Moxibustion is a traditional Chinese therapy that utilizes ignited moxa sticks or cones to produce heat that stimulates acupuncture points on the body surface. This method activates the flow of qi (气) to adjust the disordered physiological functions of the body, achieving the effects of strengthening health and preventing disease. It is a primary method for health maintenance among the general public. Compared to acupuncture, moxibustion primarily serves to warm and dispel cold, and its effects are longer-lasting for tonifying deficiencies, but it can also be used for both tonification and sedation.
When qi is abundant, it should be sedated; when deficient, it should be tonified. For tonification, do not blow on the fire; it should extinguish on its own. For sedation, blow vigorously on the fire to ensure it extinguishes quickly. — From the “Lingshu” (灵枢) chapter of the “Huangdi Neijing” (黄帝内经).
The methods of tonification and sedation in moxibustion reflect the TCM principle of differentiation and treatment. Different operational methods are applied based on the condition’s deficiency or excess, tonifying what is lacking and sedating what is excessive. Therefore, the tonification and sedation methods of moxibustion are important means to smooth the meridians, harmonize qi and blood, balance yin and yang, and support the righteous while dispelling the evil.
Principles of Tonification and Sedation
In tonification, “do not blow on the fire” allows the warmth to gradually transition from hot to warm, and from warm to cool. This sustained and gentle heat stimulation enables the meridians and acupoints to function normally over time.
In sedation, “blow vigorously on the fire” is necessary because when the warmth of the moxa is suddenly interrupted, the state of the meridians and acupoints changes rapidly from a tonifying state to a sedating state, thus achieving the therapeutic effect of dispelling evils.
Tonification Method of Moxibustion
After igniting the moxa cone, do not blow on the fire; let it burn out on its own. The heat should be mild and gentle, and the duration should be long, with a larger number of moxa cones used. After the moxibustion treatment, press on the treated acupoint to gather the true qi (真气) and prevent it from dispersing, enhancing the warming effect to smooth the meridians, dispel cold evils, support yang, benefit qi, promote blood circulation, and strengthen bodily functions.
Sedation Method of Moxibustion

After igniting the moxa cone, blow vigorously to enhance the fire, which should burn quickly and extinguish rapidly. When the patient feels a burning sensation locally, quickly replace the moxa cone and continue moxibustion. The treatment time is relatively short, and after moxibustion, do not press on the acupoint; simply allow the evil qi to disperse.
Indications: This method can be used to regulate external wind-cold fever, rheumatic diseases, traumatic bruising, etc.; acute inflammations such as tonsillitis, parotitis, and lymphadenitis often utilize fire moxibustion. Local moxibustion is commonly used for neurodermatitis, herpes zoster, and warts.
Selection of Moxibustion Points
Each acupoint has its specific therapeutic effects. Selecting different acupoints for moxibustion yields different tonification and sedation effects. For example, the Qihai (气海) point is a tonification point for qi; moxibustion at this point can significantly benefit patients with qi deficiency. The Feishu (肺俞) point is used to dispel wind and cold; for patients with wind-cold exterior syndrome, moxibustion at this point can achieve the effects of dispelling wind, releasing the exterior, and warming the lungs.
