Facial Diagnosis
The face is a holographic reflection of various parts of the body and diseases. Each part of the body is not independent but interconnected and mutually restrictive. From the five internal organs (zang) and six external organs (fu) to the limbs and skin, all are interrelated. If one part experiences a pathological change or discomfort, it can disturb or affect other parts, even the whole body.
Head and Face: Midpoint of the Forehead. Indications: Head and facial diseases, brain diseases.
Throat: Midpoint between the head and lungs. Indications: Pharyngitis, plum pit qi, etc.
Lungs: Midpoint between the eyebrows. Indications: Cough, asthma, and other respiratory diseases.
Heart: Located at the lowest point of the nasal bridge. Indications: Palpitations, insomnia, etc.
Liver: Midpoint connecting the heart and spleen areas. Indications: Liver diseases and pain in the flanks.
Gallbladder: On both sides of the liver area. Indications: Cholecystitis, gallstones, etc.
Spleen: Located at the tip of the nose. Indications: Poor appetite, abdominal distension, indigestion, etc.
Stomach: Located on both sides of the spleen. Indications: Stomach pain, vomiting.
Bladder: Corresponds to the location of the water ditch point. Indications: Lower back pain.
Uterus: Overlaps with the bladder area. Indications: Dysmenorrhea, pain in the genital area.
Large Intestine: Below the zygomatic arch. Indications: Constipation, abdominal pain, diarrhea, etc.
Small Intestine: On the inner side of the zygomatic bone. Indications: Diarrhea.
Kidney: Intersection of the horizontal line of the nostrils and the vertical line of the temples. Indications: Enuresis, etc.
Umbilicus: Slightly below the kidney area. Indications: Abdominal pain around the navel.
Chest (Breasts): Slightly above the inner canthus of the eye. Indications: Chest fullness, chest tightness, etc.
Mnemonic: In diagnosing diseases, observation comes first. Vital energy and spirit are the most important. Remember the locations of the organs.
Multiple shadows should be distinguished. Diseases have multiple causes, arising from qi and blood.
【Facial Color】
Blue complexion indicates cold pain. Glossy complexion indicates abundant qi and blood. Red complexion indicates heat. Red like makeup indicates false heat.
Black complexion indicates liver and kidney issues. Pale complexion indicates deficiency and cold. Pale without luster indicates blood deficiency. Yellow complexion indicates damp-heat.
Dark yellow complexion indicates liver and kidney disease. Bright forehead indicates good spirit. Dark forehead indicates disaster.
【Eyes】
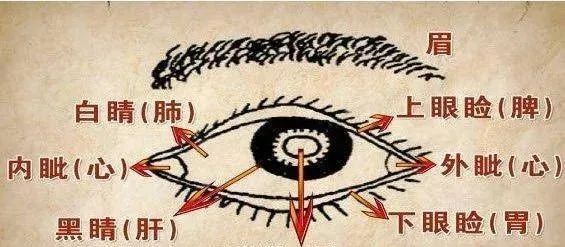
Bright eyes indicate no major illness. Dull eyes indicate deficiency of vital energy. Red eyes indicate internal heat. Yellow sclera indicates liver and gallbladder disease. Missing iris indicates brain disease. Large gastric ring indicates poisoning. Black vertical lines indicate inflammation. Black sunken eyes indicate structural damage. Itchy dermatitis indicates gray around the iris.
Hard blood vessels indicate white circular rings. Iris diagnosis is a vast field. Concentric circles are key. Multiple segments form a ring. Each ring represents the whole body. The eyes are like fish, precious and bright.
【Nose】
Glossy nose indicates no major illness. Blue nose indicates cold injury. White nose indicates blood injury. Deformed nose indicates stomach qi deficiency.
Deformed nose indicates serious illness. Moles on the nose indicate critical illness.
【Philtrum】
Clear philtrum indicates no major illness. Fullness below the tear hall indicates good health. Dark blue and dry indicates kidney deficiency. Insomnia indicates mental strain. Flat groove indicates lack of vitality. Infected philtrum indicates stomach fire. Crooked philtrum indicates short life.
【Lips】
Pale red lips indicate no major illness. White lips indicate blood injury. Blue-purple lips indicate cold pain and stasis. Glossy face indicates water accumulation. Yellow-black face indicates fatty liver.
