Cupping
A distinctive therapy in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
Cupping is a traditional therapy in China that utilizes fire or suction methods to create negative pressure within the cups, causing local bruising as the cups adhere to the skin. Nowadays, cupping is also chosen abroad to relieve muscle soreness and eliminate fatigue. However, at times, cupping is exaggeratedly recommended, such as suggesting it as a remedy for colds; or when there is excessive dampness, cupping is also recommended as a solution, as if it can resolve everything. So, is what is drawn out by cupping really the “dampness”?

HELLO AUTUMN

Cupping Techniques

There are many cupping techniques, the most common include the following:

Retention Cupping:

The retention cupping method, also known as sitting cupping, involves placing the cups on the skin and leaving them for a period of time, generally 10-15 minutes. This method is the oldest and most widely used cupping technique, suitable for most conditions. It can be divided into single cup and multiple cup methods. The single cup method treats simpler conditions with a smaller area of disease or fewer acupoints. The multiple cup method uses several cups simultaneously, suitable for more extensive, complex conditions or when multiple acupoints are selected, such as soft tissue injuries and pain in the lower back, where a larger area is involved, thus yielding better results. During multiple cup therapy, it can be further divided into dispersive cupping and排罐法 (排罐法, 排罐法). For example, placing multiple cups in a row along both sides of the spine is called 排罐法 (排罐法); while cups placed sparsely or not in a row are called dispersive cupping. Retention cupping should consider the patient’s skin, location, constitution, and the suction strength of the cups. If the suction is strong, the retention time should be shortened accordingly, and in summer or on thinner muscles, the retention time should not be too long to avoid blisters.
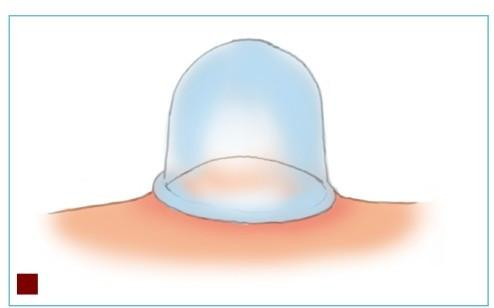

Flash Cupping:

This involves quickly removing the cups after suction, then reapplying and removing them repeatedly. Flash cupping is often used for conditions of deficiency and cold, muscle atrophy, or when specific acupoints need to be stimulated. During flash cupping, care should be taken as the temperature of the cups rises quickly, so multiple cups should be prepared for alternating use to prevent burns.
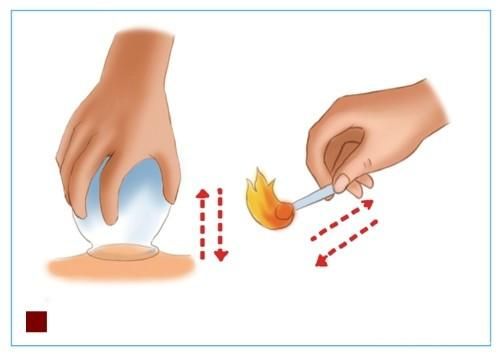

Sliding Cupping:
 This refers to the technique where, after the cups are applied, one or both hands hold the cups and gently lift them, sliding the cup over the patient’s skin. The cups can be moved in one direction or back and forth. Therefore, sliding cupping does not target a single acupoint but affects several acupoints or a section of a meridian. For example, the bladder meridian on the back is a common area for sliding cupping. Care should be taken to apply a lubricant, such as glycerin, paraffin oil, or guasha oil, on the area before sliding cupping to prevent skin injury. Sliding cupping is often used for back pain, chills, dizziness, and colds.
This refers to the technique where, after the cups are applied, one or both hands hold the cups and gently lift them, sliding the cup over the patient’s skin. The cups can be moved in one direction or back and forth. Therefore, sliding cupping does not target a single acupoint but affects several acupoints or a section of a meridian. For example, the bladder meridian on the back is a common area for sliding cupping. Care should be taken to apply a lubricant, such as glycerin, paraffin oil, or guasha oil, on the area before sliding cupping to prevent skin injury. Sliding cupping is often used for back pain, chills, dizziness, and colds.

