Health Inquiry, Health Guidance, Classic Health Preservation, No Need to Seek Help When Sick
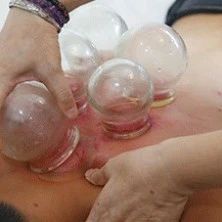
This video demonstrates the operation method of vacuum cupping.
Cupping therapy is one of the treasures of traditional Chinese medicine, used for a long time in our country. The method of cupping is recorded in the “Emergency Prescriptions for Elbow” written by the Jin Dynasty physician Ge Hong. The so-called cupping method involves using hollowed-out animal horns to suck out pus from sores. The “Secret Essentials of External Medicine” written by Wang Tao in the Tang Dynasty also introduced the use of bamboo tubes for cupping, stating: “…take a three-finger-wide green bamboo tube, one and a half inches long, leaving one end with a node, and shave the other end to be thin like a sword. Boil this tube several times, and when hot, press it on the ink dot area for a long time, then use a knife to break the cupped area. After that, boil the tube again to suck out yellow, white, and red water, and sometimes pus or worms will come out. Repeat this until all bad substances are expelled, and then it will be removed, and the vision will be clear and the body light.” From the above introduction of the cupping method and the bamboo tube cupping, it can be seen that cupping was already popular in the Jin and Tang dynasties in our country.In addition, the “Compendium of Materia Medica Supplement” written by Zhao Xue-min in the Qing Dynasty, Wu Shang-xian’s “Li Yu Jiao Wen”, and “The Golden Mirror of Medicine” provide clearer introductions regarding the origin, usage methods, and indications of cupping in our country.Cupping uses the cup as a tool, employing methods such as fire and suction to create negative pressure, allowing the cup to adhere to the body surface, causing temporary bruising in the local tissue, achieving effects such as promoting meridian flow, invigorating blood circulation, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold. Cupping is generally performed using bamboo or glass cups. Bamboo cups have thinner walls than glass cups, providing stronger suction, and are made from natural, environmentally friendly materials, making them more durable against impacts than glass cups. Glass cups have smoother surfaces and are transparent, allowing for easy observation of skin color changes during cupping. Glass cups processed with special techniques are more heat-resistant than bamboo cups and are less likely to crack, resulting in a longer usage period. Vacuum cups are often made from plastic materials like PC, eliminating open flames during cupping, reducing the risk of burns, and allowing individuals to adjust the level of negative pressure according to their comfort, making them easier to operate than fire cups. However, they lack the thermal stimulation of fire cups, making them less effective for patients with cold and damp constitutions. Individuals can choose the appropriate cupping method based on their situation, but safety precautions should be taken, and self-cupping without professional guidance is not recommended to avoid burns.Four Cupping Techniques and Correct Operation Methods
According to the severity of the patient’s condition, cupping can be divided into four techniques: flash cupping, moving cupping, retained cupping, and prick cupping.
