Click the top left corner to follow us
Atractylodes
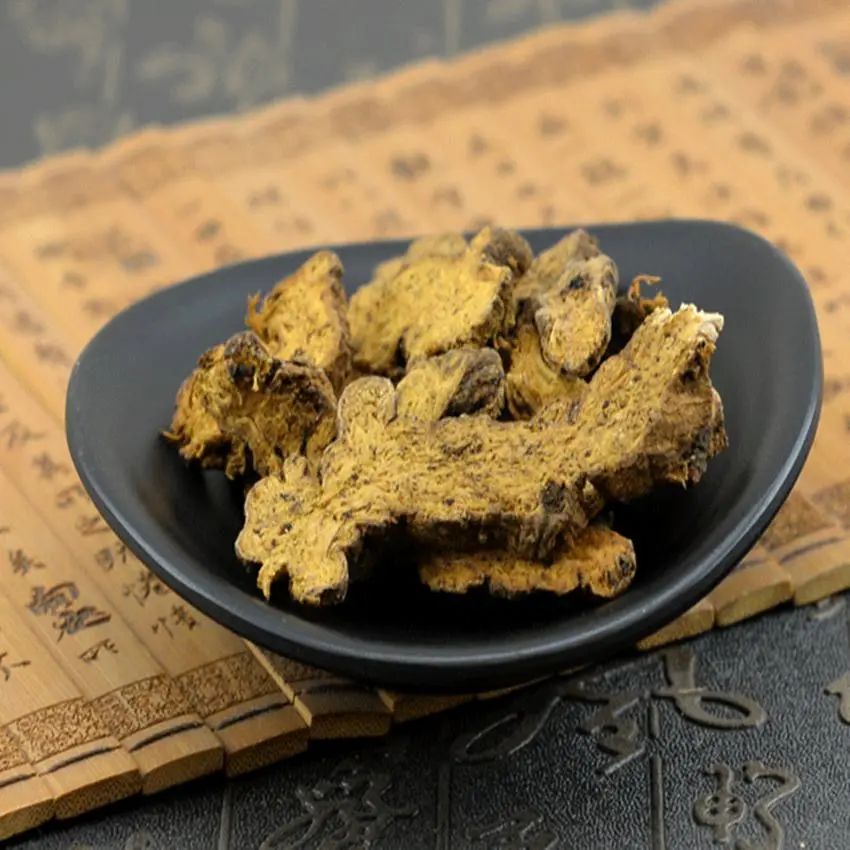


