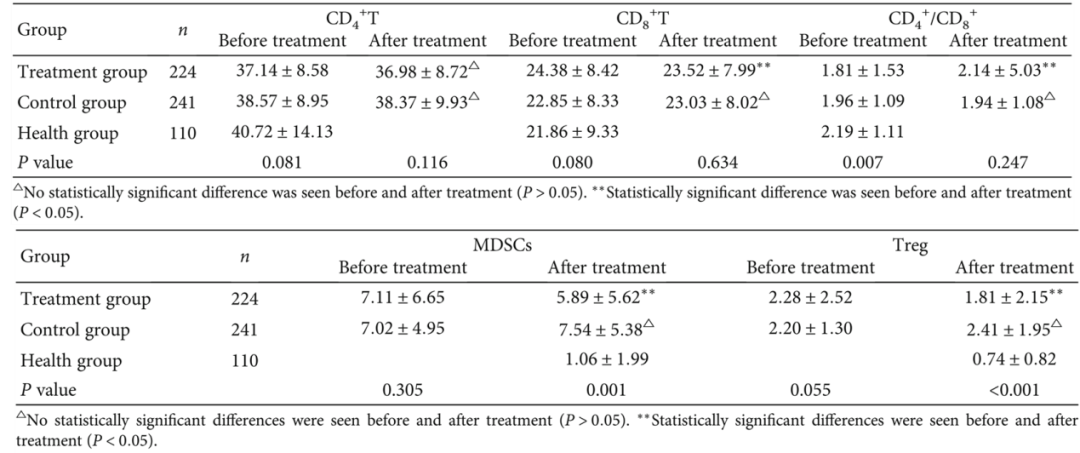
From the peripheral blood immune indicators (Table 6), the negative immune indicators (CD8+ T cells, MDSCs, Treg) significantly decreased in the treatment group receiving FZQX formula intervention, while the positive immune indicators (CD4+ T/CD8+ T) increased, and the immune function levels were closer to those of the healthy volunteer group compared to the control group. This provides strong support for the role of the FZQX formula in regulating immune function in patients after surgery for early lung adenocarcinoma.
Table 6: T Cell Subsets, MDSCs, and Treg
Conclusion: The above clinical results confirm that the FZQX formula can effectively improve the quality of life of patients after surgery for early lung adenocarcinoma and enhance long-term survival rates, which may be related to the regulation of the proportion of relevant immune cells in tumor patients.
Exploration of the Potential Immune Mechanism of the FZQX Formula Against Tumors
Based on the positive regulatory effect of the FZQX formula on immune function, the study subsequently verified its anti-tumor effect through a series of in vivo and in vitro experiments and elucidated its potential mechanisms.
The FZQX formula can inhibit tumor growth in vivo
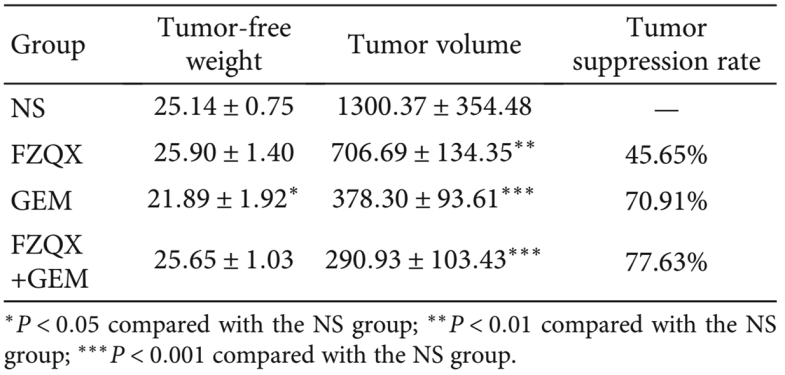
In our preliminary clinical study, we found that the FZQX formula reduced the level of MDSCs in the peripheral blood of lung adenocarcinoma patients by establishing a tumor xenograft model in C57BL/6 mice through subcutaneous injection of Lewis lung cancer cells (LLC) and using gemcitabine to establish an MDSC clearance xenograft model: saline group (NS), FZQX formula group (FZQX), gemcitabine group (GEM), FZQX formula + gemcitabine group (G+F).
