“Seven Emotions” refers to the seven normal emotional activities: joy, anger, worry, thought, sadness, fear, and shock, which are responses of human consciousness to external events. The Seven Emotions are closely related to the functions of the body’s organs. They are associated with the five organs, represented by joy, anger, thought, sadness, and fear, and are commonly referred to as the Five Emotions.
The Seven Emotions are different reflections of human responses to objective phenomena. Within a normal range of activity, they generally do not cause illness. Only sudden, intense, or prolonged emotional stimuli that exceed the body’s normal physiological activity range can disrupt the flow of Qi, leading to imbalances in the Yin, Yang, Qi, and blood of the organs, which can result in disease. Therefore, as a cause of disease, the Seven Emotions refer to excessively strong, prolonged, or sudden emotional changes that lead to imbalances in the organs’ Qi and blood, resulting in disease.
Illness caused by the Seven Emotions is termed “illness due to stagnation of emotions.” Additionally, certain chronic diseases can lead to long-term dysfunction of the organs, resulting in abnormal emotional states, referred to as “illness leading to stagnation of emotions.” The Seven Emotions are also related to the body’s tolerance and regulatory capacity.
The pathogenic effects of the Seven Emotions differ from the Six Excesses, which are external pathogenic factors (wind, cold, heat, dampness, dryness, and fire) that invade the body through the mouth, nose, or skin. In contrast, the Seven Emotions directly affect the related organs and cause disease.The Seven Emotions can not only trigger the onset of various diseases but also significantly influence the progression of diseases, promoting either improvement or deterioration.Since the Seven Emotions are one of the main pathogenic factors causing internal injuries, they are also referred to as “internal injury from the Seven Emotions.”
1
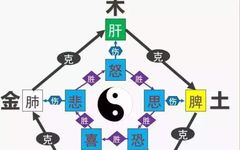
The Relationship Between the Seven Emotions and the Organs’ Qi and Blood
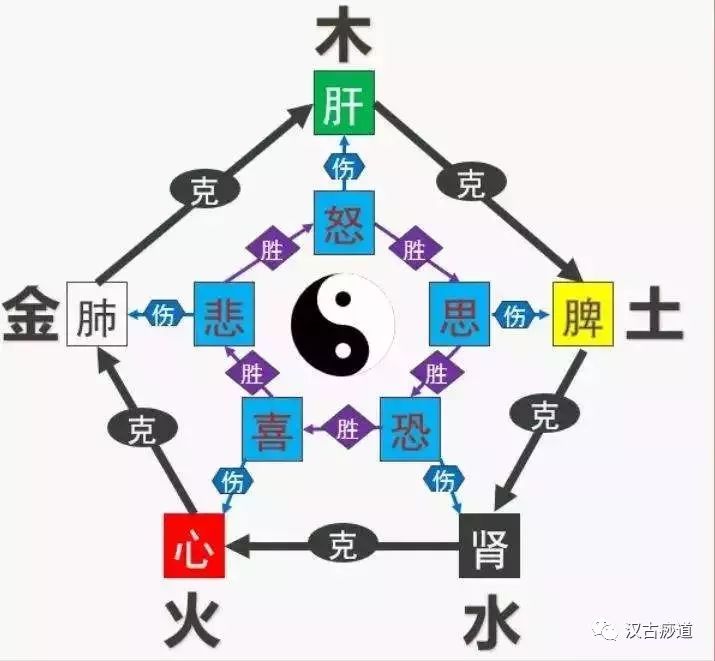
1. The relationship between the Seven Emotions and the organs: The emotional activities of the human body are closely related to the organs, and the basic principle is: the heart governs joy; excessive joy harms the heart; the liver governs anger; excessive anger harms the liver; the spleen governs thought; excessive thought harms the spleen; the lungs govern sadness and worry; excessive sadness and worry harm the lungs; the kidneys govern shock and fear; excessive shock and fear harm the kidneys. This indicates that changes in the organs can lead to corresponding emotional responses, and excessive emotional responses can damage the related organs (mutual dialectics). The theory that the Seven Emotions arise from and harm the Five Organs has significant guiding implications in diagnosis and treatment.
2. The relationship between the Seven Emotions and Qi and blood: Qi and blood are the two fundamental substances that constitute the body and maintain life activities. Qi has a warming and promoting effect on the organs, while blood nourishes the organs. Qi and blood are the material basis for emotional activities, and there is a close relationship between emotional activities and Qi and blood. Changes in the organs’ Qi and blood can also affect emotional changes, hence the saying: “when blood is abundant, there is anger; when it is insufficient, there is fear.” The physiological activities of the organs must be based on Qi and blood, while emotional activities are manifestations of the physiological functions of the organs, thus the emotional activities of the human body are closely related to the Qi and blood of the organs.
2
The Characteristics of Disease Induced by the Seven Emotions
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) studies the laws of human life, not just patients and diseases, which is quite different from Western medicine. TCM often places humans within two circles: the first circle is the natural circle, as stated in the Huangdi Neijing (Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon), “When the evil wind is excessive, it should be avoided at the right time.” For example, in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, TCM often emphasizes that when wind, cold, heat, dampness, dryness, or fire are excessive or not timely, it is referred to as “Six Excesses” or “Six Evils.” This indicates that when humans cannot coordinate with the natural world, diseases will arise, which is the first cause of disease.
The second circle is society. This circle discusses the relationship between human joy, anger, worry, thought, sadness, fear, and shock and human life and health. TCM has a saying in health preservation: “calmness and emptiness lead to true Qi.” This means that when your mood is in a very calm state, your Qi and blood will run normally. This normal flow is an important function for maintaining life activities. Conversely,when your emotions undergo abnormal changes, they can disrupt the flow of Qi and blood, leading to disease.
3
The Liver Governs Anger; Poor Liver Health Leads to Irritability
Many women are particularly prone to anger, especially around their menstrual periods. Why? Because women are primarily governed by blood and the liver is their innate organ. When menstruation approaches, blood flows downward, while Qi rises. At this time, the balance of Qi and blood is disrupted, leading to excess Qi and thus heat, which causes irritability. Therefore, women should pay attention to regulating their emotions before and during their menstrual periods, avoiding excessive anger and depression. Both excessive anger and depression are not in line with normal physiological states, and over time, they can lead to disease.

