当归 (Dāngguī) – Angelica Sinensis


补血药之当归 (Dāngguī) – The Blood Nourishing Herb
当归 (Dāngguī) has a sweet and pungent flavor, is warm in nature, and enters the liver, heart, and spleen meridians.
What is the medicinal part of Dāngguī?The medicinal part is the dried root of the plant Dāngguī (Angelica Sinensis), which belongs to the Apiaceae family.It is generally harvested in late autumn, with the fibrous roots and soil removed. After some moisture evaporates, it is bundled and dried slowly over smoke.
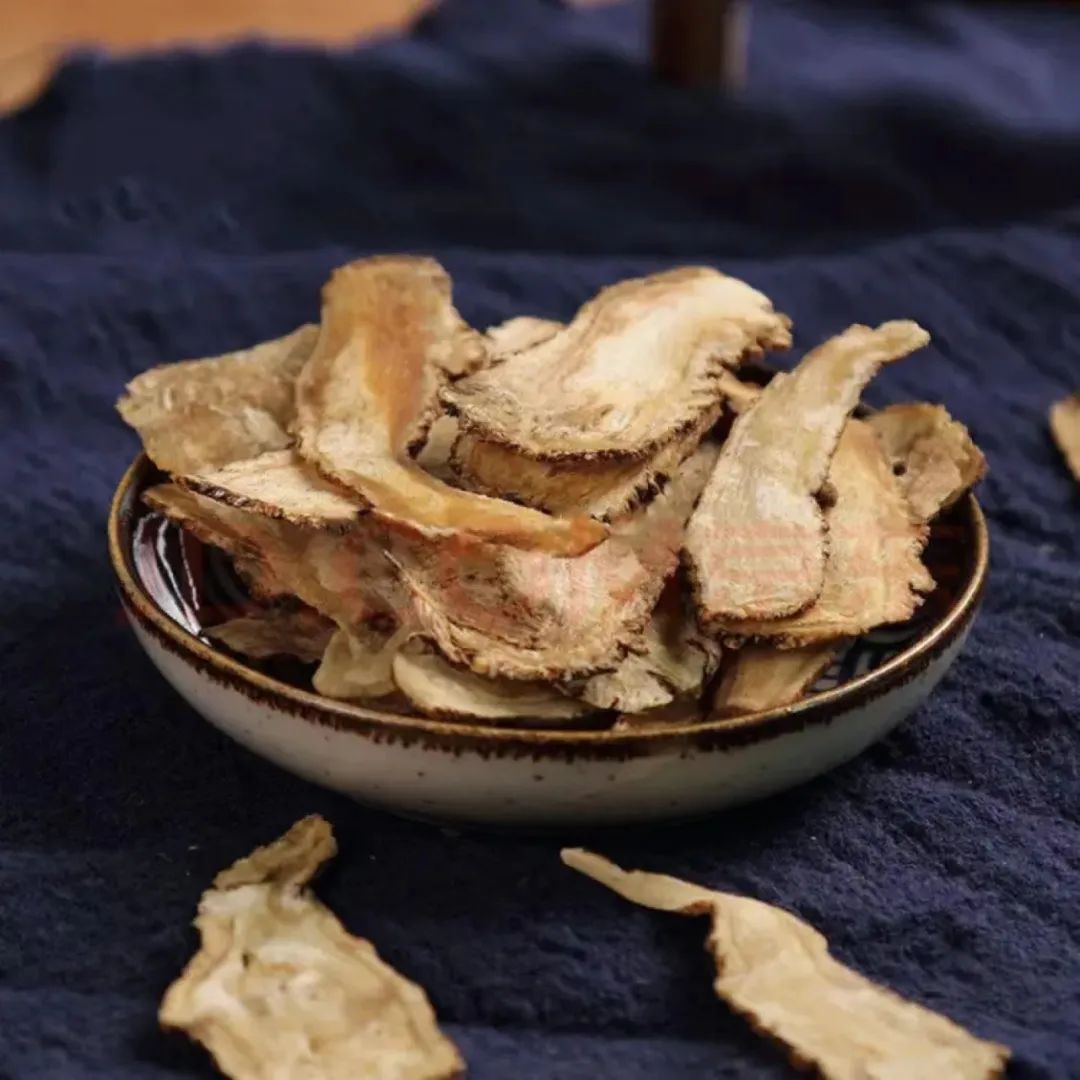