1. Shenque Point (神阙穴)
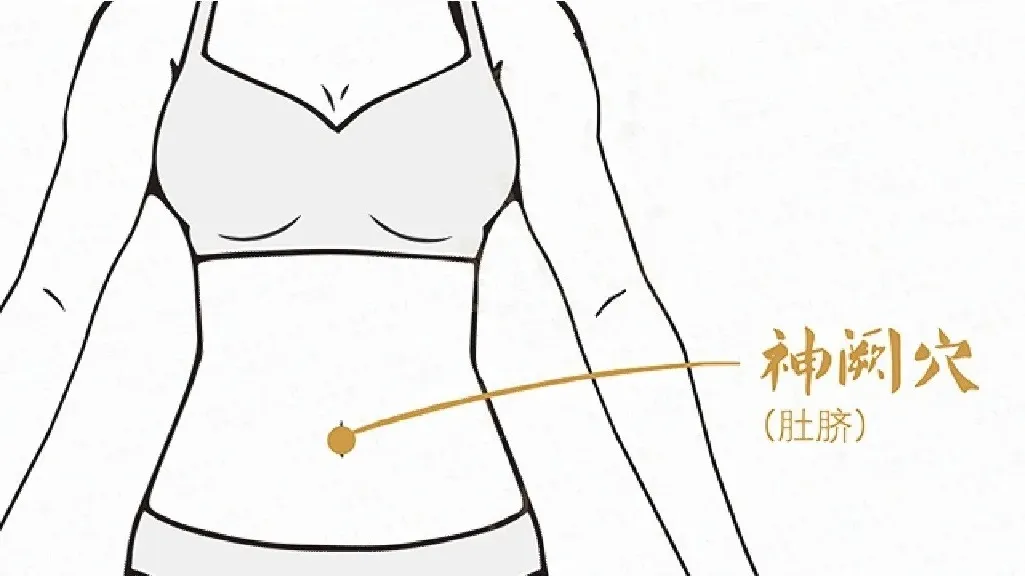
The Shenque point is located at the navel and is a commonly used point for moxibustion. It can regulate spleen and stomach functions, alleviate abdominal pain and diarrhea, promote blood circulation to relieve pain, and treat conditions such as menstrual cramps and qi-blood deficiency.
2. Guanyuan Point (关元穴)
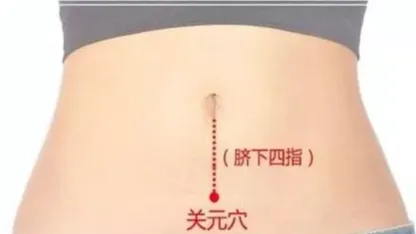
The Guanyuan point is located on the anterior midline of the lower abdomen, 3 cun below the navel. Moxibustion at this point has the effects of tonifying the kidneys, securing essence, and regulating qi and blood as well as spleen and stomach functions.
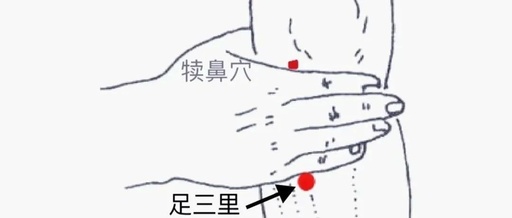
3. Zusanli Point (足三里)
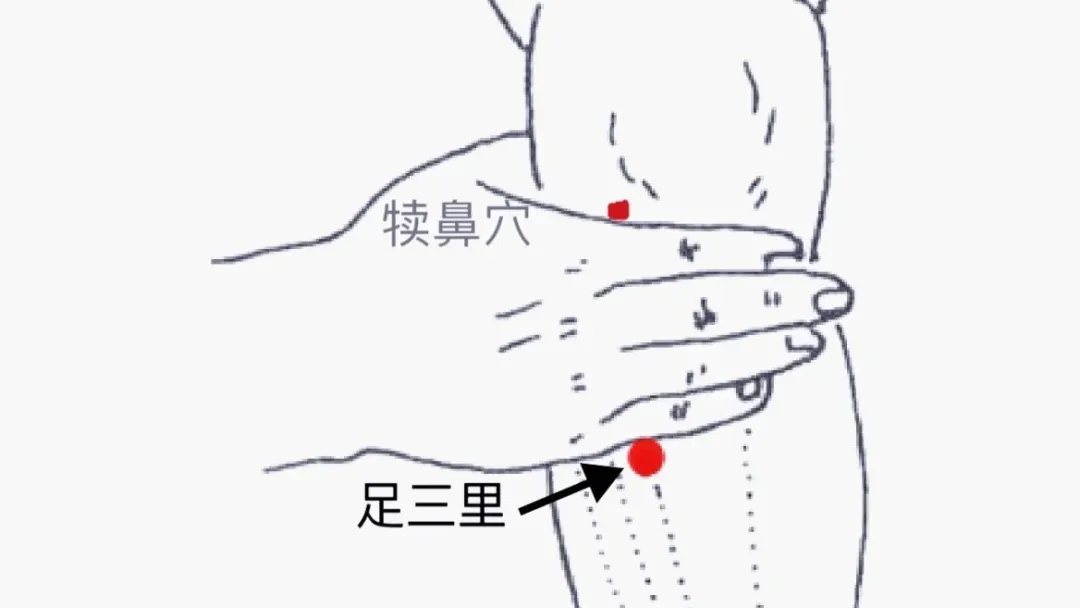
The Zusanli point is located on the lower leg. When the knee is flexed, the lateral depression below the kneecap is called the Dubi point; moving down 3 cun from this point is the Zusanli point, which has effects of regulating the spleen and stomach, tonifying qi, strengthening spleen yang, harmonizing the stomach, and dispelling cold.
