★ Cupping is the Most Excellent Physical Therapy
Cupping, like Tui Na (Chinese therapeutic massage), is a form of physical therapy and is considered one of the most effective therapies within this category. Cupping therapy, also known as “Jiao Fa,” utilizes physical stimulation and negative pressure to artificially cause capillary rupture and blood stasis, mobilizing the body’s stem cell repair functions and the absorption of necrotic blood cells. This promotes blood circulation, invigorates Qi, regulates Qi and blood, and enhances and modulates the body’s immune response.
Unlike acupuncture, cupping does not require precise location on acupuncture points; it primarily involves the combination of points, lines, and surfaces. By differentiating between cold, heat, deficiency, and excess in TCM, practitioners select areas where meridians pass through or where Qi accumulates.
Cupping therapy is a commonly used method in traditional Chinese medicine for treating various diseases. This therapy can dispel cold and dampness, unblock meridians, eliminate stagnation, invigorate blood circulation, reduce swelling and pain, and detoxify and clear heat. It helps to adjust the balance of Yin and Yang in the body, relieve fatigue, and enhance physical strength, achieving the goal of supporting the righteous Qi and expelling pathogenic factors. Therefore, many diseases can be treated with cupping therapy. The tools used in cupping therapy, known as “cups,” come in various forms, including glass cups, ceramic cups, bamboo cups, and rubber cups. Even household jars can be used for cupping. Clinically, glass cups, ceramic cups, and bamboo cups are most commonly used, while rubber cups are more popular for home use due to their convenience. They can be easily squeezed to create suction, making them easy to handle, even for those without medical knowledge, as long as they understand where the pain is located. However, rubber cups do not use fire, which is an important step, so their effectiveness is somewhat reduced, and they are generally not used in hospitals. Glass cups are smooth and transparent, allowing observation of the skin’s congestion, bruising, blistering, and bleeding during treatment, making them the most commonly used in clinical practice. Another tool used in cupping therapy is the igniter, or torch, which can be made from a thicker lead wire bent into a circle for easy handling, with the other end wrapped in cotton and gauze for soaking in alcohol and igniting.
There are many methods of cupping, primarily categorized into four types: cupping, flash cupping, moving cupping, and bloodletting cupping.
★ Analysis of Cupping Therapy Principles in Traditional and Western Medicine
Cupping is a widely used natural therapy in folk medicine. With the development of medicine and technology, cupping therapy has gained renewed vitality and is increasingly accepted by the public. Traditional and Western medicine have different explanations for the therapeutic principles of cupping therapy, which we will discuss in detail below.
In TCM, the theory of disease states that illnesses are caused by pathogenic factors leading to an imbalance of Yin and Yang, resulting in abnormal Qi movement and dysfunction of the organs. These pathogenic factors include blood stasis, Qi stagnation, phlegm, food retention, dampness, and evil heat, which arise from the invasion of wind, cold, heat, dampness, dryness, fire, toxins, or trauma, causing dysfunction of the organs. These pathogenic factors traverse the meridians and acupoints, disrupting Qi movement, stagnating the organs, and obstructing the meridians, ultimately leading to various symptoms.
Cupping can open the pores and support the righteous Qi while expelling the pathogenic factors. The vacuum created by cupping generates a strong suction force that acts on the meridian acupoints, opening the pores and causing the skin to become congested, allowing pathological products to be drawn out through the skin, thereby unblocking the meridians and adjusting organ functions to prevent and treat diseases.
Modern medicine believes that the negative pressure from cupping stimulates local blood vessel dilation, promotes local blood circulation, improves congestion, enhances metabolism, alters local tissue nutrition, increases vascular permeability, and enhances white blood cell phagocytosis, thereby boosting the body’s energy and immune capacity, which helps to eliminate diseases.
