
Zhang Zhongjing Medical Path teaches you to differentiate syndromes and provide individualized plans. Follow

Danxi Medical Path provides in-depth TCM content and health knowledge. Follow

Huangdi Medical Path Practical TCM knowledge shared daily. Follow

Zhongjing Medical Path Zhongjing Traditional Medicine, classics passed down through generations. Follow

Elephant Medical Path Great sounds are rare, great forms are formless. Yin and Yang complement each other, and the medical path merges. Follow

Angelica Medical Path Angelica Medical Path, the way of Qi and Huang. Follow

Yuan Zhi Medical Path Those who follow this account have learned skills. Follow

Apricot Forest Medical Narrative Those who love TCM are all here. Follow

Apricot Forest Medical Technique Path TCM practitioners, welcome home. Follow
Click on the “Follow” text above, or click on the public account name to follow.
What exactly is Phlegm-Dampness?
Phlegm-Dampness is a concept in TCM. “Phlegm” can be divided into tangible phlegm and intangible phlegm. Tangible phlegm can be understood as the phlegm produced during coughing, while TCM usually refers to intangible phlegm.
Dr. Yang Zhong (Chief Physician, Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Capital Medical University) states: 70% of the human body is composed of water, referred to as body fluids in TCM. These fluids transport nutrients to various parts of the body and also help eliminate waste. If the circulation of body fluids is disrupted, it will first lead to the formation of dampness. When dampness cannot be properly transformed, it will condense into phlegm. Therefore, the essence of phlegm-dampness is a part of body fluids, but it manifests in a pathological state.

Characteristics of Phlegm-Dampness: Phlegm-dampness is a condition that affects the entire body. It is characterized by heaviness and stickiness, making it difficult to eliminate once formed. Prolonged presence in the body may lead to malignant changes. Phlegm-dampness is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors.
Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution are prone to gastrointestinal tumors, colorectal cancer, lymphoma, and brain tumors.
How to distinguish a phlegm-damp constitution?
Dr. Yang shared the three major characteristics of a phlegm-damp constitution. Let’s take a look; hopefully, no one has them~
1. Observe Obesity
In normal individuals, abdominal fat does not feel bloated, and there is no significant discomfort.
In individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution, obesity is characterized by a soft and full abdomen, with a feeling of heaviness in the body.
2. Observe Stool
Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution often have sticky stools.
3. Observe the Tongue
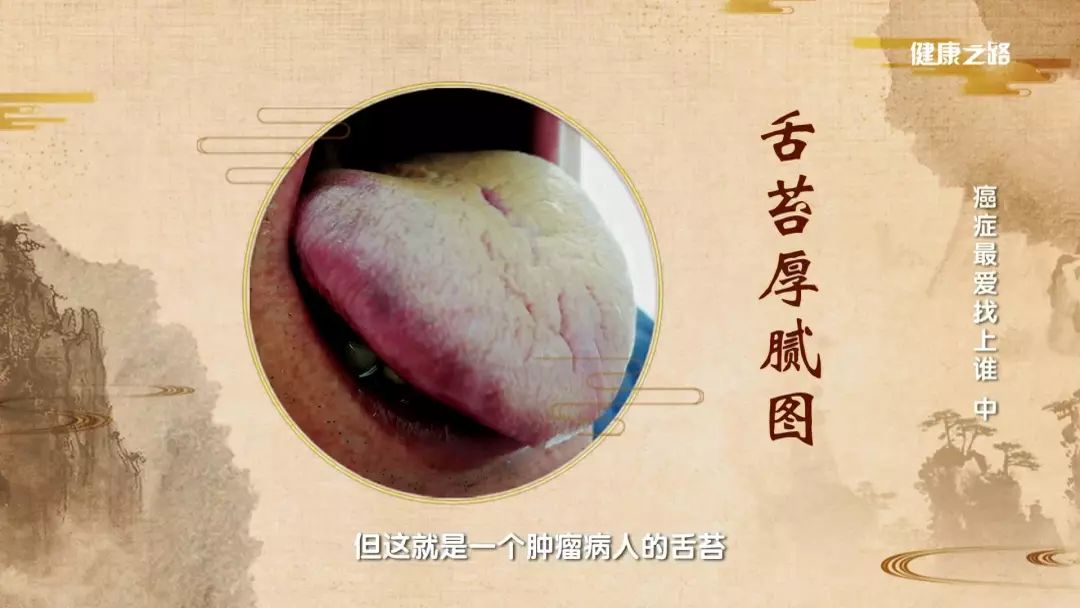
Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution usually have a thick and greasy tongue coating and may experience a bitter taste in the mouth.
How to prevent the formation of phlegm-dampness?
The following habits can lead to the formation of phlegm-dampness:
1. Love to eat cold food: Long-term consumption of cold drinks harms the spleen and stomach, primarily damaging the spleen yang. When the spleen’s function weakens, the circulation of body fluids is obstructed, leading to phlegm-dampness;
2. Love to sit for long periods: Movement promotes yang. Normal circulation of qi and blood requires movement; prolonged sitting can damage spleen yang, resulting in phlegm-dampness;

