1. Introduction
Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, commonly known as Dang Gui, is a frequently used medicinal herb in traditional Chinese medicine. It is the dried root of the plant, valued for both its medicinal and culinary properties. The primary production area of Dang Gui is in the southeastern part of Gansu Province, particularly in Min County, which is known for its high yield and quality. It is also cultivated in provinces such as Yunnan, Sichuan, Shaanxi, and Hubei. According to the classic text Ben Cao Zheng, it is stated: “Dang Gui, with its sweet and heavy flavor, is particularly effective in nourishing blood; its light and spicy nature allows it to invigorate blood circulation. It embodies both the nourishing and invigorating properties, making it a supreme herb for blood health.” This can be simply understood as Dang Gui having the effects of nourishing blood, regulating menstruation, alleviating pain, and moistening dryness to facilitate bowel movements. In medicine, it is often used to treat conditions such as constipation due to dryness in the intestines and injuries caused by blood stagnation. The name ‘Dang Gui’ is said to derive from its ability to help the qi and blood return to their rightful places.

Figure 1. Slices of Dang Gui (Image source: www.zyccst.com)
As a precious medicinal material, Dang Gui contains many active components beneficial to human health. Currently, scientists have identified 165 chemical substances extracted from Dang Gui. Among these, phenolic acids, flavonoids, coumarins, polysaccharides, and phthalides are the most critical extracts, closely linked to its efficacy[1-2]. A simple understanding of the active components in Dang Gui is insufficient; a more comprehensive popularization of its potential effects on the human body is necessary. Therefore, this article will focus on the important active substances and pharmacological effects of Dang Gui, aiming to familiarize more readers with this herb.
2. Active Substances and Pharmacological Effects of Dang Gui
2.1 Phenolic Acid Components
Phenolic acids are one of the components of Dang Gui, including ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, and others[3]. The well-known ferulic acid is a terminal product in the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway, exhibiting antioxidant properties, inhibiting platelet aggregation, preventing cardiovascular diseases, reducing myocardial ischemia, and possessing antibacterial effects[4]. The phenylpropanoid metabolism is a crucial stage in plant growth, maximizing its efficacy in response to environmental stress. Chlorogenic acid is one of the bioactive components in Dang Gui and a terminal product of the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway, possessing pharmacological effects such as preventing cardiovascular damage, antioxidant activity, inhibiting tumor growth, antibacterial properties, lowering blood sugar, immune regulation, and protection against UV and radiation[5].
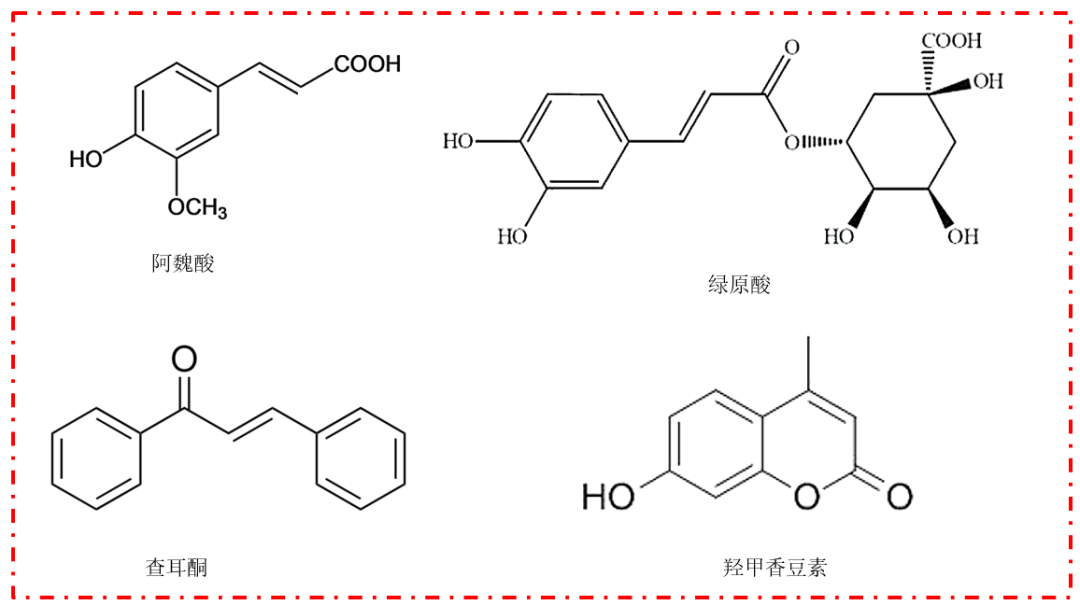
Figure 2. Structural formulas of active components in Dang Gui (Image source: Author)
2.2 Flavonoid Components
Flavonoids are a series of compounds formed by two phenolic hydroxyl groups connected by a central three-carbon atom, with the basic skeleton being 2-phenylchromone. As the most important active components of Dang Gui, they possess antiviral, antibacterial, antioxidant, tumor-inhibiting, and lipid metabolism-improving effects. Currently, derived chalcone substances and two flavonoid glycosides have been isolated from Dang Gui[6]. The chemical composition of flavonoids plays a significant role in plant growth and ecological defense, such as altering flower color, negatively regulating auxin transport, and influencing seed germination and root growth. Under stress conditions, flavonoids accumulate significantly, enhancing the plant’s resistance to environmental stress[7].
