
 Acupuncture is a unique method of treating diseases in China.It is a medical practice of “treating internal diseases externally”.It treats various diseases through the conduction of meridians and acupoints, along with specific techniques.Acupuncture therapy is part of the heritage of traditional Chinese medicine and is a unique ethnic medical method in our country.
Acupuncture is a unique method of treating diseases in China.It is a medical practice of “treating internal diseases externally”.It treats various diseases through the conduction of meridians and acupoints, along with specific techniques.Acupuncture therapy is part of the heritage of traditional Chinese medicine and is a unique ethnic medical method in our country. For thousands of years, it has made outstanding contributions to safeguarding health and promoting the nation, and it continues to fulfill this role, earning the trust of the general public.
For thousands of years, it has made outstanding contributions to safeguarding health and promoting the nation, and it continues to fulfill this role, earning the trust of the general public.
Characteristics of Acupuncture:
The characteristics of acupuncture therapy are that it does not rely on medication to treat diseases; instead, it involvesinserting needles into specific parts of the patient’s body to stimulate nerves and elicit local reactions, or using heat to burn the area to achieve therapeutic effects. The former is called needling technique, while the latter is called moxibustion, collectively referred to as acupuncture therapy.In clinical practice, the diagnosis of the cause of the disease is made according to traditional Chinese medicine diagnostic methods, identifying the key to the disease, distinguishing the nature of the disease, determining which meridian and organ the pathology belongs to, and clarifying whether it is a superficial or deep condition, cold or heat, deficiency or excess type, to make a diagnosis.Then, corresponding acupoint prescriptions are made for treatment. The goal is to unblock the meridians, regulate Qi and blood, restore relative balance of Yin and Yang, and harmonize organ functions, thus achieving the purpose of preventing and treating diseases.
Advantages of Acupuncture Therapy:
First: It has a wide range of indications and can be used for the treatment and prevention of various diseases ininternal medicine, external medicine, gynecology, pediatrics, and otorhinolaryngology.Second: The effects of treating diseases are relatively rapid and significant, especially in enhancing bodily functions, improving disease resistance, and providing calming and analgesic effects;Third: The operation methods are simple and easy to perform;Fourth: The medical costs are economical;Fifth: There are little to no side effects, making it generally safe and reliable, and it can be combined with other therapies for comprehensive treatment. These are also reasons why it remains popular among the public.
Does Acupuncture Hurt?
The sensation of pain during acupuncture depends on two factors: the practitioner and the patient.Generally, after the needle is inserted into the body, asour, numb, swollen, or heavy sensation may occur, which are reactions indicating the arrival of Qi and are considered positive signs.Of course, a relaxed patient will also cooperate with the practitioner during needle insertion, reducing the likelihood of pain. A very tense patient may frequently experience unpleasant pain, so the pain of acupuncture is not absolute; good pain can relieve the patient’s suffering.Unpleasant pain iscaused by the patient’s tension and the practitioner’s poor technique. If you can relax completely during acupuncture and find a skilled acupuncturist, you will generally not be troubled by pain.
A very tense patient may frequently experience unpleasant pain, so the pain of acupuncture is not absolute; good pain can relieve the patient’s suffering.Unpleasant pain iscaused by the patient’s tension and the practitioner’s poor technique. If you can relax completely during acupuncture and find a skilled acupuncturist, you will generally not be troubled by pain.
How to Locate Acupoints?
1. Preparation Before Needling2. Needle Insertion3. Manipulation of the Needle4. Retaining the Needle5. Needle RemovalTherefore, the study of needling techniques mainly revolves around these five points, focusing on detailed methods without overcomplicating them.For example, painless needling techniques focus on the methods of needle insertion and manipulation.
1. Preparation Before Needling
1. Selection of Needles
Choose appropriate needle length and thickness based on the patient’s gender, age, body type, condition, location of the disease, and selected acupoints.For example, for a male patient who is robust, overweight, and has a deep disease location, a slightly thicker and longer needle may be chosen.Conversely, for a female patient who is weak, thin, and has a shallow disease location, a shorter and thinner needle should be selected. Clinically, the needle should be inserted to the appropriate depth while leaving a small portion of the needle exposed above the skin.Note:Needle selection is not only about length and thickness but also includes the type of needle, such as using a three-edged needle. Even for filiform needles, there are many choices.