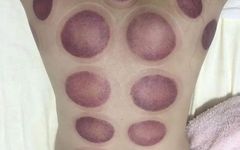
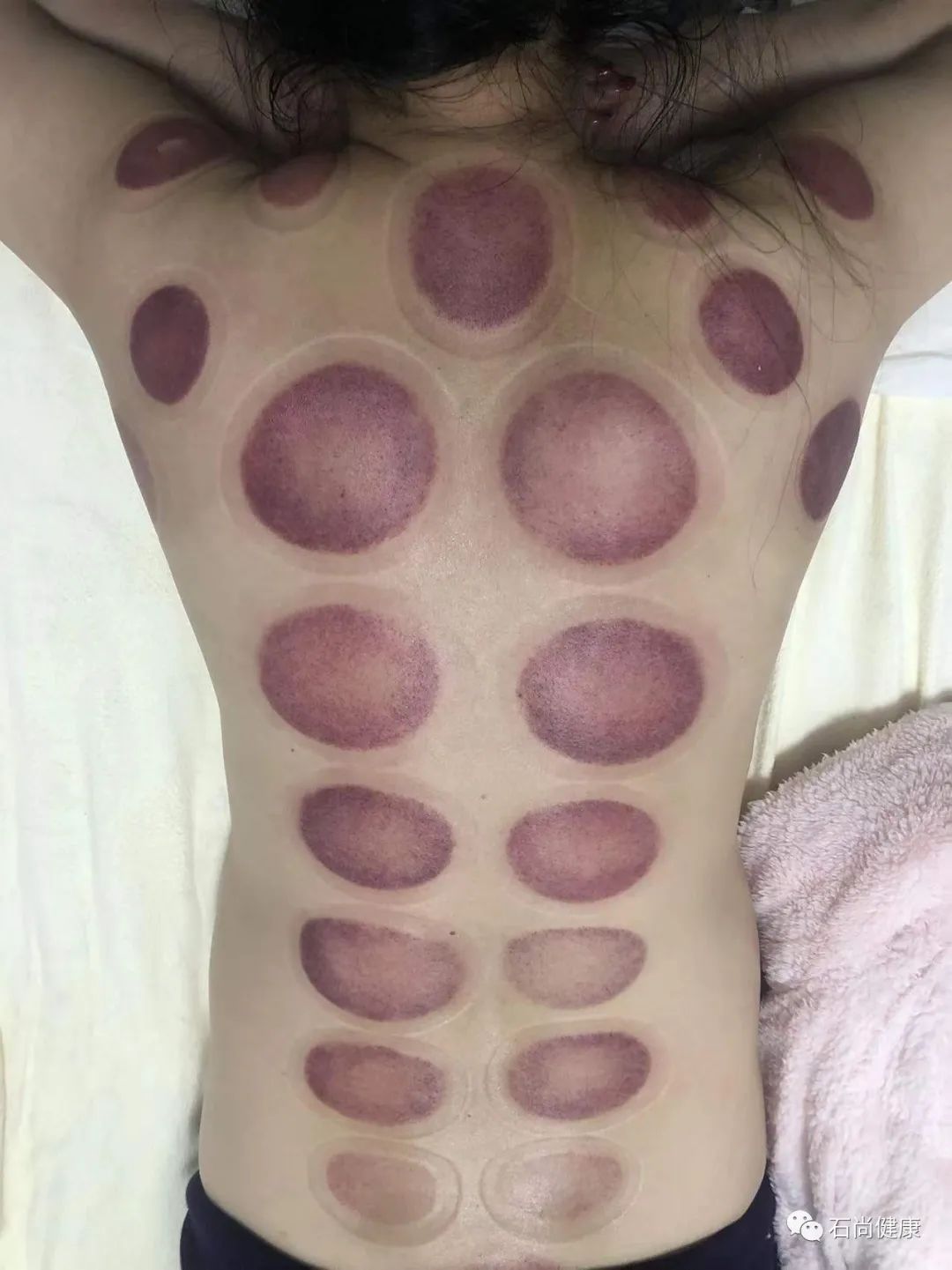
After cupping, the body typically shows varying colors of cupping marks, which have different meanings. Common cupping marks include erythema, purple-red, or purple-black bruises, and small purple-red spots, often accompanied by varying degrees of heat and pain. These skin changes are therapeutic effects of cupping therapy and can last for several days.
If the cupping marks appear as blisters, edema, or watery, it indicates the patient has excessive dampness or has been affected by dampness. If the blisters are blood-red or black-red, it indicates a pathological response of long-term dampness combined with blood stasis. If the cupping marks are deep red, purple-black, or dark purple, and are slightly painful to touch, along with body heat, it indicates the presence of heat toxin in the patient. If the cupping marks are purple-red or purple-black without dark purple and heat symptoms, it indicates blood stasis. If there is no change in skin color and it feels cool to the touch, it often indicates a deficiency-cold condition; if the cupping marks are slightly itchy or show skin lines, it often indicates a wind condition.