● Flash Cupping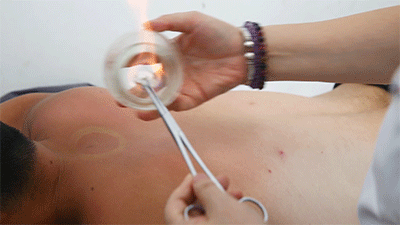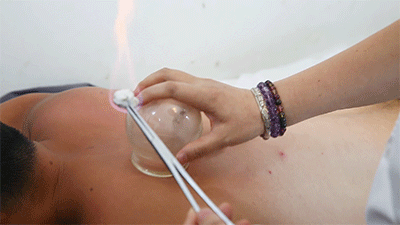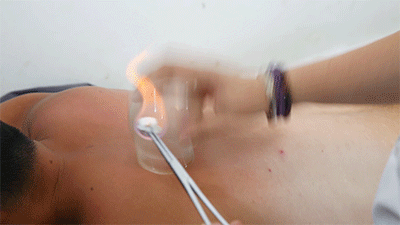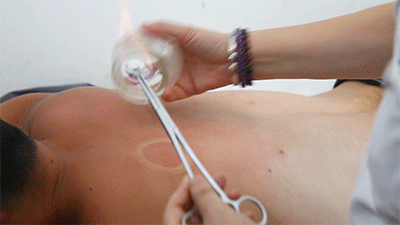 Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol.❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then immediately remove it and place the cup on the skin, then quickly lift it off.❸ Repeat the suction several times until the skin turns red.Flash cupping usually does not leave marks on the skin and is the least irritating of the four techniques.● Moving Cupping
Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol.❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then immediately remove it and place the cup on the skin, then quickly lift it off.❸ Repeat the suction several times until the skin turns red.Flash cupping usually does not leave marks on the skin and is the least irritating of the four techniques.● Moving Cupping Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol. Apply some lubricating medicine or liquid to the skin surface where cupping is to be performed. The lubricating medicine varies based on the desired therapeutic effect. The image shows the use of purple grass oil, which has blood-invigorating properties.
Steps❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol. Apply some lubricating medicine or liquid to the skin surface where cupping is to be performed. The lubricating medicine varies based on the desired therapeutic effect. The image shows the use of purple grass oil, which has blood-invigorating properties.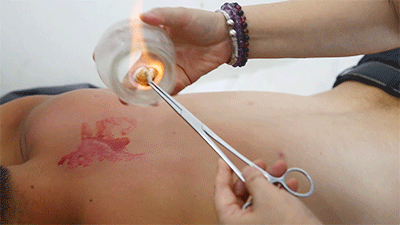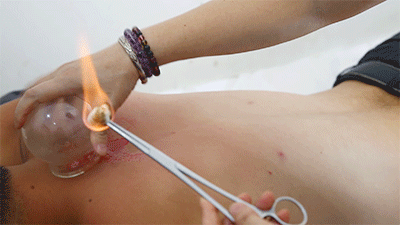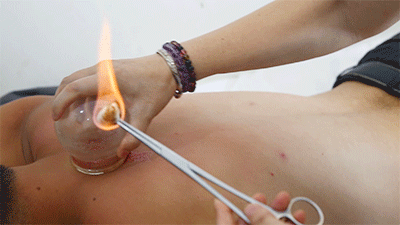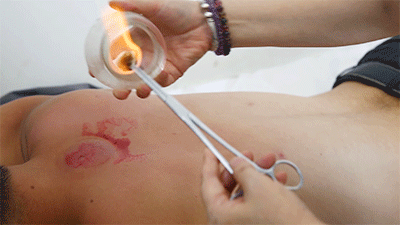

 ❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then immediately remove it and place the cup on the skin, holding the cup and moving it back and forth along the meridians. After moving cupping, if there are issues in the body, there will be large areas of cupping marks; if there are no issues, there will just be cup marks that fade quickly.● Retained Cupping
❷ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then immediately remove it and place the cup on the skin, holding the cup and moving it back and forth along the meridians. After moving cupping, if there are issues in the body, there will be large areas of cupping marks; if there are no issues, there will just be cup marks that fade quickly.● Retained Cupping


 ❶ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then immediately remove it and place the cup on the skin, leaving it for 10-15 minutes before removing it and wiping the skin clean with a cotton ball.● Prick Cupping
❶ Ignite a cotton ball soaked in 95% alcohol, quickly insert it into the glass cup, then immediately remove it and place the cup on the skin, leaving it for 10-15 minutes before removing it and wiping the skin clean with a cotton ball.● Prick Cupping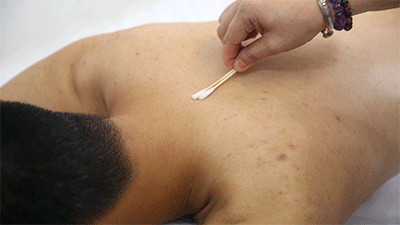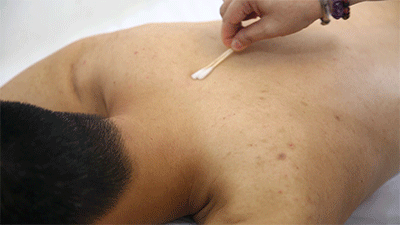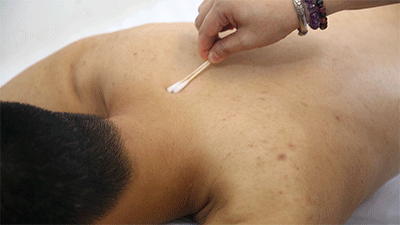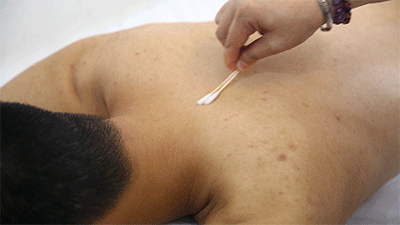 ❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol.