It was observed that the tumor volume and weight in the three intervention groups were significantly reduced. Compared to the GEM group, the FZQX group and G+F group mice had higher tumor-free weights (Table 7), indicating that the FZQX formula can effectively inhibit tumor growth with fewer side effects.
Table 7: Inhibitory Effect of Each Group on Mouse Xenograft Tumors
Using Western blot and immunofluorescence to detect the expression levels of proteins related to MDSCs immune suppression and tumor progression (Figure 1), it was found that compared to the control group, the expression levels of MMP9, PTGER2, IL-1β, p-STAT3, Bcl-2, and pNF-κB proteins were significantly reduced in the three intervention groups.
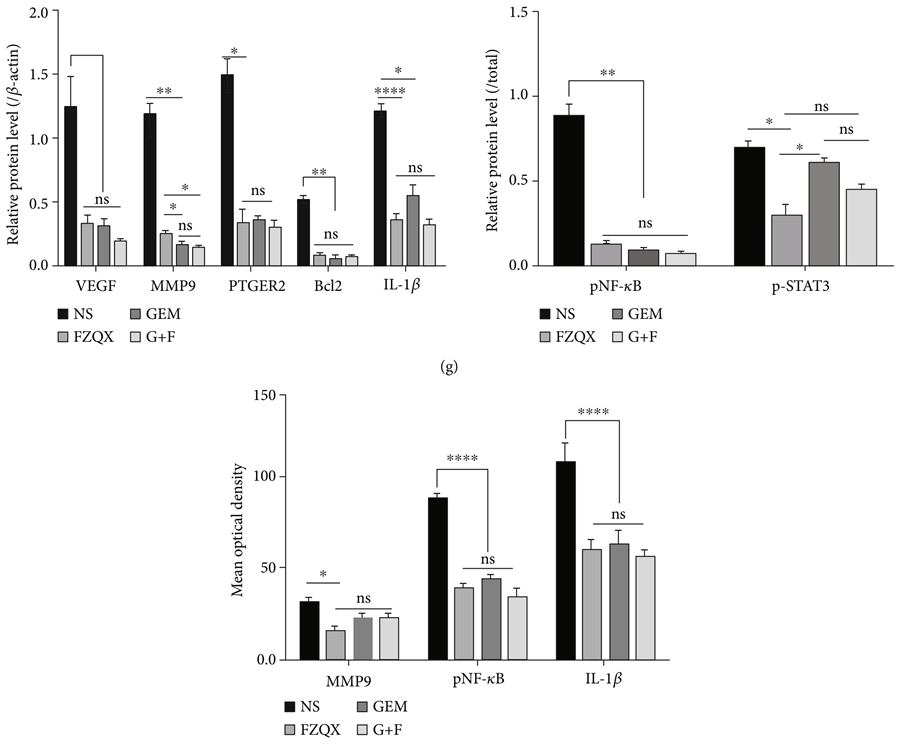
Figure 1: Western Blot Optical Density Analysis and Quantification of Immunofluorescence Signal Intensity
Conclusion: Through the MDSC clearance xenograft model, it was confirmed that the FZQX formula can effectively inhibit tumor growth in vivo with fewer side effects, and its efficacy is similar to that of the MDSC clearance model, suggesting that MDSCs may be involved in the biological process of the FZQX formula intervention in lung cancer progression.
The Key Inhibitory Role of MDSCs
The immune suppressive function of MDSCs involves various potential mechanisms, primarily associated with high expression of Arg-1 and ROS. To further explore the role of MDSCs in the tumor immune microenvironment, we examined the infiltration of immune cells in the spleen and tumor tissues. Flow cytometry results showed (Figure 2) that the infiltration of MDSCs and Treg in the tumor and spleen tissues of mice in the three intervention groups decreased, with no significant differences between groups.
