 Click the “blue words” above to follow us!
Click the “blue words” above to follow us!


Traditional Gua Sha Therapy

The traditional Gua Sha therapy is based on TCM theory, using tools (such as buffalo horn, jade, and fire cupping) to scrape the skin in relevant areas, achieving the goals of promoting blood circulation, relieving muscle tension, and expelling pathogens and toxins.
It is widely applied in clinical conditions such as colds, coughs, fevers, pharyngitis, pain syndromes, and insomnia.


Cupping Therapy

1. Concept
Cupping therapy is based on TCM meridian and organ theory, developed considering the delicate constitution of children. It involves using silicone cups to create suction on the skin for cupping therapy, a commonly used external treatment technique in pediatric TCM.
2. Efficacy
This technique combines the effects of cupping and Gua Sha, capable of expelling heat and pathogens, stimulating the body’s vital energy, and supporting the body’s defenses against illness.
3. Advantages
Soft texture, quick to produce marks, short treatment time, adjustable based on the child’s tolerance, minimal pain, and easily accepted by children. Suitable for children over 6 months and adults.
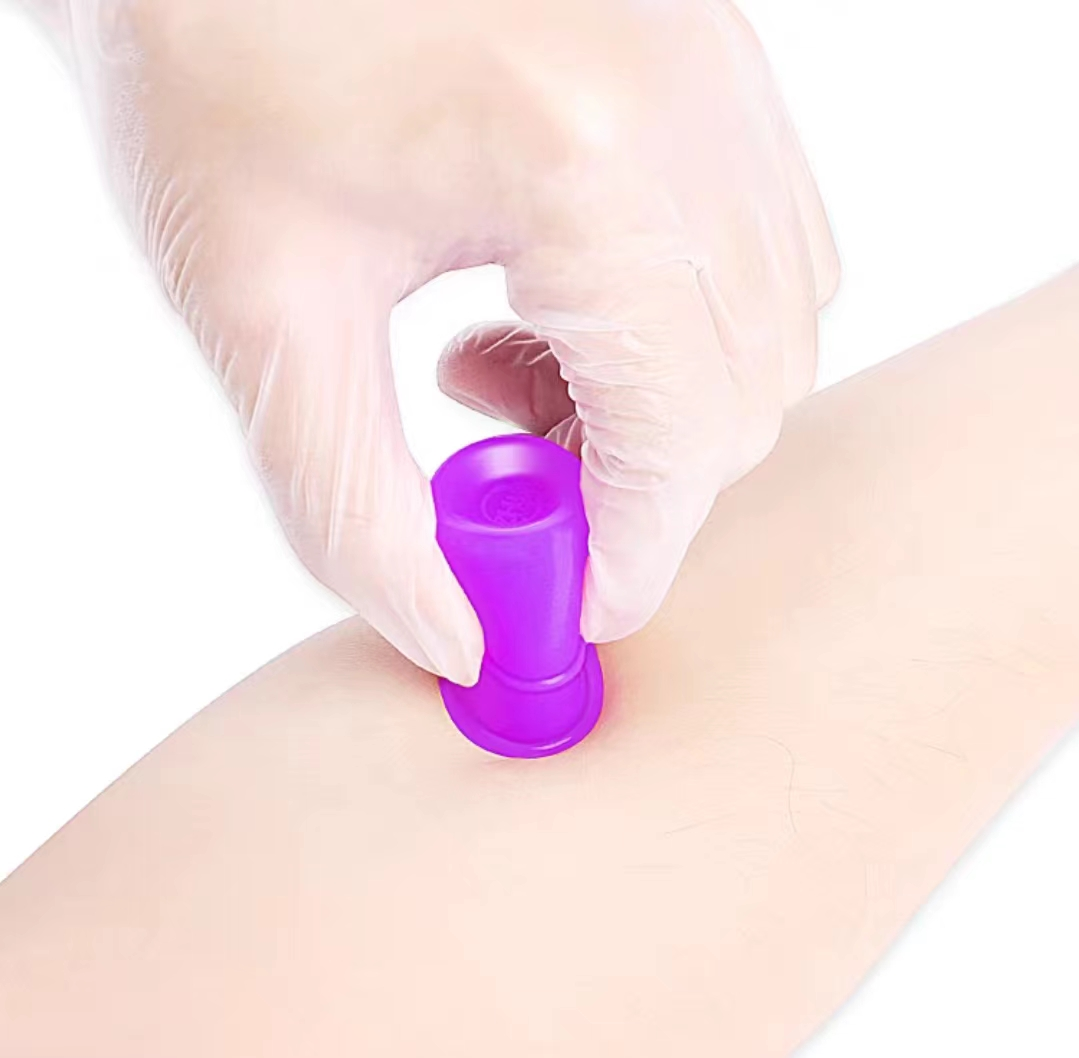
4. Traditional Gua Sha vs. Cupping

