Inheriting the legacy of Qi Huang, a public account with substance and warmth.
Ai Yu Xiang Tang
1.Six Major Principles and Pathogenesis of Cold Damage1. Taiyang Disease Pulse and Symptom Outline: The disease of Taiyang manifests as a floating pulse. Symptoms include stiffness and pain in the head and neck, along with aversion to cold.Pathogenesis: External pathogens invade the surface, causing disharmony between Ying and Wei.2. Yangming Disease Outline: The disease of Yangming is characterized by fullness in the stomach.Pathogenesis: Excessive dryness and heat, with intense conflict between the righteous and the evil.3. Shaoyang Disease Pulse and Symptom Outline: The disease of Shaoyang presents with bitter mouth, dry throat, and dizziness.Pathogenesis: Pathogens invade Shaoyang, leading to conflict between the righteous and the evil in the space between the exterior and interior, causing internal stagnation of gallbladder fire, which disrupts the function of the spleen and stomach.4. Taiyin Disease Outline: The disease of Taiyin is characterized by abdominal fullness and vomiting, inability to eat, and occasional abdominal pain. (If purged, there will be hardness below the chest.)Pathogenesis: Spleen Yang deficiency with excessive cold and dampness.5. Shaoyin Disease Outline: The disease of Shaoyin presents with a fine pulse and a desire to sleep.Pathogenesis: General deficiency of Qi and blood.6. Jueyin Disease Outline: The disease of Jueyin presents with thirst, Qi rising to the heart, heat and pain in the heart, hunger without desire to eat, and continuous diarrhea.Pathogenesis: Mixed Yin and Yang, with internal movement of wind.2.Briefly describe the main pulse and symptoms, pathogenesis, and treatment methods of Taiyang Wind and Taiyang Cold Damage.Taiyang Wind Main Symptoms: ① Fever—Wind pathogens invade the surface, causing Wei Yang to float and resist the evil externally. ② Sweating—Wei Yang is not firm, and Ying Yin is lost. ③ Aversion to wind and cold—Evil disturbs Wei Yang, causing Wei Yang to lose its warmth. ④ Nasal congestion—The lungs connect with the skin and hair, opening to the nose; when the skin and hair are affected, lung orifices are obstructed. ⑤ Dry retching—The stomach is the source of Wei, and when the surface Qi is not harmonious, Wei disturbs the stomach, causing Qi to rise. Pathogenesis: Wind pathogens invade the surface, with strong Wei and weak Ying. Treatment: Release the muscles and expel wind, harmonizing Ying and Wei (Key Formula: Gui Zhi Tang). Taiyang Cold Damage Main Symptoms: ① Headache, fever, aversion to wind—Cold pathogens injure the muscle surface. ② Body aches and joint pain—Cold condenses the meridians, obstructing Qi. ③ No sweating—Cold nature constricts, blocking sweat pores. ④ Wheezing—The lungs connect with the skin and hair; when the surface is closed, lung Qi cannot be expressed. Pathogenesis: Cold pathogens invade the surface, obstructing Wei Yang and stagnating Ying Yin. Treatment: Induce sweating and release the surface, promoting lung function and relieving wheezing (Key Formula: Ma Huang Tang).3.Differences between Zhu Ling Tang and Wu Ling San① Wu Ling San ② Zhu Ling Tang Pathogenesis and Treatment Characteristics Comparison: Floating Pulse: ① If the exterior is not resolved, Yang is floating and Yin is weak, the pulse must be floating and weak. ② If there is internal heat and external steaming, it must be floating and strong. Fever: Sweat follows heat release; the heat is lighter, only slightly warm. ② Internal heat and external steaming, the heat is heavier. Thirst: ① The functions of the three Jiao and bladder are impaired, leading to thirst and water reversal. ② Heat accumulation and water stagnation, thirst is lighter than Wu Ling San, drinking alleviates without vomiting. Urination difficulty: ① Yang deficiency in the three Jiao leads to clear urination. ② Water heat stagnation in the lower Jiao leads to red urination. Treatment: ① Ze Xie combined with Fu Ling and Zhu Ling to promote urination and Yang, Bai Zhu strengthens the spleen to drain water, Gui Zhi warms Yang and transforms Qi to move water, treating both exterior and interior. ② Fu Ling and Zhu Ling combined with Ze Xie to promote urination, Hua Shi and E Jiao clear heat and promote orifices, nourishing Yin and promoting water to drain damp-heat.4.Three Symptoms of Chest ObstructionPulse is deep and tight, pain below the heart, and hardness upon palpation are the three typical pulse symptoms of major chest obstruction, referred to by physicians as the “Three Symptoms of Chest Obstruction.”5.What is a bad disease? What are the treatment principles?A bad disease refers to a condition where misdiagnosis or mistreatment leads to deterioration, with complex symptoms that cannot be classified under the six meridian patterns. The treatment principle is: observe the pulse and symptoms, understand the reverse condition, and treat according to the symptoms (Clinical significance: this is the principle of differentiation and treatment based on patterns).6.What are the differences in headaches among the three Yang meridians?1. Taiyang headache is primarily located at the occiput, with fever and aversion to cold, and a floating pulse. This is due to wind-cold stagnation, with Taiyang meridian Qi obstructed, causing a tight sensation of pain. 2. Yangming headache is primarily located at the forehead, often with heat but not cold, and the pulse is often surging and rapid. This is due to internal heat in Yangming circulating through the meridians, with Qi stagnation presenting as distending pain. 3. Shaoyang headache is primarily on both sides, with alternating cold and heat, and the pulse is often wiry. This is due to Shaoyang meridian Qi being obstructed, with stagnant fire invading the meridians.7.How to distinguish between Taiyang Water Accumulation and Blood Accumulation?
Water Accumulation: The pathogenesis is that Taiyang evil is unresolved, following the meridians into the interior. The evil combines with water, affecting the Qi aspect, with symptoms of thirst, fever, floating pulse, difficulty urinating, and urgency in the lower abdomen. The treatment method is to promote Yang, transform Qi, and promote urination. The formula used is Wu Ling San. The characteristic is that the evil combines with water, focusing on promoting Yang and draining water.
Blood Accumulation: The pathogenesis is that Taiyang evil is unresolved, entering the interior and transforming into heat, combining with stagnant blood in the lower Jiao, affecting the blood aspect. Symptoms include a person appearing manic, frequent urination, urgency or hardness in the lower abdomen, a deep pulse, a red tongue, and the presence of purplish spots. The treatment method is to invigorate blood and resolve stasis. The formula used is Tao He Cheng Qi Tang. The characteristic is that heat combines with blood, focusing on expelling evil heat and resolving stasis.
8.Discuss the similarities and differences between Zhen Wu Tang and Fu Zi Tang in terms of symptoms, pathogenesis, and treatment.Similarities: Both are characterized by Shaoyin Yang deficiency and water dampness as a problem. Both use Fu Ling, Bai Zhu, Fu Zi, and Shao Yao. Differences: Zhen Wu Tang treats Taiyang mis-sweating leading to Shaoyin Yang deficiency, with symptoms of fever, palpitations below the heart, dizziness, and body tremors. The formula includes roasted Fu Zi to warm and strengthen kidney Yang, Bai Zhu to dry dampness and strengthen the spleen, fresh ginger to disperse and assist Fu Zi in warming Yang, Fu Ling to promote urination and assist Bai Zhu in strengthening the spleen, and Shao Yao to invigorate blood and promote urination, without using Ren Shen. Fu Zi Tang treats Shaoyin disease with Yang deficiency, cold dampness causing body pain, with symptoms of body pain, cold hands and feet, joint pain, and a deep pulse. The key points for differentiation are the harmony of the mouth and the coldness of the back. The formula includes roasted Fu Zi to warm the meridians and restore Yang, with the addition of Ren Shen to warm and tonify the original Yang, supporting the righteous and expelling the evil, along with Bai Zhu to warm and tonify the spleen Yang, transforming dampness and stopping pain, and assisting Fu Ling in strengthening the spleen and promoting urination.9.How to distinguish between Yangming abdominal fullness and Taiyin abdominal fullness?The text (255) states that abdominal fullness does not decrease, and if it decreases insufficiently, it should be purged with Da Cheng Qi Tang. The cause is Yangming bowel fullness, with obstructed bowel Qi, leading to symptoms of significant fullness and pain in the abdomen, with constipation, a yellow thick dry tongue coating, etc. Taiyin abdominal fullness is caused by spleen deficiency and cold dampness, according to the text (273) stating that Taiyin disease is characterized by abdominal fullness and vomiting, inability to eat, and occasional abdominal pain. If purged, there will be hardness below the chest. From the text, it can be seen that Yangming abdominal fullness resists pressure, with constipation and a yellow thick dry tongue coating; Taiyin spleen governs the large abdomen, with Yang deficiency in the middle Jiao, cold condensing Qi stagnation and damp obstruction, leading to unsteady pain, occurring intermittently, with a preference for warmth and pressure, with subtle abdominal pain occurring in waves, preferring warmth and pressure.10.Compare the treatment of the three formulas for damp-heat jaundice.
