Click the blue text above to follow us!
 Honeysuckle (Jin Yin Hua) (Lonicera Japonica Thunb), also known as Reinforcing Winter, Silver Flower, and Double Flower, is the dried flower bud of the honeysuckle plant from the Caprifoliaceae family. It blooms in March and produces flowers in May; initially, the flowers are white, turning yellow after one to two days, hence the name Honeysuckle. It is cold in nature, sweet in taste, and grows in moist, fertile, deep sandy loam, preferring sunlight while being tolerant to shade, drought, waterlogging, and cold. Honeysuckle is mainly produced in Shandong and Henan provinces, and it is cultivated nationwide. According to the 2015 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the common dosage for adults is 6-15 grams per day. It is now listed as a food-medicine homologous item.
Honeysuckle (Jin Yin Hua) (Lonicera Japonica Thunb), also known as Reinforcing Winter, Silver Flower, and Double Flower, is the dried flower bud of the honeysuckle plant from the Caprifoliaceae family. It blooms in March and produces flowers in May; initially, the flowers are white, turning yellow after one to two days, hence the name Honeysuckle. It is cold in nature, sweet in taste, and grows in moist, fertile, deep sandy loam, preferring sunlight while being tolerant to shade, drought, waterlogging, and cold. Honeysuckle is mainly produced in Shandong and Henan provinces, and it is cultivated nationwide. According to the 2015 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the common dosage for adults is 6-15 grams per day. It is now listed as a food-medicine homologous item.
Nutritional Components
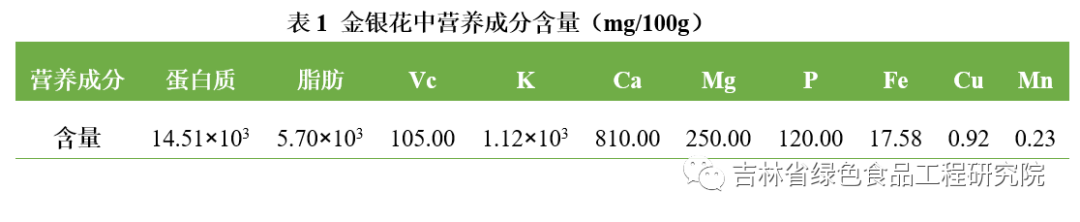
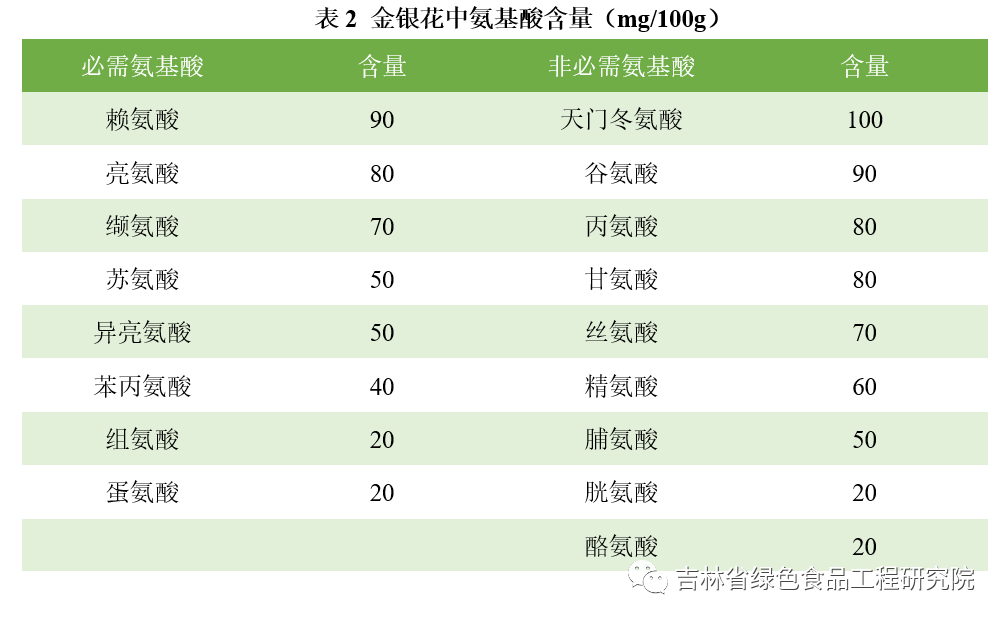
Honeysuckle contains proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, as well as 17 types of amino acids, including 8 essential amino acids. The specific content is shown in Tables 1 and 2.