2. Positioning
To ensure the patient is comfortable and can maintain the position for a long time during treatment, which facilitates acupoint selection and operation, it is essential to choose the right position for needling.Commonly used positions includesupine, prone, sitting, and lateral positions. For first-time patients, those who are tense, elderly, weak, or severely ill, it is advisable to take a supine position to avoid fainting or other accidents.Choose the position that makes the patient most comfortable (including for a long duration) to facilitate needling. Do not be too limited to the positions described in textbooks; for example, you can use cushions or props to assist.Common positions include: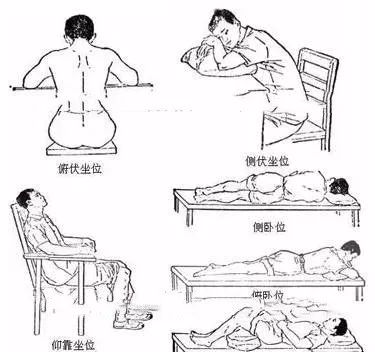
3. Disinfection
Disinfection should not only be thought of as disinfecting the acupuncture needles; it actually includes three aspects:disinfection of the needles, disinfection of the practitioner’s hands, and disinfection of the area where the needle will be inserted.Needle Disinfection: The common disinfection method is soaking in alcohol; if conditions allow, high-pressure sterilization can be used.Practitioner Hand Disinfection: Alcohol wipes are sufficient, but be careful with the wiping method (one-way, inward).Disinfection of the Acupoint Area: Generally, alcohol swabs are used for disinfection.
2. Needle Insertion
Needle insertion requires close coordination of both hands, generally using the right hand to hold the needle, referred to as the “inserting hand“, while the left hand presses or assists the needle body, referred to as the “pressing hand“.
1. Single-Handed Needle Insertion
Only the inserting hand is used, mostly for short needle operations, such as needles less than 1 inch.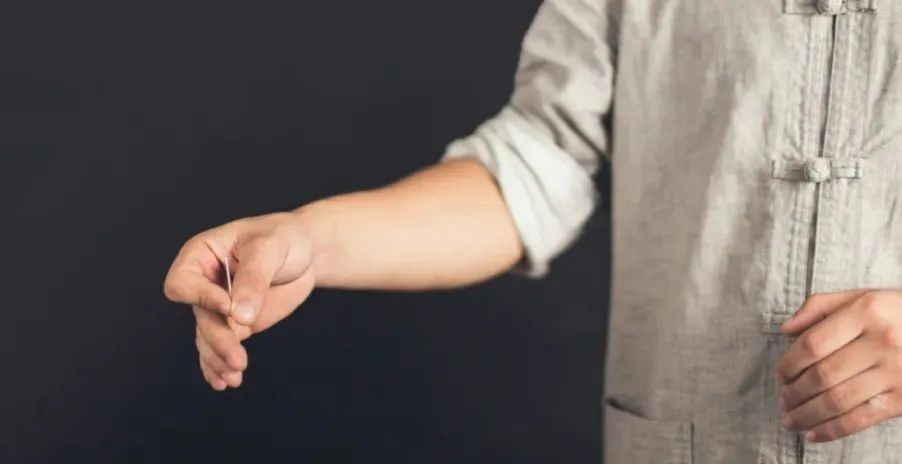
2. Finger-Cutting Needle Insertion Method
Also known as the claw-cutting needle insertion method, where the left thumb or index finger is pressed against the area beside the acupoint, and the right hand holds the needle, inserting it closely against the left fingernail.
3. Pinching Needle Insertion Method
The left thumb and index finger hold a disinfected cotton ball, pinching the lower end of the needle, fixing the needle tip on the surface of the acupoint, and the right hand twists the needle handle to insert it into the acupoint, suitable for long needle insertion.
