Wind-cold common cold is one of the common clinical diseases, primarily caused by the body’s exposure to wind and cold, along with viral invasion, leading to dysfunction of the lung system in patients.
Wind-cold common cold is one of the common clinical diseases, primarily caused by the body’s exposure to wind and cold, along with viral invasion, leading to dysfunction of the lung system in patients. 01Seasons for Wind-Cold Common Cold
01Seasons for Wind-Cold Common Cold
Generally, wind-cold common cold is most common in winter and spring, while summer colds are mostly wind-heat common colds. However, there are exceptions; for instance, if you sweat a lot in summer and then enter a cooler air-conditioned room, this cold is also considered a wind-cold common cold.The period around the Spring Festival is also a peak time for wind-cold common colds.
 02Clinical Manifestations of Wind-Cold Common Cold
02Clinical Manifestations of Wind-Cold Common Cold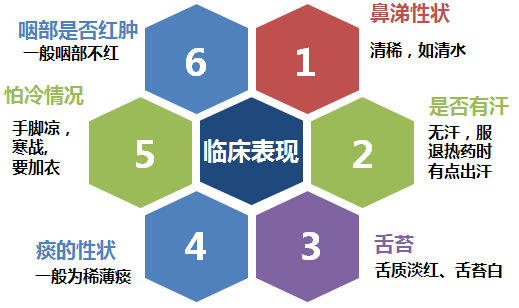 03Treatment of Wind-Cold Common Cold
03Treatment of Wind-Cold Common Cold
 If the cold symptoms are not severe, you can initially treat it with oral medications. Generally, traditional Chinese patent medicines are often the first choice for wind-cold common cold. For wind-cold common cold, one should choose patent medicines that have the effects of warming and dispersing the exterior, and dispelling cold from the lungs. The main ingredients of such patent medicines typically include Ma Huang (Ephedra), Gui Zhi (Cinnamon Twig), Qiang Huo (Notopterygium), Jing Jie (Schizonepeta), Fang Feng (Siler), Sheng Jiang (Fresh Ginger), etc., which are warming and dispersing herbs, along with Jie Geng (Platycodon) and Xing Ren (Apricot Kernel) to help descend lung qi. The efficacy of these patent medicines varies in the market, as shown in the table below.Table: Clinical Application Characteristics of Several Wind-Cold Common Cold Patent Medicines
If the cold symptoms are not severe, you can initially treat it with oral medications. Generally, traditional Chinese patent medicines are often the first choice for wind-cold common cold. For wind-cold common cold, one should choose patent medicines that have the effects of warming and dispersing the exterior, and dispelling cold from the lungs. The main ingredients of such patent medicines typically include Ma Huang (Ephedra), Gui Zhi (Cinnamon Twig), Qiang Huo (Notopterygium), Jing Jie (Schizonepeta), Fang Feng (Siler), Sheng Jiang (Fresh Ginger), etc., which are warming and dispersing herbs, along with Jie Geng (Platycodon) and Xing Ren (Apricot Kernel) to help descend lung qi. The efficacy of these patent medicines varies in the market, as shown in the table below.Table: Clinical Application Characteristics of Several Wind-Cold Common Cold Patent Medicines
| Name | Composition | Efficacy | Indications | Precautions |
| Wind-Cold Common Cold Granules | Ma Huang, Ge Gen, Zi Su Ye, Fang Feng, Gui Zhi, Bai Zhi, Chen Pi, etc. | Disperse the exterior and induce sweatingDisperse wind and dispel cold | Used for wind-cold common cold with symptoms of chills, fever, headache, no sweating, cough, nasal congestion, and clear nasal discharge. | 1. Jiu Wei Qiang Huo Granules not only have the effect of dispersing wind-cold but also can eliminate dampness and relieve pain, suitable for exterior wind-cold-damp syndrome, with key symptoms of chills, fever, no sweating, heavy headache, and body aches;2. Gui Zhi Granules is a relatively special wind-cold common cold medicine, which has the effect of harmonizing the nutritive and defensive qi, used for treating exterior wind-cold with deficiency syndrome, with key symptoms of aversion to wind, fever, and sweating. Although Gui Zhi Granules can also induce sweating, it actually releases the muscle layer and disperses the exterior, harmonizing the nutritive and defensive qi, thus can treat existing sweating symptoms. |
| Jiu Wei Qiang Huo Granules | Qiang Huo, Fang Feng, Cang Zhu, Xi Xin, Chuan Xiong, Bai Zhi, etc. | Disperse the exterior and dispel coldClear internal heat | Used for exterior wind-cold with dampness causing chills, fever, no sweating, heavy headache, and body aches. | |
| Zheng Chai Hu Granules | Chai Hu, Chen Pi, Fang Feng, Chi Shao, Gan Cao, Sheng Jiang | Disperse wind-coldRelieve heat and pain | Used for the initial onset of exterior wind-cold, with symptoms of fever, chills, no sweating, headache, nasal congestion, sneezing, itchy throat, cough, and body aches. | |
| Jing Fang Granules | Jing Jie, Fang Feng, Qiang Huo, Du Huo, Chai Hu, Qian Hu, Chuan Xiong, etc. | Induce sweating and disperse the exteriorRegulate the lungs and resolve phlegm | Used for wind-cold common cold, headache, body aches, chills, no sweating, nasal congestion, runny nose, cough. | |
| Gui Zhi Granules | Gui Zhi, Bai Shao, Gan Cao, Sheng Jiang, Da Zao | Release the muscle layer and disperse the exteriorHarmonize the nutritive and defensive qi | Used for exterior wind invasion, headache, fever, nasal congestion, dry heaving, sweating, and aversion to wind. |
When choosing medications, it is essential to pay attention to their ingredients. Many patent medicines on the market not only contain traditional Chinese herbs but also include Western medicines such as acetaminophen and chlorpheniramine maleate, like Xin Fu Fang Da Qing Ye Pian, Wei C Yin Qiao Pian, Guan Huang Gan Mao Granules, Yin Ju Qing Jie Pian, Kang Gan Ling Pian, etc. Some individuals may combine Western medicines with patent medicines without carefully checking the ingredients, which could lead to overlapping medications and adverse consequences.If your cold does not improve after taking medication, but rather worsens or new symptoms appear, you should seek medical attention promptly to avoid delaying treatment.04PrecautionsMost patent medicines for treating wind-cold common cold have strong warming and sweating effects, used for treating exterior wind-cold with excess syndrome, emphasizing symptoms of chills, fever, headache, and no sweating. If the patient has sweating, it is not advisable to use these medicines, as it may lead to excessive sweating and damage to the righteous qi. Additionally, patients with weak constitutions should use them cautiously.During a cold, to effectively eliminate pathogenic factors, a light diet is recommended. For children who have already started supplementary foods, especially those over one year old, it is advised to primarily consume congee during illness, avoiding meat and eggs, and gradually returning to a normal diet after recovery. For older children, milk should also be suspended, as these foods are hard to digest and may increase the burden on the spleen and stomach, making it difficult to eliminate pathogenic factors. For adults with wind-cold common cold, especially during the Spring Festival, a light, warm, and easily digestible diet should be prioritized, along with moderate exercise.