3. Alcohol abuse: Alcohol is considered a heavy flavor in medicine. Rich and heavy flavors are most harmful to spleen yang. Long-term alcohol abuse can weaken spleen yang, disrupt body fluid circulation, and lead to phlegm-dampness;
4. Frequent consumption of fatty meat: Regular consumption of fatty meat harms spleen yang, which over time can lead to a phlegm-damp constitution.
Once we understand the causes of phlegm-dampness, we also know how to prevent it~
Ensuring adequate sleep, maintaining regular exercise, and following a clean diet can effectively prevent phlegm-dampness. Additionally, a positive and pleasant mindset is essential, as joy promotes yang, and sufficient yang energy can help resolve phlegm-dampness.
Moxibustion for Dampness Removal: Remarkable Effects
The body’s yang energy is akin to the sun in the sky. If our yang energy is sufficient, even if dampness appears, it can be evaporated. If our internal yang energy is insufficient, dampness spreads like fog, unable to be transformed or expelled.
Moxibustion has excellent effects in replenishing yang energy and dispelling dampness. Moxibustion on the following commonly used acupoints can effectively expel dampness.
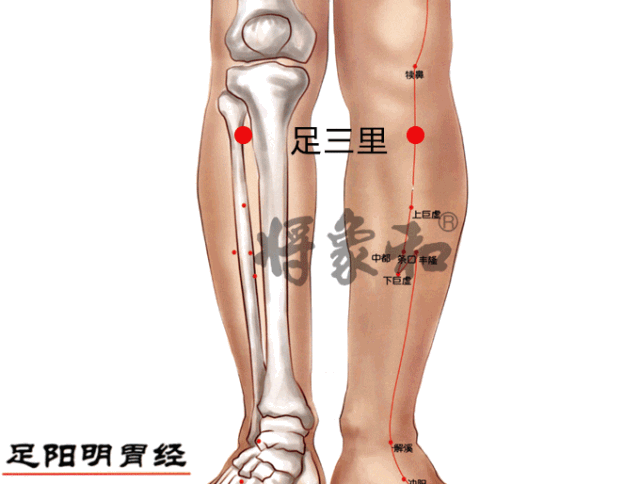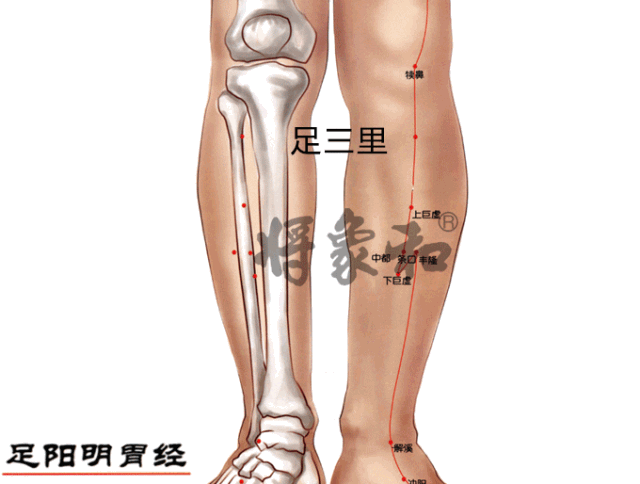
Acupoints: Zhongwan (Zhongwan Point), Guanyuan (Guanyuan Point), Zusanli (Zusanli Point), Fenglong (Fenglong Point), Yinlingquan (Yinlingquan Point)
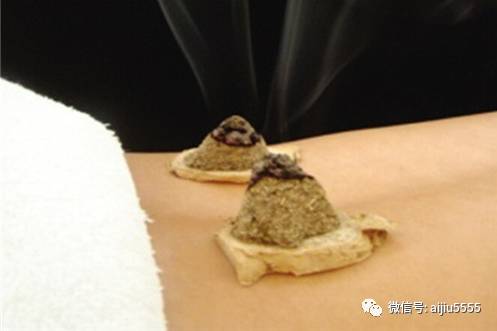
Method: Use ginger moxibustion on Zhongwan and Guanyuan points for 5 cones each; Zusanli, Yinlingquan, and Fenglong points for 3 cones on each side each time.
Perform moxibustion for 3 days and rest for one day.
Phlegm-Damp Constitution is Prone to Cancer: Do You Have These Three Characteristics?
What exactly is Phlegm-Dampness?
Phlegm-Dampness is a concept in TCM. “Phlegm” can be divided into tangible phlegm and intangible phlegm. Tangible phlegm can be understood as the phlegm produced during coughing, while TCM usually refers to intangible phlegm.
Dr. Yang Zhong (Chief Physician, Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Capital Medical University) states: 70% of the human body is composed of water, referred to as body fluids in TCM. These fluids transport nutrients to various parts of the body and also help eliminate waste. If the circulation of body fluids is disrupted, it will first lead to the formation of dampness. When dampness cannot be properly transformed, it will condense into phlegm. Therefore, the essence of phlegm-dampness is a part of body fluids, but it manifests in a pathological state.