Plant Source
It is the dried rhizome of the plants Atractylodes lancea (Thunb.) DC. or Atractylodes chinensis (DC.) Koidz. from the Asteraceae family. Other names include Chi Zhu (Red Atractylodes), Qiang Tou Cai (Spearhead Vegetable), Shan Jing (Mountain Essence), Ma Ji (Horse Thistle), Qing Zhu (Green Atractylodes), and Xian Zhu (Immortal Atractylodes). Functions: Dries dampness and strengthens the spleen, dispels wind and disperses cold. Properties: Pungent, bitter, warm; enters the spleen, stomach, and liver meridians. Characteristics of the Medicinal Material: 1. Atractylodes lancea: The rhizome is irregularly nodular or slightly cylindrical, usually unbranched, 3-10 cm long and 1-2 cm in diameter. The surface is yellow-brown to gray-brown, with fine longitudinal grooves, wrinkles, and a few residual fibrous roots. The nodes often have shallow transverse grooves, and the internodes have round stem scars, often with residual stem bases at one end. Sometimes, white crystalline substances may appear on the surface. It is solid, easily broken, with a slightly uneven fracture surface, which is whitish or yellowish-white, scattered with numerous orange-yellow or brown-red oil chambers (commonly known as vermilion dots). Under ultraviolet light (254 nm), it does not show blue fluorescence. It has a strong aroma, with a slightly sweet, bitter, and pungent taste. 2. Atractylodes chinensis: The rhizome is often nodular, sometimes cylindrical, usually curved with short branches, 4-10 cm long and 0.7-4 cm in diameter. The surface is black-brown, turning yellow-brown when the outer skin is shed. It is light and loose; the fracture surface is fibrous, with small yellow-brown oil chambers, and does not produce crystals upon storage. The aroma is weaker, with a bitter and pungent taste.Characteristics of the Processed Product:
1. Atractylodes: Irregular thick slices with uneven edges, the cut surface is yellow-white or gray-white, scattered with numerous orange-yellow or brown-red oil spots (vermilion dots), and white hair-like crystals may appear upon prolonged storage (commonly referred to as frost). The edges are gray-brown or brown-black, with wrinkles and root hair marks. It is solid, with a unique aroma, and a slightly sweet, pungent, and bitter taste. 2. Processed Atractylodes: Similar in shape to Atractylodes slices, with yellow spots or a distinctly yellowish-brown surface. It has a slight aroma.
3. Fried Atractylodes: Similar in shape to Atractylodes slices, with a slightly yellow surface.
4. Charred Atractylodes: Similar in shape to Atractylodes slices, with a charred brown surface.
5. Atractylodes Carbon: Similar in shape to Atractylodes slices, with a black-brown surface.
6. Wheat-fried Atractylodes: Similar in shape to Atractylodes slices, with a deep yellow surface and a charred aroma.
7. Soil-fried Atractylodes: Similar in shape to Atractylodes slices, with a yellow-brown surface.
8. Salted Atractylodes: Similar in shape to Atractylodes slices, with a charred black surface and a slightly salty taste.
Production Areas:
1. Atractylodes lancea: Grows in shrublands and grasslands on hillsides.
2. Atractylodes chinensis: Grows in shady slopes of low mountains, under forests, and in drier areas.
3. Atractylodes lancea: Distributed in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Shandong, Henan, Hubei, Sichuan, and other regions, with cultivation in many areas.
4. Atractylodes chinensis: Distributed in North China, Northeast China, and regions such as Shandong, Henan, Shaanxi, Gansu, and Ningxia.
5. Atractylodes lancea: Mainly produced in Jiangsu, Hubei, and Henan, with the best quality from the Maoshan area in Jiangsu, hence the name Atractylodes lancea.
6. Atractylodes chinensis: Mainly produced in Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, and Liaoning.