4. Sanyinjiao Point (三阴交)
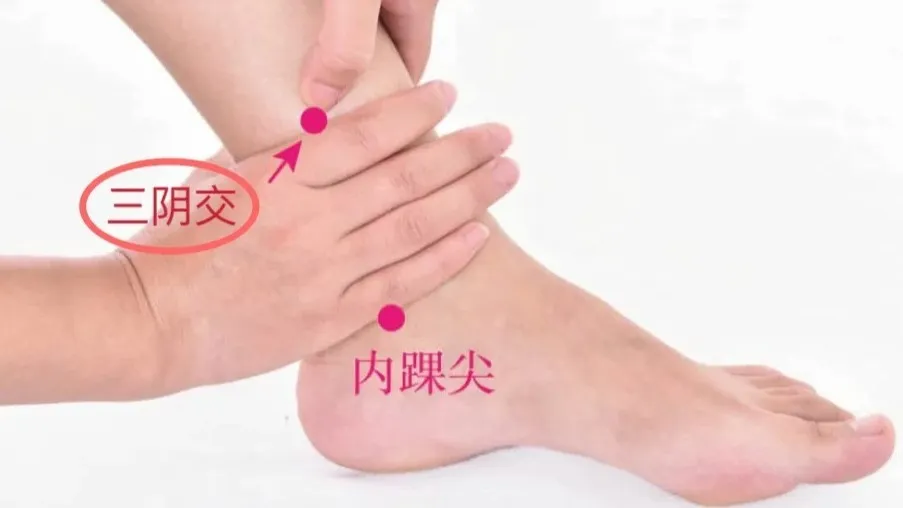
The Sanyinjiao point is located 3 cun above the tip of the inner ankle bone, where the tibia can be felt. This point is the intersection of the spleen, liver, and kidney meridians, and has effects of strengthening the spleen, regulating blood, and benefiting the kidneys while calming the liver.
Note: Before performing moxibustion, please consult a qualified hospital to determine if your constitution is suitable and to receive advice from a physician on selecting moxibustion points and methods.
Precautions for Moxibustion
1. Moxibustion should not be performed when overly hungry, overly full, intoxicated, extremely frightened, angry, or thirsty.
2. Women during pregnancy and menstruation should consult a physician for special circumstances before undergoing moxibustion.
3. Although moxibustion has a wide range of applications, it is not suitable for those with heat syndromes, yin deficiency with yang excess, five hearts heat, flushed face and ears, or internal accumulation of heat to prevent fainting.
4. The duration of each moxibustion session should not be too long. If the skin becomes overly red, itchy, or feels burning, moxibustion should be stopped immediately.
5. After moxibustion, ensure that the fire is completely extinguished to prevent fire hazards.
6. If you feel fatigued, dry mouth, or general discomfort after moxibustion, generally no treatment is needed; you can drink a little warm water and rest to recover.

↙Read the original text Online learning of moxibustion丨If this is useful to you, please clickTo see Like↘