The Eight Principles of Hand Diagnosis Based on Color Observation belong to the main theoretical foundation of the cultural school of hand diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Long-term research indicates that it primarily includes eight colors observed in hand diagnosis: red, green, purple, yellow, brown, white, black, and turbid. This differs from the five colors observed in TCM diagnosis. Understanding and experiencing the key points of color differentiation in hand diagnosis is one of the most important introductory courses in hand diagnosis medicine.
1. Hand Diagnosis of Red Color
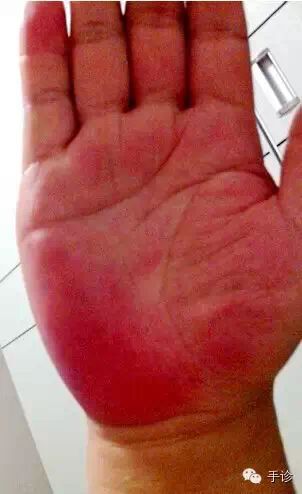
TCM: Blood heat and excess fire. Western Medicine:
Inflammation, bleeding, and the early to mid-stages of acute infectious diseases, or the early stages of certain diseases, also reflect diseases of the circulatory system; hyperfunction of the organs. Generally indicates heat-type, congestive diseases, local inflammation, bleeding, or the early stages of certain progressive diseases. Often associated with heat syndromes, blood heat, congestion, or stasis heat, and accumulated heat. Redness in the heart area often indicates heat toxin attacking the heart; redness in the spleen and stomach area indicates spleen and stomach heat stagnation or acute colitis. Redness in the kidney area indicates urinary system inflammation; redness in the liver area indicates excess liver and gallbladder fire or hypertension; redness in the heart area indicates excess heart fire or disharmony between heart and kidney.
2. Hand Diagnosis of Green Color

Green color is primarily associated with liver and gallbladder diseases, as well as cold syndromes, pain syndromes, blood stasis, and convulsions. It is also commonly seen in patients with chronic hepatitis or liver dysfunction. It can also be seen in malignant diseases. Green generally indicates severe pain. If green appears subcutaneously, it indicates blood stasis and ischemia. Especially if the main lines of the palm appear green, the condition is more critical.TCM: Cold syndrome. Qi stagnation and blood stasis syndrome, a type of tumor constitution. Manifestations: Liver qi stagnation, bile stasis. Western Medicine: ① Hypoxia of organ tissues; ② Insufficiency of organs, prone to organic lesions; ③ Tumor or hyperplastic constitution; ④ Severe functional decline; ⑤ Circulatory system diseases, decreased immunity.
Note: The green color observed in the liver area of the hand, when moist and vibrant, is not necessarily pathological, especially more common in women than in men. However, excessive greenness indicates liver blood stagnation.
3. Hand Diagnosis of Purple Color
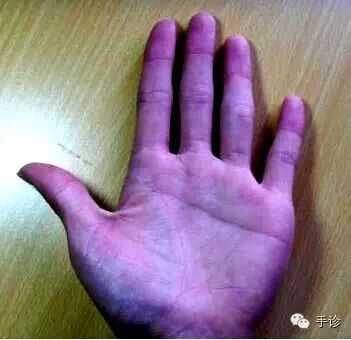
Purple color is often related to changes in blood components and blood circulation, belonging to a heavy and turbid form of red, slightly mixed with green and black. Blue-purple color: Entire hand appears purple: ① Poisoning; ② Myocardial infarction; Localized or specific areas appear blue-purple: ① Tumors or severe hyperplasia of organs; ② Inflammation accompanied by severe ulceration and erosion.
Blue-purple is commonly seen in the subcutaneous blood vessels of the palm. If blue blood vessels are observed, it indicates that the patient’s blood is viscous, capillaries are small, oxygen content in the blood is low, and blood lipids are abnormal, leading to impaired blood circulation, resulting in cold limbs, dizziness, etc. Any area under the skin of the hand showing obvious blue, gray-blue, dark blue, purple, or reddish-purple blood vessels indicates the presence of blood stasis in the corresponding part of the patient’s body. The blood flow in that area is definitely not smooth. The degree of obstruction varies with the color. Red indicates mild blood stasis. The darker and deeper the color, the more severe the blood stasis.
If blood vessels appear blue or purple, it generally indicates significant blood stasis. For example, if the blood flow to the brain is poor, purple blood vessels will appear in the corresponding head area, back of the head area, and cervical spine area during hand diagnosis.
Furthermore, if multiple areas of the palm show subcutaneous blue or purple blood vessels, it indicates poor blood lipids; it also indicates higher acidity in the blood. This reduces the oxygen content in the blood, making it easier for the blood to coagulate, leading to conditions such as cerebral thrombosis, limb thrombosis, and abdominal aortic thrombosis.
