China has a long history of cupping therapy, with the earliest records dating back to the Western Han Dynasty, where it was merely considered a common surgical technique. It wasn’t until the Tang Dynasty’s “Wai Tai Mi Yao Fang” that cupping was officially documented as a therapeutic method. So, what is cupping? Cupping is a therapy that uses cups as tools, employing methods such as fire and suction to create negative pressure, which adheres to the skin, causing local bruising to achieve effects such as promoting circulation, invigorating blood flow, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold.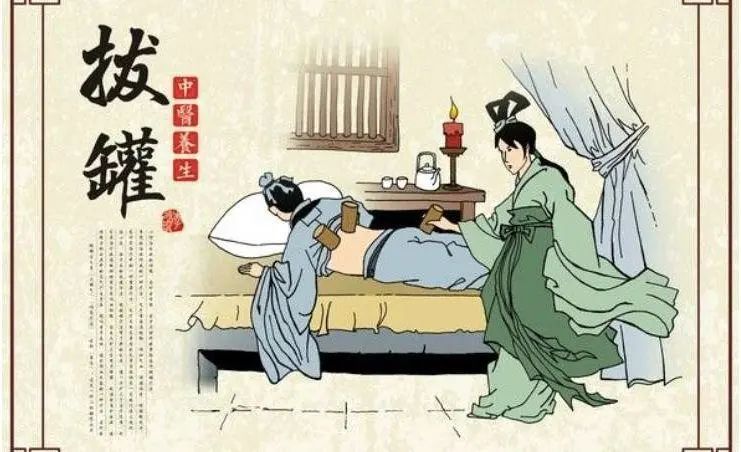 Below, I will provide a detailed introduction to the tools and methods of cupping, as well as its benefits and precautions.
Below, I will provide a detailed introduction to the tools and methods of cupping, as well as its benefits and precautions.
Cupping Tools
1. Bamboo Cups (1) Bamboo cups are made from solid, undamaged bamboo with a diameter of 3-5 cm, crafted into tubes 6-8 cm or 8-10 cm long. One end is left with a node as the base, and the other end is the opening. The green skin and inner membrane are scraped off, forming a cylindrical shape resembling a waist drum, and smoothed with sandpaper to ensure a smooth and even opening. (2) Advantages: Bamboo cups have strong suction power, making them suitable for areas with more muscle, such as the shoulders and back, as well as thinner-skinned areas like the wrists, ankles, and neck. Compared to small-diameter glass cups, bamboo cups have a significant advantage in suction power. Additionally, bamboo cups can be placed in boiling herbal solutions before cupping, enhancing local blood circulation through negative pressure and providing a dual effect with the herbal infusion. (3) Disadvantages: They are prone to cracking and leaking; being opaque makes it difficult to observe skin reactions inside the cup, thus not suitable for bloodletting cupping.2. Glass Cups (1) Glass cups are made from heat-resistant glass, shaped like a sphere with an open bottom and a wide belly, categorized by the diameter of the opening and the size of the cavity.
(2) Advantages: Bamboo cups have strong suction power, making them suitable for areas with more muscle, such as the shoulders and back, as well as thinner-skinned areas like the wrists, ankles, and neck. Compared to small-diameter glass cups, bamboo cups have a significant advantage in suction power. Additionally, bamboo cups can be placed in boiling herbal solutions before cupping, enhancing local blood circulation through negative pressure and providing a dual effect with the herbal infusion. (3) Disadvantages: They are prone to cracking and leaking; being opaque makes it difficult to observe skin reactions inside the cup, thus not suitable for bloodletting cupping.2. Glass Cups (1) Glass cups are made from heat-resistant glass, shaped like a sphere with an open bottom and a wide belly, categorized by the diameter of the opening and the size of the cavity. (2) Advantages: The smooth opening and transparent material allow for easy observation of skin congestion and bruising, helping to determine the duration of cupping. They are currently the most widely used cups in clinical practice, especially suitable for moving cupping, flash cupping, bloodletting cupping, and needle retention cupping. (3) Disadvantages: They conduct heat quickly, posing a risk of burns and are easily breakable.3. Vacuum Cups (1) Vacuum cups are made from organic glass or transparent engineering resin, using a piston at the top to control air extraction, creating negative pressure inside the cup for adhesion to selected areas.
