 Click on 【Comprehensive Knowledge of Chinese Herbs】, then click the upper right corner 【···】
Click on 【Comprehensive Knowledge of Chinese Herbs】, then click the upper right corner 【···】
Set as Star/Pin
Star/Pin for easy accessThere are always private messages inquiring about Chinese herbs. The Comprehensive Knowledge of Chinese Herbs public account has updated over 1500 types of Chinese herbs. You can click to enter the public account, click on “Chinese Herb Inquiry” below, search for the Chinese herb knowledge you want to know, and refer to the “Inquiry Method” in the public account for the steps.
for easy accessThere are always private messages inquiring about Chinese herbs. The Comprehensive Knowledge of Chinese Herbs public account has updated over 1500 types of Chinese herbs. You can click to enter the public account, click on “Chinese Herb Inquiry” below, search for the Chinese herb knowledge you want to know, and refer to the “Inquiry Method” in the public account for the steps.
PinyinDānɡ Guī

AliasGan Gui (《本经》)
Source《本经》
OriginThe root of the plant Angelica sinensis, belonging to the Apiaceae family. Generally, it must be cultivated for 3 years before harvesting. The roots are dug up in late autumn, cleaned of stems and soil, and dried in a ventilated place for a few days. They are then tied into small bundles according to size and lightly smoked until thoroughly dried. This product is oily and prone to mold and insect damage, so it must be stored in a dry place. During moldy rainy seasons, it should be treated with sulfur or appropriately dried.

Habitat DistributionDistributed in Gansu, Sichuan, Yunnan, Shaanxi, Guizhou, Hubei, and other regions. Cultivated in various places, mainly produced in Gansu and Yunnan. Additionally, Shaanxi, Sichuan, Hubei, and Guizhou also produce it.
Plant MorphologyAngelica sinensis, also known as: Bi, Shan Qi, Bai Qi (《尔雅》), Wen Wu (Cui Bao’s 《古今注》).
Perennial herb, 0.4 to 1 meter tall. The stem is erect, purple, with distinct longitudinal grooves, smooth and hairless. Leaves are 2-3 times pinnately divided, with petioles 3-11 cm long, and the basal leaf sheath is enlarged; leaflets are ovate; there are 3 pairs of leaflets, with the petioles of the pair closest to the petiole 0.5-1.5 cm long, and the pair near the apex is sessile, divided 1-2 times, with notched edges. The compound umbel inflorescence is terminal, with 10-14 peduncles of varying lengths, with 2 linear bracts at the base, or absent; there are 2-4 small bracts, linear; the small umbel has 12-36 flowers, with peduncles 0.3-1.5 cm long, densely covered with fine soft hairs; calyx teeth 5, finely ovate; petals 5, white, elongated ovate, with a narrow pointed tip, slightly folded inward, hairless; stamens 5, filaments bent inward; ovary inferior, style short, with a conical base. The double-samaras are oval, 4-6 mm long, 3-4 mm wide, easily separating at maturity; the fruit has 5 ridges, with dorsal ridges linearly raised, and lateral ridges developing into wide thin wings, with pale purple edges; the transverse section is flat on the back, with one oil duct in each groove, and two oil ducts on the joining surface. Flowering period is June to July. Fruit period is July to August.