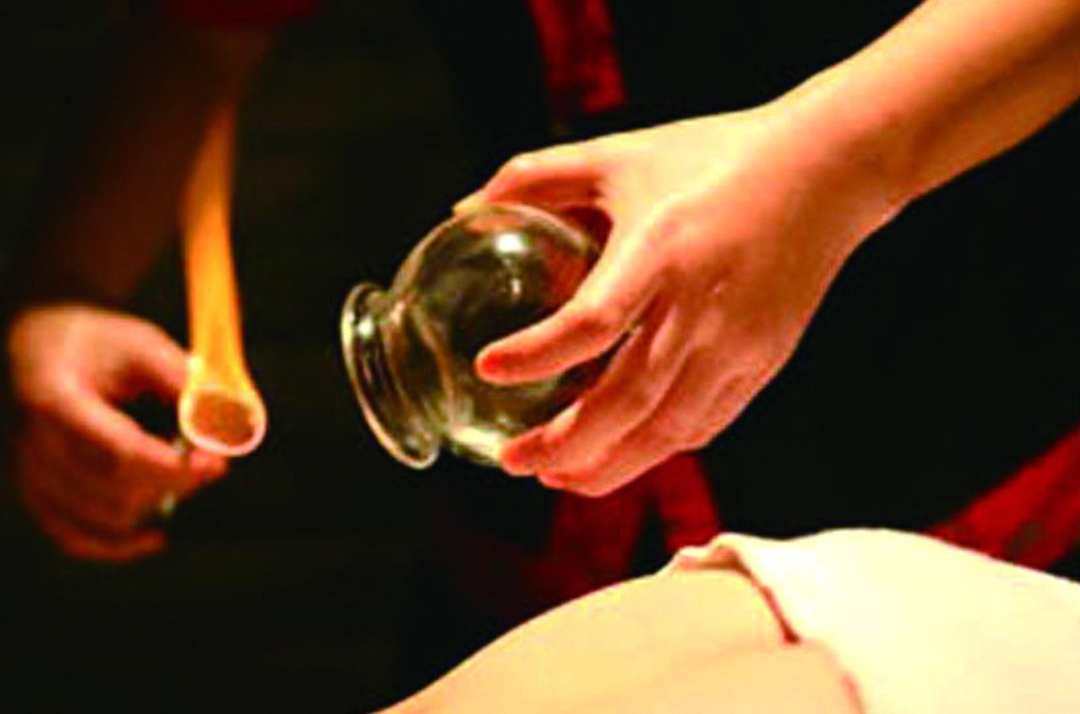
Traditional Glass Cups Silicone Cups
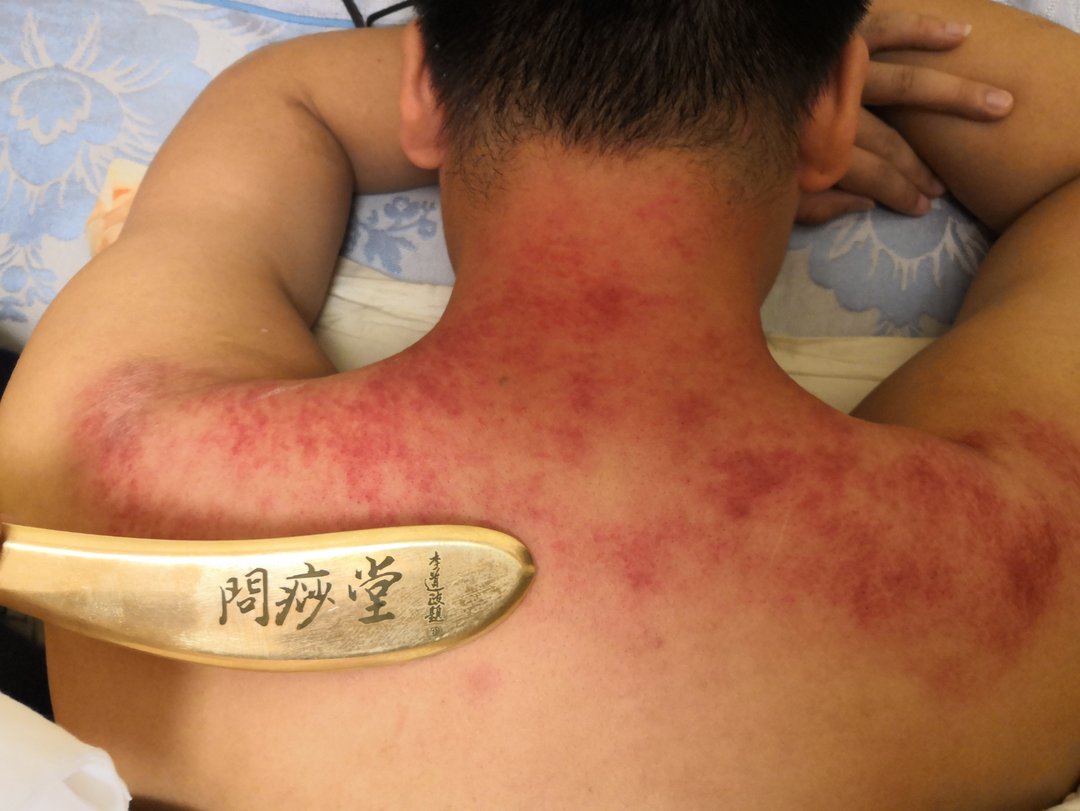
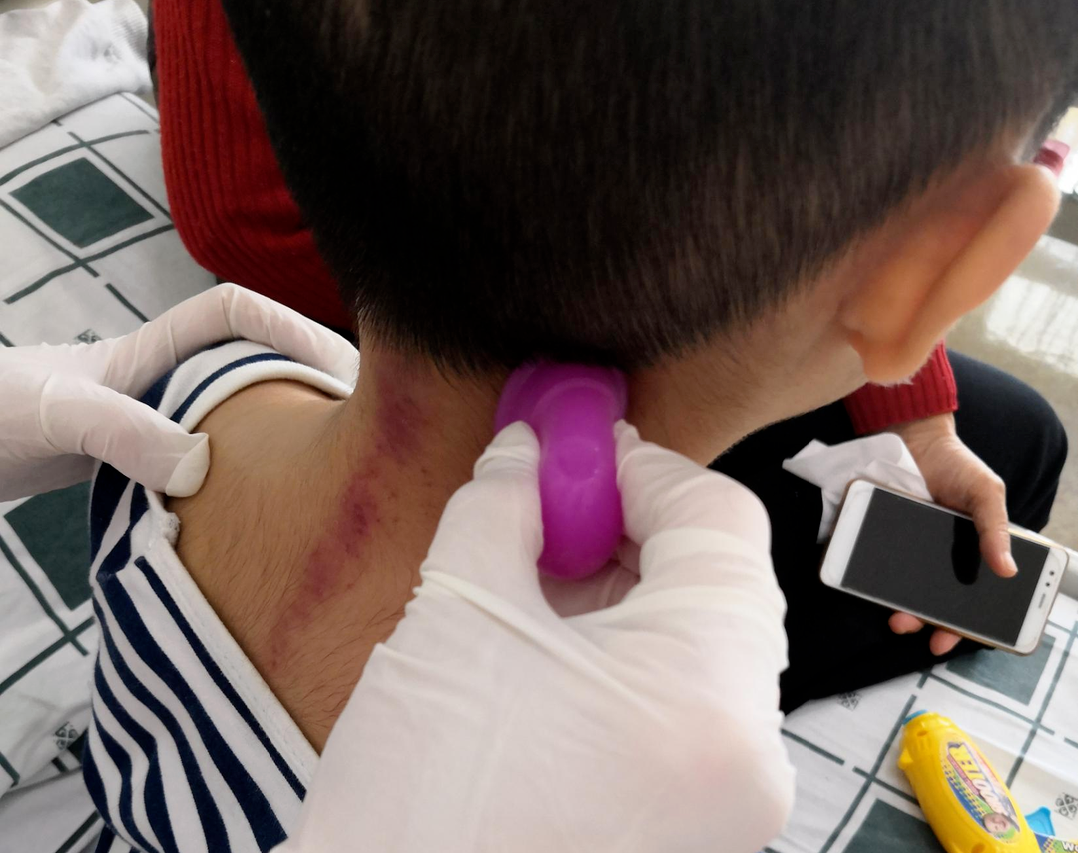
Gua Sha Cupping