(2) Advantages: The smooth opening and transparent material allow for easy observation of skin congestion and bruising, helping to determine the duration of cupping. They are currently the most widely used cups in clinical practice, especially suitable for moving cupping, flash cupping, bloodletting cupping, and needle retention cupping. (3) Disadvantages: They conduct heat quickly, posing a risk of burns and are easily breakable.3. Vacuum Cups (1) Vacuum cups are made from organic glass or transparent engineering resin, using a piston at the top to control air extraction, creating negative pressure inside the cup for adhesion to selected areas. (2) Advantages: Vacuum cups do not require fire or electricity, eliminating safety hazards and preventing burns; they are easy to operate and can be widely used for personal and family self-care, making them a popular new type of cupping device. (3) Disadvantages: They lack the warming stimulation effect of fire cups.4. Metal Cups (1) Typically made of copper, iron, or aluminum, resembling bamboo cups. (2) Advantages: They are not easily broken and are convenient for disinfection. (3) Disadvantages: They conduct heat too quickly, are expensive, and do not allow for observation of skin changes, leading to their decreased use.5. Composite Cups With advancements in science, more therapeutic devices are being integrated with cupping tools. For example, cups equipped with bloodletting devices can connect to a power source during cupping to enhance the warming effect, known as electric heat cups. Additionally, there are infrared therapy cups, ultraviolet lamps, laser emitters, and magnetic therapy cups.
(2) Advantages: Vacuum cups do not require fire or electricity, eliminating safety hazards and preventing burns; they are easy to operate and can be widely used for personal and family self-care, making them a popular new type of cupping device. (3) Disadvantages: They lack the warming stimulation effect of fire cups.4. Metal Cups (1) Typically made of copper, iron, or aluminum, resembling bamboo cups. (2) Advantages: They are not easily broken and are convenient for disinfection. (3) Disadvantages: They conduct heat too quickly, are expensive, and do not allow for observation of skin changes, leading to their decreased use.5. Composite Cups With advancements in science, more therapeutic devices are being integrated with cupping tools. For example, cups equipped with bloodletting devices can connect to a power source during cupping to enhance the warming effect, known as electric heat cups. Additionally, there are infrared therapy cups, ultraviolet lamps, laser emitters, and magnetic therapy cups.
Cupping Methods
Using the principle of thermal expansion and contraction to expel air, the fire cupping method involves using the heat from flames to expel air from the cup, creating negative pressure that adheres to the skin. This can be divided into four types:
1. Fire Insertion Method: Light a small piece of paper or cotton, quickly insert it into the cup, and immediately place the cup over the area to be treated before the flame goes out. 2. Internal Fire Method: Use tweezers to hold a lit alcohol cotton ball, circle it inside the cup, and quickly place the cup over the treatment area.  3. Cotton Adhesion Method: Use a piece of cotton about 1 cm square, slightly soaked in alcohol, stick it to the inner wall of the cup, light it, and then place the cup over the selected area. 4. Fire Support Method: Place a non-flammable, heat-resistant object (2-3 cm in diameter) on the area to be treated, place a small alcohol cotton ball on top, light it, and then cover with the cup to create strong suction.
3. Cotton Adhesion Method: Use a piece of cotton about 1 cm square, slightly soaked in alcohol, stick it to the inner wall of the cup, light it, and then place the cup over the selected area. 4. Fire Support Method: Place a non-flammable, heat-resistant object (2-3 cm in diameter) on the area to be treated, place a small alcohol cotton ball on top, light it, and then cover with the cup to create strong suction.
In terms of cupping techniques, they can be categorized as follows: (1) Single Cup: Used for small areas of lesions or obvious tender points. Select an appropriate diameter cup based on the size of the lesion or tender area. (2) Multiple Cups: Used for more extensive lesions. Several cups can be applied to the affected area, sometimes arranged in rows, known as “row cupping.” For muscle strain, cups can be arranged along the muscle bundle. For certain internal organ bruising, cups can be arranged according to the anatomical location of the organs on the corresponding body surface. (3) Flash Cupping: Cups are applied and removed quickly, repeated multiple times until the skin becomes red. This is often used for local skin numbness or functional decline. (4) Retained Cupping: Cups are left in place for a certain period, typically 5-20 minutes. For cups with strong suction, the retention time should be reduced, especially in summer or on thinner skin to avoid skin damage. (5) Sliding Cupping: Also known as moving cupping, after suction, the cup is moved back and forth on the skin surface. This is generally used for larger areas with more muscle, such as the lower back, hips, and thighs. Larger diameter cups should be used, preferably glass cups. First, apply some lubricant around the cup’s opening, then hold the base of the cup, slightly tilt it so that the back half exerts pressure while the front half is lifted slightly, and slowly push it forward, moving back and forth several times until the skin becomes red or bruised.