For healthy individuals, generally, the cupping marks show no significant changes.
★ Comprehensive Guide to Cupping Techniques
To effectively treat conditions with cupping therapy, one must first master the cupping techniques and then choose the appropriate method based on the condition.
1. Cupping methods classified by air removal include fire cupping, water cupping, and suction cupping.
(1) Fire cupping: This method uses the principle of thermal expansion and contraction to remove air. By using the heat from a burning flame, air is expelled from the cup, creating negative pressure that adheres to the skin, known as fire cupping. This can be further divided into four types:
① Fire insertion method: A small piece of paper is ignited and placed inside the cup. Before the paper burns out, the cup is quickly placed over the treatment area to create suction on the skin.
② Internal fire method: A cotton ball soaked in alcohol is held with tweezers, ignited, and quickly circled inside the cup before placing it over the treatment area to create suction.
③ Cotton sticking method: A piece of cotton about 1 cm square is slightly soaked in alcohol and stuck to the middle section of the cup’s inner wall, ignited, and then placed over the selected area to create suction.
④ Fire frame method: A non-flammable and heat-resistant object, about 2-3 cm in diameter, is placed on the treatment area, with a small piece of alcohol-soaked cotton placed on top, ignited, and then the cup is placed over it to create strong suction.
(2) Water cupping: This method uses the heat from boiling water to remove air. Generally, bamboo cups are used, which are first boiled in water. When needed, the cup is tilted to pour out the water, or a folded towel is used to cover the cup’s opening, and while hot, it is placed on the skin to create suction.
(3) Suction cupping: Air is removed by suction. The suction cup is tightly placed on the area to be treated, and air is drawn out using a syringe from the rubber stopper, creating negative pressure to adhere to the skin. Alternatively, a suction pump can be used to remove air from a plastic cup.
2. Cupping methods classified by form include single cupping, multiple cupping, retained cupping, and moving cupping.
(1) Single cupping: Used for small or clearly painful areas. The appropriate size of the fire cup is selected based on the size of the painful area. For example, cupping at the Zhongwan point for stomach issues or at the inner shoulder edge for biceps tendonitis.
(2) Multiple cupping: Used for diseases with a wide range of affected areas. Several cups can be applied to the affected area, sometimes arranged in rows, for example, when treating muscle strain.
(3) Flash cupping: The cup is applied and immediately removed, repeated multiple times. This method is used for local skin numbness or functional decline.
(4) Retained cupping: The cup is left in place for a certain period, typically 5-15 minutes. For cups with strong suction, the retention time should be reduced, especially in summer or on thin skin, to avoid skin damage.
(5) Moving cupping: The cup is moved back and forth on the skin surface after suction. This method is generally used on larger areas with thick muscles, such as the lower back and thighs. A larger cup with a smooth rim is preferred, and some lubricant should be applied to the skin to prevent skin injury during movement.
3. Cupping methods classified by comprehensive application include medicinal cupping, needle cupping, needle-medicinal cupping, and bloodletting cupping.
(1) Medicinal cupping: This involves using herbal decoctions in bamboo cups for suction, known as medicinal decoction cupping; or storing medicinal liquid in the cup, known as medicinal storage cupping.
① Medicinal decoction cupping: The prepared herbs are placed in a cloth bag, boiled in water to the appropriate concentration, and then the bamboo cup is immersed in the herbal liquid for 15 minutes before use, commonly used for rheumatic diseases.
② Medicinal storage cupping: A certain amount of medicinal liquid is pre-stored in a suction cup or glass cup, typically filling 2/3 to 1/3 of the cup, and then applied to the skin. Commonly used liquids include chili water, two-sided needle tincture, ginger juice, and rheumatic wine.
(2) Needle cupping: This involves acupuncture followed by cupping. Acupuncture is performed at specific points, and once the sensation is felt, the cup is applied over the acupuncture point. This method is often used for rheumatic pain.
(3) Needle-medicinal cupping: This involves acupuncture followed by medicinal cupping. Acupuncture is performed, and once the sensation is felt, the cup is applied over the acupuncture point.
(4) Bloodletting cupping: This involves using a three-edged needle or skin needle to draw blood before cupping. The needle is used to prick the affected area or small blood vessels until slight bleeding occurs, followed by cupping. This method is suitable for various acute and chronic soft tissue injuries, neurodermatitis, skin itching, erysipelas, neurasthenia, and gastrointestinal neurosis.