5. Key Points of Operation
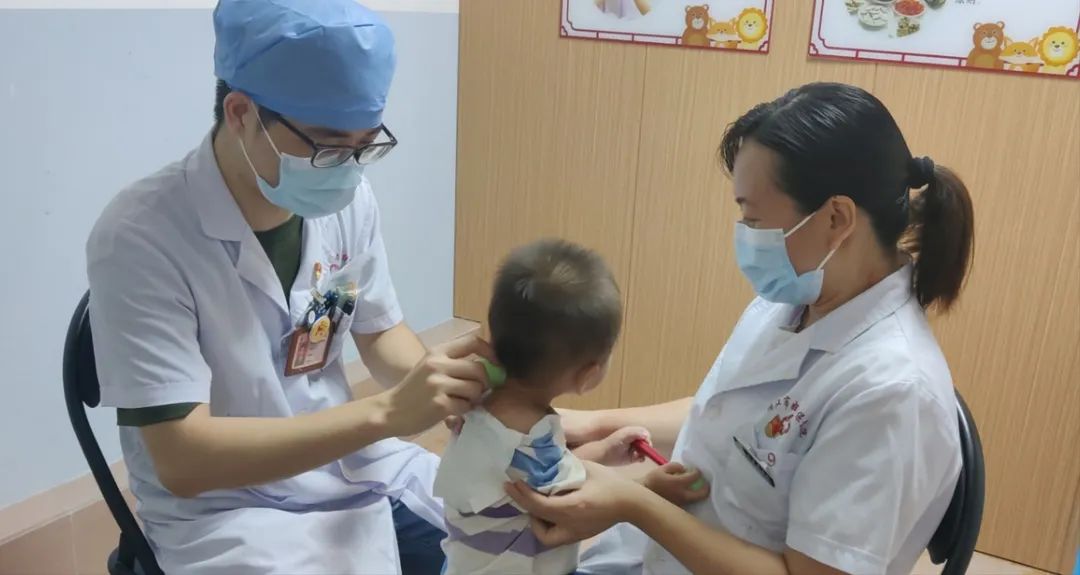
The TCM practitioner should assess the child’s symptoms, diagnose, determine the cupping locations, prepare the necessary