4. Stretching Needle Insertion Method
Using the left index and thumb to stretch the skin at the acupoint, making the skin taut, the right hand holds the needle to insert it between the left thumb and index finger. This methodis mainly used for acupoints on loose skin.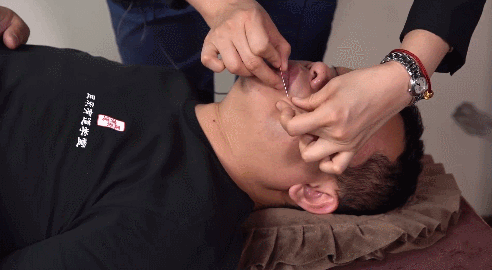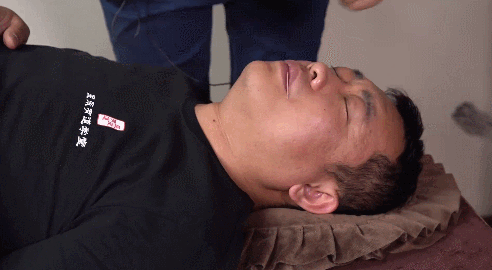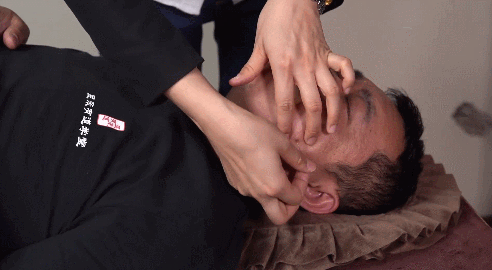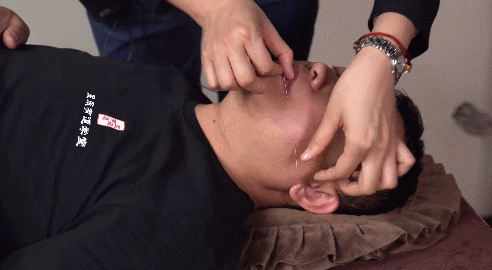
5. Pinching Needle Insertion Method
Using the left thumb and index finger to pinch the skin at the insertion site, the right hand holds the needle and inserts it from the top of the pinched area. This methodis mainly used for thin-skinned areas, such as the Yintang acupoint.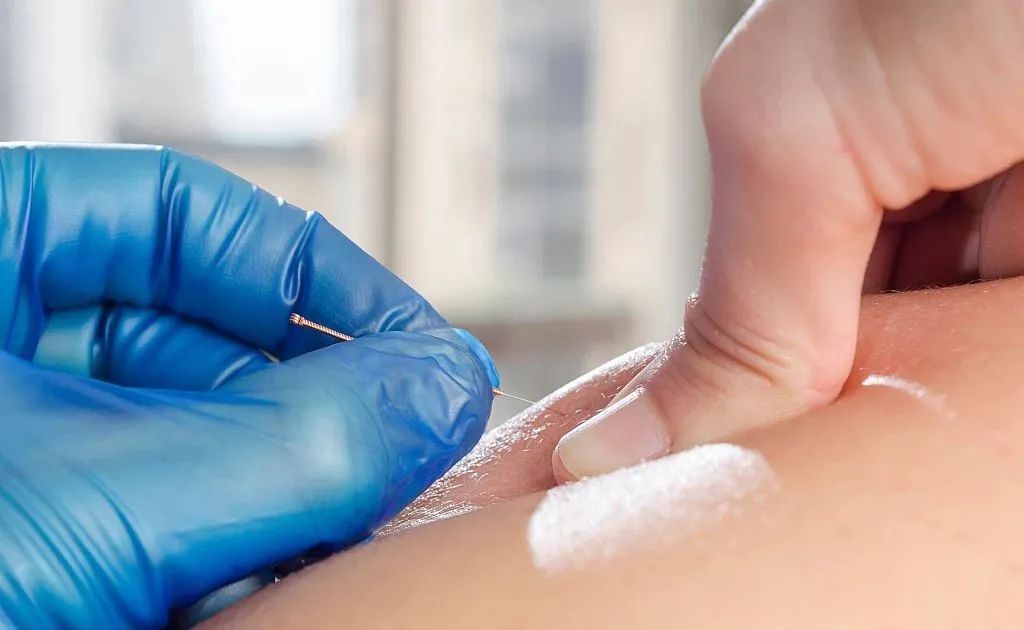 After needle insertion, two points must be noted: the angle of insertion and the depth
After needle insertion, two points must be noted: the angle of insertion and the depth
- Angle: Generally categorized asperpendicular, oblique, and horizontal, depending on whether the insertion site has sufficient muscle and whether deep insertion is appropriate.
- Depth: Should be chosen based on the condition, body type, age, and location, rather than a single criterion; for example, being strong and robust does not necessarily mean deep insertion is appropriate; it must be judged according to the condition. Specific situations should be analyzed individually.
3. Needle Manipulation
The Huangdi Neijing states: “To achieve effective needling, Qi must arrive“. This means that effective needling requires the arrival of Qi, which mainly depends on the manipulation technique.Basic Needle Manipulation Techniques:lifting and thrusting, twisting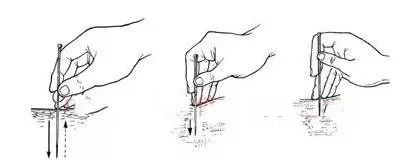 Auxiliary Needle Manipulation Techniques:
Auxiliary Needle Manipulation Techniques:
1. Circulating Method:
This involves using the left or right hand to gently press or move along the acupoint or meridian path, promoting Qi and blood flow. This method can activate Qi and blood when Qi has not yet arrived, and has the effect of promoting Qi and stimulating Qi. If the needle feels too heavy, this method can help disperse Qi and blood, making the needle feel more comfortable.