Benefits of Cupping
Cupping can invigorate blood flow, dispel wind and cold, and reduce swelling and pain, making it effective for muscle strain in the lower back and lumbar disc herniation. Cupping can also be applied to acupuncture points to treat headaches, dizziness, eye swelling, cough, asthma, and abdominal pain, and multiple cups can be used simultaneously.
Cupping can expel cold and dampness, unblock meridians, eliminate stagnation, invigorate blood flow, reduce swelling and pain, and detoxify and clear heat, helping to balance yin and yang in the body, relieve fatigue, and enhance physical strength, thus achieving the goal of strengthening the body and eliminating pathogens. Therefore, many diseases can be treated with cupping therapy. The specific effects are as follows:
1. Balancing Yin and Yang. Excessive yang leads to heat, while excessive yin leads to cold. Fever is a manifestation of excessive yang, while chills and aversion to cold are symptoms of excessive yin. Cupping at the Dazhui (大椎) point can treat febrile diseases, while cupping at the Guanyuan (关元) point can treat cold-related diseases.2. Harmonizing the Organs. Cupping therapy creates negative pressure at specific acupuncture points, causing changes such as congestion and bruising, which connect the points through meridians to the internal organs, thus treating various organ diseases.3. Unblocking Meridians. Cupping therapy stimulates acupuncture points and the skin along the meridians through its warming mechanical stimulation and negative pressure, thus unblocking the meridians, harmonizing the defensive and nutritive qi, expelling pathogenic factors, and nourishing the muscles and joints, thereby treating various diseases.4. Assisting Diagnosis. Observing changes on the skin after cupping can help infer the nature of the disease, its location, and its relationship with the internal organs.5. Expelling Pathogenic Factors. Cupping therapy, by creating negative pressure at acupuncture points, can open the pores, disperse wind and cold, and also adjust the functions of the organs and meridians, boosting the body’s righteous qi and aiding in the expulsion of pathogenic factors.6. Bidirectional Regulation. Under consistent acupuncture point selection and cupping methods, cupping therapy exhibits a bidirectional regulatory effect.
Precautions for Cupping
1. Cups must be disinfected: Generally, use a 75% alcohol cotton ball to wipe the cup’s opening and body for disinfection. After disinfection, the cups can be dried with a clean cotton ball or allowed to air dry before use.
2. Ignition Method: Generally, the flash fire method is used. One hand holds the igniter, and the other holds the cup. Light the alcohol cotton ball (ensuring not too much alcohol to prevent dripping) and quickly insert it into the cup for about 1-3 seconds before removing it. The other hand should gently place the cup on the area to be treated. Do not ignite at the cup’s opening to avoid overheating and burns.
3. When cupping, generally choose areas that are full and elastic. Be cautious with areas of skin allergies, skin damage, thin muscles, or excessive hair; pregnant women should be especially cautious.4. Choose an appropriate position, generally lying down. Once the cup is applied, do not change positions to avoid the cup falling off.5. Select appropriately sized cups based on different areas. Test the cup on the area to ensure a good fit before application.6. When using multiple cups, the distance between them should not be too close, as this can cause pain due to skin pulling and make it difficult to maintain suction due to mutual pulling of the cups.7. During sliding cupping, avoid pushing and pulling over thin skin or bony areas to prevent skin damage or the cup leaking and falling off.8. When removing the cup, the technique should be gentle. Hold the cup with the right hand and press the skin around the cup with the left thumb or index finger to allow air to enter, releasing the suction so the cup can fall off naturally. Do not pull hard or twist to avoid skin damage.9. After cupping, the area may show redness or purplish discoloration, which is normal and usually resolves within a week. If there is severe bruising, do not cup the same area again. If the cup is left on too long, blisters may form. Small blisters do not require treatment and will absorb naturally, but care should be taken to avoid breaking them; larger blisters can be punctured with a sterilized needle at the base to drain fluid, covered with a sterile bandage to prevent infection.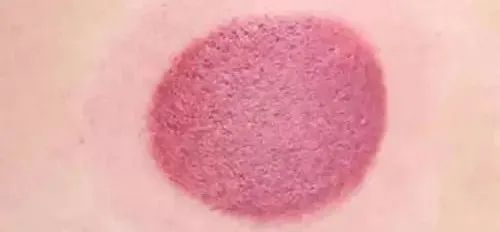 10. The room should be warm and well-ventilated. During cupping, avoid drafts from fans or air conditioning to prevent catching a cold.After cupping, the treated area should not be exposed to cold air or wind. If cupping is done on the neck, it is best to wear a high-collared shirt. For two hours after cupping, avoid bathing and do not use cold water on the treated area; bathing should be done with warm water.11. Bathe two hours after cupping. Some people try to extend the cupping duration for better therapeutic effects. However, experts advise that cupping should ideally be limited to 10-20 minutes; prolonged cupping may lead to blistering, ulceration, or even infection.12. Accurate Acupuncture Points for Cupping When cupping at home, it is essential to ensure the correct location. Cupping is not just about cupping where it hurts; TCM emphasizes syndrome differentiation and treatment. In addition to the painful area, related acupuncture points should also be cupped for better results. For example, if a patient has lower back pain, cupping may also be needed on points in the legs. 13. Prevent Infection