In the clinic, I often tell women, if you argue with your husband, make sure to tell him to let you cry it out before he leaves. Don’t let him leave while you’re still angry; otherwise, he will come back and continue the argument. Why? Because the liver governs anger. When you are angry, and you have a quarrel, your liver Qi is very strong. If he leaves at that moment, your anger will become stagnant and cannot be released. If it remains stagnant for too long, it will transform into heat, and when he returns, the argument will continue. However, if you cry, what happens? Crying is related to the lungs; when you cry, the lung Qi becomes vigorous, which calms the liver Qi. In TCM, the corresponding elements of the lungs and liver are metal and wood, which have a mutual restraining relationship. When lung Qi becomes vigorous, liver Qi calms down. You can try it; when you feel particularly depressed, find a place where no one is around and cry it out. After crying, you will feel much better.
We also see many patients with liver diseases who are particularly irritable. Why? Because the liver governs anger, and the liver meridian inherently has heat, which causes them to easily become angry. Therefore, when you feel particularly troubled and irritable for no reason, you should seek TCM help to adjust your liver. This is not the same as what Western medicine refers to as liver disease or hepatitis; rather, it is your emotional state that is problematic. This requires a process of adjustment. Many diseases transition from quantitative changes to qualitative changes. When the changes are quantitative, they may not be detected; you may go to a Western doctor who tells you that you are fine. For example, some people feel particularly uncomfortable after getting angry, experiencing headaches and pressure in the head. When you go to the hospital, the Western doctor says you are fine, and all your indicators are normal. But you still feel uncomfortable. If you take some herbs to calm the liver and regulate the Qi, it will help.
4
Heart Governs Joy; Excessive Joy Can Scatter Qi
The heart governs joy, which is happiness. We all know that we say the heart blooms with joy, not the liver. We also see many elderly patients with heart problems. Why do they often pass away after a joyful reunion with their children? Because excessive joy can scatter Qi; when one is overly happy, their heart Qi is depleted. So, while joy is a good thing, excessive joy may not necessarily be beneficial.

5
Spleen Governs Thought; Excessive Worry Harms the Spleen and Stomach
The spleen governs thought; “thought” refers to excessive worry. People who worry excessively will have problems with their spleen and stomach. Those who frequently use their brains often have poor spleen and stomach function. Why? Because we all know that we need to eat every day, and after eating, the Qi and blood go to the stomach to aid in digestion. If at this time, your blood is not going to the stomach but is instead concentrated in the brain, over time, the function of the spleen and stomach will be affected.

For example, many long-distance drivers suffer from stomach issues. Why? Because of their occupational habits; as soon as they sit in the driver’s seat, their blood naturally flows to the brain. Over time, this leads to insufficient digestion of the food they consume, resulting in diseases such as gastric ulcers and gastric prolapse. Therefore, TCM states that the relationship between thought and the spleen and stomach is that excessive worry harms the spleen, leading to Qi stagnation.
6
The Lungs Govern Sadness; Excessive Sadness Harms the Lungs
The lungs govern sadness. You may have seen the character Lin Daiyu from Dream of the Red Chamber; she certainly has lung issues, as she cries incessantly. Frequent crying and tearing are definitely related to the lungs. Recently, I treated an elderly gentleman with lung cancer who said, “Doctor, I don’t know why, but I feel like crying every time I see you.” I said, “This is because you have a problem with your lungs, as the lungs are directly related to the emotion of sadness.”

7
The Kidneys Govern Fear; Excessive Fear Scatters Kidney Qi
The kidneys govern fear, which is directly related to the kidneys. In Romance of the Three Kingdoms, when Zhang Fei shouted on Changban Bridge, he scared a person to death. I think that person must have had weak kidney Qi. Fear scatters Qi; there is a saying among the people that when someone is frightened, they lose control of their bowels. This is because the kidneys control the two excretions. When a person experiences excessive fear, their kidney Qi scatters, and the kidney’s ability to hold is weakened, leading to incontinence.

【Summary】 Therefore, the changes in emotions such as joy, anger, worry, thought, sadness, fear, and shock are closely related to the Five Organs. In fact, when we look at historical novels, such characters are everywhere. For example, why did Wang Xifeng fall ill? “Cunning schemes led to her demise.” She was always calculating against others, and in the end, heaven calculated against her. Lin Daiyu cried every day, and eventually, her tuberculosis developed. In Romance of the Three Kingdoms, Zhou Yu was so young but died because of jealousy and imbalance in his mindset, always feeling that Zhuge Liang was smarter than him. It could be said that Zhuge Liang caused his death, but it is more accurate to say that he caused his own demise.