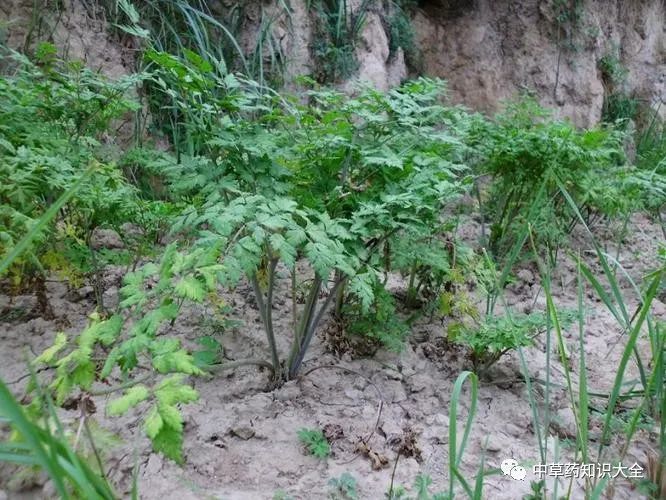
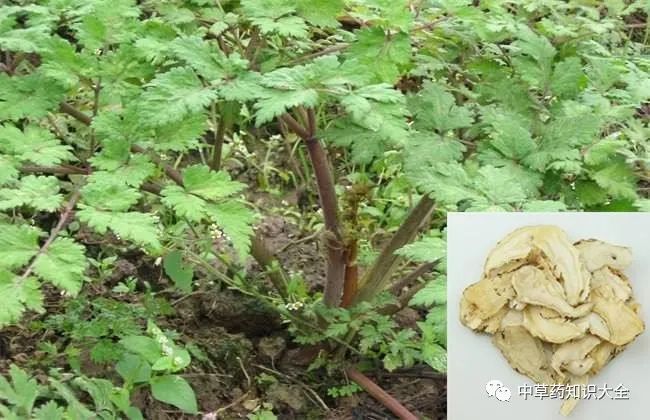


CharacteristicsThe dried root can be divided into three parts: the root head is called “Gui Tou”, the main root is called “Gui Shen”, and the lateral roots and their tips are called “Gui Wei”. The total length is about 10-25 cm, with the main body length about 3-10 cm. The diameter of the root head is 2-4 cm, and the lateral root diameter is 0.3-1 cm. The exterior is gray-brown or brown, with longitudinal wrinkles throughout, especially abundant at the lateral root part. The top of the root head is rounded and flat, with remnants of stems and leaves, often with inconspicuous ring-like wrinkles. The main body is slightly cylindrical, with an uneven surface, and 3-5 or more lateral roots grow beneath it. The lateral roots are thicker at the top and thinner at the bottom, often twisted, with small nodular traces of fibrous roots on the surface. The texture is mostly flexible, with a yellow-white cross-section, fissures, and shallow brown ring patterns in the middle layer, along with numerous brown oil spots. The best quality is characterized by a large main root, long body, few lateral roots, yellow-white cross-section, and strong aroma. Inferior quality has a small main root, many lateral roots, weaker aroma, and a reddish-brown cross-section.
It is best to select those with a large main root, long body, few lateral roots, yellow-white cross-section, and strong aroma. Inferior quality is characterized by a small main root, many lateral roots, weaker aroma, and a reddish-brown cross-section.
Chemical CompositionThe root contains volatile oil, with the Gansu Minxian variety containing 0.4%, and the Sichuan Wenchuan variety containing 0.7%. The main components of the volatile oil include: phthalide, ortho-carboxyphenyl pentanone, and Δ2,4-dihydrophthalic anhydride.
The volatile oil components are complex, with more than 10 types in the low boiling point section alone, including various hydrocarbons, including 3 types of terpenes. It also contains a large amount of sucrose (40%), vitamin B12 (0.25-40 micrograms/100 grams), and vitamin A-like substances (0.0675%). The saponifiable part of the root contains palmitic acid, stearic acid, myristic acid, and unsaturated oleic acid, while the unsaponifiable components include β-sitosterol.
The whole plant has a fragrance, indicating that all parts contain volatile oil, with particularly high content in the fruit.
The roots of Dong Angelica and Bei Hai Angelica contain about 0.2% volatile oil, with phthalide components including Dong Angelica phthalide lactone, butyl phthalide, and snake bed phthalide lactone, isosnake bed phthalide lactone. Additionally, they contain sesquiterpenes, p-coumaric acid, sucrose, vitamin B12, niacin, folic acid, and β-sitosterol. The former also contains butyl phthalide and sedative acid lactone. The volatile oils of both types of Angelica roots and fruits also contain butanol and acetic acid.