items, perform the procedure, and educate the child’s parents.
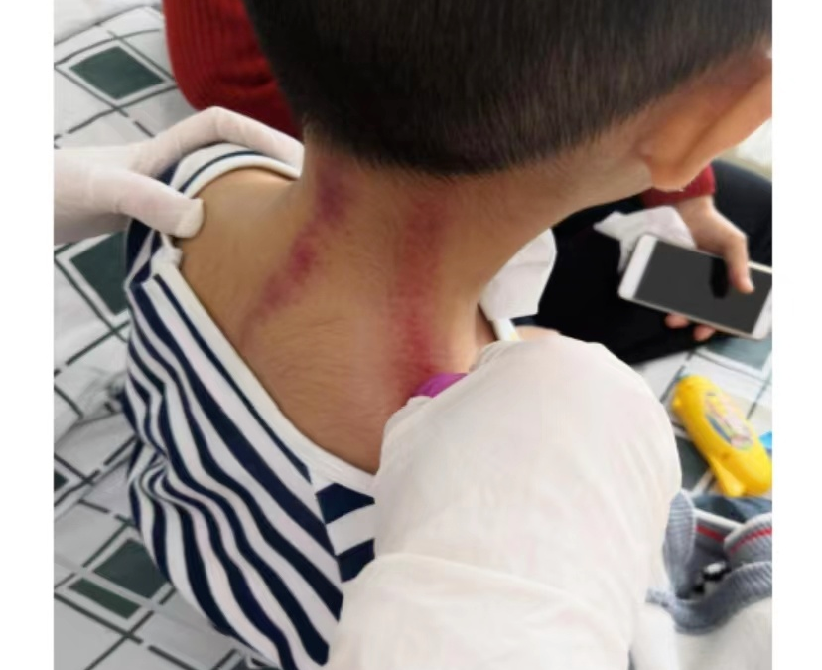
For children with wind-heat lung diseases, the cupping prescription is as follows:
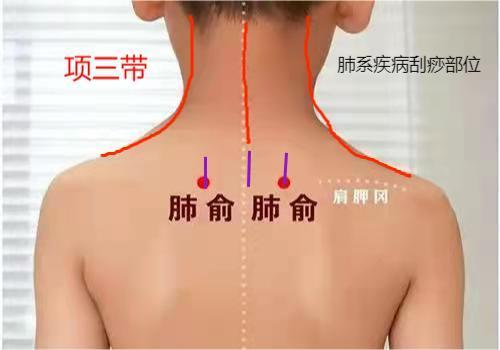
Three-Line Cupping Method
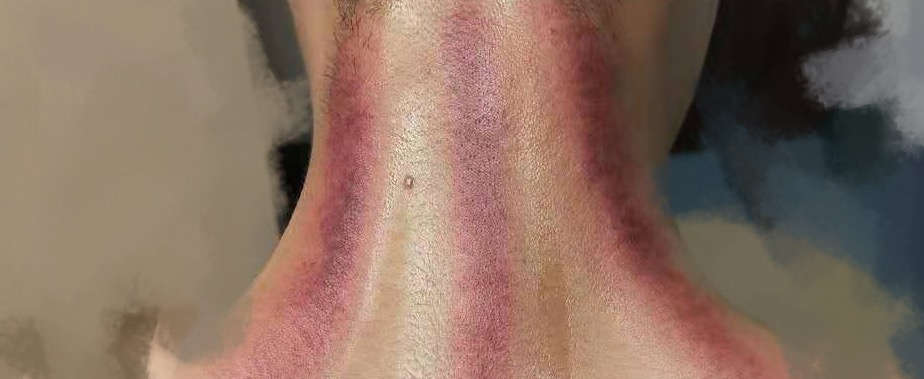
Bladder Meridian Cupping
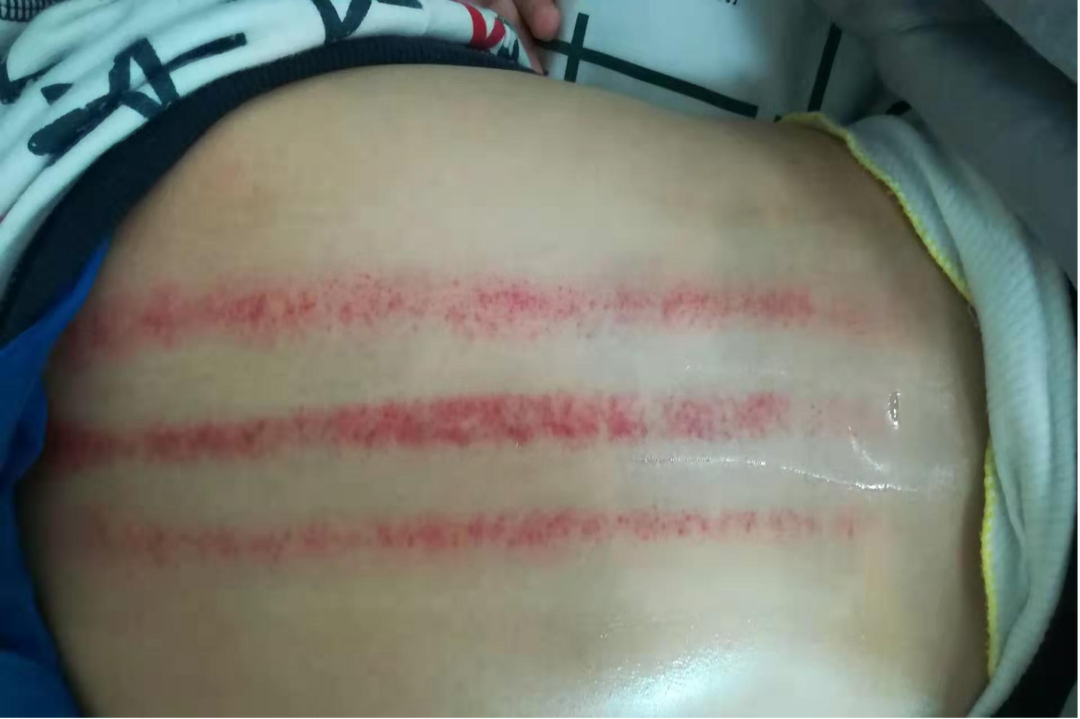