Characteristics of Phlegm-Dampness: Phlegm-dampness is a condition that affects the entire body. It is characterized by heaviness and stickiness, making it difficult to eliminate once formed. Prolonged presence in the body may lead to malignant changes. Phlegm-dampness is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors.
Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution are prone to gastrointestinal tumors, colorectal cancer, lymphoma, and brain tumors.
How to distinguish a phlegm-damp constitution?
Dr. Yang shared the three major characteristics of a phlegm-damp constitution. Let’s take a look; hopefully, no one has them~
1. Observe Obesity

In normal individuals, abdominal fat does not feel bloated, and there is no significant discomfort.
In individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution, obesity is characterized by a soft and full abdomen, with a feeling of heaviness in the body.
2. Observe Stool
Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution often have sticky stools.
3. Observe the Tongue
Individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution usually have a thick and greasy tongue coating and may experience a bitter taste in the mouth.

How to prevent the formation of phlegm-dampness?
The following habits can lead to the formation of phlegm-dampness:
1. Love to eat cold food: Long-term consumption of cold drinks harms the spleen and stomach, primarily damaging the spleen yang. When the spleen’s function weakens, the circulation of body fluids is obstructed, leading to phlegm-dampness;
2. Love to sit for long periods: Movement promotes yang. Normal circulation of qi and blood requires movement; prolonged sitting can damage spleen yang, resulting in phlegm-dampness;
3. Alcohol abuse: Alcohol is considered a heavy flavor in medicine. Rich and heavy flavors are most harmful to spleen yang. Long-term alcohol abuse can weaken spleen yang, disrupt body fluid circulation, and lead to phlegm-dampness;
4. Frequent consumption of fatty meat: Regular consumption of fatty meat harms spleen yang, which over time can lead to a phlegm-damp constitution.