2.3 Coumarin Components
Coumarin compounds, known for their aromatic properties, are widespread in the plant kingdom, primarily existing as monomers or glycosides in dicotyledonous plants. The coumarins in Dang Gui include compounds such as piperine, isofraxidin, and others[8]. Coumarins can inhibit the growth and proliferation of cancer cells and have notable effects in treating depression, arrhythmias, and reducing myocardial contractility[9]. The synthesis methods of key chemical components in coumarins have also sparked discussion, involving multiple stages of reactions leading to the formation of coumarin from phenylalanine[10].
2.4 Dang Gui Polysaccharides
Dang Gui polysaccharides are one of the bioactive substances in Dang Gui. Through detailed analysis and identification of the chemical composition of Dang Gui polysaccharides, it has been found that they are composed of glucose, galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, fucose, xylose, and galacturonic acid[11]. Researchers have discovered that Dang Gui polysaccharides possess antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-radiation, immune-boosting, anti-myocardial ischemia, tumor-inhibiting, and skin aging-delaying benefits[12].
2.5 Phthalide Compounds
Phthalide compounds are considered essential components of the volatile oil in Dang Gui. A total of 55 phthalide compounds have been identified in Dang Gui, including Z-ligustilide, E-ligustilide, and others, which can be categorized into simple phthalides, phthalide dimers, and phthalide trimers[13]. Studies have shown that phthalide compounds exhibit pharmacological effects such as alleviating asthma, inhibiting tumor growth, and preventing platelet aggregation. However, phthalide compounds are relatively unstable and can easily undergo transformation due to factors such as photosynthesis and environmental temperature, leading to a diverse range of compound structures, making research on phthalides challenging. Currently, there is still a significant gap in the global understanding of the biosynthesis of phthalide compounds in Dang Gui, with many bioactive substances, metabolic substrates, and final products yet to be discovered[14].
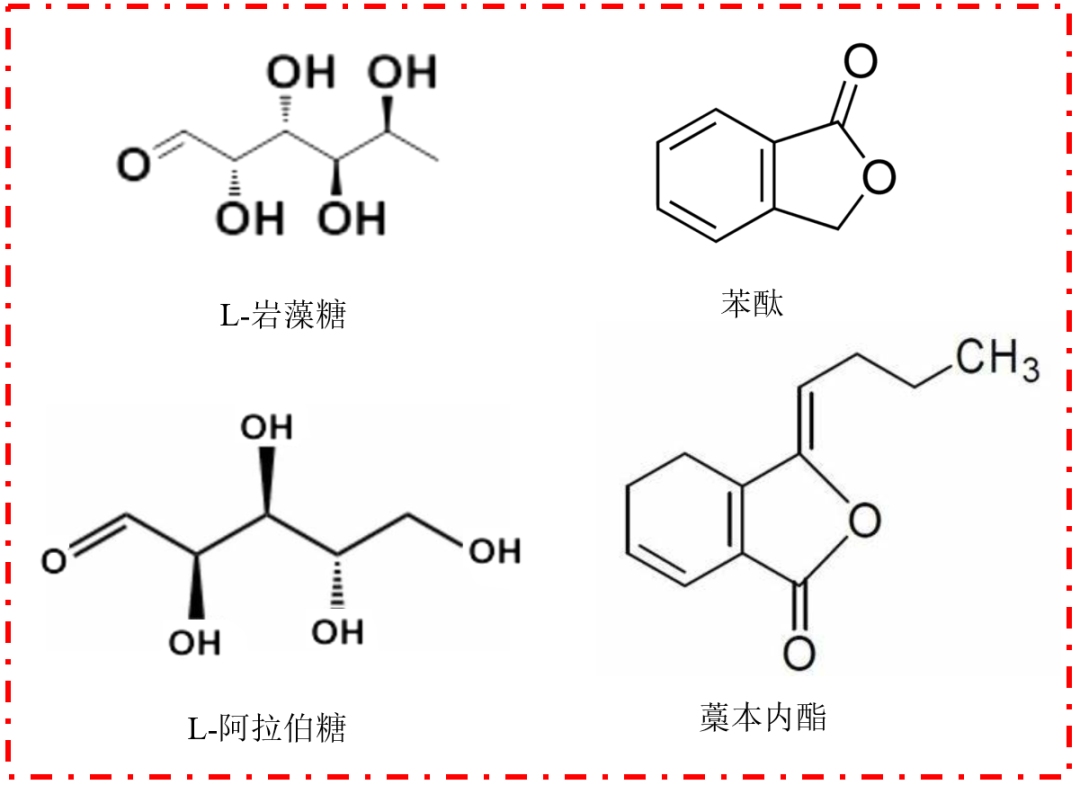
Figure 3. Structural formulas of chemical components in Dang Gui (Image source: Author)
3. Conclusion
There are many ways to consume Dang Gui; besides using it for medicinal purposes, it can also be sliced and steeped in water or cooked in soups. It not only invigorates and nourishes the blood, improving overall complexion and physical constitution, but also demonstrates excellent capabilities in enhancing the immune system, reducing the likelihood of various diseases. The important active substances in Dang Gui, such as phenolic acids, flavonoids, and coumarins, are well-studied, but there are still some unknown substances that need further exploration. Future research can focus more on clinical case studies to investigate the mechanisms of action of the active components in Dang Gui, providing more valuable references for this field.