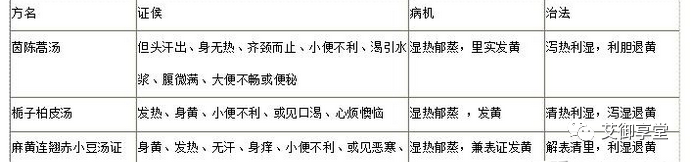
11.How to distinguish and apply the three formulas for heat diarrhea in the Treatise on Cold Damage?Heat diarrhea formulas: Bai Tou Weng Tang, Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang, Huang Qin Tang.Similarities: Fever, thirst, burning sensation in the anus, foul-smelling stools, red tongue, yellow coating, rapid pulse.Differences: Bai Tou Weng Tang—Liver meridian damp-heat pressing the large intestine, with heat dysentery as the main symptom, characterized by urgency and heaviness after defecation, with purulent blood. Treatment method: Clear heat and detoxify, cool blood and stop dysentery. Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang—Involves exterior and interior, with heat pressing the large intestine, characterized by wheezing and sweating as the main symptom, with heat dysentery and exterior symptoms. Treatment: Clear heat and stop dysentery while also dispersing the exterior. Huang Qin Tang—Shaoyang stagnant fire pressing the Yangming large intestine, with bitter mouth and wiry pulse as the main symptoms, with Shaoyang and Yangming combined dysentery. Treatment: Clear heat and stop dysentery, draining Shaoyang gallbladder fire.12.Compare the treatment of mixed cold and heat obstruction syndrome.Similarities: Spleen and stomach disharmony, mixed cold and heat, Qi stagnation, with symptoms of fullness below the heart, vomiting, and bowel sounds with diarrhea. The medicinal combinations use both cold and warm, with functions of tonifying and purging. Differences: Ban Xia Xie Xin Tang—Fullness below the heart, vomiting, diarrhea, with mis-purging leading to spleen and stomach injury, with evil heat penetrating, mixed cold and heat in the middle Jiao. Sheng Jiang Xie Xin Tang—Fullness below the heart, dry food odor, water vapor below the ribs, with abdominal rumbling as characteristics, with internal water and food stagnation, heavily using fresh ginger to warm Yang and transform fluids. Gan Cao Xie Xin Tang—Repeated mis-purging, with both fullness and diarrhea, with middle Yang damaged, food and water not transformed, dry retching, irritability, and inability to settle, using Gan Cao to warm and tonify middle Yang.13.What are the treatment principles for Taiyin abdominal pain?1. Abdominal fullness with pain—Spleen Yang is damaged, Ying and Wei are disharmonious—Gui Zhi Jia Shao Yao Tang. 2. Severe pain—Spleen injury with Qi stagnation, more severe injury to the collaterals—Gui Zhi Jia Da Huang Tang. 3. Sudden abdominal pain—Meridians affected by evil, Qi and blood deficiency—Xiao Jian Zhong Tang. 4. Abdominal pain with vomiting and diarrhea—Spleen affected by evil, Yang deficiency with cold condensation—Li Zhong Tang.14.Discuss the pathogenesis, main symptoms, and formulas of Gui Zhi Ren Shen Tang.Pathogenesis: Middle Jiao deficiency with cold, Taiyang invading the surface.Main Symptoms: Hardness below the heart, continuous diarrhea, accompanied by surface symptoms of fever, aversion to cold, headache, and thin stools, clear urination, and no thirst.Treatment method: Warm the middle and release the surface. Formula: Li Zhong Tang plus Gui Zhi.15.What are the differences in symptoms, pathogenesis, and treatment between Da Huang Huang Lian Xie Xin Tang and Fu Zi Xie Xin Tang?Da Huang Huang Lian Xie Xin TangSymptoms: Hardness below the heart, accompanied by thirst and irritability, red tongue, yellow coating, and other heat signs.Pathogenesis: Evil heat stagnating in the middle Jiao.Preparation method: Soak Da Huang and Huang Lian in boiling water for three to five minutes, take the juice and then consume.Clinical significance: Aims to take the light and floating Qi, avoiding heavy and turbid flavors, facilitating the clearing of formless heat without purging tangible evils.Fu Zi Xie Xin TangSymptoms: Hardness below the heart with discomfort, accompanied by body heat, thirst, irritability, red urination, rapid pulse, and in this context, also with aversion to cold, sweating, and insufficient Wei Yang.Pathogenesis: Evil heat stagnating in the middle Jiao (heat obstruction) combined with exterior Yang deficiency.Preparation method: Fu Zi is boiled separately to extract the juice, while the three Huang (Huang Qin, Huang Lian, Da Huang) are soaked in boiling water for three to five minutes, then the two juices are mixed and consumed.Clinical significance: The three Huang soaked in boiling water extract the light Qi to drain heat and resolve obstruction, while roasted Fu Zi is boiled separately to retain its rich and warming properties, facilitating the warming of the meridians and restoring Yang.☆Heat obstruction syndrome includes Da Huang Huang Lian Xie Xin Tang and Fu Zi Xie Xin Tang. Although both belong to heat obstruction, Da Huang Huang Lian Xie Xin Tang’s pathogenesis is solely due to stomach heat and Qi stagnation, with the main symptom being hardness below the heart, with accompanying heat signs such as irritability, thirst, and yellow-red urination. Treatment is to drain heat and resolve obstruction, using Da Huang Huang Lian Xie Xin Tang. In this formula, Da Huang drains heat and harmonizes the stomach, Huang Lian drains the fire of the stomach, and Huang Qin drains the fire of the middle Jiao. The method of soaking in boiling water aims to extract the light Qi to clear the formless heat. In contrast, Fu Zi Xie Xin Tang’s pathogenesis involves stomach heat and Qi stagnation, with the additional presence of insufficient Wei Yang. The main symptoms include hardness below the heart, irritability, thirst, and other signs of insufficient Wei Yang. Treatment is to drain heat and resolve obstruction while supporting Yang and securing the exterior, using Fu Zi Xie Xin Tang. The method involves soaking Da Huang, Huang Lian, and Huang Qin in boiling water for a short time to extract the light Qi to clear the upper evil heat, while Fu Zi is boiled separately to support Yang and secure the exterior.16.What are the differences between Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang and Zhen Wu Tang in terms of Yang deficiency and water retention?Similarities: Both involve water retention as a problem, presenting with dizziness and a deep pulse.Differences: Ling Gui Zhu Gan Tang primarily involves spleen Yang deficiency, with water retention in the middle Jiao, presenting with lighter symptoms, with water Qi rising causing fullness below the heart and Qi rising to the chest, leading to dizziness and a deep tight pulse.Zhen Wu Tang, on the other hand, involves Shaoyang Yang deficiency with cold water, with water retention in the lower Jiao, presenting with heavier symptoms, with lighter cases showing only heavy pain in the limbs, while severe cases may present with edema, fever, palpitations below the heart, dizziness, and abdominal pain, with diarrhea, or clear urination, or cough, or vomiting, or difficulty urinating.17.Briefly describe the main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, formula, and preparation of Zhi Gan Cao Tang.Main Symptoms: Pulse is intermittent, with palpitations. Pathogenesis: Deficiency of Qi and blood, leading to insufficient pulse flow.Treatment method: Nourish Yin and blood, promote Yang and restore pulse.Formula: Gan Cao 4, Sheng Jiang 3, Ren Shen 2, Sheng Di Huang 1 Jin, Gui Zhi 3, E Jiao 2, Mai Men Dong 0.5 Sheng, Ma Ren 0.5 Sheng, Da Zao 30 pieces.Preparation method: Boil the eight ingredients in seven sheng of clear wine for eight minutes, remove the residue, add E Jiao, and dissolve completely, taking one sheng warm, three times a day.18.Why does Xiao Qing Long Tang present with “thirst,” “no thirst,” and “thirst after taking the decoction”?Xiao Qing Long Tang presents with thirst due to fluid stagnation affecting Qi transformation, leading to an inability to distribute fluids upwards. No thirst indicates that internal water stagnation has not yet affected Qi transformation. Thirst after taking the decoction indicates that after the stagnation is resolved, the fluids in the upper Jiao are temporarily insufficient, leading to thirst, which will resolve as the stagnation is transformed and Qi flows smoothly, thus thirst will be eliminated.19.What are the five symptoms of heart Yang deficiency?