★ Common Positions for Cupping Therapy
The position during cupping is closely related to the treatment’s effectiveness. When cupping, the position should be chosen to fully expose the treatment area, ensure patient comfort, and facilitate the practitioner’s operation.
Common positions for cupping include:
1. Supine position. The patient lies flat on the bed, arms either at their sides or resting comfortably, legs naturally apart, with a soft pillow under the knees. This position is suitable for cupping on the head, face, chest, abdomen, inner arms, and front and sides of the legs.
2. Prone position. The patient lies face down on the bed, with a soft pillow under the chest and the ankles. This position is suitable for cupping on the neck, back, waist, hips, and back of the legs.
3. Lateral position. The patient lies on their side, with legs bent and a soft pillow under the arm. This position is suitable for cupping on the shoulders, ribs, knees, and outer sides of the limbs.
4. Sitting position. The patient sits upright in a chair. This position is suitable for cupping on the forehead, cheeks, upper chest, shoulders, arms, knees, and ankles.
5. Leaning forward sitting position. The patient leans forward while sitting, with both hands resting on the table, exposing the neck, back, and waist. This position is suitable for cupping on the back of the head, shoulders, and waist.
★ Precautions for Home Cupping
Due to the simplicity and ease of operation of cupping, many people keep cupping equipment at home and use it when feeling unwell. However, experts remind that as a professional treatment method, cupping is not as simple as it seems. Therefore, performing cupping at home can easily lead to accidents and cause harm. If the acupoints are incorrectly applied, it may even have the opposite effect. Thus, it is essential to remember some precautions when performing cupping at home and not to perform it haphazardly.
First, pay attention to the equipment used for cupping. Traditional Chinese medicine often uses bamboo tubes, while household items like glass jars or ceramic cups can also be used, but the rim must be thick and smooth to avoid injury. The bottom should preferably be wide and rounded. Before cupping, the cup should be cleaned and dried, and the patient should be comfortably positioned to expose the area to be treated. When igniting the cup, one hand holds the cup while the other holds the igniter, and the action should be quick. The igniter should be swirled inside the cup before quickly placing it on the treatment area. The cup should be pressed tightly against the skin while the flame is still burning; waiting for the flame to extinguish may result in insufficient suction. The feeling of the cup should be tight against the skin.
However, care should be taken not to heat the rim of the cup to avoid burns. The cupping duration is generally controlled at 15-20 minutes. When removing the cup, do not pull it forcefully; instead, tilt the cup to one side while pressing the skin to allow air to enter, and the cup will naturally detach from the skin.
Home cupping can also use the moving cupping method. Moving cupping involves lifting the cup slightly after applying it and sliding it back and forth on the patient’s skin. This can treat multiple areas. When moving the cup, it is advisable to apply some lubricant, such as glycerin, paraffin oil, or guasha oil, to the area to prevent skin injury.
Cupping has excellent therapeutic and health benefits, and most people can quickly learn to perform it with a little practice. Nowadays, vacuum suction cupping has been invented, which allows the cup to be placed on the desired area, and by pulling the handle, the cup adheres to the skin, making it simple and easy to operate, even without assistance. This type of cup lacks the fire element, which may reduce its effectiveness slightly, but it is much safer and suitable for home use.
★ Contraindications and Forbidden Areas for Cupping Therapy
Although cupping therapy is natural and has no toxic side effects, there are still some contraindicated conditions and areas. It is essential to remember these conditions and areas during cupping to avoid unnecessary harm to the patient.
1. Contraindicated conditions. Cupping is contraindicated for patients with moderate to severe heart disease, heart failure, systemic edema, hemorrhagic disorders, leukemia, malignant tumors; severe convulsions or spasms; severe neurosis or ulceration at surgical sites; women during menstruation, and those with fractures. Patients with these conditions should not undergo cupping.
2. Forbidden areas. Cupping should be used cautiously over major blood vessels, nipples, heart area, nose, ears, genital areas, varicose veins, superficial arteries, and the abdomen and lower back of pregnant women.
The contraindications and forbidden areas for cupping therapy are not absolute; some have used this method to treat edema, mental illness, high fever, and active pulmonary tuberculosis without adverse reactions and with good results. There are also cases of cupping over nipples, heart areas, nose, ears, and genital areas without adverse reactions. Moreover, cupping therapy can be combined with other therapies, and it is essential to consider the compatibility of conditions. However, in clinical practice, the above situations should be avoided as much as possible, and if necessary, caution should be exercised.