PreparationAngelica: Remove impurities, wash clean, moisten, and dry slightly until the internal and external humidity is suitable, then slice and sun-dry. Wine Angelica: Take Angelica slices, spray evenly with yellow wine, slightly moisten, and stir-fry over low heat, then cool. (For every 100 jin of Angelica slices, use 10 jin of yellow wine.)
According to the 《雷公炮炙论》: “For using Angelica, first remove dust and the hard tip for one part, soak in wine overnight.”
Meridian EntryEnters the Heart, Liver, and Spleen meridians.
① According to the 《汤液本草》: “Enters the Hand Shaoyin, Foot Taiyin, and Jueyin meridians.”
② According to the 《雷公炮制药性解》: “Enters the Heart, Liver, and Lung meridians.”
Properties and FlavorSweet, pungent, warm.
① According to the 《本经》: “Taste is sweet, warm.”
② According to the 《吴普本草》: “Shennong, Huangdi, Tongjun, Bianque: Sweet, non-toxic. Qibo, Leigong: Pungent, non-toxic. Li’s: Slightly warm.”
③ According to the 《别录》: “Pungent, very warm, non-toxic.”
④ According to the 《本草述》: “Taste is bitter, warm, non-toxic.”
PrecautionsUse with caution in cases of damp obstruction in the middle and diarrhea.
① According to the 《本草经集注》: “Avoid with Lu Yu. Avoid with Acorus, seaweed, and Mume.”
② According to the 《药对》: “Avoid dampness, avoid fresh ginger.”
③ According to the 《太草经疏》: “Weak intestines and stomach, diarrhea, and all spleen and stomach diseases, avoid food and lack of appetite, and should not be used, even during postpartum and before pregnancy.”
④ According to the 《本草汇言》: “If wind-cold is not cleared, avoid cold and fever, and external symptoms.”
Main Functions and IndicationsTonifies blood and regulates menstruation, alleviates pain, moistens dryness, and lubricates the intestines. Treats irregular menstruation, amenorrhea, abdominal pain, masses, and bleeding; blood deficiency headaches, dizziness, atrophy; dry intestines and constipation, post-dysentery heaviness; carbuncles and sores, trauma.
① According to the 《本经》: “Mainly treats cough, counterflow qi, warms malaria, cold and heat washing in the skin, women’s leakage, infertility, various sores and wounds, decoct and drink.”
② According to the 《别录》: “Warms the middle, alleviates pain, removes blood stasis, treats wind stroke, sweating, dampness, and evil qi, tonifies the five organs, and promotes muscle growth.”
③ According to the 《药性论》: “Stops vomiting, counterflow, cold and heat, breaks old blood, mainly for women’s bleeding, cold in the intestines and stomach, tonifies deficiencies, stops dysentery and abdominal pain. Decoction of juice treats warm malaria, mainly for women’s bleeding and waist pain, treats unbearable tooth pain. For patients with cold deficiency, use it additionally.”
④ According to the 《日华子本草》: “Treats all wind, all blood, tonifies all labor, breaks evil blood, nourishes new blood, and mainly treats masses.”
⑤ According to the 《珍珠囊》: “Head bleeding, body blood flow, tail stops bleeding. (According to the 《汤液本草》, it is quoted as ‘head stops bleeding, body harmonizes blood, tail breaks blood.’)”
⑥ Li Gao: “Angelica tail mainly treats masses, breaks evil blood, and postpartum evil blood surging, removes all sores and swellings, treats golden wounds and evil blood, warms the middle, moistens dryness, and alleviates pain.”
⑦ Wang Haogu: “Mainly treats atrophy, excessive sleeping, heat and pain in the feet. For diseases of the Chong meridian, counterflow qi, and abdominal pain, for diseases of the Dai meridian, abdominal pain, and waist feeling like sitting in water.”
⑧ According to the 《本草蒙筌》: “Expels blood clots from trauma, and treats hot dysentery with abdominal pain and stagnation in the intestines.”