Characteristics of Dāngguī:
The root is short and thick, slightly cylindrical, measuring 1.5 to 3.5 cm in length and 1.5 to 3 cm in diameter, with 3 to 5 or more branching roots that are often curved and vary in length, with a diameter of 0.4 to 1 cm. The surface is yellow-brown or brown with irregular longitudinal wrinkles and oval lenticels; the root head has transverse wrinkles, and the tip retains multiple layers of scale-like leaf bases. The texture is hard, easily absorbs moisture and becomes soft, with a cross-section that is yellow-white or light yellow-brown, forming a yellow-brown ring in the cambium, and the bark has fissures while the wood rays are dense. It has a strong aroma, with a sweet, pungent, and slightly bitter taste.
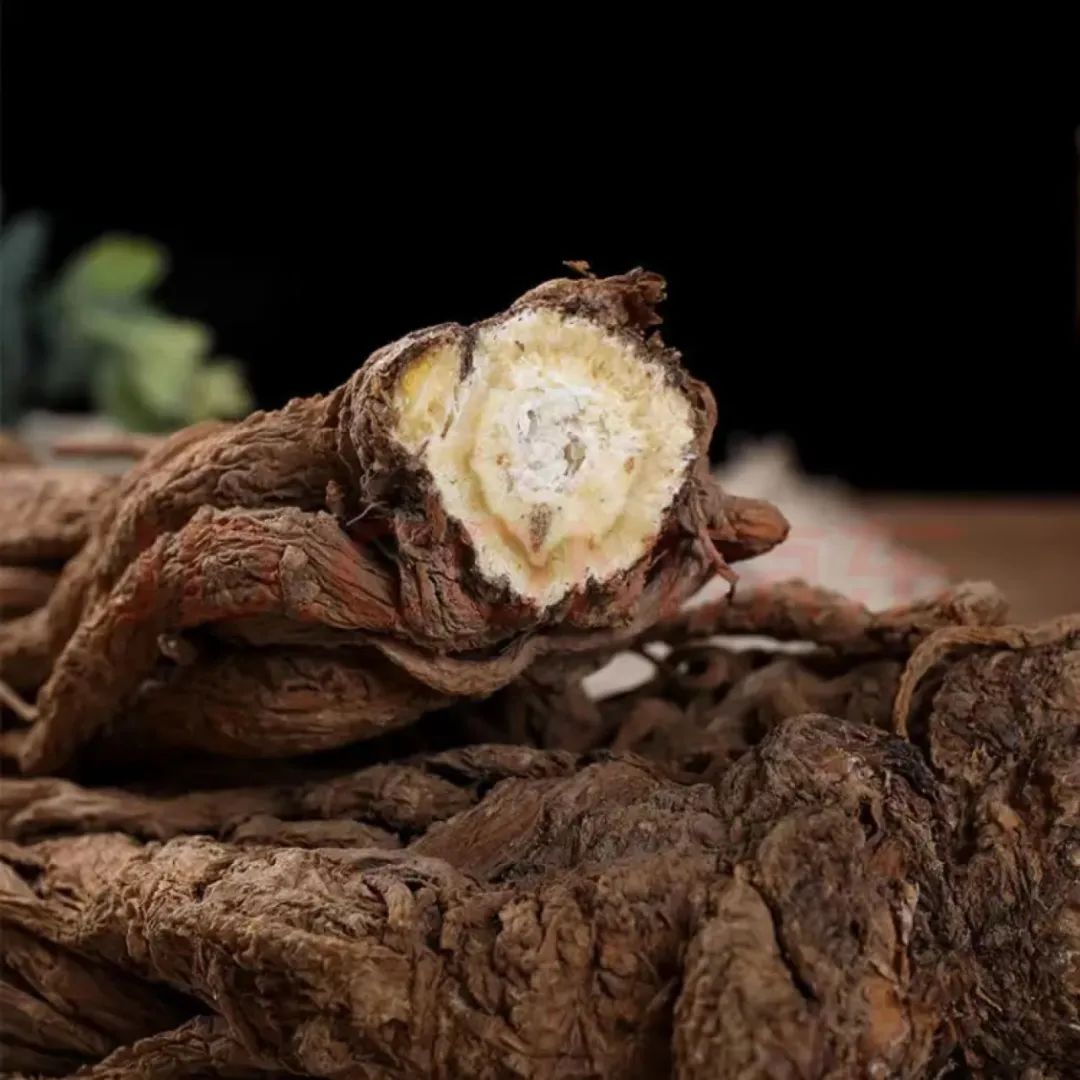

