Recently, the news of Hong Kong star Wang Zuxian opening a moxibustion clinic in Canada has attracted widespread attention. In the video, she personally administers moxibustion to customers and announces that she will dedicate the second half of her life to promoting moxibustion.
This event has made moxibustion a hot topic, and more people are curious: Is moxibustion really effective? Or is it just a psychological comfort?
Today, let science clear the fog and explore the truth.
What is Moxibustion?
Moxibustion, simply put, is the application of heat stimulation to specific acupuncture points on the body using burning moxa (mugwort).
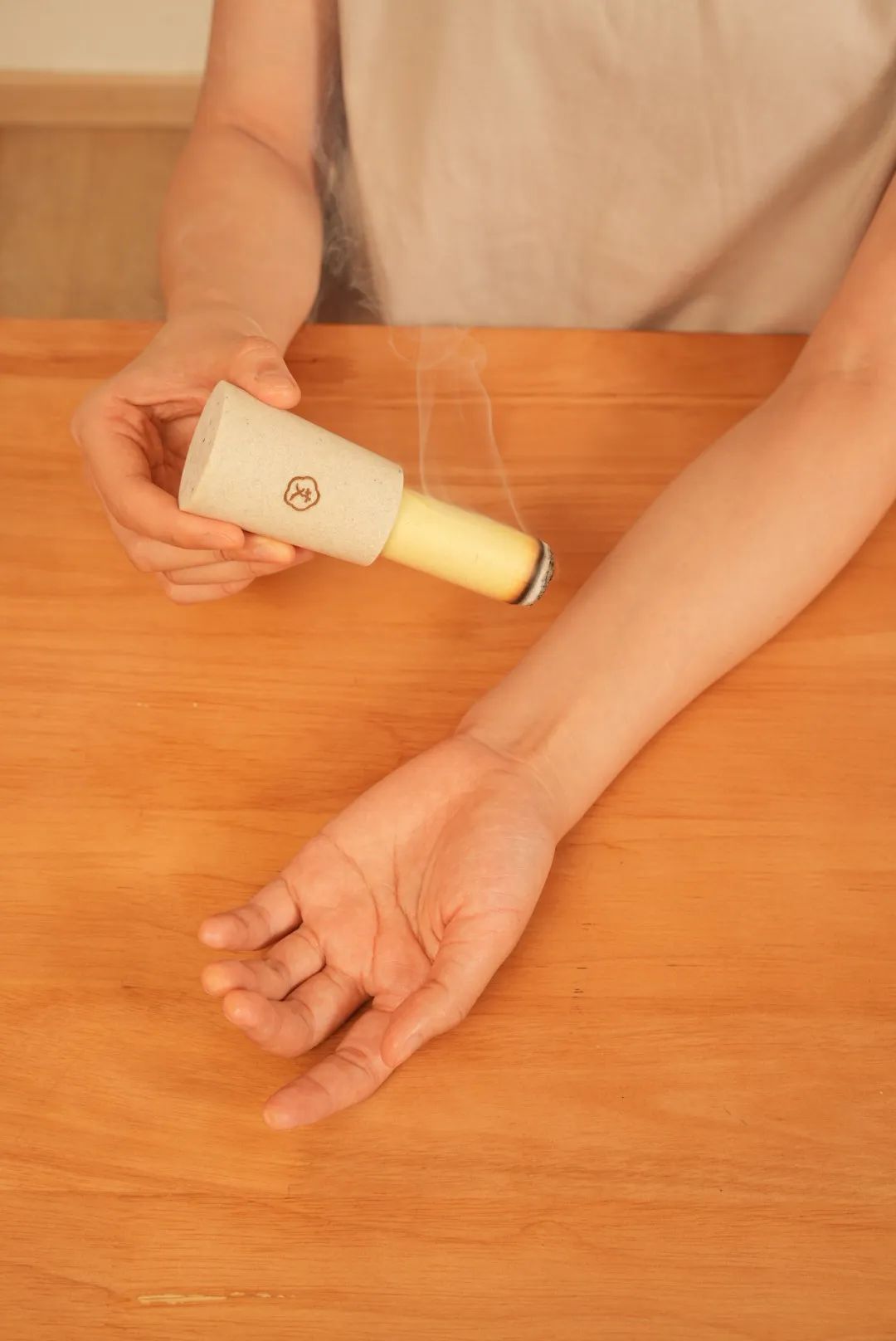