Bloodletting Cupping:

This involves using a three-edged needle to puncture specific acupoints or abscess areas before applying the cups. The stagnant blood and pus will flow out through the needle holes. Bloodletting cupping is generally used for diseases caused by fever and heat toxins.

Shaking Cupping, Rotating Cupping, Lifting Cupping:

These three methods are developed based on the retention cupping method.
Shaking cupping involves securely placing the cups on the skin and then shaking them evenly and rhythmically. During the operation, the wrist should be relaxed, the force should be gentle, and the speed should not be too fast, with an appropriate angle of movement, based on the patient’s tolerance. This repeated pulling increases the stimulation to the skin and acupoints. Any area suitable for retention cupping can be used for shaking cupping as needed.
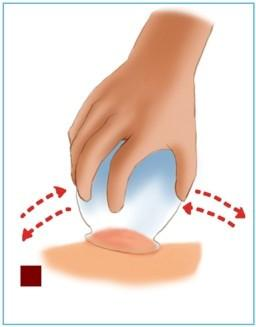
Rotating cupping is more forceful than shaking cupping, with stronger stimulation, where the cups are rotated back and forth after being applied. The technique should be gentle, and the rotation angle should be moderate, based on the patient’s tolerance. This method can create greater pulling on the skin or acupoints, enhancing the therapeutic effect, and is often used for acupoint treatment or local muscle relaxation.
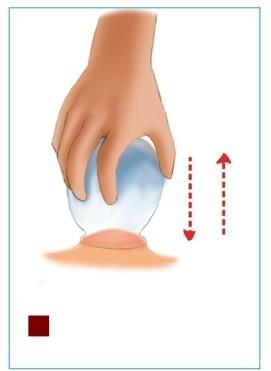
Lifting cupping is based on retention cupping, where the cups are repeatedly lifted to enhance the suction effect, about 30-40 times, causing the skin to move up and down, which has a therapeutic effect on the corresponding internal organs. This method is commonly used for abdominal conditions such as stomach pain, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and dysmenorrhea, and is quite effective.

Benefits and Effects of Cupping Therapy
 1. Negative Pressure Effect
1. Negative Pressure Effect
When the body is subjected to the negative pressure of cupping, numerous gas bubbles emerge from the skin surface, enhancing gas exchange in local tissues. Observations have shown that negative pressure alters the permeability of local capillaries and causes capillary rupture, allowing a small amount of blood to enter the interstitial space, resulting in bruising. Red blood cells are damaged, releasing hemoglobin and causing hemolysis. This self-regulation of the body produces effects such as promoting qi and blood circulation, relaxing tendons and meridians, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and dampness, acting as a beneficial stimulus to restore normal function.
2. Warming Effect
Cupping provides a certain warming stimulation to the local skin, most notably with large fire cups, water cups, and medicinal cups. Such warming stimulation can expel toxins and clear heat, dilate blood vessels, promote local blood circulation, improve congestion, enhance metabolism, accelerate the elimination of waste and toxins from the body, alter the nutritional state of local tissues, increase capillary permeability, enhance the phagocytic activity of white blood cells and reticular cells, and improve local tolerance and the body’s resistance, achieving effects such as warming meridians and dispelling cold, and clearing heat and detoxifying, thus promoting recovery from diseases. Additionally, cupping is effective for tissue injuries, lumbar disc herniation, and other conditions, alleviating pain and relieving symptoms.
3. Regulatory Effect
The regulatory effect of cupping is based on the negative pressure or warming effect, primarily regulating the nervous system. Due to hemolysis and other factors, a series of beneficial stimuli are provided to the body, acting on the peripheral receptors of the nervous system, which are transmitted centripetally to the cerebral cortex.