2. Scraping Method:
This involves inserting the needle to a certain depth, then using the thumb or index finger to press against the needle tail, frequently scraping the needle handle from bottom to top with the thumb, index, or middle finger. This method can stimulate meridian Qi and promote the arrival of Qi when it has not yet arrived.
3. Bouncing Method:This involves lightly bouncing the needle handle after insertion, causing slight vibrations in the needle body to promote the flow of Qi.
4. Twisting Method:This involves twisting the needle handle with the right thumb, index, and middle fingers in a single direction after insertion, usually for 2-3 turns or 3-5 turns, but it should be combined with lifting and thrusting to avoid entangling the needle in muscle fibers. This method has the effects of promoting Qi, stimulating Qi, and tonifying deficiency while dispersing excess.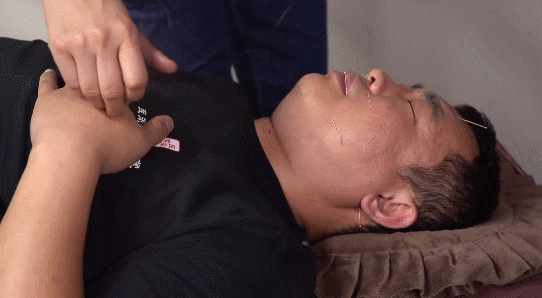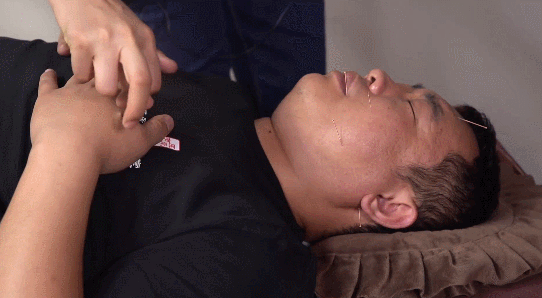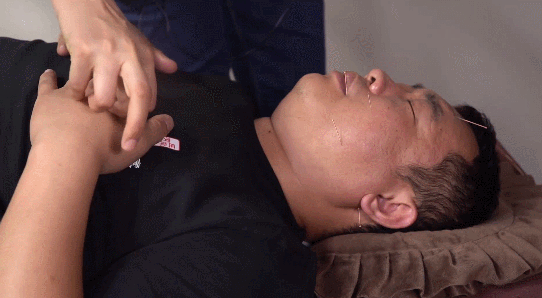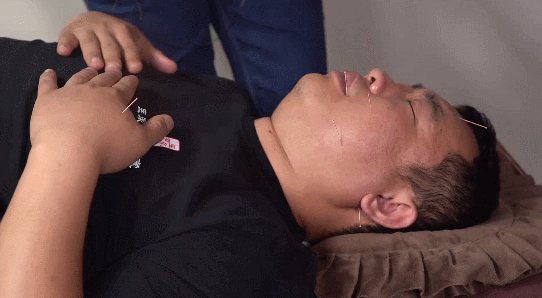
5. Shaking Method:This involves shaking the needle handle after insertion, similar to shaking a roof eave or a pulley, which can promote Qi flow.
6. Trembling Method:This involves using small amplitude, rapid frequency lifting and twisting movements with the left hand holding the needle handle, causing slight tremors in the needle body to promote Qi arrival or enhance the effects of expelling pathogens and supporting the body.
4. Retaining the Needle
The decision to retain the needle and the duration depends on the condition. For general conditions, as long as Qi is achieved under the needle, it can be removed after treatment or retained for10-20 minutes.However, for chronic, stubborn, painful, or spastic conditions, the retention time can be appropriately extended, and manipulation can be performed intermittently during retention to enhance efficacy. Retaining the needle can also serve to wait for Qi to arrive.
5. Needle Removal
When removing the needle, use the left thumb and index finger to press around the needle hole, while the right hand gently twists and slowly lifts the needle just beneath the skin, then quickly withdraws it and applies pressure with a dry cotton ball to prevent bleeding.Finally, check the number of needles to prevent omissions!
【Learn Meridians】 Click for exciting recommendations
| Human Meridian Query | Human Acupoint Query | Common Disease Query |
| Massage Technique Explanation | Technique Video Explanation | Pediatric Disease Query |
| Hand Diagnosis | Facial Diagnosis | Nine Body Constitutions |
| Tongue Diagnosis | Back Diagnosis | Foot Reflex Zones |
If you find this useful, please click the button below to  View
View