① Heart Yang deficiency with palpitations: Excessive sweating leads to cold hands and feet, palpitations below the heart, desiring pressure. Treatment method: Warm and promote heart Yang. Formula: Gui Zhi Gan Cao Tang (Gui Zhi, roasted Gan Cao). ② Heart Yang deficiency with irritability: Formula: Gui Zhi Gan Cao Long Gu Mu Li Tang (Gui Zhi, roasted Gan Cao, Long Gu, Mu Li). ③ Heart Yang deficiency with mania: Formula: Gui Zhi removes Shao Yao and adds Shu Qi Mu Li Long Gu Jiu Ni Tang (Gui Zhi, roasted Gan Cao, Sheng Jiang, Da Zao, Mu Li, Shu Qi, Long Gu). ④ Heart Yang deficiency with rebellious Qi: Formula: Gui Zhi Jia Gui Tang (Gui Zhi, Shao Yao, Sheng Jiang, roasted Gan Cao, Da Zao). ⑤ Heart Yang deficiency with impending rebellion: Formula: Fu Ling Gui Zhi Gan Cao Da Zao Tang (Fu Ling, Gui Zhi, Gan Cao, Da Zao).20.What are the main symptoms and pathogenesis of Bai Hu Jia Ren Shen Tang?The main symptoms of Bai Hu Jia Ren Shen Tang are: fever, profuse sweating, dryness of the tongue and severe thirst, accompanied by occasional aversion to wind, slight aversion to cold, and a surging pulse. The pathogenesis is: evil heat is intense, injuring both Qi and fluids.21.Briefly describe the characteristics of fever in the three Yang diseases.In Taiyang disease, fever generally correlates with the degree of aversion to cold; the more fever, the more severe the aversion to cold, and vice versa. In Shaoyang disease, fever is often more pronounced with less aversion to cold, or alternating cold and heat, while in Yangming disease, there is no aversion to cold, but rather aversion to heat, with a preference for coolness.22.What is water reversal syndrome, what is its pathogenesis, and how is it treated?Water reversal refers to a syndrome where fluid stagnation leads to thirst and vomiting upon drinking, representing a severe form of water retention. The pathogenesis is that water accumulates in the bladder, with impaired Qi transformation, causing water evil to rise and obstruct the stomach, leading to loss of harmony and subsequent vomiting. Treatment method: Transform Qi and promote water, while also releasing the exterior. Formula: Wu Ling San, using Zhu Ling, Ze Xie, Bai Zhu, Fu Ling, and Gui Zhi.23.Gui Zhi Ren Shen Tang, Ge Gen Tang, Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang, and Huang Qin Tang all treat diarrhea; how should they be distinguished?Gui Zhi Ren Shen Tang warms the middle and releases the exterior, primarily treating Taiyang disease with repeated purging leading to spleen Yang injury, with symptoms of continuous diarrhea and hardness below the heart. Ge Gen Tang releases the exterior and stops diarrhea, primarily treating Taiyang exterior evil not resolved, with internal pressure on Yangming leading to diarrhea, characterized by exterior symptoms. Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang resolves both exterior and interior, clearing heat and stopping diarrhea, primarily treating unresolved exterior symptoms with heat pressing the large intestine, leading to foul diarrhea. Huang Qin Tang clears heat and stops diarrhea, primarily treating Shaoyang evil heat pressing the intestines, with symptoms of burning diarrhea and abdominal pain.24.What are the key points for diagnosis and pathogenesis of Xiao Xian Xiong Tang?The key points for diagnosis of Xiao Xian Xiong Tang are hardness below the heart, pain upon palpation, chest tightness, wheezing with yellow phlegm, yellow greasy tongue coating, and a floating slippery pulse. The pathogenesis is phlegm-heat obstructing the heart, with shallow heat and light obstruction.25.Briefly describe the symptoms, pathogenesis, and formula of Xiao Jian Zhong Tang.The symptoms of Xiao Jian Zhong Tang include palpitations and irritability, abdominal pain, preference for warmth and pressure, or accompanied by slight aversion to cold and fever. The pathogenesis is middle Jiao deficiency with cold, Qi and blood deficiency, disturbed by evil. The formula consists of: Gui Zhi, Gan Cao, Da Zao, Shao Yao, Sheng Jiang, and Yi Tang.26.How to distinguish between Zhu Ling Tang and Zhen Wu Tang, both of which have diarrhea, cough, and vomiting symptoms?The distinguishing point is that Zhu Ling Tang’s occurrence is due to evil in the Taiyang, requiring sweating to resolve, while using purging methods would damage the Yang of the spleen and stomach, leading to internal water stagnation, while Yang deficiency cannot rise to clear the upper, thus causing dizziness. Zhen Wu Tang, on the other hand, is due to Taiyang disease with improper sweating, where the exterior symptoms are resolved, but the Yang energy of Shaoyin is severely damaged, leading to Yang deficiency and water evil flooding, with symptoms of dizziness. Therefore, both syndromes involve water as a disease, which can lead to dizziness, but one is in the spleen and the other in the kidney. Thus, the former should focus on warming Yang and tonifying the spleen, using Bai Zhu Gan Cao Tang, while the latter should focus on warming the kidney and promoting water, using Zhen Wu Tang.27.Briefly describe the characteristics and functions of Zhu Ling Tang.Zhu Ling Tang has the effects of clearing heat, promoting water, and nourishing Yin. The formula includes Zhu Ling, Fu Ling, and Ze Xie for light drainage and promoting water, combined with E Jiao and Hua Shi to nourish Yin, clear heat, and promote water, ensuring that water is drained without harming Yin, and that heat is cleared and Yin nourished without obstructing water drainage.28.How to distinguish between damp-heat jaundice and cold-damp jaundice in symptoms?Damp-heat jaundice and cold-damp jaundice both present with yellowing of the eyes, skin, and yellow urine, but damp-heat jaundice presents with bright yellow, indicating a heat excess syndrome, with symptoms of fever, thirst, abdominal fullness, constipation, red tongue with thick yellow greasy coating, and rapid or wiry pulse. Cold-damp jaundice presents with dull yellow, indicating a deficiency-cold syndrome, with symptoms of abdominal fullness that decreases, loose stools, pale tongue with white greasy coating, and slow weak pulse.29.Compare the formulas of Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang, Da Cheng Qi Tang, and Xiao Cheng Qi Tang in terms of composition, function, and the differences in the symptoms they treat.Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang, Da Cheng Qi Tang, and Xiao Cheng Qi Tang all contain Da Huang, thus all have the effect of purging heat and excess, primarily treating Yangming bowel excess syndrome, with symptoms of fever or tidal heat, irritability, abdominal fullness, and constipation. Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang combines Da Huang with a large dose of Mang Xiao, supplemented with Gan Cao, providing good laxative and heat-purging effects, while purging without harming the intestines and stomach, suitable for Yangming bowel excess with severe dryness and lighter accumulation, clinically presenting with steaming heat, significant irritability, and abdominal fullness with hard stools. Da Cheng Qi Tang combines Da Huang with Mang Xiao, along with Hou Po and Zhi Shi, providing purging and heat-clearing effects, suitable for Yangming heat with significant bowel accumulation, with symptoms of tidal heat, irritability, abdominal fullness and pain, and constipation. Xiao Cheng Qi Tang combines Da Huang with a small dose of Hou Po and Zhi Shi, although it has purging and guiding effects, it is lighter, suitable for Yangming bowel excess with lighter symptoms, with symptoms of slight heat, or tidal heat, slight irritability, and hard stools.30.What are the characteristics of Da Cheng Qi Tang’s bowel movements, tongue appearance, and pulse?Stool is dry and hard or diarrhea, urine is yellow, tongue coating is yellow (thick) with little moisture, pulse is wiry (slippery) and rapid.31.Briefly describe the characteristics of Chai Hu Gui Zhi Tang’s formula and treatment method.The main indication is for symptoms of Shaoyang combined with exterior cold. The formula’s characteristic is that it combines half the amounts of Xiao Chai Hu Tang and Gui Zhi Tang, thus having the characteristic of lightly resolving both the exterior and interior.32.Compare the similarities and differences between Da Chai Hu Tang and Xiao Chai Hu Tang in terms of symptoms and treatment.Both syndromes involve the invasion of Shaoyang, with obstructed pivot. However, Da Chai Hu Tang also involves Yangming interior excess, in addition to the symptoms of Xiao Chai Hu Tang, such as bitter mouth, dry throat, dizziness, alternating cold and heat, fullness in the chest and ribs, aversion to food, irritability, and a wiry pulse. Treatment for Xiao Chai Hu Tang is to harmonize and resolve Shaoyang; treatment for Da Chai Hu Tang is to harmonize and resolve Shaoyang while also clearing the interior excess. The formula for Xiao Chai Hu Tang is Xiao Chai Hu Tang minus Ren Shen and Gan Cao, adding Shao Yao and Zhi Shi. Although both formulas are named after Chai Hu, their compositions differ in size and their targeted pathogenesis and symptoms vary, thus requiring clinical differentiation for application.33.What are the characteristics of Taiyin disease diarrhea?The pathogenesis of Taiyin disease diarrhea is due to spleen Yang deficiency, leading to the failure of clear Qi to rise, characterized by self-diarrhea without thirst, and may also present with abdominal fullness and pain.34.Why should Da Huang and Shao Yao be reduced when treating Taiyin abdominal pain?Shao Yao and Da Huang are cold and tend to break and drain, which should be used cautiously in patients with spleen and stomach Qi deficiency, as Taiyin disease primarily involves spleen and stomach Yang deficiency. Using Shao Yao and Da Huang carelessly may harm the spleen and stomach, leading to diarrhea, thus they should be reduced.35.What is the significance of “harmonious mouth” in the diagnosis of Fu Zi Tang?In Fu Zi Tang, “harmonious mouth” is not a disease symptom, but indicates that the mouth is not bitter, dry, or thirsty, serving as a distinguishing criterion to rule out heat syndromes.36.What are the differences in pathogenesis between Zhu Ling Tang and Zhen Wu Tang, both of which present with diarrhea, cough, and vomiting symptoms?Zhu Ling Tang is caused by Shaoyin heat transformation, with Yin deficiency and water-heat mutual obstruction; while Zhen Wu Tang is caused by Shaoyin cold transformation, with Yang deficiency and water flooding.37.What are the differences in the composition of Zhen Wu Tang and Fu Zi Tang, which differ by only one ingredient, and how do their symptoms and treatments differ?Zhen Wu Tang consists of Fu Zi, Bai Zhu, Fu Ling, Sheng Jiang, and Shao Yao; Fu Zi Tang consists of Fu Zi, Bai Zhu, Fu Ling, Ren Shen, and Shao Yao. Both formulas treat kidney Yang deficiency, with water evil or cold dampness stagnating as the problem. The common ingredients are Fu Zi, Bai Zhu, Fu Ling, and Shao Yao, which is the similarity. However, Zhen Wu Tang focuses on Shaoyin Yang Qi deficiency, with water evil flooding in the interior, with symptoms of abdominal pain, difficulty urinating, heavy pain in the limbs, diarrhea, or clear urination, or vomiting, with the treatment focusing on warming Yang, transforming Qi, and promoting water, thus using Sheng Jiang with Fu Zi to warm Yang and disperse water evil. Fu Zi Tang focuses on Shaoyin Yang Qi deficiency, with cold dampness remaining in the meridians, with symptoms of aversion to cold in the back, harmonious mouth, body pain, joint pain, and cold hands and feet, with the treatment focusing on warming Yang, transforming dampness, and relieving pain, thus using Ren Shen with Fu Zi, with Fu Zi’s dosage being doubled compared to Zhen Wu Tang, aiming to warm and tonify the original Yang to support the righteous and expel the evil.38.How to distinguish between the thirst of Jueyin disease and the thirst of Taiyang water accumulation?The thirst in Jueyin disease is caused by the burning of fluids by wood and fire, leading to an upper heat syndrome, accompanied by a red tongue and rapid pulse, with symptoms of heat and thirst. The thirst in Taiyang water accumulation is due to the bladder’s Qi transformation dysfunction, leading to an inability to rise, with symptoms of floating pulse, fever, and difficulty urinating.39.Why does Dang Gui Si Ni Jia Wu Zhu Yu Sheng Jiang Tang not use Gan Jiang or Fu Zi, but instead use Wu Zhu Yu and Sheng Jiang?In Dang Gui Si Ni Tang, the “Si Ni” refers to blood deficiency and cold condensation. “Long-term cold” is due to liver and stomach deficiency and cold, with the disease not in the spleen and kidney, but in the liver and stomach. Fu Zi and Gan Jiang are very spicy and hot, entering the kidney to warm the Yang within; Wu Zhu Yu and Sheng Jiang are bitter and descend directly into Jueyin. At the same time, Jueyin wind wood organs internally house the fire, and Fu Zi and Gan Jiang’s spicy heat can easily dry and injure Yin. Wu Zhu Yu and Sheng Jiang, on the other hand, disperse and descend, expelling cold without injuring Yin and blood.40.Compare Bai Tou Weng Tang and Tao Hua Tang in terms of differences.Bai Tou Weng Tang and Tao Hua Tang can both present with diarrhea with purulent blood, but the pathogenesis has differences in cold-heat and deficiency-excess. The pathogenesis of Tao Hua Tang is due to spleen and kidney Yang deficiency, leading to instability in the lower Jiao, with symptoms of diarrhea with purulent blood that is not foul-smelling, with more white than red, and severe cases may present with pure white discharge, accompanied by abdominal pain that is continuous, preferring warmth and pressure, with a pale tongue and white coating, and a weak pulse. The treatment is to warm, astringe, and secure the lower. Bai Tou Weng Tang’s mechanism is due to liver failure to disperse, with excessive heat and Qi stagnation, pressing the large intestine, leading to damp-heat fire toxicity, obstructing the intestines, damaging the intestinal collaterals, with symptoms of diarrhea with purulent blood, with more red than white or pure fresh blood, accompanied by abdominal pain, urgency, and significant fever, thirst, red tongue, yellow coating, and rapid pulse. The treatment is to clear heat, dry dampness, and cool the liver to stop diarrhea.41.What are the pathologies and main symptoms of cold obstruction, roundworm obstruction, blood deficiency cold obstruction, and Qi obstruction?Cold obstruction: The pathogenesis is due to insufficient Yang Qi and excessive internal cold, leading to cold obstruction; clinical manifestations include coldness in the limbs, accompanied by general aversion to cold, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever due to external cold and sweating. Treatment should focus on rescuing Yang, using Si Ni Tang. Roundworm obstruction: The pathogenesis is due to roundworms causing Qi disturbance, leading to obstruction; symptoms include a history of roundworm vomiting, cold hands and feet, but the body is not cold, with alternating calm and agitation, vomiting after eating, and abdominal pain; treatment should focus on warming the upper and descending, using Wu Mei Wan. Blood deficiency cold obstruction: The pathogenesis is due to blood deficiency and cold obstruction, leading to poor circulation of Qi and blood, with symptoms of coldness in the limbs and a fine pulse, along with dizziness and pale complexion; treatment should focus on nourishing blood and promoting circulation, using Dang Gui Si Ni Tang. Qi obstruction: The pathogenesis is due to Yang Qi stagnation, leading to poor circulation, with symptoms of coldness