【Ears】
Burnt ear surface indicates cancer risk. Clear and thin face indicates caution. If healthy, there should be flesh growth. Clear features from ten steps away indicate longevity. Clear areas indicate good health.Knowing colors can ensure safety.
Facial spots indicate disease signs.
A. Spots at the hairline are related to gynecological diseases, such as hormonal imbalance and endocrine disorders! B. Spots on the eyelids are common in pregnancy and excessive abortions, as well as hormonal imbalances! C. Spots at the temples and outer corners of the eyes are related to hypothyroidism, pregnancy, menopause, nervousness, and psychological stress! D. Spots below the nose are common in ovarian diseases! E. Spots around the eyes are common in uterine diseases, excessive abortions, and emotional instability due to hormonal imbalances! G. Scars around the mouth are common in those who overeat! H. Spots on the jaw are seen in blood acidification and excessive leucorrhea! I. Forehead spots are common in hormonal, adrenal, and ovarian abnormalities!
Eye Diagnosis
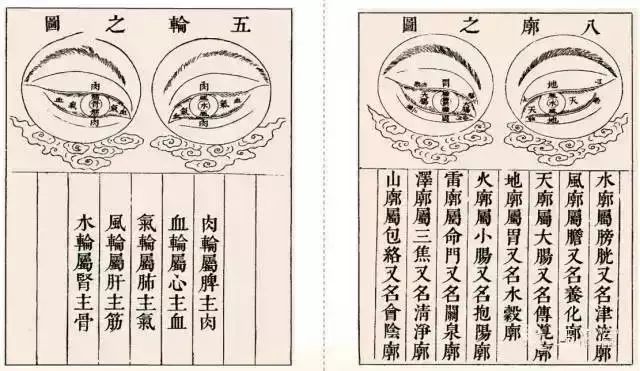
The Five Wheel Theory: Based on the Five Elements perspective, the eye is divided into five parts: inner wheel, blood wheel, qi wheel, wind wheel, and water wheel, each corresponding to specific organs, explaining the physiological and pathological mechanisms of the eye, guiding clinical diagnosis and treatment.
The Eight Trigrams Theory: Divides the eye according to the positions of the Eight Trigrams, each corresponding to the six fu organs, pericardium, and life gate. When the eye is diseased, observing the position, color, thickness, and quantity provides a basis for treatment.
The Five Wheel Theory originates from the theory in the “Inner Canon” regarding the relationship between the eye and internal organs, which has been a consensus among ophthalmologists throughout history.
The “Spiritual Pivot: Great Confusion” states: “The essence and qi of the five zang and six fu all ascend to the eyes and become the essence. The essence of the eye is the pupil, the essence of the bone is the iris, the essence of the sinews is the black eye, the essence of the blood is the network, the essence of the qi is the white of the eye, and the essence of the muscles is the restraint.” This indicates the parts of the eye, such as the pupil, white of the eye, and black of the eye, and generally explains the relationship between the main parts of the eye and the internal organs. Later generations of physicians gradually formed and perfected the Five Wheel Theory based on this discussion, becoming an important theory for guiding differential diagnosis and treatment in ophthalmology.
Correspondence between the Five Wheels and the Five Zang
(1) The meat wheel refers to the upper and lower eyelids, corresponding to the spleen, which governs muscles, hence called the meat wheel. The physiology and pathology of the eyelids are related to the spleen and stomach.
(2) The blood wheel refers to the inner and outer canthi and the blood vessels at the canthi, corresponding to the heart. The heart governs blood, hence called the blood wheel. The physiology and pathology of the canthi are related to the heart and small intestine. The large canthus has small openings called tear halls, which participate in tear drainage. Tears are the fluid of the liver, and the tear hall connects to the lungs, hence diseases of the tear apparatus are related to the liver, lungs, and heart.
(3) The qi wheel refers to the white of the eye, including the superficial conjunctiva and the deeper sclera, which is relatively tough and white, hence corresponding to the lungs, which govern qi, called the qi wheel. The physiology and pathology of the white of the eye are related to the lungs and large intestine.