⑨ According to the 《纲目》: “Treats headaches, abdominal pain, lubricates the intestines, muscles, skin, and bones. Treats carbuncles, drains pus, alleviates pain, harmonizes and tonifies blood.”
⑩ According to the 《本草再新》: “Treats all body swelling, blood vessels not harmonizing, insufficient yin, stabilizes pregnancy, and prevents miscarriage.”
Dosage and AdministrationInternal use: Decoction, 1.5-3 qian; soaked in wine, concentrated, or made into pills or powders.
Formulas① Regulates and nourishes the Wei and Ying, tonifies qi and blood. Treats Chong and Ren deficiency, menstrual irregularities, abdominal masses, bleeding, blood stasis, pain, pregnancy cold, and instability, continuous bleeding, and postpartum deficiency, wind-cold internal obstruction, lochia not expelling, masses forming, and lower abdominal pain with intermittent cold and heat: Angelica (remove the reed, soak in wine, stir-fry), Chuanxiong, Bai Shao (white peony), Shu Di Huang (cooked rehmannia) (steamed with wine) in equal parts. Grind into coarse powder. Take 3 qian each time, with 1.5 cups of water, decoct to 8 parts, strain and take hot before meals. (According to the 《局方》, this is the Four Substance Decoction.)
② Treats young women’s menstrual obstruction: Angelica (sliced, roasted) 1 liang, Gan Qi (stir-fried until smoke comes out), Chuanxiong each half liang. Grind the three ingredients into powder, mix with honey, and form pills the size of a wutong seed. Take 20 pills each time, with warm wine. (According to the 《圣济总录》, this is the Angelica Pill.)
③ Treats menstrual flow reversing from the mouth and nose: First use Jing Mo to grind juice to stop it, then use Angelica tail and safflower each 3 qian, with 1.5 cups of water, decoct to 8 parts, take warm. (According to the 《简便单方》.)
④ Treats blood collapse: Angelica 1 liang, dragon bone 2 liang (stir-fried until red), Xiangfu 3 qian (stir-fried), and 5 qian of palm hair ash. Grind into powder, mix with rice drink, take 3-4 qian on an empty stomach. (According to the 《儒门事亲》, this is the Angelica Powder.)
⑤ Treats blood masses with pain and stagnation: Angelica 3 liang, cinnamon heart 2.5 qian, Bai Shao 2.5 qian (stir-fried with wine), Puhuang 2 liang (stir-fried), Xuejie 3 liang, and Yanhusuo 2.5 qian. Grind into powder, decoct with wine 3 qian, strain and take warm. (According to the 《医略六书》, this is the Angelica Puhuang Powder.)
⑥ Treats women with five-colored discharge, abdominal pain, emaciation, and poor appetite: Angelica 1 liang (chopped, slightly roasted), turtle shell 1 liang (vinegar roasted until slightly yellow, remove skirt), Chuan Dahuang 1 liang (chopped, slightly roasted), Bai Zhu 3 fen, pepper 0.5 liang, Haritaki peel 3 fen, betel nut 3 fen, and bitter orange peel 3 fen (roasted with bran until slightly yellow, remove the pulp), and 0.5 liang of pepper. Grind the above herbs into powder, mix with honey, and form pills the size of a wutong seed. Take 30 pills before meals with warm wine. (According to the 《圣惠方》, this is the Angelica Pill.)
⑦ Treats women during pregnancy with abdominal masses: Angelica 3 liang, Bai Shao 1 jin, Fu Ling 4 liang, Bai Zhu 4 liang, Ze Xie 0.5 jin, and Chuanxiong 0.5 jin (the latter can also be 3 liang). Grind into powder, take a small spoonful mixed with wine, three times a day. (According to the 《金匮要赂》, this is the Angelica Bai Shao Powder.)
⑧ Treats difficulty in urination during pregnancy, with normal appetite: Angelica, Fritillaria, and bitter gentian each 4 liang. Grind the three into powder, mix with honey, and form pills the size of a small bean. Take 3 pills. (According to the 《金匮要略》, this is the Angelica Bitter Gentian Pill.)