❶ Wipe the area to be cupped with a cotton ball soaked in 75% alcohol.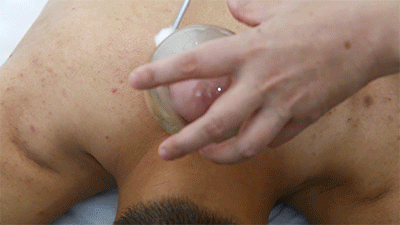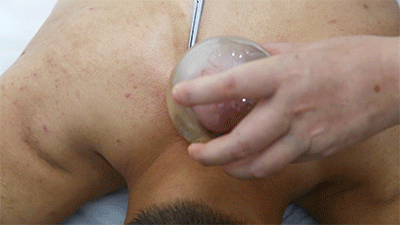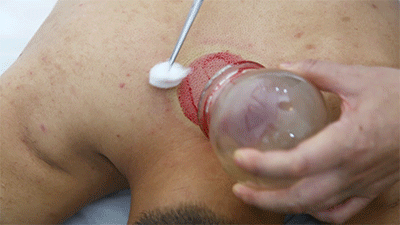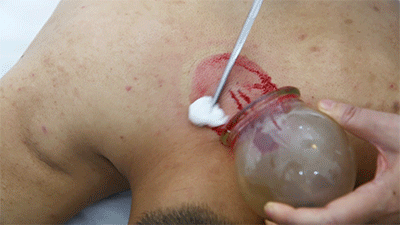 ❷ Use a disposable blood collection needle to prick the skin locally.
❷ Use a disposable blood collection needle to prick the skin locally. ❸ Retain the cup.
❸ Retain the cup. ❹ Remove the cup and wipe away the blood that flows out with a cotton ball.Cupping therapy has effects such as promoting meridian flow, invigorating blood circulation, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold. What do the cupping marks left on the body represent in terms of health issues? Let’s explore “Cupping Mark Diagnosis” together.Cupping Mark Diagnosis
❹ Remove the cup and wipe away the blood that flows out with a cotton ball.Cupping therapy has effects such as promoting meridian flow, invigorating blood circulation, reducing swelling and pain, and dispelling wind and cold. What do the cupping marks left on the body represent in terms of health issues? Let’s explore “Cupping Mark Diagnosis” together.Cupping Mark Diagnosis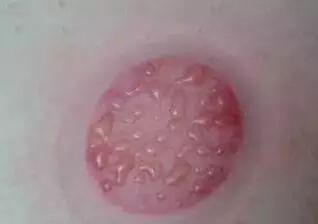
Cupping marks showing water vapor, blisters, or edema indicate that the patient has excess dampness, cold, or has been affected by cold and dampness causing disease;
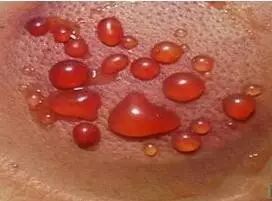
Cupping marks with blood-red or black-red blisters indicate a pathological reaction of long-term illness with dampness and blood stasis;

Cupping marks that are purple-red or purple-black, without stasis or fever, indicate that the patient has cold with blood stasis, with varying degrees of severity;
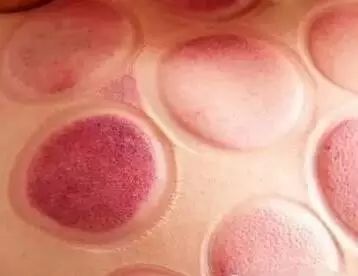
Cupping marks that are purple-red or purple-black, or show stasis, slight pain upon touch, and concurrent body heat indicate that the patient has heat toxin syndrome;

Cupping marks that are slightly itchy or show skin patterns indicate that the patient has wind syndrome;
