Click the blue text to follow us

Creams and Ointments
Do you know how to use them correctly?
Author of this issue

Qiu Zengliang, Chief Pharmacist of the Pharmacy Department at Kaifeng People’s Hospital, specializes in medication dispensing, intravenous drug preparation, prescription review, and rational drug use guidance, familiar with relevant laws, regulations, standards, and technical specifications in this field.
Skin diseases are common ailments, and topical medications are essential formulations for treating skin conditions. Topical preparations include solutions, mixtures, tinctures, creams, ointments, gels, etc. Do you understand how to use these various topical formulations?
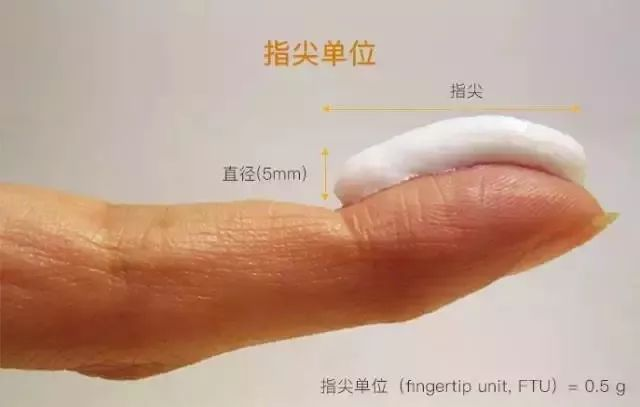
First, we need to understand the concept of fingertip units. In dermatology, when applying these formulations, the fingertip unit method is generally used, which means that the amount of ointment squeezed out should cover the fingertip to the first joint, typically around 0.5 grams, which can cover an area the size of two palms. Due to the limited absorption capacity of the skin, the amount of medication should be appropriate, not excessively thick, as this not only wastes medication but can sometimes worsen the condition. If the doctor prescribes both solutions and ointments, apply the solution first, wait for it to dry, and then apply the ointment or gel. If the doctor prescribes two or more ointments, it is best to wait two hours after applying one before applying another; if time is tight, at least wait half an hour before applying the next ointment.
However, there are several important considerations when using certain topical medications:
1. Hormonal medications. Hormonal medications are very effective in treating some skin diseases, but long-term use can lead to skin thinning, atrophy, hypertrichosis, pigmentation, and telangiectasia. More severe cases may develop folliculitis and steroid-dependent dermatitis. Therefore, when using hormonal medications, it is essential to strictly follow the doctor’s instructions or the package insert to avoid prolonged use and potential side effects.
2. Some photosensitive topical medications. It is known that some individuals may experience allergies after consuming seafood or coming into contact with pollen. However, it is less known that exposure to ultraviolet light after using certain medications can also cause allergic reactions, known in medicine as drug-induced photosensitivity. These medications should ideally be used at night or in the morning, and after application, one should avoid sun exposure. If a photosensitive reaction occurs, first stop the medication immediately, then place the patient in a shaded area to avoid sunlight, and seek medical treatment promptly. During transport to the hospital, wear clothing and use an umbrella to minimize sun exposure.

3. Some topical medications with special applications, such as those for treating acne, are oxidizing agents that can slowly release new ecological oxygen on the skin, destroying the living environment of microorganisms and effectively killing Propionibacterium acnes. During use, adverse reactions may occur, such as localized itching, redness, swelling, and dryness with peeling. In cases of significant local inflammation, these should be used sparingly, applying 1-2 times to the affected area rather than widespread application, and should be avoided in cases of acute inflammation or ulceration.
Friendly reminder: There are various topical preparations for treating skin diseases. Always read the instructions carefully or consult a professional physician or pharmacist before use to achieve the best therapeutic effect.
Provided by: Pharmacy Department
Edited by: Publicity Department