Once we understand the causes of phlegm-dampness, we also know how to prevent it~
Ensuring adequate sleep, maintaining regular exercise, and following a clean diet can effectively prevent phlegm-dampness. Additionally, a positive and pleasant mindset is essential, as joy promotes yang, and sufficient yang energy can help resolve phlegm-dampness.
Phlegm-Resolving and Dampness-Removing Herbal Tea
Dr. Yang recommends a herbal tea suitable for individuals with a phlegm-damp constitution for daily consumption:

The root cause of phlegm-dampness is spleen deficiency. Fu Ling (Poria), Bai Zhu (White Atractylodes) strengthen the spleen, Chen Pi (Dried Tangerine Peel) and Pei Lan (Eclipta) dispel dampness. If you have symptoms of obesity, thick tongue coating, and sticky stools, you can use this simple formula for self-regulation.
Moxibustion for Dampness Removal: Remarkable Effects
The body’s yang energy is akin to the sun in the sky. If our yang energy is sufficient, even if dampness appears, it can be evaporated. If our internal yang energy is insufficient, dampness spreads like fog, unable to be transformed or expelled.
Moxibustion has excellent effects in replenishing yang energy and dispelling dampness. Moxibustion on the following commonly used acupoints can effectively expel dampness.
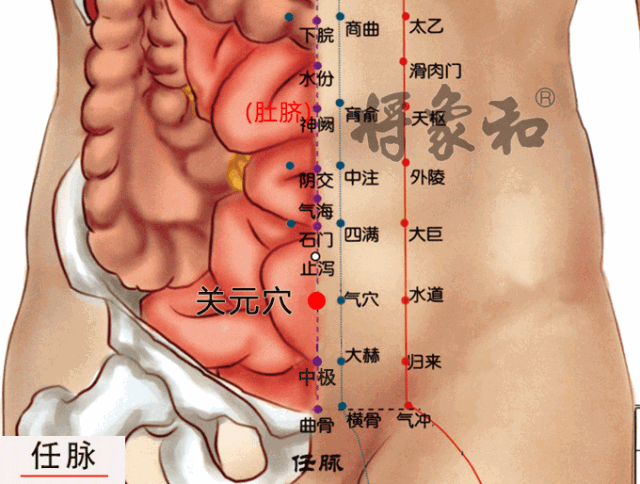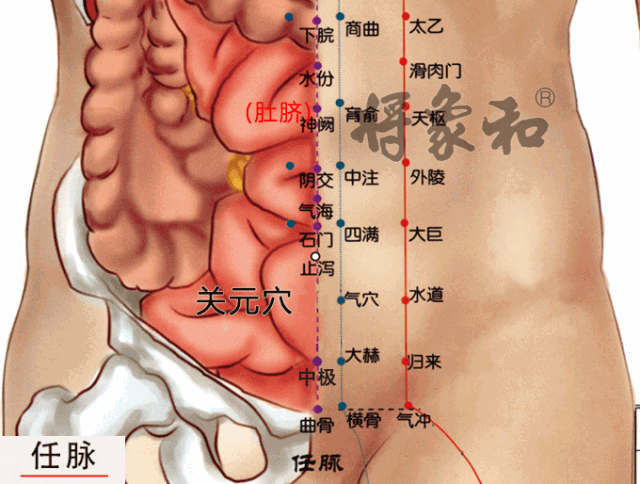
Acupoints: Shenque (Shenque Point), Guanyuan (Guanyuan Point), Zhongwan (Zhongwan Point), Shuifen (Shuifen Point), Yinlingquan (Yinlingquan Point), Fenglong (Fenglong Point).
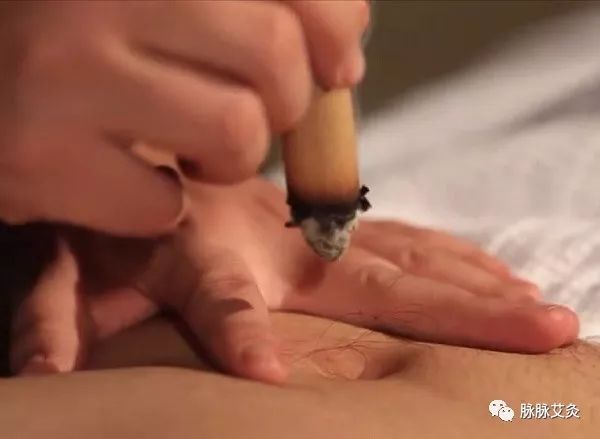