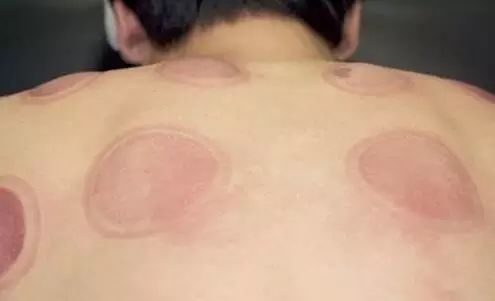
Cupping marks with no color change and feel cool to the touch indicate that the patient has deficiency-cold syndrome.
If there are no cupping marks or if the marks disappear immediately after cupping, it indicates that the body is in a relatively healthy state.
If the marks do not fade after a few days, it indicates that the condition has persisted for a long time, requiring more attention to treatment and care. As the condition improves, the cupping marks will also lighten, indicating recovery.
Indications, Main Points, and Contraindications for Cupping
1. Indications and Main Acupoints:
Respiratory System Indications
Acute and chronic bronchitis, asthma, pulmonary edema, pneumonia, pleurisy. Main points: Dazhù (大杼), Fengmén (风门), Píngyǔ (肺俞), Yīngchuāng (膺窗).
Digestive System Indications
Acute and chronic gastritis, gastric neuralgia, dyspepsia, hyperacidity. Main points: Gān yǔ (肝俞), Pí yǔ (脾俞), Wèi yǔ (胃俞), Gé yǔ (隔俞), Zhāngmén (章门).
Acute and chronic enteritis. Main points: Pí yǔ (脾俞), Wèi yǔ (胃俞), Dàcháng yǔ (大肠俞), Tiānshù (天枢).
Circulatory System Indications
Hypertension. Main points: Gān yǔ (肝俞), Dǎn yǔ (胆俞), Pí yǔ (脾俞), Shèn yǔ (肾俞), Wěizhōng (委中), Chéngshān (承山), Zú sān lǐ (足三里). Focus on the back and lower limbs.
Arrhythmia. Main points: Xīnyǔ (心俞), Shèn yǔ (肾俞), Gé yǔ (膈俞), Pí yǔ (脾俞).
Insufficient blood supply to the heart. Main points: Xīnyǔ (心俞), Gé yǔ (膈俞), Gāohuāng yǔ (膏肓俞), Zhāngmén (章门).
Musculoskeletal System Indications
Cervical joint pain, shoulder joint and scapular pain, elbow joint pain. Main points: Tender points and surrounding joints for cupping. Back pain, lumbar pain, sacral pain, hip pain. Main points: Cupping based on the location of pain and surrounding joints. Knee pain, buttock pain, heel pain. Main points: Use small glass cups for cupping at the site of pain and surrounding joints.
Nervous System Indications
Neurogenic headache, occipital neuralgia. Main points: Dàzhuì (大椎), Dàzhù (大杼), Tiānzhù (天柱) (with a face cushion), Zhìyáng (至阳).