References
[1] Liu Yanru, Tang Zhishu, Song Zhongxing, et al. Screening quality markers of Dang Gui based on the relationship between active components and efficacy [J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 2021, 52(9): 2626-2637.
[2] Zhao Jing, Xia Xiaopei. Current research status of chemical components and pharmacological effects of Dang Gui [J]. Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use, 2020, 13(6): 172-174.
[3] Liu Yanru, Tang Zhishu, Song Zhongxing, et al. Screening quality markers of Dang Gui based on the relationship between active components and efficacy [J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 2021, 52(9): 2626-2637.
[4] Zhang Xin, Gao Zengping. Research progress on ferulic acid [J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2020, 22(1): 138-147.
[5] Wang Qinghua, Du Tingting, Zhang Zhihui, et al. Research progress on the pharmacological effects and mechanisms of chlorogenic acid [J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2020, 55(10): 2273-2280.
[6] Li Gucai, Wei Wenting, Gao Tangjie, et al. Extraction and in vitro antibacterial activity of total flavonoids from Dang Gui [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011, 22(2): 310-311.
[7] Ge Shibei, Zhang Xue Ning, Han Wenyan, et al. Research progress on the biosynthesis of plant flavonoids and their mechanisms of stress resistance [J]. Journal of Horticulture, 2023, 50(1): 209-224.
[8] Wang Yanghai, Liu Lu, Zhao Bonian, et al. Research progress on traditional medicinal uses, coumarin components, and pharmacological toxicology of plants in the Angelica genus [J]. Pharmaceutical Research, 2023, 42(6): 403-408.
[9] Wang Changming, Jiang Ruibin, Li Feng. Research progress on the chemical components and anti-tumor mechanisms of Dang Gui [J]. Mutation Research, 2019, 31(2): 162-165.
[10] Wang Rongxiang, Song Jia, Sun Bo, et al. Research progress on the functions and biosynthesis of coumarin compounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2022, 42(12): 79-90.
[11] Nai J J, Zhang C, Shao H L, et al. Extraction, structure, pharmacological activities and drug carrier applications of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide [J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 183: 2337-2353.
[12] Xie J H, Jin M L, Morris G A, et al. Advances on bioactive polysaccharides from medicinal plants [J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2016, 56(Suppl 1): S60-S84.
[13] Zhang Qingqing, Feng Yuan, Li Chunhua, et al. Rapid identification of phthalide and organic acid components in Dang Gui based on UPLC-Q-TOF/MS technology [J]. Chinese Pharmacy, 2022, 33(5): 579-585.
[14] Yang Yalin, Feng Yang, Chen Hao, et al. Research progress on phthalide compounds and their biological activities [J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2022, 34(8): 1439-1453.
Author: Shang Zhi
Editor: Wei Lang
Submission Email: [email protected]
We welcome everyone to submit articles enthusiastically.

Gansu Province Science and Technology Popularization Association · Seeking Truth in the Fields

