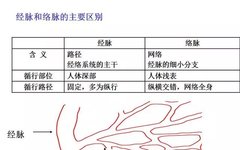
1. Meridians1. Definition of Meridians: Meridians refer to the Jingmai (经脉) and Luomai (络脉), which are pathways that connect the internal and external aspects of the body, linking the organs and limbs, and facilitating the flow of Qi (气) and blood.Jingmai — the main trunk of the meridian system.Jing: means a pathway, connecting the upper and lower parts, and linking the internal and external.Luomai — branches that diverge from the Jingmai.Luo: implies a network, smaller than the Jingmai, crisscrossing and spreading throughout the body.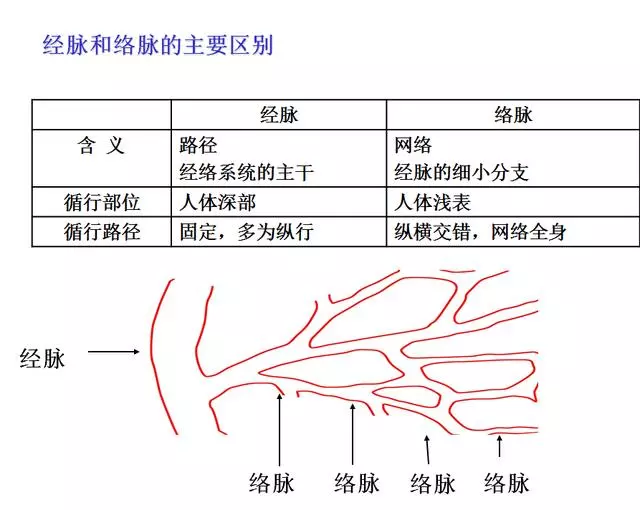 2. What are Meridians?(1) The pathways that connect points (acupoints) on the body with each other, as well as with the organs, sensory organs, and between the organs themselves, are called meridians.(2) Meridians are the channels of Qi and blood in the human body. They serve to connect the internal and external, linking the upper and lower parts, and connecting the left and right sides, forming a unified organic whole that integrates the external muscles, vessels, skin, sensory organs, and the internal organs.As mentioned in the “Ling Shu, Hai Lun” chapter: “The twelve Jingmai are internally connected to the organs and externally linked to the limbs.”(3) Meridians are the living map of the human body! Meridians are the pathways within the body that facilitate the flow of Qi and blood, connecting the organs and limbs, and linking the internal and external aspects. Only when the meridians are unobstructed can the Qi and blood flow freely, preventing health issues!(4) Meridians are the rivers and mountains of the human body, flowing endlessly.Meridians are like rivers and mountains, flowing continuously, surging without obstruction, facilitating the flow of Qi and blood, and connecting like a loop!(5) Meridians are the control center for human health! As stated in the “Ling Shu, Jingmai”: “The meridians determine life and death, address various diseases, and regulate deficiency and excess; they must be unobstructed.” The reasons for life and disease, as well as the healing process, all lie within the meridians! The meridians play a crucial role in maintaining life activities, regulating various diseases, and balancing the body’s deficiency and excess. Therefore, it is said that meridians are the control center for human health!(6) Meridians are our personal physicians!