in the hands and feet or slight coldness in the fingers, along with other signs of Qi stagnation; treatment should focus on using Si Ni San to smooth Qi and promote circulation.42.What is the meaning of the Yangming disease outline “the stomach is full”?This refers to excessive dryness and heat in the stomach and intestines, with “stomach” referring to the stomach and intestines, and “full” referring to the nature of the disease, which is the excess of evil Qi.43.How to understand “Yangming disease, the stomach is full”?The phrase “the stomach is full” reflects the characteristics of Yangming disease symptoms and reveals the pathogenesis of Yangming disease. From the symptom perspective, “stomach” refers to the stomach and intestines, while “full” refers to the presence of evil Qi. Therefore, “the stomach is full” generally refers to the syndrome of dryness and heat in the stomach and intestines, which includes both Yangming heat syndrome and the clinical symptoms presented by Yangming excess syndrome. From the pathogenesis perspective, “the stomach is full” reflects the characteristics of Yangming disease being characterized by dryness and heat. Thus, both the formless excess of evil (Yangming heat syndrome) and the tangible excess of evil (Yangming excess syndrome) are part of the pathogenesis of “the stomach is full.”44.Briefly describe the main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, and formula of Xiao Chai Hu Tang.Main Symptoms: Symptoms include alternating chills and fever, fullness in the chest and ribs, irritability, and a wiry pulse. Pathogenesis: Involves Shaoyang, with stagnation of gallbladder fire and Qi obstruction, leading to symptoms of fullness and irritability. Treatment method: Harmonize and resolve Shaoyang. Formula: Xiao Chai Hu Tang.45.What are the pathogenesis, symptoms, treatment method, formula composition, and explanation of Da Chai Hu Tang?① Pathogenesis: Evil enters Shaoyang, leading to Qi obstruction, with the evil being more concentrated in the half interior. ② Symptoms: Symptoms include vomiting, stopping diarrhea, fullness below the heart, and slight irritability. ③ Treatment method: Pivot Shaoyang and open the Qi obstruction. ④ Formula composition: Chai Hu disperses the Shaoyang evil, Huang Qin clears heat, and together they resolve the half exterior and half interior evil, Ban Xia opens the Qi obstruction, and Sheng Jiang descends the Qi to stop vomiting, while Zhi Shi and Shao Yao open the Qi obstruction below the heart (removing Ren Shen and Gan Cao, as the evil is heavy and the heart is obstructed, avoiding the harm of sweetening the middle). 46.Briefly describe the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of Da Xian Xiong Tang.① Pathogenesis: Taiyang disease mis-purged, leading to deficiency of stomach Qi, with evil heat penetrating and combining with water in the chest. ② Main Symptoms: Symptoms include delayed pulse, indicating stagnation and obstruction, with internal rejection of pain, hardness below the heart due to water-heat mutual obstruction. Shortness of breath indicates chest obstruction, with lung Qi being obstructed. Irritability and restlessness indicate heat obstructing the chest, disturbing the spirit. ③ Treatment method: Drain heat, expel water, and break obstruction. ④ Formula: Da Xian Xiong Tang, with Da Huang and Mang Xiao draining heat and softening hardness, while Gan Sui aggressively expels water.47.Briefly describe the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of Xiao Xian Xiong Tang.① Pathogenesis: Phlegm-heat obstruction, with a lighter condition. ② Main Symptoms: Symptoms are localized below the heart, with pain upon palpation, indicating shallow obstruction, with a floating pulse indicating heat and a slippery pulse indicating phlegm obstruction, thus confirming phlegm-heat obstruction. ③ Treatment method: Clear heat, expel phlegm, and break obstruction. ④ Formula: Xiao Xian Xiong Tang, with Huang Lian clearing heat, Ban Xia expelling phlegm and breaking obstruction, and Gua Lou clearing heat and transforming phlegm, thus widening the chest and breaking obstruction.48.Briefly describe the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of Xiao Qing Long Tang.① Pathogenesis: Taiyang cold damage combined with internal water stagnation. ② Treatment method: Induce sweating and release the surface, while transforming water. ③ Main Symptoms: Symptoms include fever indicating unresolved Taiyang surface, dry retching and cough indicating water Qi obstructing the stomach, with water stagnating in the lungs, leading to cough, with possible thirst (indicating internal stagnation of the righteous fluids), or diarrhea (indicating water descending to the large intestine), or choking (indicating water Qi rising to the throat), or difficulty urinating, with fullness in the lower abdomen (indicating water stagnation in the bladder, leading to Qi transformation failure), or wheezing (affecting lung Qi). ④ Formula: Xiao Qing Long Tang—Ma Huang combined with Gui Zhi to induce sweating and release the surface, while Ma Huang promotes urination and relieves wheezing, and Gui Zhi promotes Yang and transforms water. Sheng Jiang, Xi Xin, and Wu Wei Zi warm the lungs and restrain the lungs, treating the cold water invading the lungs. Ban Xia descends and expels phlegm, Shao Yao harmonizes and promotes urination, and Gan Cao harmonizes the various herbs, thus achieving the effects of inducing sweating, releasing the surface, and transforming water.49.Briefly describe the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of Da Qing Long Tang.① Pathogenesis: Taiyang cold damage combined with Yang depression and irritability. ② Treatment method: Open the surface and induce sweating, clear heat and relieve irritability. ③ Main Symptoms: Symptoms include a tight floating pulse, aversion to cold and fever, body aches, and absence of sweating, which are typical symptoms of Taiyang cold damage. Irritability indicates that the cold evil is heavily obstructed, preventing Yang Qi from dispersing, thus disturbing the chest. ④ Formula: Da Qing Long Tang, with increased Ma Huang and Sheng Jiang for strong sweating to disperse surface cold, while Shi Gao clears heat and relieves irritability, and roasted Gan Cao, along with Da Zao, tonifies the middle and supports the righteous, thus providing a source for sweating while preventing Shi Gao from being overly cold and harming the righteous.50.What are the main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, and formula composition of Fu Zi Tang?Pathogenesis: Shaoyin disease with Yang deficiency, with cold dampness obstructing the back. Main Symptoms: Harmonious mouth, aversion to cold in the back, body pain, cold hands and feet, joint pain, and a deep pulse. Treatment method: Warm Yang and transform dampness. Formula: Fu Zi (roasted), Bai Zhu, Ren Shen, Fu Ling, and Shao Yao.51.What are the differences in treatment between Si Ni Tang and Tong Mai Si Ni Tang?