[Shenque Point]
Located at the center of the navel, often treated with ginger moxibustion or suspended moxibustion, it has the effect of warming the middle and dispersing cold, and can also be used for daily health care and treatment of deficiency-cold diseases.
[Guanyuan Point]
Located in the lower abdomen, 3 inches below the navel, on the anterior midline. Guanyuan Point has the function of nourishing the source and stabilizing the foundation, beneficial for any deficiency of vital energy.
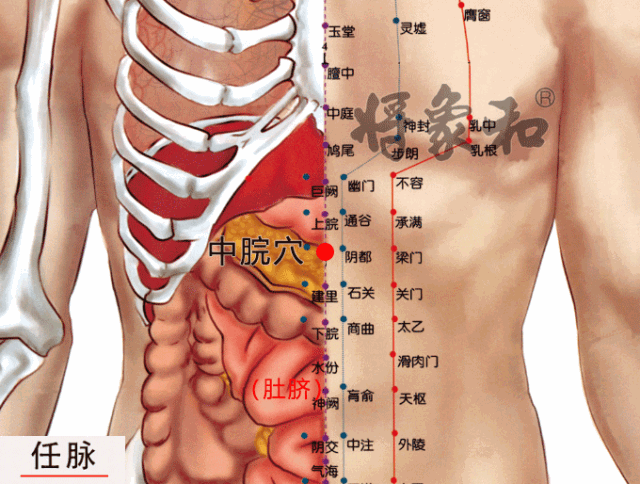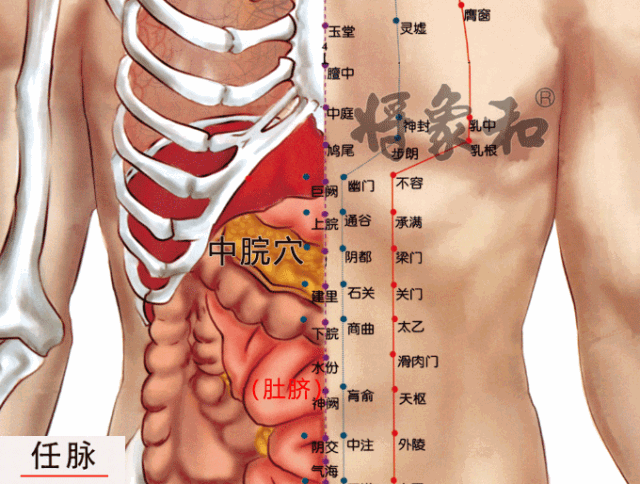
[Zhongwan Point]
Located 4 inches above the navel, it is a Ren Meridian point. It has the effects of warming the stomach, stopping vomiting, dispersing cold, alleviating pain, harmonizing the stomach, strengthening the spleen, and promoting the flow of qi. It is suitable for individuals with a weak spleen and stomach constitution.
[Shuifen Point]
Located 1 inch above the navel, on the anterior midline. This point’s function is related to its name, effective for abdominal diseases, and has good effects on edema and urinary difficulties caused by water retention.
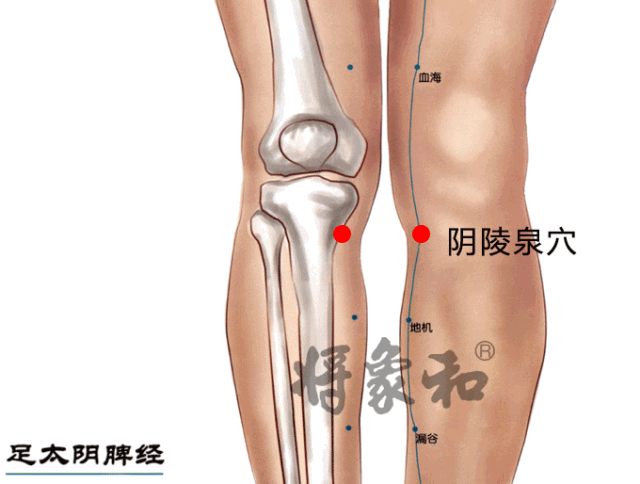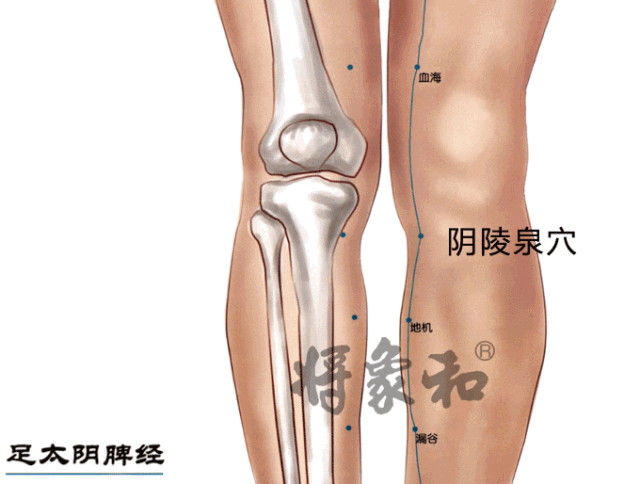
[Yinlingquan Point]