10. The room should be warm and well-ventilated. During cupping, avoid drafts from fans or air conditioning to prevent catching a cold.After cupping, the treated area should not be exposed to cold air or wind. If cupping is done on the neck, it is best to wear a high-collared shirt. For two hours after cupping, avoid bathing and do not use cold water on the treated area; bathing should be done with warm water.11. Bathe two hours after cupping. Some people try to extend the cupping duration for better therapeutic effects. However, experts advise that cupping should ideally be limited to 10-20 minutes; prolonged cupping may lead to blistering, ulceration, or even infection.12. Accurate Acupuncture Points for Cupping When cupping at home, it is essential to ensure the correct location. Cupping is not just about cupping where it hurts; TCM emphasizes syndrome differentiation and treatment. In addition to the painful area, related acupuncture points should also be cupped for better results. For example, if a patient has lower back pain, cupping may also be needed on points in the legs. 13. Prevent Infection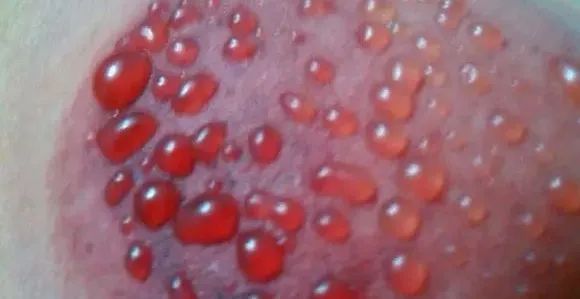 After cupping, if the skin shows redness or itching, do not scratch; this will dissipate after a few hours or days. If blisters, water droplets, bleeding points, or bruising occur, these are normal therapeutic responses. Minor blisters only need to be protected from breaking and will absorb naturally; larger blisters can be punctured at the base with a sterilized needle to drain fluid, covered with a sterile bandage to prevent infection. 14. Pregnant women should avoid cupping, or if cupping is necessary, it should be done by a professional. Cupping during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage. Cupping therapy during pregnancy can negatively affect the mother and the baby’s development. If pregnant women experience back pain or fatigue, they can use a warm towel for relief or consult a doctor for safe medications, and regular prenatal check-ups are recommended. In summary, cupping is not recommended during pregnancy. If feeling fatigued, simple massages from a partner can help alleviate pregnancy fatigue. 15. Children can undergo cupping, but due to their delicate skin, the duration should not exceed 10 minutes, and the cups should not be too tight. Cupping can benefit children, especially those with weaker constitutions, as it can improve immunity. When cupping children, timing is crucial; cupping should be done until the skin turns red. However, cupping is not suitable for children with blood disorders, skin swelling, ulcers, or other skin injuries, and those with thrombocytopenic purpura should also avoid cupping.
After cupping, if the skin shows redness or itching, do not scratch; this will dissipate after a few hours or days. If blisters, water droplets, bleeding points, or bruising occur, these are normal therapeutic responses. Minor blisters only need to be protected from breaking and will absorb naturally; larger blisters can be punctured at the base with a sterilized needle to drain fluid, covered with a sterile bandage to prevent infection. 14. Pregnant women should avoid cupping, or if cupping is necessary, it should be done by a professional. Cupping during pregnancy can lead to miscarriage. Cupping therapy during pregnancy can negatively affect the mother and the baby’s development. If pregnant women experience back pain or fatigue, they can use a warm towel for relief or consult a doctor for safe medications, and regular prenatal check-ups are recommended. In summary, cupping is not recommended during pregnancy. If feeling fatigued, simple massages from a partner can help alleviate pregnancy fatigue. 15. Children can undergo cupping, but due to their delicate skin, the duration should not exceed 10 minutes, and the cups should not be too tight. Cupping can benefit children, especially those with weaker constitutions, as it can improve immunity. When cupping children, timing is crucial; cupping should be done until the skin turns red. However, cupping is not suitable for children with blood disorders, skin swelling, ulcers, or other skin injuries, and those with thrombocytopenic purpura should also avoid cupping.