 References:[1] Cao Ying, Fan Shengkai, Shi Zhengzheng, et al. Discussion on the Relationship between Wind-Cold Pathogenic Qi and Externally Contracted Febrile Diseases [J]. Beijing Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 34(10): 800-802.[2] Ruan Feng. Differentiating Five Major Types of Common Cold Patent Medicines [J]. China Pharmacy, 2015, 8: 76-78.[3] Wang Zhiqiang. First Differentiate Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat before Taking Cold Medicine [J]. China Health and Wellness, 2018, 9: 61-62.[4] Hao Hongwen. For Colds, Distinguish between Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat [J]. China Reproductive Health, 2018, 3: 49-49.[5] Li Wenye. What are the Differences between Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat Colds [J]. Rural All-Purpose, 2016, 10: 51-51.Source: First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Medical UniversityImage Source: Internet, please delete if infringing
References:[1] Cao Ying, Fan Shengkai, Shi Zhengzheng, et al. Discussion on the Relationship between Wind-Cold Pathogenic Qi and Externally Contracted Febrile Diseases [J]. Beijing Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 34(10): 800-802.[2] Ruan Feng. Differentiating Five Major Types of Common Cold Patent Medicines [J]. China Pharmacy, 2015, 8: 76-78.[3] Wang Zhiqiang. First Differentiate Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat before Taking Cold Medicine [J]. China Health and Wellness, 2018, 9: 61-62.[4] Hao Hongwen. For Colds, Distinguish between Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat [J]. China Reproductive Health, 2018, 3: 49-49.[5] Li Wenye. What are the Differences between Wind-Cold and Wind-Heat Colds [J]. Rural All-Purpose, 2016, 10: 51-51.Source: First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Medical UniversityImage Source: Internet, please delete if infringing Recommended HighlightsQuestions for Nursing Mothers: Should I Take Medicine for a Fever or Not? Continue Breastfeeding or Stop? Are You Still Troubled by Obesity? Want to Get Slim? Check Here! As Winter Approaches, Beware of Overusing Allergy Medications! Should Medications be Taken Before or After Meals? If You Don’t Know, Read My Comprehensive Guide
Recommended HighlightsQuestions for Nursing Mothers: Should I Take Medicine for a Fever or Not? Continue Breastfeeding or Stop? Are You Still Troubled by Obesity? Want to Get Slim? Check Here! As Winter Approaches, Beware of Overusing Allergy Medications! Should Medications be Taken Before or After Meals? If You Don’t Know, Read My Comprehensive Guide
Authoritative Review Expert

Cao Junling
-
Director of the Pharmacy Department, Dongfang Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine
-
Vice Chairman of the Clinical Rational Drug Use Professional Committee of the China Pharmaceutical Education Association
-
Chairman of the Hospital Pharmacy Branch of the Chinese Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine
-
Chairman of the Talent Cultivation Working Committee of the Beijing Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine
-
Chairman of the Clinical Pharmacist Branch of the Chinese Pharmacists Association
-
Chairman of the Textbook Construction Guidance Committee for Clinical Pharmacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Higher Education
-
Expert in the National Health and Family Planning Commission’s Drug Policy Expert Database
-
Leader of the National Key Specialty Collaborative Group for Clinical Pharmacy
-
Director of the Beijing Pharmaceutical Society
-
First Batch of Key Talent Guidance Teachers for Traditional Chinese Medicine in Beijing
-
Deputy Editor of “Evaluation and Analysis of Hospital Medication in China”, Editorial Board Member of “Drug Evaluation”, Editorial Board Member of “China Pharmacy”, Editorial Board Member of “Chinese New Drug Journal”, Editorial Board Member of “World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine”, Editorial Board Member of “Global Traditional Chinese Medicine”; Reviewer for “Medical Chemistry Research”, etc.
-
Has presided over projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation, awarded as an Excellent Pharmacist by the China Pharmaceutical Association, and recipient of the Second Purple Crystal Award—Pharmaceutical English Award. Chief editor of 10 works, deputy editor of 2 works, and published over 100 papers.

Waiting for your “Like”