Active Components
Honeysuckle contains various active components such as flavonoids, polysaccharides, triterpenoids, and volatile oils. Among them, the main flavonoid is chlorogenic acid (49.0 mg/g); the polysaccharide content is 65.8 mg/g; and the total triterpenoid content is 37.1 mg/g.
Functions and Effects
- Antioxidant
The chlorogenic acid in Honeysuckle has a strong ability to scavenge 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH•) free radicals, and this scavenging ability increases with the concentration of the sample.
- Antibacterial
The total triterpenoids in Honeysuckle inhibit various bacteria including Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhimurium, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Anti-inflammatory
Research has shown that total saponins from Honeysuckle have a certain inhibitory effect on xylene-induced ear swelling in mice, indicating its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Liver Protection
Total saponins from Honeysuckle can effectively increase serum superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and reduce malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, thereby protecting the liver.
- Immune Enhancement
Honeysuckle polysaccharides can significantly improve the organ index, serum hemolysin levels, and interleukin-2 (IL-2) content in immunocompromised mice, restoring them to normal levels and significantly enhancing immune activity.
Additionally, Honeysuckle has effects such as anti-ultraviolet, lowering blood sugar, lowering blood lipids, anti-tumor, and anti-viral properties.

References
[1]Liu Jingsheng. Research Progress on the Nutrition of Honeysuckle and Its By-products[J]. Feed Research, 2016(11):8-9,24.
[2]Liu Yufeng, Li Lupan, Ma Haiyan, et al.. Research Progress on the Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Effects of Honeysuckle[J]. Journal of Liaoning University, 2018,45(3):255-262.
[3]Guan Xiufeng, Wang Rui, Li Xiaolong, et al.. New Advances in the Study of Chemical Composition and Pharmacological Effects of Honeysuckle[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2020,34(4):59-62.
[4]Kong Fanqin, Yang Feng, Wang Baidong. Honeysuckle Cultivation Management in Jilin Province[J]. Special Economic Animals and Plants, 2010,13(9):35.
[5]Wang Wei, Zhou Zhengli, Li Jian, et al.. Determination of Amino Acid Content in Honeysuckle Using Pre-derivatization Method with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography[J]. Journal of Liaoning Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2010,37(11):2212-2213.
[6]Li Dongmei, Xia Riyue, Du Lianduo, et al.. Analysis of Nutritional Components in Different Parts of Honeysuckle[J]. Food Research and Development, 2018(18):190-194.
[7]Zhang Yanling. Comparative Study of Chemical Components in Different Parts of Honeysuckle[J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019,9(1):59-61.
[8]Shi Qi. Study on the Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Chlorogenic Acid and Polysaccharides from Honeysuckle[J]. Applied Chemistry, 2015,44(7):1268-1271.
[9]Chang Xia, Jing Bingnian, Fan Yi, et al.. Extraction Process of Total Triterpenoids from Honeysuckle and Its Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019,47(16):198-202.
[10]Shi Yanbing, Li Wenjing. Response Surface Optimization of Chlorogenic Acid Extraction Process from Honeysuckle and Its Antioxidant Activity Study[J]. Food Research and Development, 2019,40(21):152-158.
[11]Li Xiansheng. Study on the Anti-inflammatory and Liver Protective Effects of Total Saponins from Honeysuckle[J]. Food Industry, 2009,30(4):4-6.
[12]Mao Shumin, Xu Jiazhen, Jiao Fangwen, et al.. Effects of Honeysuckle Polysaccharides on Immune Function in Immunocompromised Mice[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016,18(2):18-20.
[13]Qing Jie Chao, Lin Ziran, Mo Kailin. Preliminary Study on the Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anti-ultraviolet Effects of Honeysuckle and Dandelion[J]. Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology, 2018,39(6):55-57.
[14]Shi Junying, Guo Chengjun. Study on the Effective Parts of Honeysuckle Against Influenza Virus In Vitro[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2010,34(2):178-180.
▲ Scroll up and down to see more
Contributed by/Zhang YuheReviewed by/Wang Ying, Wang GuoliangTypeset by/Jiang Shanshan