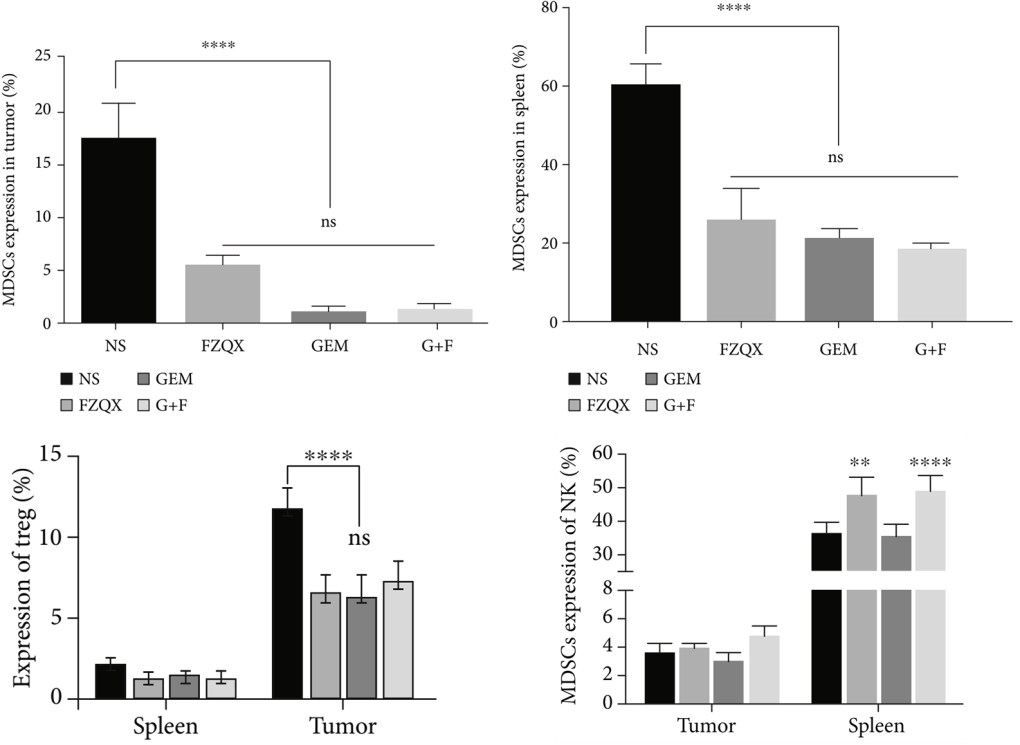
Figure 2: Expression Levels of MDSCs, Treg, and NK Cells in Tumor and Spleen Tissues of Each Group
Compared to the control group and GEM group, both the FZQX group and G+F group promoted the expression of the NKG2D receptor in spleen tissues. RT-qPCR and ELISA results showed (Figure 3) that the expression of Arg-1 and iNOS mRNA in tumor tissues of the three intervention groups was significantly downregulated, and the serum IL-1β concentration significantly decreased; only the G+F group showed a significant decrease in serum CCL4 concentration.
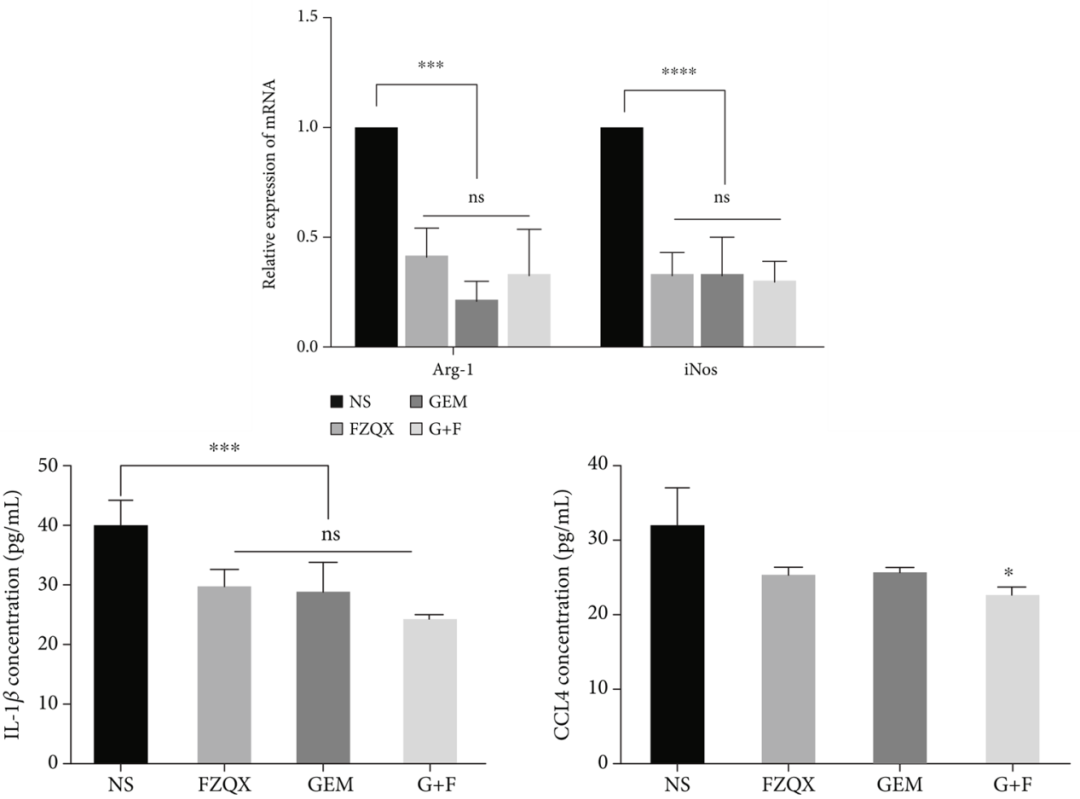
Figure 3: Expression Levels of Arg-1 and iNOS mRNA and Concentrations of IL-1β and CCL4
Conclusion: The above results confirm that MDSCs are one of the key cell populations in the prevention of lung cancer recurrence and metastasis by the FZQX formula.
The FZQX Formula Regulates MDSCs to Inhibit LLC/A549 Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion
Flow cytometry analysis showed (Figure 4) that the FZQX formula significantly reduced the level of MDSCs in a dose-dependent manner, and as the concentration of the FZQX formula increased, the mRNA levels of MDSC activation-related genes (Arg-1, iNOS, NO) significantly decreased.
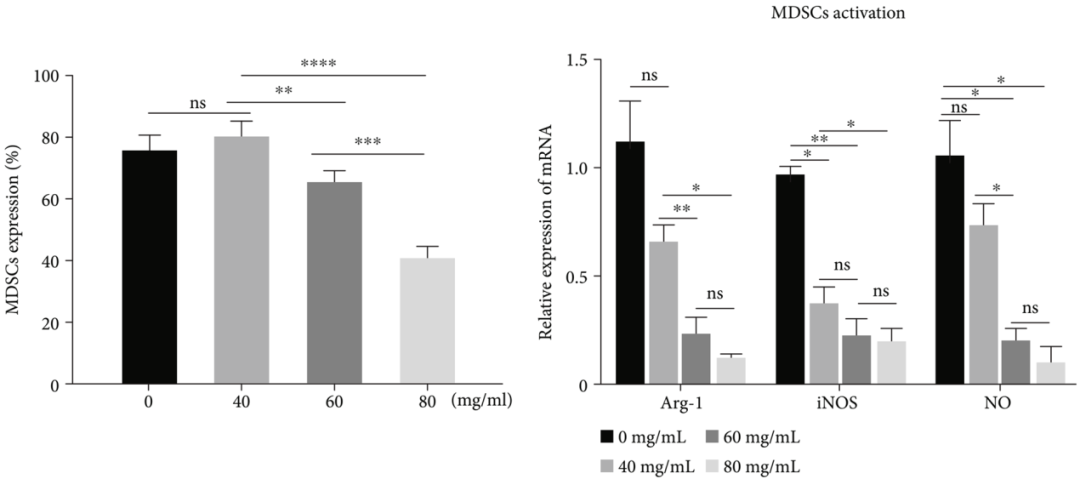
Figure 4: Frequency of MDSCs and mRNA Expression Levels of MDSC Activation-Related Genes at Different Drug Concentrations
Considering the critical role of MDSCs in promoting tumor immune evasion in the tumor microenvironment, we established an in vitro co-culture system of MDSCs and LLC/A549 to simulate the immune microenvironment of lung cancer. The results of colony formation experiments (detecting LLC/A549 cell proliferation), wound healing assays (detecting LLC/A549 cell migration), and Transwell invasion assays (detecting LLC/A549 cell invasion) showed that MDSCs-CM group significantly promoted the proliferation, migration, and invasion of LLC/A549 cells; while the FZQX-CM group significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion activity of the cells, showing a significant difference from the FZQX group.