⑨ Treats fetal movement instability and abdominal pain: Angelica 0.5 liang (chopped), scallion white 1 fen (finely chopped). Mix the two, first boil with 3 cups of water until reduced to 2 cups, add good wine 1 cup, boil a few more times, strain, and divide into three doses. (According to the 《圣济总录》, this is the An Tai Decoction.)
⑩ Treats postpartum blood not dispersing, forming lumps (commonly called child pillow), with unbearable pain: Angelica 1 liang (chopped, slightly roasted), Gui Jian Yu 1 liang, and red-blue flower 1 liang. Grind the herbs into powder, take 3 qian with wine in a medium cup, decoct to 6 parts, strain, and take warm without time restriction. (According to the 《圣惠方》, this is the Angelica Powder.)
⑪ Treats tremors, or postpartum unconsciousness, with phlegm: Angelica, and Schizonepeta spike in equal parts. Grind into fine powder, take 3 qian with 1 cup of water and a little wine, decoct to 7 parts, and swallow immediately. (According to the 《妇人良方》, this is the Jiao Jia Powder.)
⑫ Treats abdominal masses postpartum, and abdominal cold hernia with deficiency: Angelica 3 liang, fresh ginger 5 liang, and lamb 1 jin. Mix the three with 8 liters of water, boil to obtain 3 liters, take 7 he, three times a day. (According to the 《金匮要略》, this is the Angelica Ginger Lamb Soup.)
⑬ Treats constipation: Angelica, Bai Zhi in equal parts, grind into powder, take 2 qian with rice soup. (According to the 《圣济总录》.)
⑭ Treats muscle heat and dryness, thirst leading to drinking, red eyes, and red face, with a pulse that is large and weak, and no response to pressure: Huang Qi 1 liang, Angelica (washed with wine) 2 qian. Mix the herbs into one dose, with 2 cups of water, decoct to 1 cup, strain, and take warm on an empty stomach before meals. (According to the 《内外伤辨》, this is the Angelica Blood-Tonifying Decoction.)
⑮ Treats white tiger wind, with persistent pain: Angelica 1 liang, cinnamon heart 1 liang, earthworm 1 liang (slightly roasted), white silkworm 1 liang (slightly roasted), Wei Ling Xian 1 liang, and Pueraria 1 liang, and Chuanxiong 1 liang, Bai Zhi 1 liang. Grind the herbs into fine powder, take 2 qian with hot wine without time restriction. (According to the 《圣惠方》, this is the Angelica Powder.)
⑯ Treats blood dysentery with urgency and heaviness, with abdominal pain: Angelica 3 fen (chopped, slightly roasted), Huang Lian 1 liang (remove beard, slightly roasted), and dragon bone 2 liang. Grind the three into fine powder. Take 2 qian with porridge drink without time restriction, twice a day. (According to the 《圣济总录》, this is the Angelica Powder.)
⑰ Treats night sweats: Angelica, Sheng Di Huang, Shu Di Huang, Huang Bo, Huang Qin, Huang Lian in equal parts, with Huang Qi doubled. Grind into coarse powder, take 5 qian with 2 cups of water, decoct to 1 cup, take before meals, and reduce the dose for children. (According to the 《兰室秘藏》, this is the Angelica Six Huang Decoction.)
⑱ Treats all sores and swellings, whether broken or unbroken, with severe swelling: Angelica, Huang Qi, Gua Lou, Mu Xiang, Huang Lian in equal parts, grind into coarse powder, decoct 1 liang. (According to the 《素问病机保命集》, this is the Angelica Powder.)
⑲ Treats abscesses and all evil sores: Angelica 0.5 liang, licorice 1 liang, 12 mountain yellow fruits, and 1 wood beetle (remove skin). Grind into fine powder, take 3 qian with cold wine. (According to the 《奇效良方》, this is the Angelica Powder.)