2. What are Meridians?(1) The pathways that connect points (acupoints) on the body with each other, as well as with the organs, sensory organs, and between the organs themselves, are called meridians.(2) Meridians are the channels of Qi and blood in the human body. They serve to connect the internal and external, linking the upper and lower parts, and connecting the left and right sides, forming a unified organic whole that integrates the external muscles, vessels, skin, sensory organs, and the internal organs.As mentioned in the “Ling Shu, Hai Lun” chapter: “The twelve Jingmai are internally connected to the organs and externally linked to the limbs.”(3) Meridians are the living map of the human body! Meridians are the pathways within the body that facilitate the flow of Qi and blood, connecting the organs and limbs, and linking the internal and external aspects. Only when the meridians are unobstructed can the Qi and blood flow freely, preventing health issues!(4) Meridians are the rivers and mountains of the human body, flowing endlessly.Meridians are like rivers and mountains, flowing continuously, surging without obstruction, facilitating the flow of Qi and blood, and connecting like a loop!(5) Meridians are the control center for human health! As stated in the “Ling Shu, Jingmai”: “The meridians determine life and death, address various diseases, and regulate deficiency and excess; they must be unobstructed.” The reasons for life and disease, as well as the healing process, all lie within the meridians! The meridians play a crucial role in maintaining life activities, regulating various diseases, and balancing the body’s deficiency and excess. Therefore, it is said that meridians are the control center for human health!(6) Meridians are our personal physicians!
- When the meridians are open, there is no pain; when there is pain, the meridians are blocked!
- Meridians are the barometer of our health!
- Meridian health maintenance not only treats existing diseases but also prevents future illnesses!
- Acupoints are our personal medicine bags!
- By learning meridian health maintenance, everyone can be a doctor!
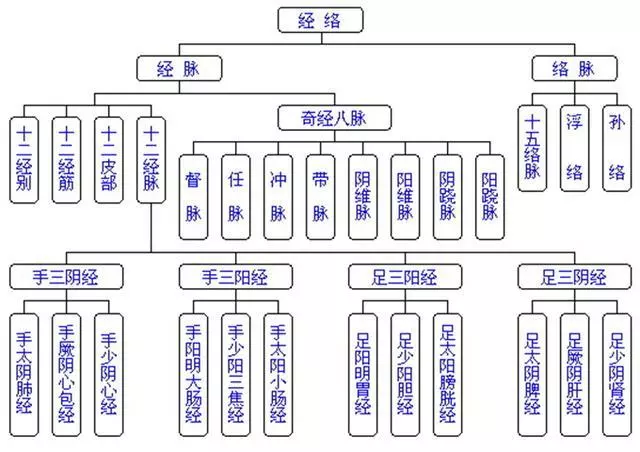
3. Composition of the Meridian System
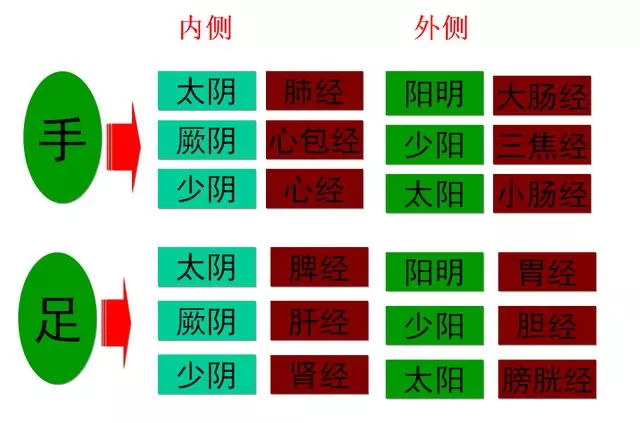
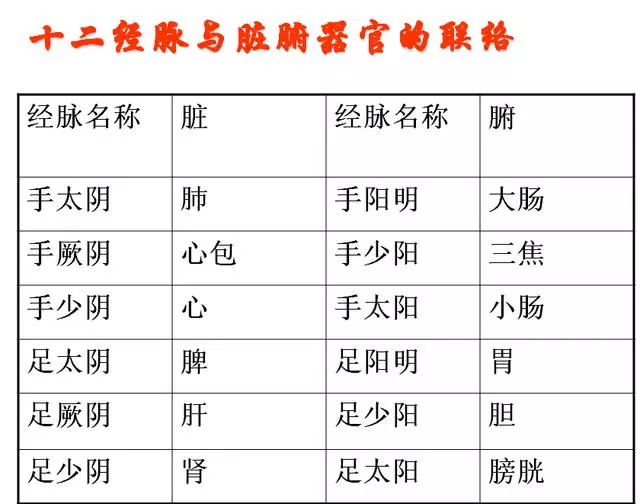
1. Names of the Twelve Meridians(1) Naming Principles1. Upper for hands, lower for feet: Those running in the upper limbs are hand meridians, while those in the lower limbs are foot meridians.2. Internal for Yin, external for Yang: The inner sides of the limbs are classified as Taiyin, Jueyin, and Shaoyin; the outer sides are classified as Yangming, Shaoyang, and Taiyang.3. Yin corresponds to organs, Yang corresponds to bowels: Yin meridians belong to organs, while Yang meridians belong to bowels.





