
Angelica Sinensis
(Dang Gui)

Angelica Sinensis, known as “the herb of ten directions and nine returns” and “the king of herbs”, is particularly effective in treating gynecological diseases, often referred to as the “sacred medicine for women” and “the remedy for all blood-related ailments”. Let’s explore the benefits and functions of Angelica Sinensis.
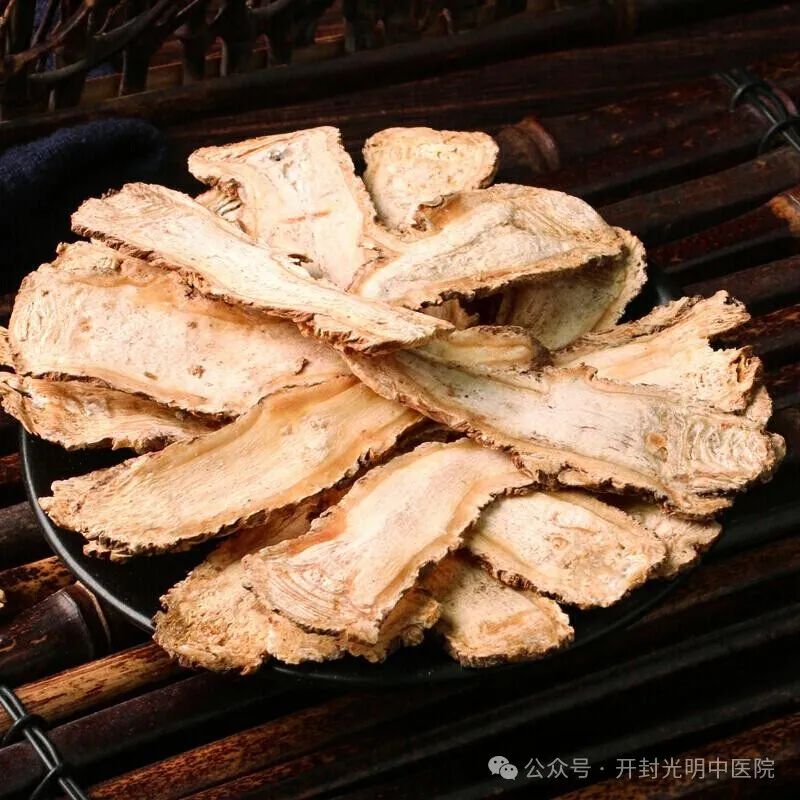
Angelica Sinensis, a traditional Chinese medicine, is the dried root of the plant Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, belonging to the Apiaceae family. It is primarily produced in the southeastern part of Gansu Province, with Min County being the largest producer of high-quality roots, followed by Yunnan, Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Hubei provinces, all of which cultivate this herb. It is known for its ability to nourish blood and invigorate blood circulation, regulate menstruation, relieve pain, and moisten the intestines to alleviate constipation. It is commonly used for conditions such as blood deficiency, pale complexion, dizziness, palpitations, irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, abdominal pain due to cold, rheumatic pain, traumatic injuries, abscesses, and constipation due to dryness.