⑳ Treats burns from boiling water, with severe pain: White wax 1 liang, sesame oil 4 liang, and Angelica 1.5 liang (freshly chopped). First, fry the Angelica in oil until charred, filter out the residue, then add wax, wait for it to dissolve, stir quickly, and let cool in a ceramic box for application. (According to the 《神效白膏》, this is the Angelica White Ointment.)
Clinical Applications① Treats muscle, joint pain, and neuralgia
Using Angelica liquid for acupuncture point injection, treating lumbar muscle strain, muscle rheumatism, limb joint sprains, arthritis, and various neuralgias (sciatica, intercostal neuralgia, occipital neuralgia, etc.), with good results. According to the treatment results of 1000 cases of muscle, joint, nerve, and vascular tissue diseases, the effective rate reached 89.1%, with 381 cases cured and 510 cases improved. In another observation of 50 cases of occipital neuralgia, after 1-15 treatments, 33 cases were cured, and the rest also showed varying degrees of improvement. The vast majority of cases experienced basic pain relief or significant reduction within 1-3 minutes after the first injection, with pain relief lasting 2-8 hours, and subsequent injections remained effective. Practice has proven that Angelica acupuncture point injection not only has significant pain relief effects but also relaxes muscles, reduces inflammatory responses in soft tissues, and improves peripheral nerve and vascular function. Method: Use 5-10% Angelica liquid to inject along meridians at pain points or sensitive points, or within tendon sheaths. Choose 1-4 points each time, injecting 1-5 ml at each point. Insert the needle into the muscle layer, feeling a sour, swollen sensation, and after aspirating without blood, inject the liquid. Generally, there are no side effects, but when injected into tendon sheaths, local swelling and severe pain may occur a few hours after injection, affecting functional activity, which requires no special treatment and will subside within 1-3 days, showing therapeutic effects. It is not suitable for patients with lumbar or limb joint pain caused by tuberculosis or tumors, local trauma, purulent lesions, and skin diseases, as well as severe local bruising and swelling from acute injuries. Use with caution in pregnant women.
② Treats chronic bronchitis
Injecting 5% Angelica liquid into the Xuan Zhong, Lung Shu, Ding Chuan, and Kong Zui points. Each time, inject 0.5-1 ml into each point. After inserting the needle (about 1.5 cm deep), use a shaking motion and slight lifting technique to create a sour, swollen sensation, then slowly inject the liquid. In a study of 93 patients over 50 years old, 5 cases were cured, 26 cases significantly improved, 52 cases improved, and 10 cases were ineffective, with a total effective rate of 89.3%.
③ Treats chronic pelvic inflammatory disease
Using Angelica tissue liquid for acupuncture point injection. In a treatment of 5 cases, after 1-2 treatment courses, patients showed significant improvement or disappearance of symptoms and signs, with reduced abdominal pain and normal menstruation, all achieving pregnancy within 6 months post-treatment. Acupuncture points and methods: Two groups of points, the first group includes Wei Bao (bilateral), San Yin Jiao (left), and Zu San Li (right); the second group includes Guan Yuan through Zhong Ji, San Yin Jiao (right), and Zu San Li (left). Alternate injections between the two groups, once daily or every other day, or twice a week, injecting 2-6 ml of liquid at each point, with 6-10 treatments per course. Before injecting, twist the needle to ensure it is “energized,” then inject the liquid. Stop treatment during menstruation. After injection, a local sour, swollen sensation radiates downwards. Three cases reported a sensation of heartbeat and coldness after injection, lasting 5 minutes and resolving spontaneously without treatment.
④ Treats menstrual disorders
Soak 20 grams of Angelica and 10 grams of safflower in 50 ml of 50% alcohol for 48 hours, filter, mix, and add alcohol to 100 ml. Take 3 ml three times a day after meals, stopping during menstruation. This was used to treat 54 cases of irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and uterine hypoplasia, with 60-600 ml of medication taken, with only 7 cases showing no improvement, while the rest were effective. Among 11 dysmenorrhea patients re-examined, 7 became pregnant; among 16 patients with uterine hypoplasia, 8 became pregnant (most in conjunction with hormone therapy); and among 26 patients with menstrual abnormalities, 6 became pregnant.