Conclusion: The above functional experiments indicate that the FZQX formula can inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion of LLC/A549 cells by regulating the quantity and function of MDSCs.
The FZQX Formula Inhibits Lung Cancer Progression by Suppressing the IL-1β/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in MDSCs
Further exploration of the potential molecular mechanisms by which the FZQX formula regulates MDSCs to intervene in lung cancer progression was conducted using activators and inhibitors of MDSC-related signaling pathways.
In vitro experiments found (Figure 5) that IL-1β activators could promote the phosphorylation of key proteins in the IL-1β/NF-κB signaling pathway and significantly upregulate the expression of tumor proliferation and migration-related proteins; while the expression levels of PCNA, Bcl-2, VEGFR, and MMP9 proteins in the FZQX group were significantly lower than those in the IL-1β group. This indicates that IL-1β plays a key role in MDSC-mediated lung cancer cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis. Additionally, there was no significant difference in protein expression between the FZQX group and the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) group, indicating that the inhibitory effect of the FZQX formula is comparable to that of IL-1RA.
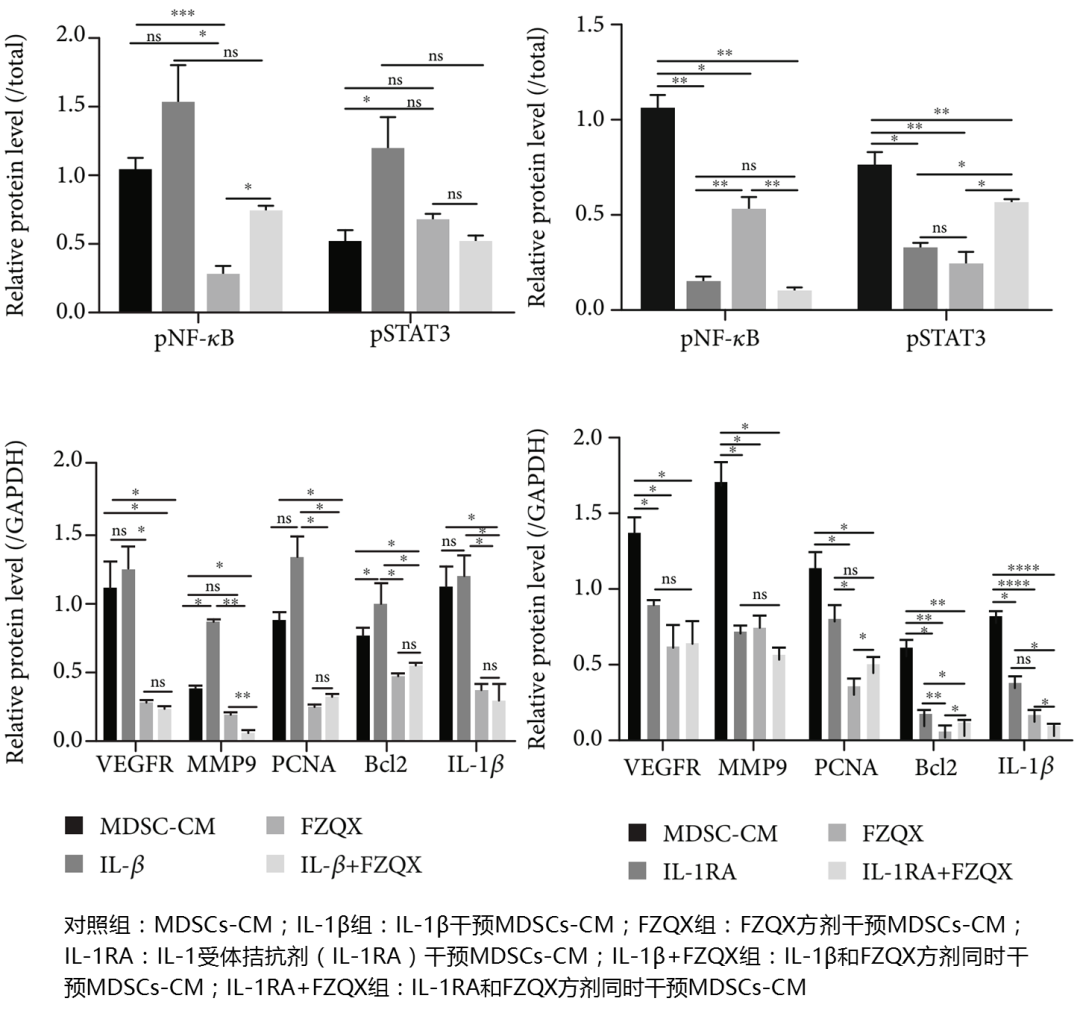
Figure 5: Expression Levels of Key Proteins Related to Tumor Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion (VEGFR, MMP9, PCNA) and Key Proteins Involved in the Signaling Pathway (Bcl2, IL-1β, NF-κB, STAT3) in the IL-1β/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
In vivo experiments found (Figure 6) that NF-κB inhibitors could inhibit the IL-1β/NF-κB signaling pathway and significantly downregulate the expression levels of tumor progression-related proteins (MMP9, PCNA, IL-1β) and MDSC proliferation and activation-related proteins (COX2, PDL1). There was no significant difference in protein expression levels between the NF-κB inhibitor group and the NF-κB inhibitor + F group.
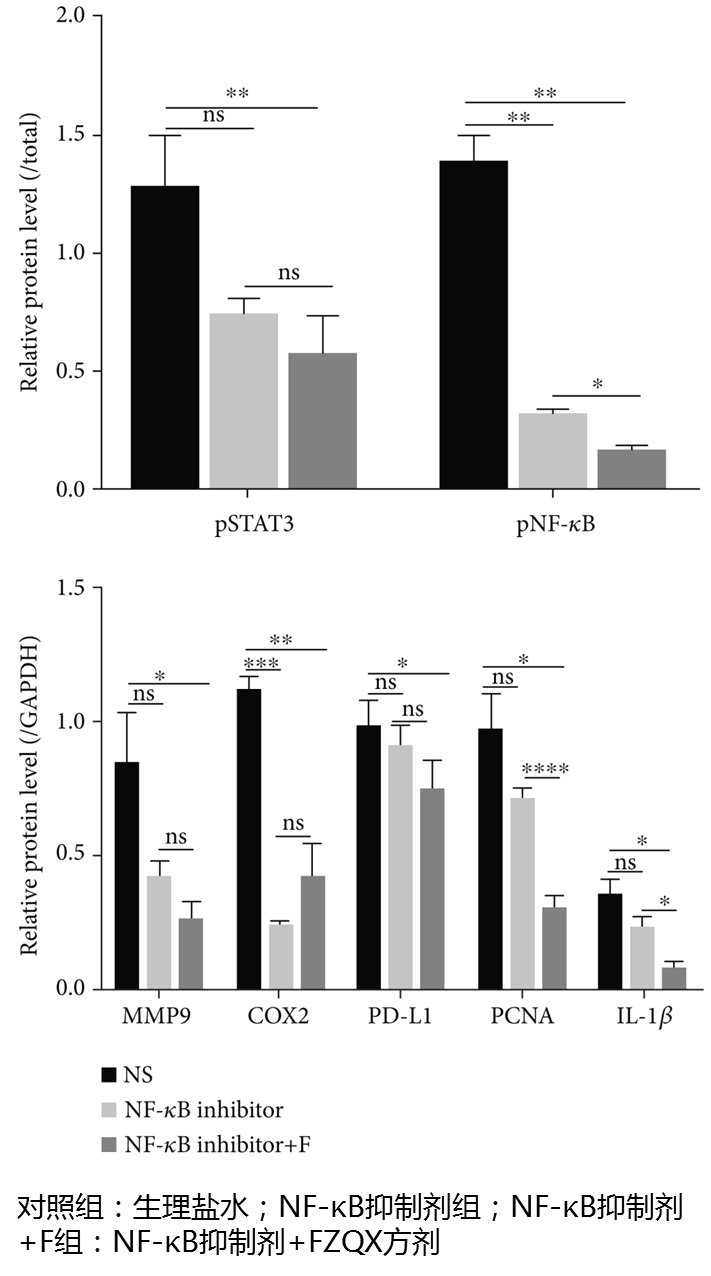
Figure 6: Expression Levels of Tumor Progression-Related Proteins and MDSC-Related Key Proteins in the IL-1β/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Conclusion: In vivo and in vitro experiments reveal that inhibiting the IL-1β/NF-κB signaling pathway is one of the important mechanisms by which the FZQX formula regulates MDSCs to prevent lung cancer progression.