The history of moxibustion can be traced back to ancient times.
Ancient people discovered that when certain parts of the body were heated by fire or came into contact with warm stones, pain would be alleviated, leading to the formation of the early practice of moxibustion.
During the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods, moxa began to be used as a material for moxibustion, a practice that continues to this day.
Mugwort is a common Chinese herb, and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) believes it has the effects of warming the meridians, dispelling cold, and invigorating blood circulation.
The “Shen Jiu Jing Lun” states: “Using the pungent aroma of mugwort to create moxa cones can penetrate the twelve meridians, enter the three yin, and regulate qi and blood,” laying the theoretical foundation for the application of moxibustion.
What is the Scientific Basis of Moxibustion?
In recent years, more and more scientific research has begun to focus on the mechanisms of moxibustion.

Here are several key scientific findings:
-
Infrared Stimulation
The near-infrared rays released during the burning of mugwort resonate highly with the vibrational frequency of human cellular molecules, penetrating the skin to promote blood circulation and metabolism.
This “biological resonance effect” can elevate local temperature, helping to alleviate pain and inflammation.
-
Active Ingredients in Mugwort
Mugwort contains active components such as volatile oils and flavonoids.
Research indicates that flavonoids like isorhamnetin and chrysin possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties.

-
Biological Mechanism of Acupuncture Point Stimulation
Moxibustion acts on specific acupuncture points, which are closely related to nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels.
Studies have found that moxibustion can activate the autonomic nervous system and regulate endocrine and immune functions by stimulating acupuncture points.
What are the Effects of Moxibustion?
Although the scientific mechanisms of moxibustion are gradually being revealed, its effects still vary from person to person.

Here are some application scenarios of moxibustion supported by scientific research:
-
Regulating Immune Function
Modern experimental studies show that moxibustion can regulate imbalanced immune functions in the body, mainly by modulating immune molecules (cytokines, immunoglobulins, complement molecules) and immune cells (leukocytes, T lymphocytes, macrophages, NK cells).
Specifically, moxibustion can affect various immune organs, immune cells, immune regulatory factors, and immunoglobulins, thereby enhancing the body’s immune function.
-
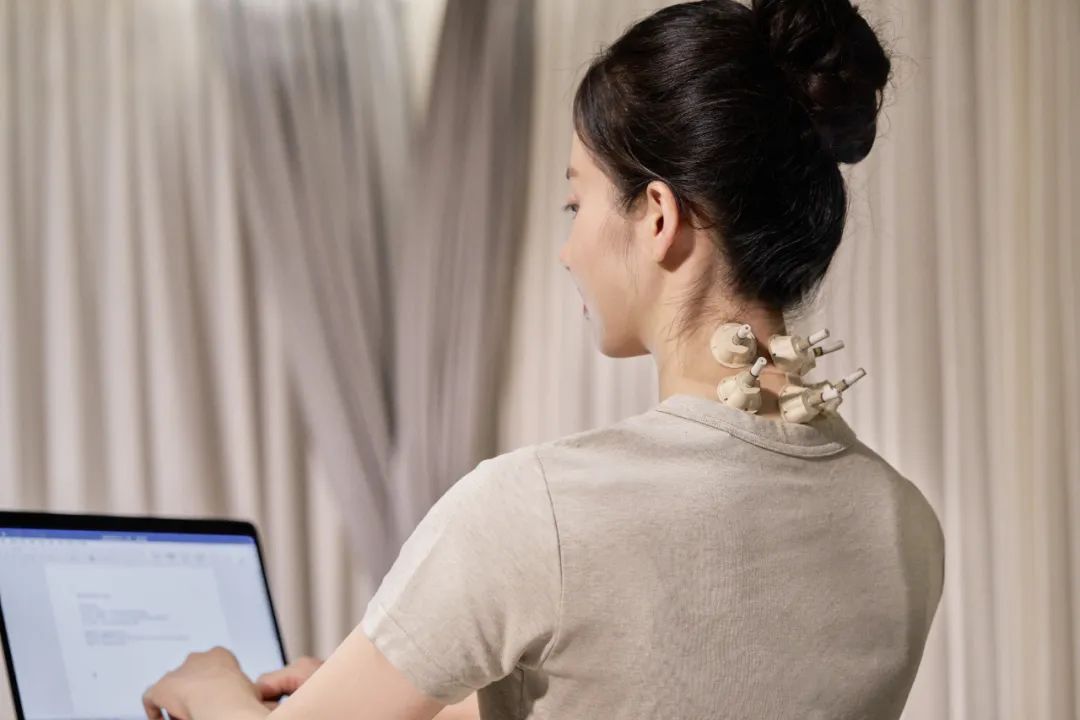
Alleviating Pain
Multiple studies indicate that moxibustion has a certain alleviating effect on chronic pain (such as arthritis, low back pain, shoulder periarthritis, etc.).
A study published in the “International Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine” pointed out that the improvement rate of chronic low back pain with moxibustion combined with heat therapy reached 72.3%.