Retention Cupping Treatment
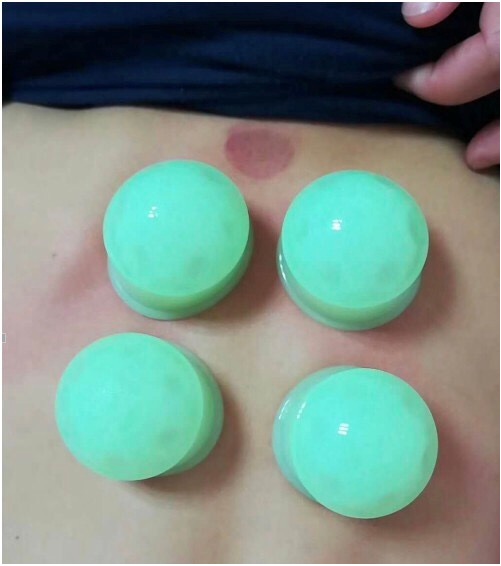
5. Indications
This therapy is commonly used for pediatric lung diseases and spleen-stomach disorders, followed by kidney-related diseases. It is mainly suitable for excess and heat syndromes, effectively improving symptoms of excess heat, shortening the duration of illness, and alleviating discomfort caused by illness.
Lung Diseases:
Fever, colds, cough, tonsillitis, herpetic pharyngitis, recurrent respiratory infections (due to food stagnation and internal heat), pneumonia.
Spleen-Stomach Disorders:
Food stagnation, constipation, anorexia.
Otorhinolaryngological Diseases:
Adenoid hypertrophy, sinusitis.
Other Diseases:
Enuresis, tic disorders, peripheral facial paralysis, cerebral palsy, etc.