(4) The wind wheel refers to the black of the eye, i.e., the cornea, which is governed by the liver, which governs wind, hence called the wind wheel. The liver and gallbladder are interrelated, so the physiology and pathology of the black of the eye are related to the liver and gallbladder. Although the black of the eye refers to the cornea, clinical changes in the yellow of the iris are also related to the liver and gallbladder.
(5) The water wheel refers to the pupil, which corresponds to the kidneys, which govern water, hence called the water wheel. The kidneys and bladder are interrelated, so the physiology and pathology of the pupil are related to the kidneys and bladder. The pupil has a narrow and broad definition; the narrow definition refers to the pupil, while the broad definition refers to the retina, optic nerve, uvea, and other intraocular tissues. The pupil in the context of the Five Wheel Theory refers to the broad definition. Traditional Chinese ophthalmology states that the pupil is governed by the kidneys, which has two meanings: first, the pupil is extremely important, born of congenital qi and formed by acquired qi, representing the subtle use of yin and yang, the essence of water and fire, and is the center of vision, which relies on essence and qi, as the kidneys store essence; second, the pupil is rich in water and needs nourishment from water, hence the water wheel. As stated in the “Examination of the Precious Box”: “Blood nourishes water, water nourishes essence, essence protects the pupil,” fully reflecting the function of water in nourishing the pupil.
Ears Diagnosis
Holographic ear therapy is based on the theory of meridians in traditional Chinese medicine, developed from acupuncture. Through ear acupoint magnetic moxibustion, it can fundamentally regulate the operation of the patient’s internal organs’ qi and blood, unblock blood vessels, and achieve the goal of seeking the root cause and treating the disease at its source.
Lips Diagnosis
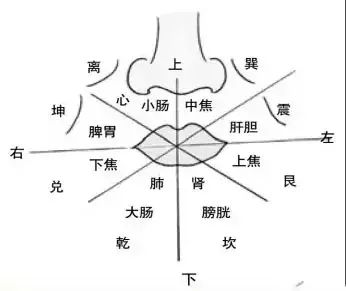
The lips are the hub of the fourteen meridians, the key point of the internal organs, and we use the Eight Trigrams diagram to illustrate the correspondence between the internal organs and the lips.
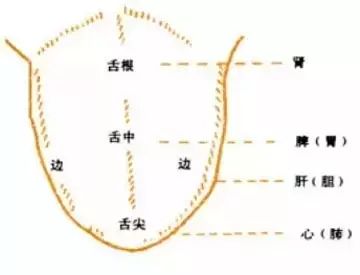
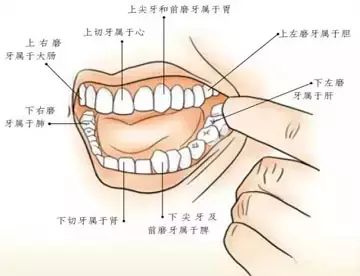
Teeth Diagnosis
Traditional Chinese medicine believes that “teeth are the surplus of bones,” and “gums are the network of the stomach.” Teeth are closely connected to the internal organs through various meridians.
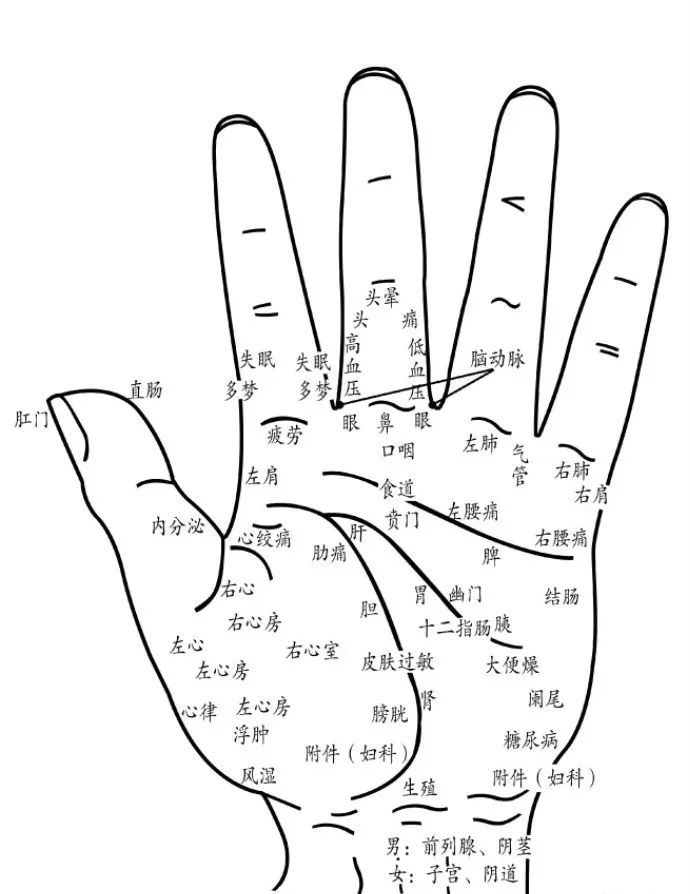
Hand Diagnosis
The “Hand Diagnosis Mnemonic” states:
Palms sweating indicates lung and spleen deficiency, fingertips reddening indicates high blood lipids; blue veins on finger joints indicate poor peripheral circulation.