-
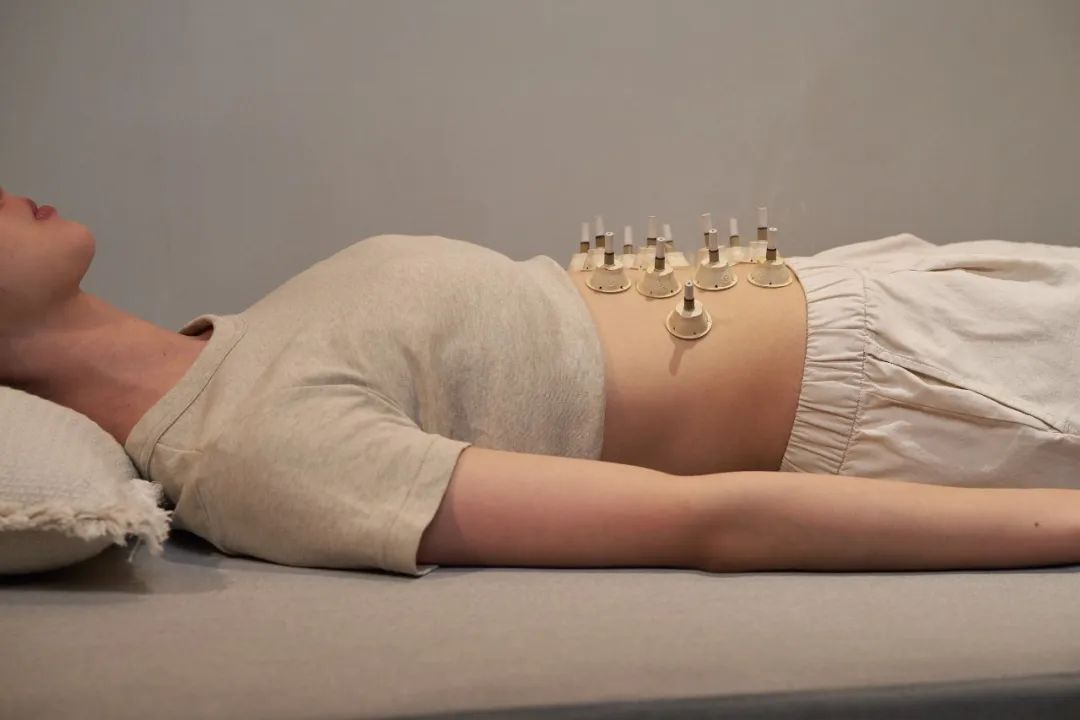
Improving Digestive Function
Research has found that moxibustion at the Shenque (Ren 8) point can regulate gastrointestinal function by improving periumbilical microcirculation, achieving an auxiliary effect on digestive system diseases.
Many people experience increased gas production and improvement in symptoms of bloating and constipation after moxibustion, indicating that moxibustion enhances gastrointestinal function and promotes metabolism.

-
Relieving Anxiety and Stress
The warm stimulation of moxibustion can be transmitted to the central nervous system through skin receptors, regulating the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, helping to alleviate anxiety and depressive emotions.
How to Use Moxibustion Correctly?
While moxibustion is beneficial, it must be used correctly and applied based on syndrome differentiation to maximize its value.

Here are some important considerations when using moxibustion:
-
Identifying Body Constitution
Before using moxibustion, one should identify their body constitution to avoid blind application. People allergic to mugwort, pregnant women, and patients with high fever, coma, or convulsions are advised against using moxibustion.
-
Operational Precautions
Avoid moxibustion when extremely fatigued, on an empty stomach, overly full, or after drinking alcohol. If dizziness or chest tightness occurs after moxibustion, stop immediately and consult a professional.
-
Post-Moxibustion Care
Drink warm water after moxibustion, avoid getting cold, and ensure adequate rest.

Moxibustion carries the wisdom of the Chinese nation accumulated over thousands of years, and with the in-depth research of modern science, its mechanisms and effects have been further validated.
May this “Eastern thermal energy” ignite the path to health for more people.