★ Cupping Therapy for Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is a common and frequently occurring disease that can harm human health, with an incidence rate of about 15%. Cervical spondylosis refers to the clinical symptoms and signs resulting from changes in the cervical spine. Currently, the internationally accepted view is that it is caused by degenerative changes in the cervical intervertebral discs and secondary degenerative changes in the intervertebral joints, leading to damage to the spinal cord, nerves, and blood vessels.
1. Needle cupping
Acupoints: Dazhui (大椎), Jianjia (颈夹脊).
Treatment method: Use a skin needle to prick the affected area and Dazhui point, followed by cupping for 2-3 times, leaving the cup in place for about 5 minutes.
Treatment course: Twice a week, with 7 sessions per course.
2. Plum blossom needle cupping
Acupoints: Dazhui (大椎), Dazhu (大杼), Jianjing (肩井), Jianzhong (肩中腧), Jianwai (肩外腧).
Treatment method: Use a plum blossom needle to prick the above acupoints 3-5 times until the skin turns red with slight bleeding. After pricking, apply cupping and leave it for 15-20 minutes to draw out blood stasis.
Treatment course: Once every other day, with 7 sessions per course, and a 5-day interval between courses. Significant effects can be seen after 3-4 courses.
In addition, patients with cervical spondylosis should also pay attention to balancing work and rest, maintaining regular sleep, ensuring the pillow’s height and firmness are appropriate, and keeping the neck and shoulders warm.
★ Cupping Therapy for Lumbar Disc Herniation
Lumbar disc herniation is a common and frequently occurring disease caused primarily by degeneration of the intervertebral disc, rupture of the annulus fibrosus, or protrusion of the nucleus pulposus, leading to a series of symptoms due to stimulation or compression of the spinal nerves and spinal cord.
Degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc occur in adults, where the fibers in the annulus fibrosus become thickened and brittle, eventually leading to rupture, causing the disc to lose its original elasticity and unable to bear the original pressure. Under excessive strain, sudden changes in posture, forceful movements, or violent impacts, the annulus fibrosus can bulge outward, causing the nucleus pulposus to protrude through the ruptured annulus fibrosus, resulting in lumbar disc herniation.
Many patients with lumbar disc herniation lack knowledge of prevention and treatment, some ignore the condition, leading to worsening symptoms; others are misled and mismanaged, resulting in wasted resources. Cupping therapy is the most natural treatment method for lumbar disc herniation.
1. Needle cupping method
Acupoints: Dazhong (大肠腧), Guanyuan (关元腧), Shen (肾腧), Huantiao (环跳), Fengshi (风市), Chengfu (承扶), Yinmen (殷门), Weizhong (委中), Chengshan (承山), Yanglingquan (阳陵泉).
Treatment method: First, needle at Chengfu, Yinmen, Weizhong, and Yanglingquan. Use flash fire cupping on other acupoints, leaving the cups for 15-20 minutes.
Treatment course: Once daily.
2. Needle cupping method
Acupoints: Huantiao (环跳), Kunlun (昆仑), Yanglingquan (阳陵泉), Guanyuan (关元腧), Dazhong (大肠腧).
Treatment method: Deeply needle at Huantiao to transmit the sensation to the foot to eliminate deep pathogens. Other acupoints can be needled until a sensation is felt, followed by cupping for 20 minutes.
Treatment course: Once daily, with 7 sessions per course.
3. Bloodletting cupping method
Acupoints: Shen (肾腧), Ah Shi (阿是穴).
Treatment method: Use a three-edged needle to prick the upper acupoint until slight bleeding occurs, then immediately apply cupping, leaving it for 15-20 minutes.
Treatment course: Once every other day, with 5 sessions per course.
In addition, patients with lumbar disc herniation should sleep on a firm bed, keep the lower back warm, use a wide belt to support the lower back, and reduce activities that involve bending forward or backward. After improvement, strengthen back muscle exercises.
★ Cupping Therapy for Insomnia
Sleep is essential for everyone daily. Good hypnotic agents are necessary for helping insomnia patients improve their sleep and avoid the serious health risks associated with insomnia. A person’s sleep time exceeds one-third of their life, yet many suffer from insomnia, leading to exhaustion and fatigue. Long-term reliance on medication can harm the body, making cupping the most natural therapy for insomnia.