当
归 (Dāngguī)
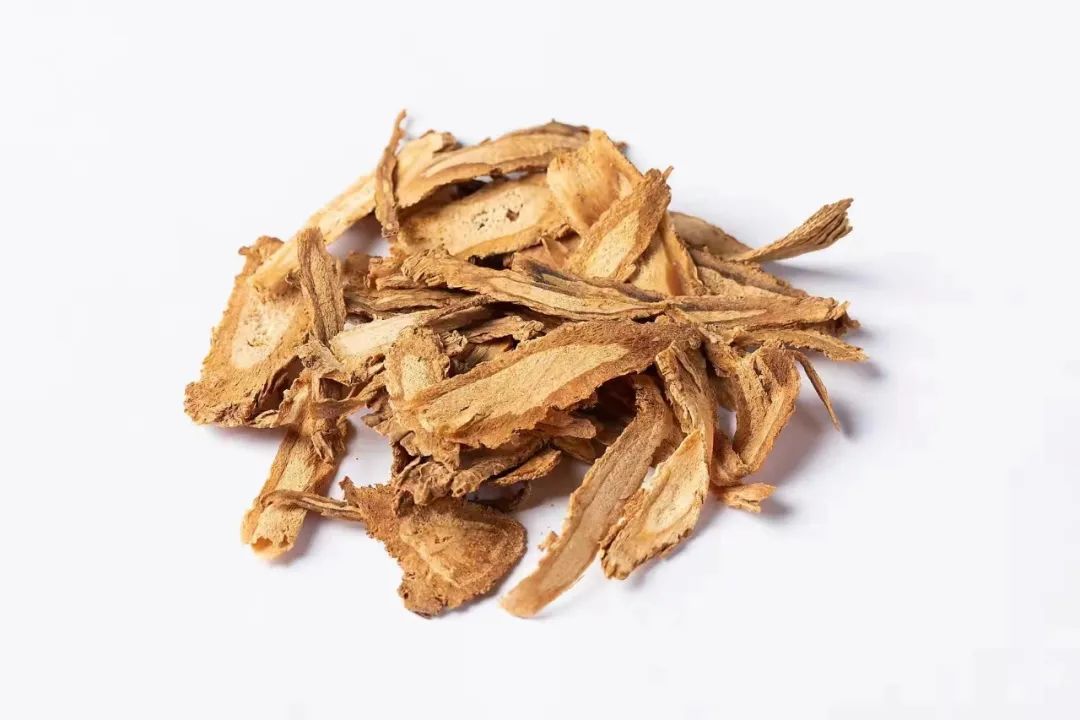



The main effects of Dāngguī are to nourish blood, invigorate blood circulation, regulate menstruation, and relieve pain.