Purple-red: ① Entire hand: Increased blood pressure, blood lipids, and blood viscosity, indicating the body is about to develop cardiovascular diseases. ② Inflammation of the corresponding organ is ongoing and severe. Acute local tissue congestion and edema, with a possibility of bleeding in the local organ, prone to infectious diseases.
4. Hand Diagnosis of White Color
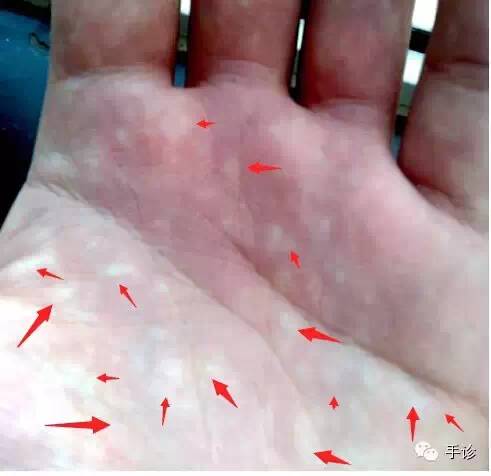
TCM: Primarily indicates lung and large intestine diseases. Qi deficiency, deficiency syndromes, cold syndromes (deficiency of qi and blood, insufficient middle qi, spleen and stomach yang deficiency, kidney qi deficiency), blood loss, qi collapse, pain syndromes.
Western Medicine:
Anemia, folic acid deficiency, reduced red blood cells, also seen in leukemia, respiratory diseases, decreased immunity, microcirculation disorders, and reduced organ function, etc.
Generally indicates pain (general pain), inflammation (painful inflammation); also indicates qi stagnation; and indicates qi deficiency. For example, if a white area is seen in the kidney region, it indicates kidney qi deficiency. If a white area is seen in the spleen and stomach region, it indicates spleen and stomach deficiency, insufficient middle qi. White also indicates cold syndrome, which is an internal cold syndrome. White color appearing in the heart area indicates myocardial ischemia; white in the spleen and stomach area indicates spleen and stomach deficiency and reduced digestive absorption function; white in the kidney area indicates kidney deficiency, also indicating excessive menstrual bleeding or flooding in gynecology. Any area of the hand showing white color indicates a deficiency in the corresponding organ’s function.
5. Hand Diagnosis of Yellow Color
 TCM: Primarily indicates spleen and stomach, liver and gallbladder. Deficiency syndromes, damp syndromes. Western Medicine:
TCM: Primarily indicates spleen and stomach, liver and gallbladder. Deficiency syndromes, damp syndromes. Western Medicine:
Digestive system diseases, some liver and gallbladder (jaundice) diseases. Also seen in trace element deficiency syndromes, anemia, chronic bleeding, etc. Yellow color is often seen in late-stage tumors. (In TCM, the spleen is not located on the hand; the TCM spleen encompasses the functions of the entire digestive system.)
Generally, individuals with liver and gallbladder diseases will have yellow palms, especially those with jaundice. However, a few cases may be due to genetic reasons. Generally, patients with parents of blood types AB and O often have skin that appears yellow. As long as it is not due to ABO hemolytic disease, this yellow color is still considered normal. However, it also indicates that these individuals are inherently prone to liver, gallbladder, and blood-related diseases.
Yellow: ① Long course of disease; ② Chronic diseases (for example: if yellow is present in the throat area, it indicates chronic pharyngitis. If the skin is also raised, it indicates that the patient’s mucosa has thickened.)
6. Hand Diagnosis of Brown Color
 Brown color is primarily yellow, slightly mixed with green and black, characterized by a dirty appearance.
Brown color is primarily yellow, slightly mixed with green and black, characterized by a dirty appearance.
Gray-brown:Yellowish and dark with a hint of green, appearing turbid. ① Cold damp syndrome (TCM); ② Severe decline in liver and gallbladder function; ③ Mid to late stages of hepatitis; ④ Chronic hepatitis; ⑤ Liver cirrhosis; ⑥ Liver and gallbladder duct stones; ⑦ Liver cancer.
Yellow-brown:Color is yellowish and dark, as if the palm is covered in dust. TCM: Phlegm-damp constitution, Western Medicine: Increased blood lipids, increased blood, liver and gallbladder toxins, and waste.
7. Hand Diagnosis of Black Color
 Black color in hand diagnosis does not appear alone, often mixed with other colors, characterized by dark and turbid hues. TCM: Primarily indicates kidney, kidney deficiency, blood stasis, cold syndrome, pain syndrome, water retention, blood stasis syndrome. Also seen in chronic injuries. Western Medicine: ① Nephrotic syndrome, kidney diseases, sexual dysfunction, urogenital diseases; ② Tumor constitution (malignant); ③ Circulatory system diseases;
Black color in hand diagnosis does not appear alone, often mixed with other colors, characterized by dark and turbid hues. TCM: Primarily indicates kidney, kidney deficiency, blood stasis, cold syndrome, pain syndrome, water retention, blood stasis syndrome. Also seen in chronic injuries. Western Medicine: ① Nephrotic syndrome, kidney diseases, sexual dysfunction, urogenital diseases; ② Tumor constitution (malignant); ③ Circulatory system diseases;
Localized black coloration: ① Tumors; ② Organic injuries; ③ Blood stasis; ④ Old lesions.