① Si Ni Tang treats Shaoyin deficiency-cold syndrome, with symptoms of wanting to vomit but unable to, irritability, desiring to sleep, diarrhea with thirst, and white urine, with a deep pulse. The treatment method is to rescue Yang and reverse the condition, with the formula including Fu Zi (raw), Gan Jiang, and Gan Cao. ② Tong Mai Si Ni Tang treats Shaoyin excess Yin obstructing Yang, with symptoms of diarrhea with clear stools, cold hands and feet, a weak pulse, no aversion to cold, red complexion, abdominal pain, dry retching, and difficulty urinating. The treatment method is to vigorously rescue Yang and warm the Qi, with the formula including heavy doses of ginger and Fu Zi.52.Compare the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of the three Cheng Qi Tang formulas.In cases of internal heat but not severe excess, with some stagnation, but the stool is not yet hard, Tiao Wei Cheng Qi Tang should be used to drain heat and harmonize the stomach. If there is severe heat in the stomach, with irritability, the formula should be Da Cheng Qi Tang, which drains heat and opens the obstruction. If there is severe heat and excess, with hard stools, the formula should be Xiao Cheng Qi Tang, which drains heat and promotes bowel movements.53.What is the pathology of obstruction and the main symptoms?The pathogenesis is due to the disconnection of Yin and Yang Qi, presenting with coldness in the hands and feet.54.What are the symptoms and characteristics of cough in Ma Huang Tang, Ma Xing Gan Shi Tang, Xiao Qing Long Tang, and Gui Zhi Jia Hou Po Xing Zi Tang?Ma Huang Tang: Cough due to the lungs connecting with the skin and hair, with the surface closed and lung Qi not being expressed, presenting with cough without sweating, headache, fever, body aches, and aversion to wind and cold, with a white tongue coating and a floating tight pulse. Ma Xing Gan Shi Tang: Cough due to evil heat pressing the lungs, with symptoms of cough, phlegm, sweating, no significant fever, thirst, yellow tongue coating, and rapid pulse. The pathogenesis is due to evil heat obstructing the lungs, with the lungs losing their ability to express. Xiao Qing Long Tang: Cough due to internal water stagnation affecting the lungs, with symptoms of cough, dry retching, fever, and difficulty urinating, with fullness in the lower abdomen. Gui Zhi Jia Hou Po Xing Zi Tang: Cough due to wind-cold pressing the lungs, with symptoms of spontaneous sweating, fever, aversion to cold, headache, white tongue coating, and a floating pulse.56.What are the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of Pi Yao syndrome?① Pathogenesis: The stomach is strong while the spleen is weak, leading to the spleen’s inability to transport fluids, resulting in a lack of fluids in the stomach and intestines. ② Main Symptoms: Hard stools, frequent urination (with fluid seeping), and no significant discomfort even after several days without bowel movements. ③ Treatment method: Moisten the intestines, promote Qi, and facilitate bowel movements. ④ Formula: Ma Zi Ren Wan, Xing Ren, Shao Yao (to moisten), Da Huang, Hou Po, Zhi Shi (to drain heat and promote Qi), and Bai Mi (to soften the stool).57.Compare the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of the three formulas for damp-heat jaundice.Yin Chen Hao Tang: ① Pathogenesis: Damp-heat jaundice is primarily internal. ② Main Symptoms: Sweating from the head, no sweating from the body, yellowing of the entire body, and slight abdominal fullness. ③ Treatment method: Clear heat, promote dampness, and reduce jaundice. ④ Formula: Yin Chen Hao, Zhi Zi, and Da Huang. Ma Huang Lian Qiao Chi Xiao Dou Tang: ① Pathogenesis: Damp-heat jaundice is primarily external. ② Main Symptoms: Yellowing accompanied by fever, no sweating, and itching. ③ Treatment method: The evil is obstructed externally, thus it is necessary to guide the treatment to open the ghost gate, inducing sweating, dispersing heat, and expelling dampness. ④ Formula: Lian Qiao, Sheng Zhi, Bai Pi, Chi Xiao Dou, Gan Cao, and Da Zao (to promote fluid flow). Zhi Zi Bai Pi Tang: ① Pathogenesis: Damp-heat jaundice is primarily heat-heavy. ② Main Symptoms: Fever is the main symptom, with yellowing of the body, eyes, and urine. ③ Treatment method: Primarily clear heat, with dampness drying. ④ Formula: Bai Pi, Zhi Zi, and Gan Cao.58.What is the mechanism of cold-damp jaundice?Cold-dampness obstructs the liver and gallbladder, leading to abnormal bile flow and resulting in yellowing of the skin.59.What are the principles for using Xiao Chai Hu Tang?The principle of use is that “if one symptom is present, it is sufficient; there is no need for all symptoms to be present,” but this “symptom” must reflect the pathology of Shaoyang fire being obstructed, or the evil being trapped in the hypochondrium, in order to use Xiao Chai Hu Tang; otherwise, it should not be used. This indicates that this symptom is not without criteria, such as “alternating chills and fever, fullness in the chest and ribs, irritability, and a wiry pulse” are all valid. The clinical significance includes ① differentiation and treatment based on patterns, and ② focusing on the main symptoms.60.What are the applications of Wu Zhu Yu Tang in the Treatise on Cold Damage, and how are they distinguished?One application is in the Yangming disease section, “desiring to vomit after eating grains,” primarily discussing Yangming cold syndrome, revealing that Yangming is not only heat excess but also has cold variations, emphasizing dual-directional dialectical thinking, with the pathogenesis being cold in the Yangming, leading to stomach cold and producing turbidity, treated by warming the stomach and dispersing cold, descending and stopping vomiting. The second application is in the Shaoyin disease section, “vomiting and diarrhea, cold hands and feet, irritability and desire to die,” primarily discussing the dialectical significance of distinguishing Shaoyin cold transformation crisis syndrome, with the pathogenesis being deficiency in the middle Jiao, with cold turbidity obstructing, requiring warming to descend and resolve turbidity. The third application is in the Jueyin disease section, “dry retching and vomiting foamy saliva, headache,” primarily discussing the main symptoms of Jueyin disease, comparing it with Jueyin heat syndrome, revealing the reverse pathogenesis and symptom patterns of Jueyin liver disease, with the pathogenesis being liver and stomach deficiency, with cold turbidity rising, requiring warming the liver and descending turbidity. Although the three applications differ in location, the pathogenesis of liver and stomach deficiency with internal cold and rising turbidity is consistent, and Wu Zhu Yu Tang is effective for liver and stomach, adept at descending turbidity. Thus, it treats different diseases with the same method (Wu Zhu Yu, Ren Shen, Sheng Jiang, Da Zao).61.What are the modifications and significance of Xiao Chai Hu Tang in the Treatise on Cold Damage?① Da Chai Hu Tang is Xiao Chai Hu Tang minus Ren Shen and Gan Cao, adding Shao Yao and Zhi Shi (significance as mentioned above). ② Chai Hu Gui Zhi Tang is made by combining Xiao Chai Hu Tang and Gui Zhi Tang in equal amounts, primarily treating light symptoms of Shaoyang combined with Taiyang disease, presenting with fever, aversion to cold, slight irritability, and fullness below the heart. ③ Chai Hu Jia Mang Xiao Tang is Xiao Chai Hu Tang plus Mang Xiao, treating Shaoyang combined with Yangming tidal heat syndrome, presenting with fullness in the chest and ribs, and vomiting. ④ Chai Hu Gui Zhi Gan Jiang Tang is Xiao Chai Hu Tang minus Ban Xia, Ren Shen, Da Zao, and Sheng Jiang, adding Gui Zhi, Gan Jiang, Gua Lou root, and Mu Li, primarily treating Shaoyang combined with phlegm-dampness obstruction syndrome, presenting with difficulty urinating, thirst without vomiting, but with sweating, alternating chills and fever, irritability, and fullness in the chest and ribs. ⑤ Chai Hu Jia Long Gu Mu Li Tang is Xiao Chai Hu Tang minus Gan Cao, adding Long Gu, Mu Li, and Qian Dan, primarily treating post-cold damage with irritability and confusion, presenting with fullness in the chest and ribs, difficulty urinating, and confusion.62.What are the indications of Yin Chen Hao Tang, Da Cheng Qi Tang, and Gui Zhi Jia Da Huang Tang, and what are the roles of Da Huang in each?