Performance Characteristics
Indicated for damp obstruction in the middle jiao, wind-damp bi syndrome, wind-cold with damp exterior syndrome, night blindness, and blurred vision.
1. Damp obstruction in the middle jiao: This product is bitter and warm, drying dampness to eliminate turbidities, and pungent and aromatic to strengthen the spleen and harmonize the spleen and stomach. It is most suitable for symptoms of damp obstruction in the middle jiao, spleen dysfunction leading to abdominal distension, nausea, reduced appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, and a white greasy tongue coating.
2. Wind-damp bi syndrome: This product is pungent and drying, excelling at dispelling dampness, thus particularly suitable for bi syndrome with dampness predominating.
3. Wind-cold with damp exterior syndrome: This product is pungent and aromatic, capable of opening the skin and inducing sweating, dispelling wind-cold exterior pathogens, and due to its ability to overcome dampness, it is most suitable for wind-cold exterior syndrome with dampness.
4. This product can also brighten the eyes, used for night blindness and blurred vision.
5. Western medicine diagnoses chronic gastroenteritis as damp obstruction in the middle jiao, gastrointestinal neurosis, and gastrointestinal flu, while acute gastroenteritis belongs to summer-damp exterior syndrome, and enteric fever belongs to the initial stage of damp-heat.
Clinical Applications
1. For damp obstruction in the middle jiao, spleen dysfunction leading to abdominal distension, nausea, reduced appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue, it is often combined with Hou Po (Magnolia Bark), Chen Pi (Dried Tangerine Peel), etc., such as in the Ping Wei San formula (from the He Ji Ju Fang). 2. For spleen deficiency with damp accumulation, phlegm-damp retention, or external edema, it can be used with Fu Ling (Poria), Ze Xie (Alisma), Zhu Ling (Polyporus), etc., such as in the Wei Ling Tang formula (from the Zheng Zhi Zhun Sheng). 3. For damp-heat or summer-damp syndrome, it can be used with heat-clearing and damp-drying herbs. 4. For bi syndrome with dampness predominating, it can be used with Yi Yi Ren (Job’s Tears), Du Huo (Angelica Pubescens), etc., such as in the Yi Yi Ren Tang (from the Lai Zheng Zhi Cai).
5. For damp-heat bi pain, it can be combined with Shi Gao (Gypsum), Zhi Mu (Anemarrhena), etc., such as in the Bai Hu Jia Cang Zhu Tang formula (from the Pu Ji Ben Shi Fang).
6. For damp-heat atrophy syndrome, it can be used with Huang Bai (Phellodendron), Yi Yi Ren (Job’s Tears), Niuxi (Achyranthes), etc., such as in the Si Miao San formula (from the Cheng Fang Bi Du).
7. For lower damp turbidity, leukorrhea, damp sores, eczema, etc., it can be used with Long Dan (Gentiana), Huang Qin (Scutellaria), Zhi Zi (Gardenia) to clear heat and dry dampness.
8. For wind-cold exterior syndrome with dampness, it is often combined with Qiang Huo (Notopterygium), Bai Zhi (Angelica Dahurica), Fang Feng (Saposhnikovia), etc., such as in the Shen Shu San formula (from the Tai Ping Hui Min He Ji Ju Fang).
9. For night blindness and blurred vision, it can be used alone or cooked with lamb liver or pig liver for consumption.
Related Combinations
1. Atractylodes combined with Qiang Huo: Atractylodes is pungent and aromatic, capable of opening the skin and inducing sweating, dispelling wind-cold exterior pathogens, and excels at overcoming dampness; Qiang Huo is good at ascending and dispersing, with strong exterior-releasing and wind-damp dispelling effects. The combination enhances the ability to release the exterior and overcome dampness, thus most suitable for wind-cold exterior syndrome with dampness. 2. Atractylodes combined with Sheng Shi Gao: Atractylodes is pungent and warm, able to open the skin to induce sweating and strengthen the spleen and stomach to dry dampness; Sheng Shi Gao is pungent and sweet, very cold, good at clearing and dispersing, and excels at clearing heat pathogens. The combination can release the exterior and dispel dampness to resolve exterior pathogens, while also clearing heat and drying dampness to eliminate damp-heat. It is suitable for summer-heat or damp-heat causing strong fever, thirst, and heavy body with red urine. 3. Atractylodes combined with Hou Po: Atractylodes is bitter, warm, and pungent, good at drying dampness and strengthening the spleen; Hou Po is bitter, warm, and pungent, good at drying dampness and relieving fullness. The combination enhances the effects of strengthening the spleen and drying dampness, suitable for damp stagnation in the middle jiao, abdominal distension, etc.
4. Atractylodes combined with Fu Ling: Atractylodes strengthens the spleen and dries dampness; Fu Ling promotes urination and drains dampness. The combination enhances the effects of strengthening the spleen and draining dampness, suitable for spleen deficiency with damp accumulation, phlegm-damp retention, or external edema.
5. Atractylodes combined with Xiang Fu: Atractylodes is pungent and aromatic, good at ascending and dispersing, able to strengthen the spleen and dry dampness, eliminate turbidities to benefit the spleen, and resolve damp stagnation to promote qi; Xiang Fu is pungent and dispersing, good at descending and draining, able to soothe liver qi to resolve stagnation and relieve fullness. The combination of ascending and descending enhances the effects of promoting qi and resolving stagnation, suitable for chest and abdominal fullness, vomiting, acid regurgitation, and abdominal pain caused by emotional distress and stagnation.
6. Atractylodes combined with Di Yu: Atractylodes is good at drying dampness and strengthening the spleen; Di Yu is good at cooling blood and stopping bleeding. The combination has the effects of drying dampness and cooling blood to stop bleeding, suitable for dysentery, blood in stool, and hemorrhoids with bleeding caused by damp-heat in the large intestine.
7. Atractylodes combined with Bai Jie Zi: Atractylodes dries dampness and strengthens the spleen, dispelling wind and eliminating dampness; Bai Jie Zi resolves phlegm and disperses nodules, unblocking meridians and relieving pain. The combination is effective in eliminating superficial phlegm-dampness and relieving pain, suitable for joint pain and numbness caused by wind-damp phlegm obstruction in the meridians.
8. Atractylodes combined with Hei Zhi Ma: Atractylodes brightens the eyes; Hei Zhi Ma nourishes the liver and kidneys. The combination has the effect of nourishing the liver and kidneys to brighten the eyes, suitable for internal and external obstructions, night blindness, and cataracts.
Distinguishing Medicinal Uses
1. Atractylodes and processed Atractylodes, fried, charred, and Atractylodes: There are four commonly used processed varieties. Raw Atractylodes is warm and drying, pungent and strong, effective in drying dampness, dispelling wind, and scattering cold. It is used for wind-damp bi pain, numbness of the skin, knee pain, wind-cold flu, body pain, damp-heat fever, and joint pain. Processed Atractylodes has similar functions but is soaked in rice wash water to moderate its drying and pungent properties, with a harmonizing effect on the stomach. Wheat-fried Atractylodes reduces its pungency, moderates its drying properties, and enhances its aromatic qualities, strengthening its effects on the spleen and stomach. It is used for spleen-stomach disharmony, phlegm-damp stagnation, abdominal fullness, night blindness, and cataracts. Charred Atractylodes significantly reduces its pungency, focusing on solidifying the intestines and stopping diarrhea, suitable for spleen deficiency diarrhea, chronic dysentery, or women’s leukorrhea with white discharge. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that the “drying property” of Atractylodes is related to its volatile oil content. The processing methods of soaking in rice wash water, wheat frying, and charring can all reduce the volatile oil content, achieving the effect of “moderating the drying property.” 2. Atractylodes and Huo Xiang: Both belong to aromatic damp-transforming herbs, with functions of aromatic damp transformation and exterior-releasing. They are indicated for damp obstruction in the middle jiao, abdominal fullness, vomiting, and diarrhea, and can also be used for exterior syndromes and damp-heat fever. However, Huo Xiang is pungent, warm, and enters the spleen, stomach, and lung meridians, with excellent functions of awakening the spleen, transforming dampness, and opening the appetite, suitable for damp obstruction in the middle jiao, spleen dysfunction, and stomach disharmony causing chest fullness and lack of appetite; it is also good for stopping vomiting due to dampness and can be used for morning sickness during pregnancy. Atractylodes is pungent, bitter, warm, and enters the spleen and stomach meridians, with stronger drying and aromatic properties than Huo Xiang, excelling at drying dampness and strengthening the spleen, suitable for damp obstruction in the middle jiao, abdominal fullness, vomiting, and diarrhea; it can also promote the spleen and drain dampness, thus often used for phlegm-damp retention and spleen deficiency edema. Atractylodes has a strong aroma, dispelling foulness, and can dispel wind and dampness, thus suitable for exterior wind-cold dampness syndromes, wind-damp bi pain, and lower limb weakness; it can also be used for night blindness and cataracts.

