Some friends experience a lack of appetite due to irregular eating habits, and consuming cold foods can trigger stomach pain, often accompanied by the occurrence of sour regurgitation.

Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) believes that Spleen and Stomach Yang Deficiency is characterized by the deficiency of Yang Qi in the spleen and stomach, with an excess of Yin and cold.
The main causes are poor dietary habits, such as irregular eating, frequent consumption of cold drinks or chilled foods, combined with a fast-paced lifestyle and high mental stress, which can easily lead to stomach diseases. Spleen and Stomach Yang Deficiency can also develop from Spleen and Stomach Qi Deficiency.
 What Are the Symptoms of Spleen and Stomach Yang Deficiency?
What Are the Symptoms of Spleen and Stomach Yang Deficiency?
Individuals with Spleen and Stomach Yang Deficiency may experience symptoms such as abdominal distension, abdominal pain, lack of appetite, pale and sallow complexion, cold sensation in the stomach leading to diarrhea, weak pulse, thick white tongue coating, and fatigue.
 How to Alleviate Spleen and Stomach Yang Deficiency in Daily Life?
How to Alleviate Spleen and Stomach Yang Deficiency in Daily Life?
1. Dietary Regulation
In daily life, we should pay attention to regular eating habits, consuming meals at fixed times and in appropriate amounts. Additionally, it is important to keep warm, avoid raw and cold foods, and consume more warm foods.

2. Balance Work and Rest
Regular exercise is essential, but it is advisable to choose gentler forms of exercise, such as walking, jogging, or practicing Tai Chi. Intense exercise should be avoided as excessive sweating can deplete fluids and damage Qi.
3. Emotional Regulation
It is important to maintain a cheerful mood and a balanced mindset, learning to relax and relieve stress.
 Warm Reminder
Warm Reminder
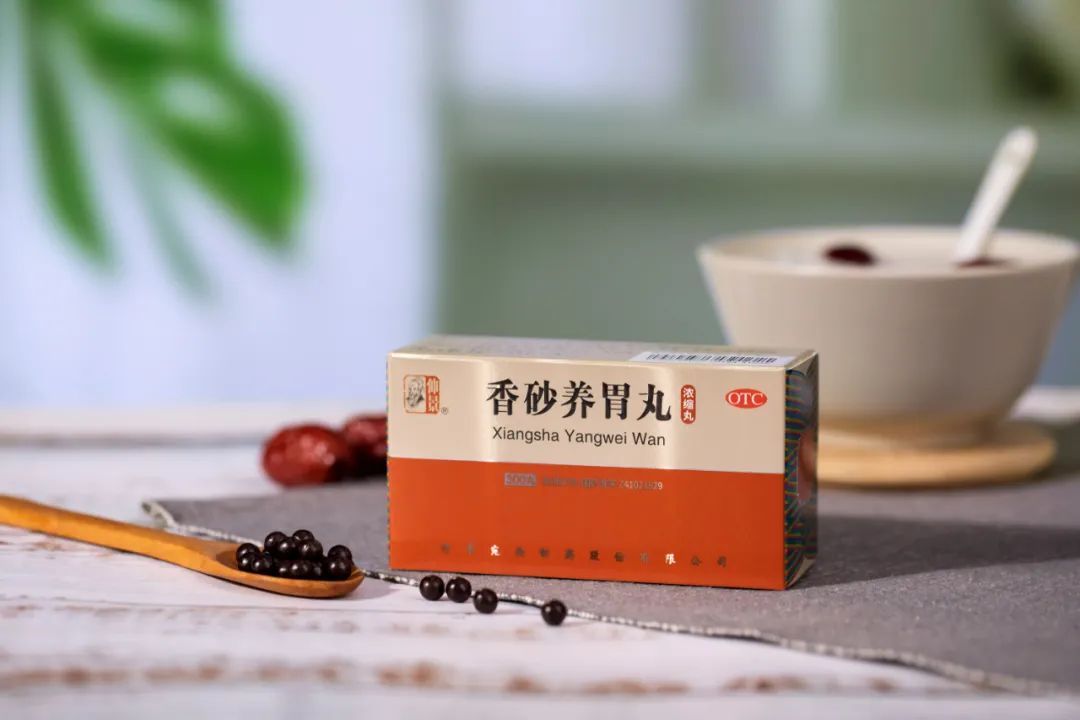
If you continue to experience a lack of appetite, stomach pain triggered by cold foods, and sour regurgitation, you may consider using some Chinese patent medicines, such as Xiangsha Yangwei Wan (Xiangsha Stomach Nourishing Pill). This formula warms the middle and harmonizes the stomach, primarily suitable for symptoms like lack of appetite, fullness and discomfort in the stomach, or sour regurgitation.
Xiangsha Yangwei Wan is composed of Mu Xiang (Aucklandia), Sha Ren (Amomum), Bai Zhu (White Atractylodes), Chen Pi (Dried Tangerine Peel), Fu Ling (Poria), Ban Xia (Pinellia, processed), Cu Xiang Fu (Cyperus), Zhi Shi (Bitter Orange, roasted), Dou Kou (Cardamom, shelled), Jiang Hou Po (Magnolia Bark), Guang Huo Xiang (Patchouli), Gan Cao (Licorice), Sheng Jiang (Fresh Ginger), and Da Zao (Jujube). In this formula, Bai Zhu tonifies Qi and strengthens the spleen, dries dampness, and promotes urination as the monarch herb. Sha Ren and Dou Kou transform dampness and move Qi, harmonizing the middle and stopping vomiting; Chen Pi and Hou Po move Qi and harmonize the middle, drying dampness and eliminating stagnation. Mu Xiang and Xiang Fu regulate Qi, relieve depression, and alleviate stomach pain, serving as ministerial herbs. Fu Ling strengthens the spleen and resolves dampness; Zhi Shi breaks Qi stagnation and eliminates accumulation, dispersing clumps and relieving fullness; Ban Xia descends rebellious Qi, stops vomiting, and disperses clumps, serving as assistant herbs. Gan Cao harmonizes the properties of the herbs as the envoy herb. The entire formula works together to strengthen the spleen, eliminate dampness, move Qi, and harmonize the middle.

Warm Reminder:
1. Over-the-counter medications should be taken according to the instructions or under medical advice; please read the instructions carefully before use.
2. Prescription medications should be taken under the guidance of a qualified physician.3. Use medications with caution; TCM emphasizes syndrome differentiation and treatment, and different conditions require different medications. Therefore, if you feel unwell, it is best to visit a local reputable hospital for a professional consultation.
4. For patients with chronic diseases such as hypertension, heart disease, or liver disease, if you feel unwell, it is advisable to seek medical attention promptly and not to self-medicate.
Previous Content
1. Autumn Health Tips for Women: Focus on Liver Qi Regulation
2. What to Do When You Are Prone to Colds During Seasonal Changes?3. What is “Chronic Fatigue Syndrome”?4. After Autumn Begins, Skin Becomes Prone to Dryness and Itching; What Should Be Done?5. Preventing Diabetes: Don’t Overlook These Small Details~
Some images are sourced from Shetu Network,Copyright belongs to Shetu Network
Zhongjing Health Hotline400-1515-688
Welcome to inquire!