① Yin Chen Hao Tang treats damp-heat jaundice, with Da Huang clearing and draining heat. ② Da Cheng Qi Tang treats Yangming bowel excess syndrome, with Da Huang draining heat and purging excess. ③ Gui Zhi Jia Da Huang Tang treats Taiyang mis-purging with heat entering the Taiyin, with Da Huang breaking blood and resolving stasis, assisting Shao Yao in promoting circulation and stopping abdominal pain.63.What are the distinguishing points between Bai Hu Tang and Bai Hu Jia Ren Shen Tang? What is the role of Ren Shen?Both formulas can present with fever, sweating, thirst, irritability, and confusion, with the pathogenesis being due to the excess of formless heat invading the interior, belonging to Yangming heat syndrome, with both treatment methods focusing on clearing heat. Bai Hu Tang is the basic formula, but may also present with internal heat obstructing Qi, leading to abdominal fullness and heaviness, difficulty in bowel movements, and a lack of appetite. Bai Hu Jia Ren Shen Tang presents with internal heat being intense, injuring both Qi and fluids, thus presenting with aversion to wind, slight aversion to cold, and dryness of the tongue. The treatment method combines the effects of nourishing Qi and fluids, which is the role of Ren Shen.64.What are the differences between Shaoyin and Taiyin diarrhea?Taiyin diarrhea is self-limiting without thirst, due to the heavy dampness of Taiyin. Shaoyin diarrhea is accompanied by thirst, due to the deficiency of both Yin and Yang, with insufficient Yang Qi leading to an inability to transform fluids.65.What are the differences between Si Ni Tang and Si Ni San?Both formulas are named after “Si Ni,” thus both formulas are used to treat “Si Ni” symptoms. However, the pathogenesis differs. Si Ni Tang treats Yang deficiency with cold, presenting with symptoms of wanting to vomit but unable to, irritability, desiring to sleep, diarrhea with thirst, and white urine, with a deep pulse. The treatment method is to rescue Yang and reverse the condition, with the formula including Fu Zi (raw), Gan Jiang, and Gan Cao. Si Ni San treats Qi stagnation leading to cold obstruction, with symptoms of coldness in the limbs, irritability, and a wiry pulse. The treatment method is to smooth Qi and promote circulation, with the formula including Chai Hu, Bai Shao, Zhi Shi, and Gan Cao.66.What are the differences in pathogenesis between Bai Hu Jia Ren Shen Tang and Fu Zi Tang, both of which present with slight aversion to cold?Bai Hu Jia Ren Shen Tang presents with slight aversion to cold due to internal heat obstructing the Qi, preventing Yang Qi from reaching the back; Fu Zi Tang presents with slight aversion to cold due to Shaoyin Yang deficiency, with cold dampness obstructing the Qi, preventing Yang Qi from reaching the back, leading to a lack of warmth.67.Why is Shao Yao removed from Gui Zhi Jia Shao Yao Tang? Why is Shao Yao added to Gui Zhi Jia Shao Yao Tang?Gui Zhi Jia Shao Yao Tang is used for Taiyang disease mis-purging, with symptoms of chest Yang not being vigorous (pulse rapid and fullness), thus Shao Yao, which suppresses Yang and assists Yin, is not suitable for cases where chest Yang is obstructed, thus it is removed to facilitate the action of Gui Zhi Tang in promoting Yang. Gui Zhi Jia Shao Yao Tang is used for symptoms of Ying deficiency and body pain, with symptoms of body pain and a deep pulse, thus increasing the dosage of Shao Yao to take advantage of its bitter and draining properties to remove blood stasis, promote circulation, and stop abdominal pain in cases of Taiyang mis-purging, where the evil has invaded the Taiyang.68.What are the main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, and formula composition of Huang Lian E Jiao Tang?① Pathogenesis: Shaoyin heat transformation syndrome (often due to pre-existing Yin deficiency, leading to external evil, and after two to three days, the evil transforms into heat, causing excessive fire). ② Main Symptoms: Irritability, inability to sleep, dry mouth and throat, red tongue with little coating, and a fine rapid pulse. ③ Treatment method: Clear heat and nourish Yin. ④ Formula: Huang Lian, Huang Qin, E Jiao, Shao Yao, and Ji Zi Huang.☆What are the main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, and formula composition of Huang Lian E Jiao Tang?Answer: The main symptoms are irritability and inability to sleep; often accompanied by dry throat and mouth, red tongue with little coating, and a fine rapid pulse. The pathogenesis is due to Shaoyin evil transforming into heat, with kidney water being deficient below and heart fire being excessive above, leading to disharmony between the heart and kidney. The treatment method is to clear heat and nourish Yin. The formula is Huang Lian E Jiao Tang, composed of Huang Lian, Huang Qin, E Jiao, Shao Yao, and Ji Zi Huang.69.What are the differences in symptoms, pathogenesis, and treatment between Tao Hua Tang and Bai Tou Weng Tang?Both Tao Hua Tang and Bai Tou Weng Tang can present with diarrhea with purulent blood, but the pathogenesis has differences in cold-heat and deficiency-excess. The pathogenesis of Tao Hua Tang is due to spleen and kidney Yang deficiency, leading to instability in the lower Jiao, with symptoms of diarrhea with purulent blood that is not foul-smelling, with more white than red, and severe cases may present with pure white discharge, accompanied by abdominal pain that is continuous, preferring warmth and pressure, with a pale tongue and white coating, and a weak pulse. The treatment is to warm, astringe, and secure the lower. Bai Tou Weng Tang’s mechanism is due to liver failure to disperse, with excessive heat and Qi stagnation, pressing the large intestine, leading to damp-heat fire toxicity, obstructing the intestines, damaging the intestinal collaterals, with symptoms of diarrhea with purulent blood, with more red than white or pure fresh blood, accompanied by abdominal pain, urgency, and significant fever, thirst, red tongue, yellow coating, and rapid pulse. The treatment is to clear heat, dry dampness, and cool the liver to stop diarrhea.70.What is the significance of “Shaoyin disease, pulse is deep, urgent warming”?The phrase “urgent warming” emphasizes that the disease has entered the Shaoyin, which involves the fundamental aspects of the body, often leading to rapid Yang loss and many fatal cases. Therefore, the treatment of Shaoyin is crucial and should be done promptly. The deep pulse indicates signs of Yang deficiency, thus urgent warming is necessary to prevent the transformation of Yang loss. If treatment is delayed at this time, it may lead to severe illness and difficulty in treatment, reflecting the preventive treatment philosophy of traditional Chinese medicine.71.What are the pathogenesis, main symptoms, treatment method, and formula composition of Dang Gui Si Ni Jia Wu Zhu Yu Sheng Jiang Tang?Pathogenesis: Blood deficiency and cold obstruction leading to cold extremities; main symptoms include cold hands and feet, a fine pulse, and a desire to sleep; treatment method is to warm the liver, nourish blood, and disperse cold; formula includes Dang Gui, Shao Yao, Gui Zhi, Xi Xin, Da Zao, Gan Cao, and Tong Cao.72.List four different pathogenesis leading to irritability, and describe their key points and treatment methods.① Internal heat stagnation, unable to disperse, such as in Da Qing Long Tang syndrome, with symptoms of a tight floating pulse, fever, aversion to cold, body aches, and no sweating, leading to irritability. Treatment method: Ma Huang, Gui Zhi, Xing Ren, Gan Cao, Sheng Jiang, Da Zao, and Shi Gao. The treatment should focus on warming and releasing the exterior while also clearing internal heat. ② Heart Yang damage, leading to restlessness, such as in Gui Zhi Gan Cao Long Gu Mu Li Tang syndrome, with symptoms of irritability accompanied by chest tightness and palpitations. Treatment method: Warming and promoting heart Yang while calming the spirit. Formula: Gui Zhi, Gan Cao, Long Gu, Mu Li. ③ Mis-purging leading to deficiency of both Yin and Yang, such as in Fu Ling Si Ni Tang syndrome, with symptoms of irritability accompanied by no heat and aversion to cold, cold hands and feet, and a fine pulse. Treatment method: Rescuing Yang and calming the spirit. Formula: Fu Zi, Fu Ling, Ren Shen, Gan Jiang, Gan Cao. ④ Excess heat, leading to obstruction and disturbance of the spirit, such as in Da Cheng Qi Tang syndrome, with symptoms of tidal heat, sweating, difficulty in bowel movements, and irritability. Treatment method: Draining heat and resolving obstruction. Formula: Da Huang, Mang Xiao, Zhi Shi, Hou Po.