Located on the inner side of the lower leg, below the inner condyle of the tibia, where a depression can be felt. This point is often sore in individuals with heavy dampness; those with spleen deficiency may easily accumulate dampness here, leading to a yellowish complexion over time. Regular moxibustion on Yinlingquan can transform dampness, clear damp-heat, strengthen the spleen, and regulate qi.Yinlingquan and the following Fenglong are commonly used and effective points for dispelling phlegm-dampness. Yinlingquan also treats abdominal distension, edema, and other water retention diseases.
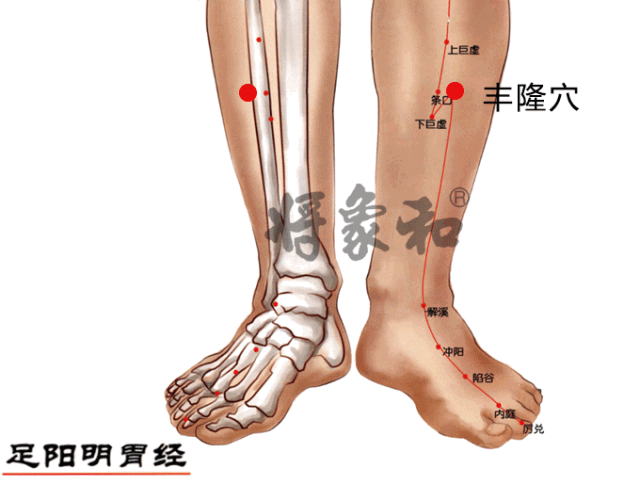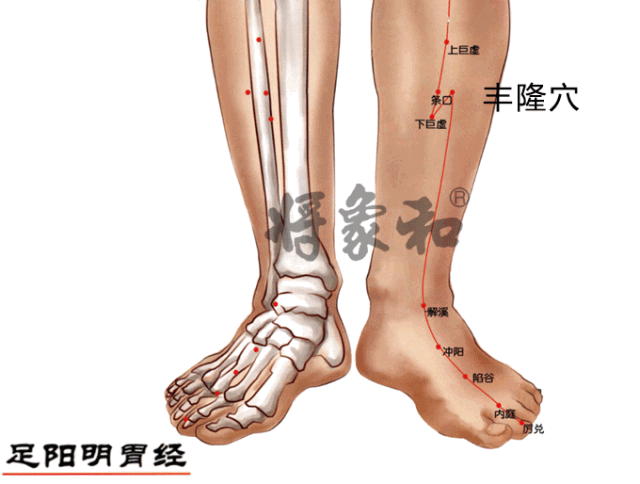
[Fenglong Point]
Located on the outer side of the lower leg, 8 inches above the outer ankle tip, at the outer edge of the tibialis anterior muscle, 1 inch lateral to the tibialis anterior muscle (Tibialis anterior: on the outer side of the lower leg, 8 inches below the knee, along the line connecting the knee and the lateral malleolus). The stomach and spleen meridians converge here, making Fenglong a key point for dispelling phlegm-dampness, often used in conjunction with Yinlingquan.
Individuals with spleen or kidney deficiency can add Pishu (Spleen Shu Point) and Shenshu (Kidney Shu Point).
Those who know moxibustion are blessed; those who practice it well live long.
Disclaimer: The images in this article are sourced from the internet, and this platform focuses on communication and sharing, not for commercial use. If there is any infringement, please contact the editor for deletion.