1

Functions and Benefits of Angelica Sinensis
It nourishes blood, invigorates blood circulation, regulates menstruation, and relieves pain. It is used for blood deficiency, pale complexion, dizziness, palpitations, irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, abdominal pain due to cold, rheumatic pain, traumatic injuries, abscesses, and constipation due to dryness.
Angelica Sinensis is warm in nature, sweet and pungent in flavor, and enters the liver, heart, and spleen meridians. It has the functions of nourishing blood, invigorating blood circulation, regulating menstruation, and relieving pain. The Qing Dynasty’s “Compendium of Materia Medica” states: “Angelica Sinensis is an essential herb for blood-related issues… it is indeed a key ingredient for nourishing blood.” When used separately, the root of Angelica Sinensis is better for nourishing blood and moistening the intestines, while the tail is better for invigorating blood and relieving pain.
1. Nourishing Blood
Angelica Sinensis has the ability to nourish blood and is considered the top herb for this purpose. It is suitable for symptoms caused by heart and liver blood deficiency, such as pale or sallow complexion, fatigue, pale lips and nails, dizziness, palpitations, and insomnia. When combined with Shu Di Huang (Rehmannia), Bai Shao (White Peony), and Chuan Xiong (Szechuan Lovage), it forms the representative blood-nourishing formula, Si Wu Tang (Four Substance Decoction), which has the function of regulating menstruation and nourishing blood, especially suitable for treating postpartum blood deficiency. When combined with Huang Qi (Astragalus), it forms the “Dang Gui Bu Xue Tang (Angelica Sinensis Blood Nourishing Decoction)”, which can tonify qi and nourish blood, showing good therapeutic effects for blood deficiency (anemia).
2. Invigorating Blood and Regulating Menstruation
Angelica Sinensis not only nourishes blood but also invigorates blood circulation and relieves pain, making it particularly suitable for conditions like irregular menstruation, dysmenorrhea, and blood deficiency-related amenorrhea, earning it the title of “special medicine for women” in ancient texts. When combined with Tao Ren (Peach Kernel), Hong Hua (Safflower), Shu Di Huang, Bai Shao, and Chuan Xiong, it forms the famous gynecological formula, Tao Hong Si Wu Tang (Peach Blossom Four Substance Decoction), which has the effects of nourishing blood and invigorating blood circulation, commonly used for early menstruation and dysmenorrhea.
3. Moistening the Intestines and Alleviating Constipation
Traditional Chinese medicine believes that blood and body fluids share the same source; thus, those with blood deficiency also lack body fluids, leading to dry intestines and constipation. Angelica Sinensis can moisten the intestines and alleviate constipation, often used in combination with Ma Ren (Hemp Seed), Ku Xing Ren (Bitter Apricot Kernel), and Da Huang (Rhubarb) to treat blood deficiency-related constipation; or combined with Fang Feng (Siler), Chuan Xiong, Bai Shao, Da Huang, Bo He (Mint), Ma Huang (Ephedra), Lian Qiao (Forsythia), Mang Xiao (Glauber’s Salt), Shi Gao (Gypsum), Huang Qin (Scutellaria), Hua Shi (Talc), Sheng Gan Cao (Raw Licorice), Jing Jie (Schizonepeta), Bai Zhu (White Atractylodes), and Zhi Zi (Gardenia) to form Fang Feng Tong Sheng San, which can clear heat and promote bowel movements.

2

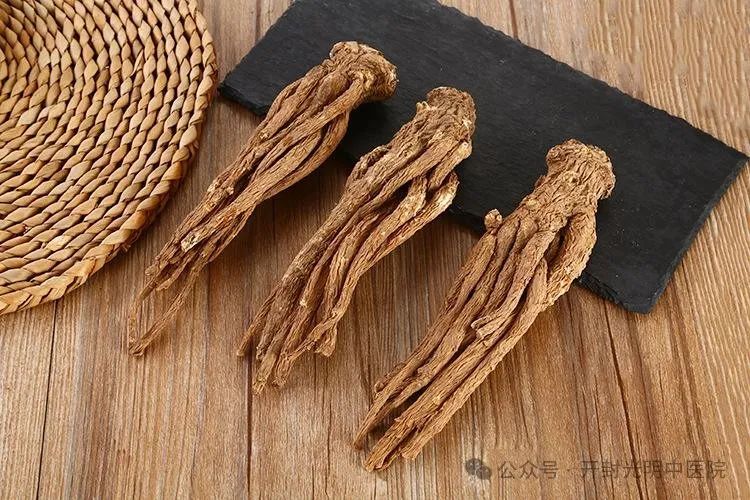
Methods of Consuming Angelica Sinensis
(1) Combinations for Consumption
It is mainly added as an auxiliary ingredient in porridge or soup.
Generally, it is used raw; to enhance blood circulation, it can be stir-fried with wine. For blood nourishment, the root of Angelica Sinensis is preferred, while the tail is better for invigorating blood, and the charred form is used for stopping bleeding. The wine-prepared form can enhance its invigorating properties; for harmonizing blood (nourishing and invigorating), the whole Angelica Sinensis is used.
For symptoms of heart and liver blood deficiency, such as pale complexion, pale lips and nails, dizziness, palpitations, and numbness, it can be combined with Shu Di Huang, Bai Shao, and Chuan Xiong for a stronger blood-nourishing effect.
For irregular menstruation due to liver qi stagnation, it can be used with Chai Hu (Bupleurum), Bai Shao, and Bai Zhu.
For the elderly, postpartum women, and those with chronic illness leading to blood deficiency and dry intestines causing constipation, it can be combined with Huo Ma Ren (Hemp Seed), Zhi Ke (Bitter Orange), and Sheng Di Huang (Raw Rehmannia).
(2) Common Preparations of Angelica Sinensis
1. Angelica Sinensis Blood Nourishing Soup