Generally, gray-black is more common, and absolute black is not very significant in diagnosis. If darkening occurs, consider the possibility of tumors.
For example, if the entire palm (especially the other four fingers besides the thumb) shows a layer of gray-black skin, it indicates high blood lipids in the patient, also indicating that the individual exercises less, and the waste produced in the body daily is not expelled, leading to fatigue and insufficient mental energy, all due to low metabolic function. Light black: Kidney deficiency, blood stasis.
8. Hand Diagnosis of Turbid Color
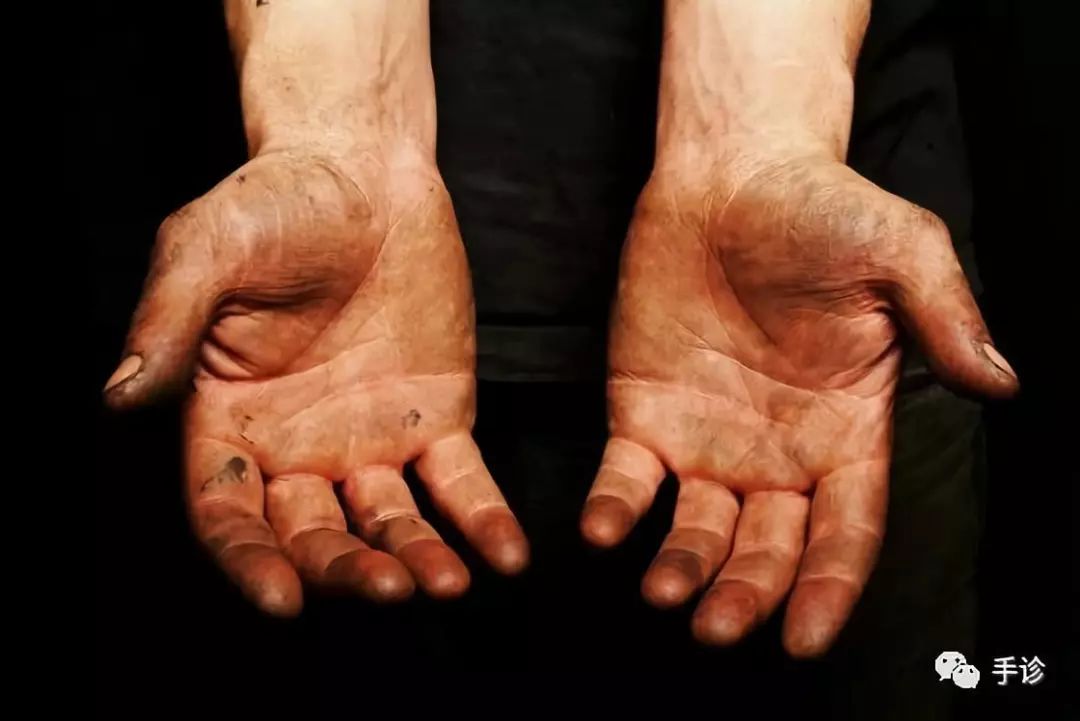

Turbid color can appear in any color, characterized by a mixed, dark, and dull appearance, looking dirty. Turbid color is primarily characterized by overall murkiness, obscuring at least three or more colors that cannot be completely distinguished. In today’s world, many people do not understand health preservation, leading to an increasing number of palms with this color, resulting in a loss of precision in single-color diagnosis.
Turbid color murky and dull:
Commonly seen in the accumulation of bodily toxins, abnormal metabolism, which can show slightly elevated blood lipids, elevated uric acid, and is also seen in chronic diseases that are difficult to heal. Often due to long-term irregular diet and lifestyle, physical exhaustion, especially common in those who consume large amounts of monosodium glutamate, seasonings, or chemical beverages, as well as high-fat, heavily flavored fast food. Immediate targeted adjustments are recommended.
Turbid color mixed and bright:
Turbid color appears in multiple colors, unevenly bright and dark, indicating deep pathogenic qi and turbid qi in the body, or seen during the occurrence of chronic diseases, or multiple complications, also seen during treatment, with accumulated drug toxicity.
Please watch the hand diagnosis color observation video course in a Wi-Fi environment.
Latest Hand Diagnosis Basic Introductory Course Directory
(Click the bottom menu [Hand Diagnosis Introduction] to access)
-
Seven Colors of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven Qualities of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven States of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven Types of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven Lines of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven Patterns of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven Touches of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven Points of Hand Diagnosis
-
Seven Signs of Hand Diagnosis