Digestive absorption can be seen in the five fingers, gaps between fingers indicate gastrointestinal deficiency; vertical ridges on nails indicate liver disease, raised nail roots indicate poor bowel movements.
The thenar has deep lines, indicating arrhythmia and easy palpitations; the wrist extending to the hypothenar, prominent blue veins indicate lower back pain.
Nail color often turns white, indicating the need to tonify blood and kidneys; the right hand’s tiger mouth palm surface quickly locates the liver.
Poor vision has coarse lines, while fine lines indicate poor tendons; palm color red, blue, gray indicates stomach issues.
Disordered lines at the base of the thumb indicate early prevention of stomach diseases; the left hand’s tiger mouth palm surface indicates the spleen is easy to assess.
Morning and evening massage promotes health, fresh breath strengthens immunity; for women, check the right hand for breast health, and palpate the sides of the wrist.
Roughness and lumps indicate early prevention of breast hyperplasia; index finger nails indicate cerebral blood vessels, prominent ridges indicate hardening.
Menstrual pain and blood clots, blue veins at the base of the middle finger; reproductive diseases are hardest to diagnose, remember male left and female right.
1. Cool hands: indicates spleen and kidney yang deficiency, poor absorption, weak constitution. Weak and cold.2. Hot hands: indicates heart and kidney yin deficiency, irritability, insomnia, and dreams. Tension.3. Wet hands: indicate high stress, fatigue.Heart and spleen deficiency.4. Dry hands: indicates lung and spleen deficiency, dry skin, prone to colds.5. Excessive sweating: often indicates spleen and stomach heat accumulation, heart fire, mental tension.6. Sticky hands: indicates endocrine disorders, often seen in diabetes.7. Temperature:1. Real heat: the more you touch, the hotter it gets. [When shaking hands, if it feels hotter, it indicates a real heat disease, often with inflammation.]2. False heat: first hot, then not hot when touched again. [If it feels hot again, it often indicates false fire, seen in hyperthyroidism, kidney and liver yin deficiency.][Often seen in false fire rising, insomnia, irritability, dry mouth, bitter taste, pharyngitis, hypertension, diabetes, yin deficiency heat syndrome, etc.]3. Hot fingers: constipation, thick blood, high triglycerides.4. Hot palms: insomnia, irritability, dry mouth, bitter taste, pharyngitis, etc.5. Cool fingers: poor blood circulation, easy fatigue, unclear mind, difficulty sleeping.Cool fingers: [can be seen in spleen and kidney yang deficiency, hypothyroidism, microcirculation disorders, poor meridian flow. Easily fatigued, prone to colds, irregular menstruation. Often a symptom of poor blood circulation, easily fatigued, difficulty sleeping, vivid dreams, palpitations, unclear mind, dizziness, headaches].6. Cool palms: often indicate spleen and stomach cold deficiency, poor digestive absorption, prone to indigestion, loose stools, fatigue, anemia, often seen in women with gynecological diseases, irregular menstruation.7. Alternating cold and hot palms: often seen in hot weather fearing heat, cold in winter, hot food causing heat, cold food feeling cold, unable to tolerate supplements, irregular menstruation.Restlessness, insomnia, easily sore throat, cold hands and feet, etc., indicate endocrine disorders.A healthy hand should be warm in winter and cool in summer.Palms that fear cold in winter and heat in summer often indicate blood deficiency.Alternating cold and hot: indicates yin-yang imbalance.8. Color:Soft hands: thick with flesh, elastic, energetic, strong constitution, adaptable. Strong adaptability. [If too soft and weak, it indicates poor energy, fatigue.]Hard hands: stiff and thin palms often indicate digestive system issues, stubbornness, and lack of adaptability.Color comparison of palms:1. Overall palm color compared to the wrist color: the redder the palm, the