⑤ Treats hypertension
Using 20% compound Angelica injection (Angelica, safflower, and Chuanxiong in equal parts) 2 ml mixed with 2 ml of 10% glucose solution, or 1 ml of 75% compound Angelica injection mixed with 3 ml of 10% glucose solution, alternating injections at both sides of the Quchi and Zusanli points, 2 ml at each point, for 10 treatments per course. Generally, 4 courses are used. The first course is once daily, the second course is every other day, the third course is twice a week, and the fourth course is every other day. Using a No. 5 needle, after inserting the needle into the acupuncture point, wait for the patient to feel a sour, numb, swollen sensation, then slowly inject the liquid. Preliminary observations of 7 cases showed varying degrees of blood pressure reduction, with systolic pressure dropping 16-56 mmHg and diastolic pressure dropping 2-30 mmHg; symptoms such as dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision, and insomnia also improved or disappeared, with some cases showing a slowing of heart rate.
⑥ Treats herpes zoster
Grind Angelica into powder, taking 0.5 or 1 gram depending on age, every 4-6 hours. In a treatment of 54 cases of pediatric herpes zoster, 22 cases had pain relief after 1 day; 32 cases after 2 days. Herpes zoster generally shows partial withering after 3 days of medication, with no new rashes, and scabbing by the 4th day. Additionally, using 0.5 grams of Angelica in pill form, taking 2-4 pills every 4 hours, also achieved similar results in 23 adult patients.
⑦ Treats rhinitis
Using 5% Angelica liquid for acupuncture point injection at Ying Xiang (bilateral) and Yin Tang points, injecting 0.3-0.5 ml at each point. Once daily for 5 days constitutes one treatment course. Generally, one course is sufficient to see results, typically performing 2 courses. After injecting the drug, there is mild pain and a sour, numb sensation locally, with no other adverse reactions. In treating 120 cases of chronic simple, hypertrophic, allergic rhinitis, and sinusitis, 73 cases were cured (60.8%), 45 cases were effective (37.5%), and 2 cases were ineffective (1.7%). Practice has proven that Angelica liquid acupuncture point injection has anti-inflammatory, anti-swelling, pain-relieving, anti-allergic, hemostatic, and regulates nasal autonomic function, with a special effect on eliminating nasal headaches. The shorter the course of the disease, the better the effect.
NoteThe roots of the following plants are sometimes used as Angelica in some regions, but their quality is inferior.
① The root of Dong Angelica, also known as: Yanbian Angelica, Japanese Angelica. The root is large and soft, with more branches, resembling a horse tail. The texture is brittle, with less oil content. Produced in Jilin Yanbian.
② The root of green Angelica, also known as: wild Qin Gui, Yunnan wild Angelica. The root is conical, 5-10 cm long, with a diameter of about 1-2 cm at the root head, and the exterior is brown or blackish-brown. The texture is hard and not easily broken; the cross-section is yellow-white. Produced in Yunnan.
③ European Angelica, which is cultivated in China, has been tried as a substitute for Angelica in medicine.
Excerpt from the “Dictionary of Chinese Medicine”
Note:This account aims to spread TCM culture. The TCM knowledge mentioned in the text is for learning and communication purposes only.
WeChat has been revamped! If youneither★starred me nor liked or “viewed” my articles,the system will assume you do not need to know about Chinese herbal knowledge, and in the end,you will not receive our article updates
End of text. Thank you for your patience in reading. If you find it good, please click “ Like” and “
Like” and “ View”~
View”~
As the ancient saying goes, “In a group of three, there must be my teacher.” For the convenience of mutual integration and exchange of knowledge among TCM practitioners, we are preparing to establish a communication group. If you wish to join, please add the editor’s WeChat and indicate your identity. The editor invites you to join the group.