In summary, clinical research confirms that the FZQX formula can effectively improve the 3-year disease-free survival and quality of life of patients after surgery for early lung adenocarcinoma, while increasing positive immune indicators and decreasing negative immune indicators in peripheral blood. A series of in vivo and in vitro experiments confirm that targeting MDSCs is a key step in the FZQX formula’s role in inhibiting lung adenocarcinoma progression, while the IL-1β/NF-κB signaling pathway is one of the key pathways through which the FZQX formula regulates MDSCs to prevent lung adenocarcinoma recurrence and metastasis.
Commentary
Thanks to the rapid progress of interdisciplinary research between traditional Chinese medicine and oncology, immunology in recent years, the exact efficacy and scientific basis of traditional Chinese medicine in preventing and treating malignant tumors are increasingly recognized. The research team of Professor Li Yan at the Oncology Clinical Medicine Center of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, guided by the academic thought of “supporting the righteous and treating cancer” by Master Liu Jiaxiang, has achieved significant research results in the prevention and treatment of lung cancer through years of clinical experience accumulation and academic exploration: the research results indicate that the treatment group patients who received the Fu Zheng Qu Xie formula intervention had higher 1-year, 2-year, and 3-year disease-free survival rates than the control group patients who only received follow-up, and the quality of life of the treatment group patients significantly improved. The research also confirmed that targeting MDSCs and regulating the tumor immune microenvironment is an important aspect of the FZQX formula’s role in inhibiting lung cancer recurrence and metastasis, while the IL-1β/NF-κB signaling pathway is a key pathway through which the FZQX formula exerts its regulatory effects.
This high-quality article on the clinical application and potential mechanism exploration of the Fu Zheng Qu Xie method in preventing recurrence and metastasis after surgery for early lung adenocarcinoma presents a typical research approach worth emulating for colleagues in the field of traditional Chinese medicine!
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity is a high-level international journal related to oxidative medicine, covering various research topics including aging, tumors, and immunity. The publication of this research result indicates that traditional Chinese herbal formulas have gained internationally recognized evidence-based medical support and reveals the potential mechanisms of the Fu Zheng Qu Xie formula in intervening in lung cancer recurrence and metastasis from the perspective of regulating the tumor immune microenvironment, establishing the important position of both “supporting the righteous” and “expelling the toxic” in the prevention and treatment of lung cancer, enriching the academic connotation of the thought of “supporting the righteous in treating cancer”, and promoting the international dissemination of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of malignant tumors. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81673947, 81973795) and the Shanghai Municipal Project for Accelerating the Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2018-2020) (ZY(2018-2020)CCCX-4001-01).
We look forward to more academic achievements in “Chinese Medicine Explained in Western Terms” to promote the charm of traditional Chinese medicine!
References
Zhang SF, Chen WQ, Wang YL, et al. Chinese Herbal Prescription Fu-Zheng-Qu-Xie Prevents Recurrence and Metastasis of Postoperative Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Prospective Cohort Study Followed with Potential Mechanism Exploration. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2021,2021:6673828.
Editor: Oncology News – Bree Layout Editor: Oncology News – Bree Copyright Statement: This article is for the reference of medical professionals only and may not be published or distributed without the author’s permission. At the same time, individuals are welcome to share, and any other media or website wishing to reproduce or quote the content owned by this website must obtain authorization and indicate “Reprinted from: Liangyi Hui – Oncology Doctor APP” in a prominent position.