· Clinical Applications ·
What are the clinical applications of Dāngguī?Dāngguī is primarily used for blood nourishment; the head of Dāngguī is used for hemostasis, while the tail is used for invigorating blood circulation. The whole Dāngguī is used for harmonizing blood (nourishing and invigorating blood).
1. Blood deficiency syndromes: Dāngguī has excellent blood-nourishing properties, suitable for blood deficiency syndromes, often used with Shú Dì Huáng (Rehmannia Glutinosa), Bái Sháo (White Peony), and Chuān Xiōng (Ligusticum Chuanxiong).
2. Menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea: This herb can both nourish and invigorate blood, as well as regulate menstruation and relieve pain, making it essential in gynecology, especially for menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea, and dysmenorrhea due to blood deficiency, blood stasis, and disharmony of qi and blood.
3. Abdominal pain due to deficiency and cold, rheumatic pain, trauma: This herb is effective in invigorating blood and relieving pain, warming and dispersing cold, and can nourish blood, suitable for pain caused by blood deficiency, blood stasis, and cold accumulation.
4. Carbuncles and sores: This herb can nourish blood, invigorate blood circulation, and eliminate toxins, commonly used in surgery for carbuncles and sores.
5. Dry intestines and constipation: This herb can moisten the intestines and relieve constipation, suitable for dry intestines and constipation, especially in the elderly, weak individuals, and postpartum women with blood deficiency and dry intestines, often used with blood-nourishing and intestinal-moistening herbs.
Common medicinal recipes using Dāngguī are as follows:
1. For menstrual irregularities due to blood deficiency and blood stasis:
Hóng Huā (Carthamus Tinctorius), Dāngguī (Angelica Sinensis), Dān Shēn (Salvia Miltiorrhiza), glutinous rice. First, decoct the herbs, strain the residue, and then add rice to cook into porridge. Consume on an empty stomach.
2. For chronic illness with body weakness, fatigue, and weight loss:
Shàn Yú (Eel), Dāngguī (Angelica Sinensis), Dǎng Shēn (Codonopsis Pilosula). Remove the head, bones, and internal organs from the eel, wash clean, and cut into strips. Wash and slice Dāngguī and Dǎng Shēn, wrap in gauze, and add to a pot with an appropriate amount of water, simmer for 60 minutes, remove the herb bag, and add salt, scallions, ginger, and other seasonings. Serve in portions with meals, eating the eel and drinking the soup.
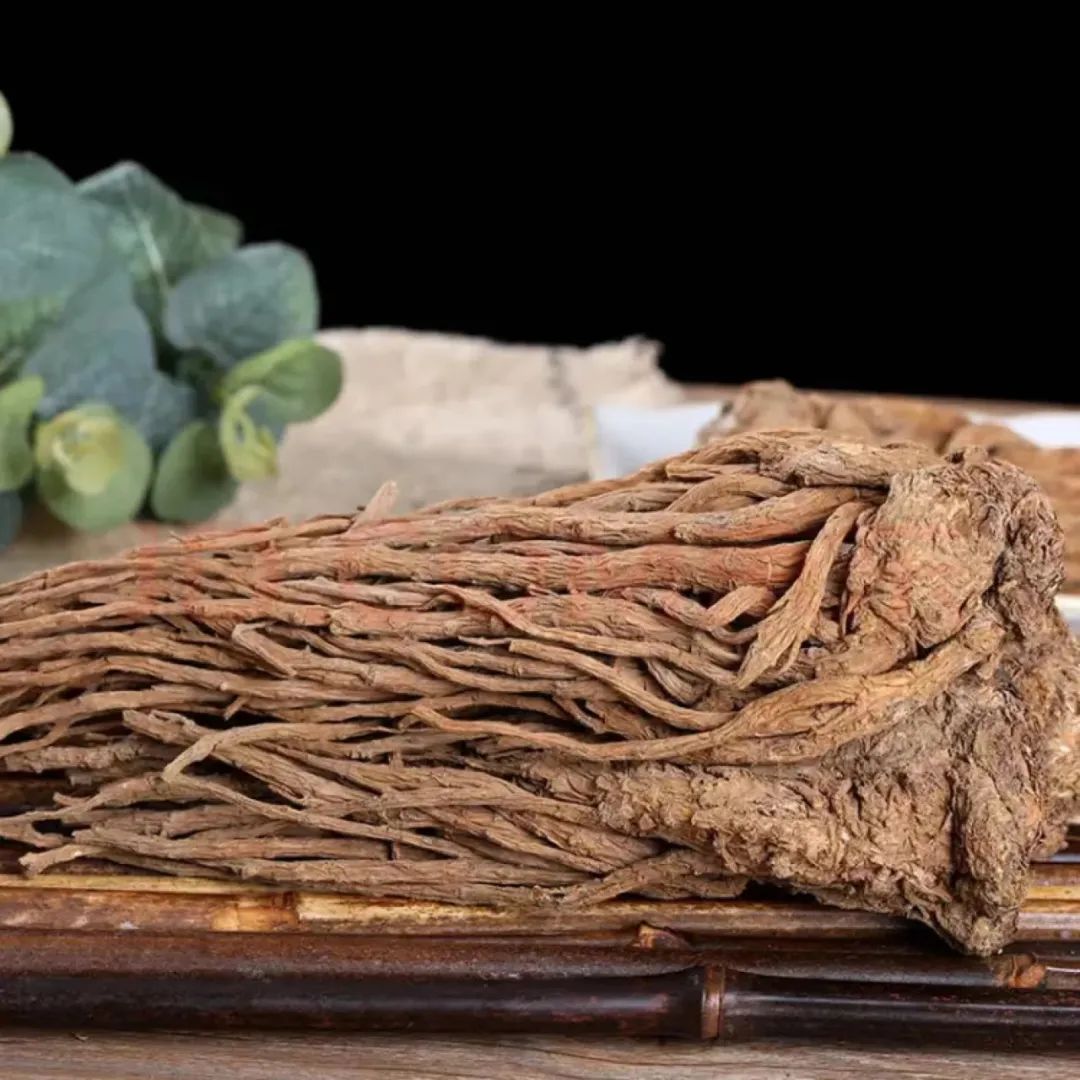


· Precautions ·
What precautions should be taken when using Dāngguī?Avoid using in cases of damp-heat fullness, lung heat phlegm-fire, yin deficiency with yang excess, and loose stools.
Note: The use of Chinese medicinal materials must be based on syndrome differentiation and treatment, and should be used under the guidance of a professional TCM practitioner. Self-medication and reliance on folk remedies and advertisements are strongly discouraged.
Contributed by: Qín Xīn from the Chinese Medicine Pharmacy
Welcome to followthe Taiyuan Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospitalvideo account
END
If you find this article useful
please share and forward it to your friends
and feel free to leave us a message
Thank you
Previous
Issues
Highlights
01
【生活中的中药】金银花 (Honeysuckle)
02
【重拳出击】严厉打击收受红包专项行动
03
【医生医事】被打破的静夜
04
院士工作站科研课题研讨会
05
健康教育大讲堂开讲啦!
06
【学史力行 坚定信仰担使命】

Long press to recognize the QR code
Party History Learning Education