【Also】Zhi Zi Chi Tang—deficiency irritability, Zhu Ling Tang—irritability with inability to sleep, Wu Zhu Yu Tang—irritability leading to death, Da Chai Hu Tang—depression and slight irritability, Huang Lian E Jiao Tang—irritability and inability to sleep, Wu Mei Wan—intermittent irritability and calmness.73.What are the treatment principles for treating both exterior and interior diseases?The principles include treating the exterior first, then the interior, treating the interior first, then the exterior, and treating both exterior and interior simultaneously. ① Treating the exterior first and then the interior is suitable for cases where the exterior symptoms are prominent while the interior symptoms are not significant. For example, in cases of fullness with exterior symptoms, “it is not appropriate to attack fullness; the exterior must be resolved first, and only then can fullness be attacked,” thus Gui Zhi Tang should be used first. In Taiyang disease with exterior symptoms, the exterior is the main focus, with a floating pulse, thus Gui Zhi Tang should be used first. ② Treating the interior first and then the exterior is suitable for cases where the interior symptoms are urgent and severe or the interior is deficient and cold. For example, in cases of Taiyang disease mis-purging leading to diarrhea, with symptoms of clear stools and body aches, belonging to spleen and stomach Yang deficiency, with unresolved exterior symptoms, urgent treatment should focus on the interior, using Si Ni Tang. In cases of Taiyang blood accumulation with unresolved exterior symptoms, urgent treatment should focus on the interior, using Di Dang Tang. ③ Treating both exterior and interior simultaneously, such as in cases of Taiyang disease mis-purging leading to continuous diarrhea, with hardness below the heart, indicating both Taiyang exterior and Taiyang spleen and stomach deficiency, using Gui Zhi Ren Shen Tang; in cases of Taiyang and Shaoyin simultaneous invasion, “Shaoyin disease, initially acquired, leads to fever, with a deep pulse,” using Ma Huang Xi Xin Fu Zi Tang.74.Briefly describe the similarities and differences between Da Qing Long Tang and Xiao Qing Long Tang in terms of main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, and formula composition.Both Da Qing Long Tang and Xiao Qing Long Tang present with symptoms of exterior excess, such as fever, headache, no sweating, and a tight floating pulse. The pathogenesis is that both involve cold evil obstructing the exterior, with Wei Yang being obstructed, and Ying Yin being stagnant, with treatment methods focusing on inducing sweating and releasing the exterior. The formulas both use Ma Huang, Gui Zhi, Gan Cao, and Sheng Jiang. The differences are that Da Qing Long Tang presents with irritability, while Xiao Qing Long Tang presents with cough and wheezing; the pathogenesis of Da Qing Long Tang involves internal heat, while Xiao Qing Long Tang involves internal water stagnation; the treatment method for Da Qing Long Tang involves clearing internal heat, while Xiao Qing Long Tang involves transforming internal water; the formula for Da Qing Long Tang includes additional Sheng Jiang, Xing Ren, Da Zao, and Shi Gao, while Xiao Qing Long Tang includes additional Gan Jiang, Xi Xin, Shao Yao, Ban Xia, and Wu Wei Zi.75.How to distinguish between Ge Gen Tang and Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang, both of which can present with diarrhea?Ge Gen Tang and Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang both present with diarrhea, but there is a distinction between cold and heat diarrhea. Ge Gen Tang’s main symptom is that the exterior is not resolved, with cold water pressing the large intestine, leading to diarrhea with watery stools, without burning sensation in the anus. Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang, on the other hand, presents with unresolved exterior symptoms transforming into heat, pressing the large intestine, leading to heat diarrhea with burning sensation in the anus. The former emphasizes the exterior, while the latter emphasizes the interior.76.What are the similarities and differences between Zhen Wu Tang and Fu Zi Tang in terms of main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, and formula composition?Both Zhen Wu Tang and Fu Zi Tang share common main symptoms of cold limbs, no thirst, aversion to cold, and a deep pulse. The common pathogenesis is kidney Yang deficiency with water dampness as a problem. The treatment methods for both should focus on warming Yang and dispelling dampness. The formulas both include roasted Fu Zi, Bai Zhu, Fu Ling, and Shao Yao. The differences are that Fu Zi Tang also presents with body pain, cold hands and feet, joint pain, and aversion to cold in the back, while Zhen Wu Tang presents with dizziness, palpitations below the heart, and body tremors, with symptoms of abdominal pain, difficulty urinating, and edema. The pathogenesis of Fu Zi Tang is due to cold dampness obstructing the meridians, while Zhen Wu Tang is due to Yang deficiency leading to water flooding. The treatment for Fu Zi Tang focuses on warming the meridians and dispelling cold, while Zhen Wu Tang focuses on warming Yang, transforming Qi, and promoting water. The formula for Fu Zi Tang includes Ren Shen, while Zhen Wu Tang includes Sheng Jiang.77.What are the symptoms of cough in both exterior and interior diseases? Briefly describe the main symptoms, pathogenesis, treatment method, and formula composition of each.Both exterior and interior diseases can present with cough, with formulas including Gui Zhi Jia Hou Po Xing Zi Tang, Taiyang and Yangming combined disease, Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang, and Xiao Qing Long Tang. 1. The main symptoms of Gui Zhi Jia Hou Po Xing Zi Tang include cough, headache, fever, sweating, aversion to wind, and a floating pulse. The pathogenesis is that patients with a history of cough are affected by wind-cold, invading the muscles and pressing the lungs, leading to cold Qi rising. The treatment method is to release the muscles and expel wind, descending Qi and stabilizing cough. The formula includes Gui Zhi, Gan Cao, Sheng Jiang, Shao Yao, Da Zao, Hou Po, and Xing Zi. 2. The main symptoms of Taiyang and Yangming combined disease include cough and fullness in the chest, with fever and aversion to cold, headache, and no sweating. This is a combined disease of the two Yangs, with external cold binding the lungs and obstructing the Qi of the stomach. Although this is a combined disease, the condition is more focused on the exterior, thus the treatment method is to use Ma Huang Tang to induce sweating and release the exterior, allowing the interior to harmonize. The formula includes Ma Huang, Gui Zhi, Gan Cao, and Xing Zi. 3. The main symptoms of Ge Gen Qin Lian Tang include diarrhea as the main symptom, accompanied by fever, cough, and sweating. This is due to unresolved exterior symptoms transforming into heat entering the interior, with heat pressing the large intestine. The treatment method is to resolve both exterior and interior, with the formula including Ge Gen, Gan Cao, Huang Qin, and Huang Lian. 4. The main symptoms of Xiao Qing Long Tang include cough with copious white phlegm, fever, aversion to cold, headache, and no sweating. The pathogenesis is due to wind-cold binding the exterior and water-cold invading the lungs. The treatment method is to release the exterior and transform water, with the formula including Ma Huang, Shao Yao, Gan Jiang, Wu Wei Zi, Gan Cao, Gui Zhi, Ban Xia, and Xi Xin.For clinical reference only, non-professional doctors should not attempt acupuncture or medication.
Copyright Statement:Editor/Lao Jun Zhi Lu Proofreader/Feng Tu/Source from publicly available online materialsCopyright belongs to the original author.
If you find this useful, please give a thumbs up or look at it!