 Related Discussions
Related Discussions
1. Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing: “Indicated for wind-cold damp bi, dead muscle spasms. Long-term consumption of decoction can lighten the body and prolong life without hunger.”
2. Ming Yi Bie Lu: “Indicated for headaches, phlegm-water elimination, expelling wind-water swelling, relieving fullness under the heart, and treating cholera with persistent vomiting and diarrhea, warming the stomach and promoting appetite.”
Related Medicinal Products/Prescriptions
1. Shu Gan Ping Wei Wan, Xiang Sha Ping Wei Wan (granules), Yu Zhi Ping An Wan.
2. Wan Dai Tang (from Fu Qing Zhu Nu Ke), Yue Ju Wan (from Dan Xi Xin Fa), Ping Wei San (from Jian Yao Ji Zhong Fang), Bu Huan Jin Zheng Qi San (from Yi Jian Fang), Chai Ping Tang (from Jing Yue Quan Shu), Er Miao San (from Dan Xi Xin Fa), San Miao Wan (from Yi Xue Zheng Chuan).
Dosage and Administration
Internal use: Decoction, 5-10 g.
External use: None.
Precautions
Contraindicated for those with yin deficiency and internal heat, and those with qi deficiency and excessive sweating.
Adverse Reactions/Contraindications
Dietary contraindications: Avoid sparrow meat, green fish, peaches, plums, cabbage, coriander, and garlic.

Medicinal Cuisine and Dietary Therapy

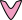

Atractylodes and Pig Liver Congee: 1. Function: Nourishes the liver and brightens the eyes, suitable for blurred vision. 2. Ingredients: 100 g pig liver, 9 g Atractylodes, 150 g millet. 3. Method: Dry and grind Atractylodes into powder, cut the pig liver into two connected slices, mix the medicine inside, tie with hemp thread, and cook with millet and appropriate water in a clay pot until done. 4. Usage: Eat the liver and drink the congee once a day for one week.
Methods of using Chinese medicine vary by individual; please follow medical advice before use.

End