Ingredients: 2 Red Crabs (approximately 750 grams), 10 grams of Angelica Sinensis, 50 grams of Huang Qi (Astragalus), 50 grams of Goji Berries, 50 grams of Du Zhong (Eucommia), 100 grams of Black Dates, 250 grams of Rice Wine, and appropriate amount of water.
Preparation:
1. Clean the red crabs, remove the shells and gills, and cut into pieces for later use.
2. Place the cut red crabs into a pot, add Angelica Sinensis, Huang Qi, Goji Berries, Du Zhong, Black Dates, and an appropriate amount of water, then add rice wine. Simmer on low heat for about 1 hour.
Effects: Huang Qi and Angelica Sinensis nourish qi and generate blood; Du Zhong tonifies the liver and kidneys, strengthens bones, and stabilizes pregnancy; Goji Berries nourish the liver and kidneys, benefit essence, and improve vision; Black Dates have similar properties to Red Dates but are more effective in nourishing blood. Together, they work to tonify qi and nourish blood.
Application: Suitable for symptoms of qi and blood deficiency, such as fatigue, pale complexion, and lack of energy.
2. Angelica Sinensis Porridge

1. Wash Angelica Sinensis and soak it in about 600 ml of warm water for 10 minutes in a clay pot, then decoct it twice, boiling each time and simmering for 20 to 30 minutes, collecting 150 ml of the decoction.
2. Soak and wash the red dates.
3. Wash the japonica rice.
4. Combine the japonica rice, red dates, and sugar in a pot, add the medicinal decoction, and an appropriate amount of water to cook the porridge.
3. Ginger and Angelica Sinensis Lamb Porridge

Ingredients: 20 grams of Ginger, 15 grams of Angelica Sinensis, 100 grams of Lamb, and 250 grams of Japonica Rice.
Seasoning: 2 teaspoons of Shaoxing Wine, 1/2 teaspoon of Salt, 1/3 teaspoon of MSG, 1 tablespoon of Chicken Fat, 10 grams of Green Onion, and 3/5 teaspoon of Pepper.
Preparation: Combine the japonica rice, ginger, green onion, Shaoxing wine, lamb, and Angelica Sinensis in a pot, add 800 grams of water, bring to a boil over high heat, then simmer for 35 minutes. Add salt, MSG, pepper, and chicken fat, stir well, and serve.
3

Side Effects of Angelica Sinensis
1. Excessive dosage, such as with Angelica Sinensis tincture, may cause fatigue and drowsiness, which can disappear after stopping the medication, but should not be taken in large amounts.
2. Allergic reactions may occur with some injectable forms of Angelica Sinensis, potentially leading to anaphylactic shock, requiring special attention.
3. Improper use: Angelica Sinensis is a sweet, warm, and moistening tonic; it should not be used in cases of heat excess and bleeding. Caution is advised for those with fullness and loose stools.
4. The essential oil of Angelica Sinensis should not be consumed due to the presence of trace carcinogenic substances.
5. Patients with chronic diarrhea or abdominal distension should avoid Angelica Sinensis.
6. Pregnant women should not use Angelica Sinensis.
7. Children should not use Angelica Sinensis.

【Copyright Statement】
Some content is sourced from the internet and other public platforms. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal within 24 hours. The content is for reference only and does not guarantee the accuracy of the article. All information should not be used for individual diagnosis, medication, or treatment, and cannot replace the advice of healthcare professionals. If you suffer any loss or damage from using the information published by this account, this account bears no legal responsibility. By browsing the content published by this account, your browsing behavior will be regarded as acceptance of all the contents of this statement.



Welcome to follow Kaifeng Guangming Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital
WeChat Video Account
Sharing Ophthalmology Knowledge
Contributed by: Hou Bao, Wang Zi Lu
Reviewed by: Liu Hao