thicker the blood, possibly high blood lipids.2. Finger color compared to palm color: the redder the fingertips, the more fatigued.3. Finger color compared to finger joints: darker colors between joints indicate digestive system issues, often stagnation.4. Observing palm color is key to assessing overall condition. Local abnormalities often represent corresponding internal organ diseases.Palmar color:1. White: overall white often indicates cold syndrome, deficiency syndrome; local white abnormalities often indicate corresponding organ inflammation.2. Yellow: indicates damp syndrome, chronic inflammation.Yellow calluses on the palm indicate chronic or consumptive diseases.3. Red: overall red indicates qi and blood stagnation.4. Local redness: indicates aggravated inflammation.5. Local bright red spots: indicate organ bleeding.6. Blue: overall blue indicates qi and blood stagnation, local indicates pain.When a person’s emotions cannot be expressed, liver qi stagnation occurs, leading to blue areas in the liver region.7. Black: indicates past serious illness or long-term medication.Black spots in the elderly indicate physiological aging.When the entire palm is dull and lacks luster, and black spots with unclear edges appear, consider cancerous changes.
Foot Diagnosis
First observe the shape and posture of the feet. Flat feet are caused by the disappearance of the foot arch, leading to numbness and pain after prolonged standing or walking. The toes swell first, then gradually extend to the ankles, shins, and knees:
Blue color of the soles often indicates liver qi stagnation, qi stagnation, blood stasis, and varicose veins. Red soles often indicate blood quality issues, and can also appear during fever. Yellow soles often indicate hepatitis and damp-heat. Pale soles are common in patients with lung deficiency. Black soles are often seen in vascular inflammation.Gray-white soles often indicate kidney deficiency.
In elderly patients, the feet may appear deep rose-colored, with burning pain at night, and nail atrophy and deformation may indicate the onset of diabetes. In young and middle-aged patients, dark red feet with pain may indicate the possibility of occlusive vascular inflammation. Very pronounced foot lines may indicate depression. Women with net-like coarse lines on the skin of the foot’s ventral side and pinhole-like damage may have various symptoms of hormonal secretion disorders, such as irregular menstruation and decreased libido. Unnatural concave and convex phenomena on the ventral side of the toes may indicate drug-related pathological reactions due to excessive medication.
Nail Conditions and Their Reflections Pale nails may indicate anemia. Gray-white nails may indicate onychomycosis. Half red and half white nails may indicate kidney disease. Blue nails may indicate cardiovascular disease. Yellow nails may indicate nephrotic syndrome, hypothyroidism, or jaundice. Purple nails often indicate heart and lung disease. Blue or black nails may indicate paronychia or drug effects. Horizontal white lines on nails may indicate arsenic poisoning, lead poisoning, rough skin disease, or chronic kidney disease. Longitudinal stripes on nails indicate extreme fatigue and low immunity, making one susceptible to diseases. Horizontal ladder lines on nails can estimate the time of illness; generally, each horizontal line represents one month. Spoon-shaped nails, medically known as koilonychia, indicate a tendency for tuberculosis, hookworm disease, hyperthyroidism, onychomycosis, etc. Thickened nails may indicate cor pulmonale, psoriasis, syphilis, etc. If all five nails are raised, it may indicate significant mental stress. Curved nails may indicate the presence of tumors. Nails that are bent backward may indicate a tendency for chronic alcoholism. Nails can diagnose diseases. Therefore, it is essential to regularly clean and trim nails, leaving 1-2mm to avoid dirt accumulation and protect the skin at the nail base.