Contraindications and Precautions

Contraindications
1. Patients with chronic illness, extreme fatigue, after intense exercise, or those who are overly hungry or full should avoid or use with caution.
2. Severe heart disease, various bleeding disorders, infectious diseases, skin lesions, and ulcerative dermatitis are not suitable for this treatment.
Precautions
1. The area to be cupped should be fully exposed before the procedure, and care should be taken to prevent infection.
2. Choose a comfortable position; the treatment area should be relaxed and not moved to prevent the cups from falling off.
3. For patients with weak constitutions or first-time cupping, the duration should be short, and it is not necessary to force the marks; the pressure should be gentle, stopping at light marks.
4. When removing the cups, do not pull hard or twist the cups, as this may cause pain or even skin injury.
5. After cupping, keep the area warm, avoid wind and cold, do not wet the cupped area with cold water on the same day, and avoid cold, raw, or fishy foods.

Pediatric Rehabilitation Specialists Introduction
The Pediatric Rehabilitation Department features multidisciplinary collaboration and integration of Chinese and Western medicine, undertaking early rehabilitation interventions for high-risk children, developmental delays, language disorders, autism, and other common developmental and behavioral diseases, providing integrated rehabilitation interventions, technical guidance, public education, and research and teaching, serving over 30,000 people annually, and offering quality rehabilitation services for children in the western Guangdong region. The main TCM rehabilitation projects include: acupuncture, moxibustion, electroacupuncture, acupoint injection, bloodletting, needle tapping, herbal plaster, herbal hot compress, auricular acupressure, pediatric tui na, herbal baths, pediatric foot therapy, wax therapy, and physiotherapy, effectively shortening treatment duration and reducing side effects. Utilizing TCM techniques to treat brachial plexus nerve injuries, cerebral palsy, hemiplegia, developmental delays, language development delays, intellectual disabilities, and autism spectrum disorders can significantly improve rehabilitation outcomes for children; among these, pediatric scalp acupuncture has achieved industry-leading status in the Zhanjiang area, attracting surrounding hospitals and grassroots maternal and child health hospitals for observation and learning.
Liu Yue
Attending TCM Physician, Master’s Degree

Member of the Pediatric Rehabilitation Professional Committee of the Guangdong Provincial Maternal and Child Health Association, member of the expert group for infant care services for children under three years old in Zhanjiang, and member of the Shanghai Acupuncture Society. Previously studied at the Fudan University Affiliated Children’s Hospital, specializing in high-risk child management and follow-up, GMS assessment, developmental delays, tic disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cerebral palsy, intellectual disabilities, learning disabilities, enuresis, and other common developmental and behavioral diseases with integrated TCM and Western medicine treatment and acupuncture.
Hou Shuling
TCM Physician

Engaged in pediatric rehabilitation treatment for many years, with experience studying at the Nanhai Maternal and Child Health Hospital. Specializes in brachial plexus nerve injuries, cerebral palsy, hemiplegia, developmental delays, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, intellectual disabilities, learning disabilities, and enuresis with integrated TCM and Western medicine treatment and acupuncture.
Long Fusheng
TCM Physician

Previously studied at the Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Specializes in developmental delays, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cerebral palsy, hemiplegia, intellectual disabilities, learning disabilities, sleep disorders, and common pediatric diseases with TCM diagnosis and treatment, including acupuncture, tui na, floating needle, cupping, and other external TCM therapies.


END
Submitted by: Zhan Yingjie
Editor: Guo Haiyan
Reviewed by: Chen Liqin