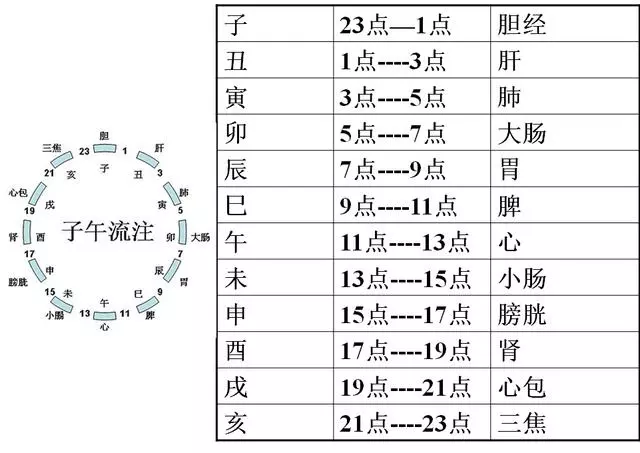

1. Pressing and Rubbing Acupoints
Acupoints, also known as Shu (腧) points or Qi (气) points, are special locations on the body where the functional activities of the organs and meridians accumulate on the surface, such as the Hegu (合谷) point and Zusanli (足三里) point. By massaging specific acupoints, one can unblock the meridians, regulate Qi and blood, and adjust bodily functions, achieving health maintenance or treating diseases.

2. Pushing and Rubbing the Meridians

3. Tapping the Meridians
Tapping the meridians requires a greater stimulus than rubbing!

4. How to Accurately Locate Acupoints?
Look for reactions — when there are abnormalities in the body, various reactions will appear at the acupoints, including:
- Tenderness: Pressing with a finger causes pain or swelling;
- Hard nodules: Hard nodules can be felt upon touching with a finger;
- Heightened sensitivity: A slight stimulus causes itching on the skin;
- Pigmentation: Appearance of dark spots or patches;
- Temperature changes: There is a temperature difference compared to the surrounding skin, such as feeling cold or hot.
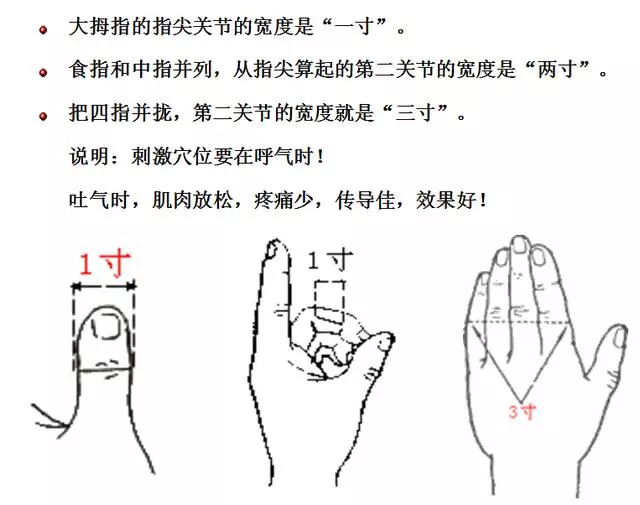
Disclaimer: The content of this article, if it involves formulas or therapies, is for reference only and should not be used indiscriminately. The article and images are sourced from the internet; if there is any infringement, please contact for removal.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), the most brilliant treasure of the Chinese nation, has run through the entire history of the Chinese people and involves various cultural fields. As an ancient form of medicine, it still radiates its immortal light today!