Intercostal neuralgia. Main points: Zhāngmén (章门), Qīmén (期门), and the intercostal pain area for cupping.
Sciatica. Main points: Zhìbiān (秩边), Huán tiào (环跳), Wěizhōng (委中).
Peripheral nerve paralysis due to rheumatic damage. Main points: Dàzhuì (大椎), Gāo máng yǔ (膏盲俞), Shèn yǔ (肾俞), Fēngshì (风市), and the affected area.
Cervical muscle spasm. Main points: Jiān jǐng (肩井), Dàzhuì (大椎), Jiān zhōng yǔ (肩中俞), Shēnzhù (身柱).
Gastrocnemius muscle spasm. Main points: Wěizhōng (委中), Chéngshān (承山), and the affected gastrocnemius area.
Facial nerve spasm. Main points: Xiàguān (下关), Yìntáng (印堂), Jiá chē (颊车), using small cups, only leave the cup for 6 seconds, then remove it, and repeat 10 to 20 times.
Diaphragmatic spasm. Main points: Gé yǔ (隔俞), Jīngmén (京门).
Gynecological Indications
Dysmenorrhea. Main points: Guānyuán (关元), Xuèhǎi (血海), Àshìxué (阿是穴).
Amenorrhea. Main points: Guānyuán (关元), Shèn yǔ (肾俞).
Menorrhagia. Main points: Guānyuán (关元), Zǐgōng (子宫).
Leukorrhea. Main points: Guānyuán (关元), Zǐgōng (子宫), Sān yīn jiāo (三阴交).
Pelvic inflammatory disease. Main points: Zhìbiān (秩边), Yāo yǔ (腰俞), Guānyuán yǔ (关元俞).
Indications for Surgical Sores and Ulcers
Boils. Main points: Shēnzhù (身柱) and the boil area, using small cups with face cushions for cupping.
Multiple folliculitis. Main points: Zhìyáng (至阳), local small cups with face cushions for cupping.
Lower limb ulcers. Main points: Local small cups with face cushions for cupping.
Acute mastitis. Main points: After applying a warm towel soaked in hot water to the area, use medium or large cups for cupping, which can be repeated 5 to 6 times.

2. Contraindications for Cupping
High fever, convulsions, spasms; skin allergies or ulcerated areas; areas with thin muscles or uneven bones and areas with excessive hair are not suitable for cupping; pregnant women should be cautious with cupping on the lumbar and abdominal areas.
3. Cupping Precautions
1. Do not take a cold shower or drink cold beverages within two hours after scraping and cupping; if taking a shower after two hours, use hot water.
2. Avoid using air conditioning or fans during scraping and cupping to prevent air convection.
3. Do not perform cupping when overly full, hungry, or after drinking; wait at least one hour after meals before cupping.
For conditions such as:low back pain, gynecological issues, male reproductive issues, kidney tonification, lumbar disc herniation, back pain, leg pain, knee pain, cervical spondylosis, liver disease, stomach disease, constipation, frequent urination, diarrhea,abdominal protrusion, dysmenorrhea, mammary gland hyperplasia, breast cancer, postpartum recovery, acne, white hair, hair loss, breast enhancement, beauty, skin diseases, age spots, aging, yin deficiency,colds, coughs, fever, insomnia, stones, pharyngitis, sore throat, headaches, toothaches, snoring, oral ulcers, bad breath, rhinitis, tinnitus, eye diseases, thyroid issues, dandruff, athlete’s foot, hemorrhoids, cold hands and feet, rheumatism, night sweats, cancer,cerebral hemorrhage, hypertension, diabetes, asthma, heart disease, cardiovascular diseases, fatty liver, gout, senile dementia, varicose veins, qi tonification,blood tonification, calcium supplementation,thinness, obesity, pediatric diseases, leg slimming, waist slimming, dampness, spleen strengthening, hiccups, body odor, cramps, smoking cessation,meridians, Chinese patent medicines,foot baths… and more