Flash fire cupping method
Acupoints: Shenmen (神门), Sanyinjiao (三阴交), Xin (心腧), Pi (脾腧), Wei (胃腧), Gan (肝腧).
Treatment method: Choose appropriately sized glass or vacuum cups, use flash fire cupping on the back at Xin, Pi, Wei, and Gan points, then move the cup back and forth several times until the skin turns red. Finally, apply cupping at the Xin point and leave it for 10 minutes.
Treatment course: Once every two days, with 15 sessions per course.
★ Cupping Therapy for Gastritis
Gastritis refers to inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which can be classified into acute and chronic types. Acute gastritis is caused by various factors leading to acute inflammation of the gastric mucosa, while chronic gastritis is caused by harmful factors reaching the gastric mucosa through the bloodstream.
1. Simple cupping method (for gastric pain)
Acupoints: Zhongwan (中脘), Shenque (神阙).
Treatment method: Use the simple cupping method, leaving the cup for 10-15 minutes.
Treatment course: Once daily.
2. Needle cupping method (for gastric ulcers)
Acupoints: Fengchi (风池), Dazhu (大杼), Ge (膈腧), Pi (脾腧), Zusanli (足三里); Tianzhu (天柱), Jianjing (肩井), Gan (肝腧), Wei (胃腧), Sanjiao (三焦腧), Shangjuxu (上巨虚).
Treatment method: Select one group each time, first perform light acupuncture, then apply cupping, leaving it for 10-15 minutes.
Treatment course: Once daily, with 10 sessions per course.
In addition, patients with gastritis should maintain a balanced diet, avoiding overeating or undereating. Meals should be regular, with a maximum interval of 30 minutes before and after eating. Eating should be slow and mindful, avoiding excessive drinking of water before, during, or after meals, and distractions such as reading or watching TV. Beneficial foods can be consumed in moderation, while harmful foods should be minimized or avoided.
After meals, patients should avoid lying down or engaging in vigorous activities, instead sitting quietly for 10-30 minutes.
★ Cupping Therapy for Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, which can have various causes, the most common being viral infections, as well as autoimmune causes. Alcohol abuse can also lead to hepatitis. Hepatitis can be classified into acute and chronic types.
Bloodletting cupping method
Acupoints: Dazhui (大椎), Gan (肝腧), Pi (脾腧); Zhiyang (至阳), Qimen (期门), Dan (胆腧).
Treatment method: The patient lies prone, and a three-edged needle is used to prick until slight bleeding occurs, followed by cupping for 15-20 minutes.
Treatment course: Once daily, with 10 sessions per course, with a 7-day interval between courses.
Additionally, hepatitis patients should avoid consuming canned foods, fried or pan-fried foods, instant noodles, and sausages. Preservatives and food colorings in canned foods can burden the liver’s metabolism and detoxification functions. Fried foods are high in fat, difficult to digest, and can lead to malabsorption and fatty diarrhea. Repeatedly fried oils may contain carcinogens, which can lead to the progression of hepatitis to liver cancer.
★ Cupping Therapy for Cholecystitis
The gallbladder is a small organ located directly beneath the liver, responsible for storing bile for fat digestion. Inflammation and swelling of the gallbladder are often caused by stones blocking the normal flow of bile from the gallbladder to the intestines. Additionally, cholecystitis can result from intestinal infections spreading upwards. Patients with cholecystitis experience severe pain in the right upper abdomen, often accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting. Severe cases may lead to jaundice and require immediate medical attention, as a ruptured gallbladder can cause severe peritonitis.
Massage cupping method
Acupoints: Dan (胆俞).
Treatment method: First, apply cupping at the Dan point, leaving it for 10-15 minutes. After removing the cup, massage the Dan point with the right thumb for 15 minutes.
Treatment course: Once daily, with 6 sessions per course.
It is important to note that during an acute cholecystitis attack, solid foods should be avoided for several days, and only distilled or mineral water should be consumed. Afterward, fruit juices such as pear juice, beet juice, and apple juice can be consumed for three days before gradually reintroducing solid foods, starting with finely chopped raw beets mixed with olive oil, fresh lemon juice, and fresh applesauce, which can be very beneficial for patients.
Follow “Shishang Health” for more health and wellness knowledge!